- What does a normal tongue look like?
- White spots on a child's tongue
- Red spots on a child's tongue
- How to treat spots on the tongue
- Imudon® in the fight against inflammatory diseases
The tongue is considered an indicator of health, so the appearance of spots on it should alert parents, even in the absence of other manifestations. However, before you begin to calculate the reasons that caused the formation of plaque, analyze your baby’s diet. Very often, tongue spotting is caused by eating dyes or foods containing chemical dyes3.
Spots in the oral cavity of children are formed from the influence of various factors. This symptom does not always indicate a disease in the oral cavity. Parents' attentiveness to the baby's condition allows the disease to be quickly detected and eliminated.
What it is
In a healthy child, the tongue has a uniform pink color without spots or plaque. But in the presence of any pathology, spots of various colors and sizes may appear, which represent:
- An uneven accumulation of plaque on the surface of the tongue, which consists of exfoliated epithelium, tiny food particles, and microorganisms.
- Excessive proliferation of epithelium in certain areas of the mucous membranes.
- Limited inflammation.
- Benign or malignant neoplasms.
Let's look at the main reasons for the appearance of various spots and methods of treating them.
When to see a doctor
Visit your dentist if the spots don't go away within a week. White spots, cracks, ulcers and leukoplakia can cause oral cancer. In this case, the sooner a dangerous disease is recognized, the more favorable the outcome awaits the patient [6].
“According to WHO, in the Russian Federation alone in 2015, 589,341 cases of malignant neoplasms were identified (including 270,046 and 319,335 in male and female patients, respectively).
The increase in this indicator compared to 2014 was 4.0%, and these numbers are growing” Mikhalchenko D.V., Associate Professor, Head of the Department of Volgograd State Medical University [6]
White
In a baby, the appearance of white spots on the tongue most often indicates thrush - a fungal infection of the mucous membranes due to a decrease in immune defense in the body or when taking antibiotics. Such spots are located asymmetrically, can have a variety of sizes, and are often covered with a cheesy coating.
If a child shows signs of thrush on his tongue, then it is necessary to visit a pediatrician who will find out the reasons for its appearance. Delay in treatment can cause progression of the disease and inflammation of the mucous membrane, which will cause pain and discomfort in the child. You cannot try to remove the plaque on your own; this can lead to additional trauma. To eliminate such white spots, it is most often recommended to treat the child’s oral cavity with a weak solution of baking soda or ordinary brilliant green. In more severe cases and with relapse of the disease, it may be necessary to take antifungal drugs.
Possible complications.
More often, the disease passes without dangerous consequences for the patient. But with weak immunity, especially in young children, severe herpes sore throat can lead to serious complications caused by the spread of the virus to other organs:
- serous meningitis
- heart pain, myocarditis
- pyelonephritis
- encephalitis
- conjunctivitis.
To exclude the development of serous meningitis, you need to consult a neurologist; if you have heart complaints, you need to contact a pediatric cardiologist. If there are changes in the general urine test, you must make an appointment with a pediatric nephrologist.
With proper and effective treatment of herpes sore throat complicated by meningitis, the prognosis is usually favorable. But at the same time, the treatment of the youngest patients requires careful attention. With myocarditis the situation is more severe. Any complications of herpetic sore throat require the intervention of specialists!
Geographical
If red spots and a white coating along their edges appear on the tongue, then this is a sign of a geographic tongue - desquamative glossitis. The disease is not inflammatory in nature and may indicate some hormonal disorders, worms and problems in the digestive system. Such spots do not have smooth outlines, they quickly change their location and do not bother the child in any way. They can be oval, round or have fancy shapes.
This disease lasts a long time and often goes away on its own after some time, even without specific therapy. Sometimes antiseptics, vitamins and drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration processes are used to treat geographic tongue. But most experts (for example, Dr. Komarovsky) believe that there is no need to treat geographic spots.
If formed at the tip
If redness in the form of a spot appears at the very tip of the tongue of an infant, then it is most likely caused by a malfunction of the digestive system. In this case, the middle part is often covered with a whitish coating.
In older children, there are a large number of factors that cause such damage. These include common injuries - biting, cuts from hard food or candy, burns from hot drinks or food
.
An improperly formed bite is also a constant source of injury.
, especially some varieties of this pathology. Then, while eating, the child often bites the tip of his tongue.
Reds
The appearance of red spots on a child’s tongue is a sure sign of an infectious or inflammatory process in the oral cavity:
- stomatitis;
- glossitis;
- bacterial dermatosis;
- herpetic infection.
Also, red spots may be due to an allergic reaction or consumption of foods that are bright red in color.
Very often, such formations are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms: pain in the tongue, a feeling of discomfort, increased salivation. Due to pain, children may be capricious and refuse to eat or drink. The general condition may also suffer - body temperature rises.
Only a doctor should treat red spots. After establishing an accurate diagnosis, the following may be prescribed:
- treatment of lesions with antiseptic agents;
- taking antibiotics or antivirals;
- use of anti-inflammatory medications.
Clinical manifestations of different types of seizures
Different pathologies are characterized by a variety of muscle contractions. Seizures are classified into the following types:
- Small ones. They manifest themselves in the form of weak twitching of the limbs, blinking, trembling of the eyelids, and facial movements. Minor seizures are often not noticed by parents.
- Tonic. Characteristic of premature babies. They are manifested by pronounced tension in the muscles of the body, throwing back the head. Respiratory cessation may occur due to spasm of the airways.
- Clonic. They may affect one or more muscle groups, depending on this they are divided into:
- focal, or focal (occur in one area of the body);
multifocal, or multifocal (spread to several parts of the body);
- generalized (muscles of the whole body are involved).
- Myoclonic. Manifested by convulsive twitching of the muscles of one or more limbs.
- Febrile. Triggered by hyperthermia (high temperature).
With clonic convulsions, the child loses consciousness, and blueness (cyanosis) of the skin is observed.
Young children may experience convulsive twitching when falling asleep or during sleep. If they are not accompanied by specific symptoms and elevated body temperature, then they are considered safe and are regarded as the body’s reaction to the formation of the nervous system and the development of its activity.
If a convulsive attack develops, when breathing stops and consciousness is impaired, the child needs emergency medical care.
Dark
Dark spots on the tongue often occur when eating food that contains dark pigments that color the plaque on the surface of the mucous membranes. Such spots do not pose any danger to the child and disappear after hygiene procedures. But there are a number of conditions that manifest as dark spots in the mouth and which can have very serious consequences.
Black
Black spots on the tongue in children most often appear during a long course of antibiotic therapy as a result of the active proliferation of microorganisms and fungi. Blackening of the tongue develops gradually and can last up to 2-3 weeks. The main treatment for this condition is to restore normal microflora in the child’s intestines and oral cavity. For this purpose, eubiotic drugs are prescribed (for example, Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin).
It is extremely rare that black spots on the tongue appear as a result of deep degenerative processes accompanied by necrosis of areas of the mucous membrane. This condition is very dangerous and requires emergency medical attention. The treatment of such spots is often surgical.
Blue
Blue spots in a child's mouth are a rare occurrence. They may appear in the following situations:
- The presence of severe heart failure due to heart disease and defects. Spots on the tongue appear due to stagnation of blood in the venous bed and are accompanied by blue discoloration of the lips and limbs. Their treatment consists of eliminating cardiac pathology and normalizing blood microcirculation in the vessels.
- With the growth of a benign vascular tumor - hemangiomas. This blue spot is most often single. Treatment is only possible through surgery.
Diagnosis of seizure disorders in children
If convulsive twitching is not accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the child’s well-being, they can go unnoticed by his parents for a long time. In addition, newborns experience twitching of the limbs during sleep, various movements of the arms and legs. Alarming symptoms require consultation with a neurologist and a thorough examination of the body.
Electroencephalography is used to study brain activity, but minor seizures are not detected on the EEG.
For the purpose of additional diagnostics to identify the cause of convulsive syndrome, the following is indicated:
- CT scan of the brain;
- examination of cerebral vessels (angiography);
- carrying out blood tests for sugar, the content of trace elements in it, etc.
Bald
Normally, the lingual surface is covered with a large number of small taste buds, which give it a velvety appearance. If such papillae die or atrophy for any reason, “bald” spots appear. They are pink in color, irregular in shape and do not spread to the mucous membranes of the cheeks, lips or gums.
Reasons that can cause the appearance of such pink “bald” spots:
- Inflammatory diseases (glossitis, stomatitis).
- Tongue injuries.
- Burns from heat or chemicals.
“Bald” spots do not cause any inconvenience to children, but may slightly change the taste sensations. It is impossible to cure such formations, since the taste buds cannot be restored.
If you find that your one-year-old or older child’s tongue has become spotted, you should not panic and try to treat it yourself. Also, the appearance of spots on the tongue should not be ignored, as they may indicate the presence of serious diseases. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will find out the exact cause of such changes and, if necessary, select appropriate treatment for the child.
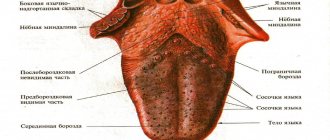
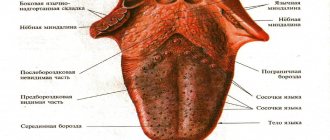
What does a healthy tongue look like?
When a person is healthy, his tongue is smooth, soft, and pale pink in color. The movement does not cause discomfort. The papillae on the tongue are not smoothed out: small at the tip, larger closer to the middle. Plaque is white in small quantities and can be easily removed with a toothbrush. The sense of taste is not impaired [1].
In order not to miss the development of unpleasant diseases, regularly conduct an independent examination of your tongue. To do this, follow a few rules:
- Examine your tongue in the morning before brushing your teeth.
- Use natural light.
- Don't strain your tongue.
- Consider what you ate the day before. For example, beets or blueberries color the tongue.
You can comprehensively assess the state of the language by honestly answering a number of questions:
- Tongue color.
- How smooth it is.
- Is there any plaque, what color and density?
- Is the language homogeneous in its structure?
- Are your teeth imprinted on your tongue?
- Cracks in the tongue, ulcers, wounds.
- Is there bad breath?
Treatment of desquamative glossitis
Desquamative glossitis does not belong to the category of dangerous diseases with serious consequences. Many parents, seeing that their son or daughter’s tongue is peeling off, panic, fearing that such changes in the mucous membrane could develop into oncological tumors. These fears are completely unfounded. Desquamative glossitis never develops into cancer.
If geographic tongue is a secondary symptom of another, underlying disease, treatment should be comprehensive.
To eliminate discomfort, itching and burning on the mucous surface of the tongue, painkillers can be used. In order to save yourself from discomfort, you must definitely exclude from your diet all spicy, salty, sour, too hot and cold foods.
Antiseptic rinsing of the mouth is necessary several times a day. For this purpose, special disinfectant medications are used, which are prescribed by the doctor.- An oil bath gives an excellent effect. You can take sunflower, corn or olive oil, which is heated in a water bath for 20-25 minutes.
- A thorough sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out - timely treatment of carious teeth, gum diseases, systematic cleaning.
- Taking multivitamin complexes will be an effective addition to the course of treatment. But in no case should you choose them yourself - you should definitely consult with a specialist.
Adult men and women are recommended to give up many bad habits - smoking, frequent consumption of strong alcoholic drinks, as well as sweets and other foods with a lot of sugar.
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at preventing infection. This presents certain difficulties, since the vast majority of the population is infected with it. It is better if the child gets sick from it at an older age.
For this it is recommended:
- avoid contact with infected people;
- will provide personal utensils and personal hygiene products for the child;
- Kissing people with herpetic rashes is prohibited;
- strengthening the baby's immune system.
It is recommended that the child be provided with adequate nutrition and regularly given vitamin and mineral complexes.
Types of plaque and reasons for its appearance
To understand why the tongue becomes spotted, you need to take a closer look at the plaque covering it. Usually it precedes spots that form as a result of a violation of its structure or after the plaque “peels off.” The film on the tongue of an infant or older child can be of the following shades:
ThrushThin white coating . Often observed in newborns and children in the first year of life. Appears in the morning, structurally it is a thin, transparent film of whitish color. It is enough to remove the deposits with a damp gauze swab so that they no longer appear during the day. This plaque is an allergic reaction of the baby to an artificial formula or to products that make up the mother’s diet (during breastfeeding).
- Curdled white coating. A dense film of rich white color with hidden ulcers, foul-smelling and difficult to remove - a symptom of thrush (candidiasis) or stomatitis. In infants with such diseases, instead of a solid plaque, white spots of very impressive size often form.
- Yellow plaque . Formed when there is a malfunction of the child’s liver, kidneys or bile ducts.
- Fungal infection of the tongue
Gray plaque . The initial sign of dangerous childhood diseases - scarlet fever and diphtheria. Sometimes this appearance of the taste organ indicates severe dehydration. In both cases, you need to start treating the root cause of the symptom as soon as possible, since such diseases are dangerous not only for the health, but also for the life of the baby.
- Plaque in the form of green spots . The manifestation indicates a fungal infection in the oral cavity of a small patient. Usually the rash spreads to the palate, cheeks, and mucous membranes of the lips.
- Brown deposits . The result of a malfunction of the digestive system, accompanied by stagnation of bile in the bile ducts. In infants, the symptom often signals dehydration; in older children, it indicates a deficiency or malabsorption of B vitamins. In addition, if brown spots appear on the baby’s tongue, an allergy to herbs can be suspected, even if the nursing mother takes them.
- Black deposits . They are a consequence of taking certain antibiotics, overdose or the body’s rejection of the drug. Sometimes the reasons for the appearance of black plaque lie in intestinal disorders: colitis, enteritis and gastritis.