Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Let's figure out how to determine that gum inflammation has begun after tooth extraction, how to quickly get rid of it and prevent its occurrence.
What to do after wisdom tooth removal
On this day, it is better to go home and relax: sleep, read a book, watch your favorite show or movie. It is not recommended to move a lot and intensively, or engage in physical labor.
Starting from the second day, it is necessary to rinse your mouth with antiseptics and take antibiotic medications to prevent the development of infectious and inflammatory diseases. The doctor decides which antibiotics to take after wisdom tooth removal. If there are no recommendations, then you can choose any medications with a wide spectrum of action.
Intense rinsing is not recommended, licking the blood clot is strictly prohibited, otherwise this will lead to the effect of a dry socket. A plug of clotted blood protects the resulting cavity and jaw bones from food particles and bacteria getting inside.
Do not consume hot or too cold foods, drinks, or overheat the body. Visiting the beach, baths, saunas is prohibited.
Smokers will have to give up cigarettes for 2, 3 days, or better yet for a week. Nicotine does not allow the wound to heal quickly, as it constricts blood vessels. Tissues are poorly saturated with oxygen and nutrients, and are more easily susceptible to infection.
A repeated visit to the doctor is necessary, even if the stitches do not need to be removed. The doctor will examine the wound, be able to identify complications in time and prescribe the correct treatment. You should not wait until the date of re-appointment if there is severe, ongoing pain, or the appearance of pus in the socket.
Folk remedies
Let's look at useful rinse recipes that are used to treat gingivitis and alveolitis after tooth extraction.
One tablespoon of dry crushed chamomile (sage, calendula) should be steamed with 250 ml of boiling water. The mixture should be left for an hour, wrapped in a towel, then filtered and used for rinsing. It is recommended to rinse your mouth every 2-3 hours.
The following healing recipes will help relieve inflammation and relieve discomfort:
- Mix 20 drops each of tea tree oil, cloves and liquid vitamins A and E, add a pinch of cayenne pepper. Moisten a cotton swab with the resulting medicine and apply it to the painful area.
- Wet baking soda with water to form a paste and apply it to the inflamed area.
ASEPTA gel with propolis will help you quickly cope with gum inflammation. This unique product containing the waste product of bees relieves inflammation of the gums by 31%, has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effects against gram-positive bacteria, as well as antipruritic and analgesic effects (reduces the pain of affected tissues), accelerates the process of regeneration and epithelization of wound surfaces, stimulates metabolic processes.
We hope that our recommendations for the treatment of gum inflammation after tooth extraction will be for informational purposes only. Treat yourself carefully and remember: at the first symptoms - acute pain in the gums, sudden changes in temperature, severe swelling of the gums, discharge of purulent exudate - consult a doctor as soon as possible. A lesion can be disastrous, so take care of yourself after surgery.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Comparative clinical evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of traumatic lesions of the oral mucosa IORDANISHVILI A.K. *,** Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Professor of the Department *Department of Orthopedic Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education “North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (rector - Doctor of Medical Sciences Sayganov S.A.); **Department of Maxillofacial Surgery and Surgical Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Military Educational Institution of Higher Education “Military Medical Academy named after S.M. Kirov" of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation (chief - Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Professor A.Ya. Fisun).
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on clinical trials of anti-inflammatory balm for gums "Asepta" adhesive, St. Petersburg State Medical University, 2007
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
If your temperature rises after wisdom tooth removal
The symptom may occur immediately after extirpation. This is due to the action of the immune system in response to tissue injury and invasion of foreign elements into the body.
Doctors recommend taking antipyretics and using cold compresses to remove heat locally.
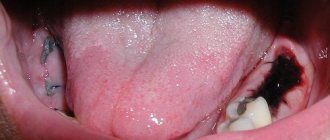
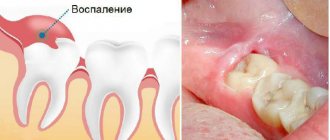
If the patient then develops a fever several days after extirpation, this may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process. The most common is alveolitis. It is accompanied by acute pain, which can radiate to the throat, temple, ear, depending on where the hole is located. If, when you probe the hole with your tongue, you feel an empty cavity, then you need to urgently go to the dental clinic where the surgery was performed.
Complications of alveolitis
If alveolitis is not treated in a timely manner, the following complications may develop:
- Odontogenic sinusitis is an inflammation of the maxillary sinus caused by the spread of infection from the inflamed sockets after the removal of premolars or molars of the upper jaw;
- Phlegmon - purulent inflammation spreads to the surrounding soft tissues;
- Acute periostitis - pus accumulates in the periosteum area;
- Odontogenic osteomyelitis is a purulent-necrotic lesion of the jaw bone;
- Sepsis - an infection enters the bloodstream, causing it to become infected.
Alveolitis itself is not so dangerous, but its complications are life-threatening. Therefore, if you notice symptoms of alveolitis, contact your doctor immediately.
How to relieve pain after wisdom tooth removal
The doctor prescribes drugs for pain relief to the patient. If there is no list, but the pain is severe, then you can buy Tempalgin, Baralgin, Ketanov and similar medications. Medicines must be taken according to instructions. If you take too many tablets, it will lead to side effects. One tablet is usually enough to stop an attack. Take three times a day.
In addition to medications, pain can be reduced with cold. A cold compress is applied to the cheek for 15 to 30 minutes up to four times a day. You can use pieces of ice or frozen food from the freezer. They are placed in a plastic bag and a towel, and then applied to the sore spot.
Additional physiotherapy treatment (click to expand)
Physiotherapeutic treatment is an important addition to drug therapy; with the help of physiotherapy, the intensity of inflammation can be significantly reduced and healing time can be accelerated. For alveolitis, the following techniques are used:
- UV therapy - the hole is irradiated with short-wave ultraviolet light, which kills pathogenic microorganisms and reduces the level of inflammation.
- SMV therapy is a method of treatment with an electromagnetic field, based on the effect of centimeter waves on the area of inflammation. The procedure helps improve blood circulation and metabolism, due to which toxic substances are removed from tissues faster and regeneration processes are accelerated. SMV therapy also has an analgesic effect.
- UHF therapy – the body is exposed to a high-frequency electromagnetic field. For alveolitis, UHF therapy is used if the patient's regional lymph nodes are enlarged.
- Electrophoresis – medications are injected into inflamed tissue using electrical impulses. For post-extraction alveolitis, electrophoresis is used to reduce pain. For this purpose, solutions of novocaine, lidocaine, trimecaine are used.
- Fluctuarization is a treatment technique with pulsed currents of a sinusoidal shape with a low frequency. As a result of the procedure, blood circulation and lymph flow improves, swelling resolves, and the level of inflammation decreases.
- Laser therapy - the hole is exposed to infrared laser radiation, which has an anti-inflammatory effect, reduces swelling and redness of soft tissues, and accelerates healing.
What can you eat after wisdom tooth removal?
It is forbidden to put anything in your mouth for two hours after extraction. During this time, a plug of condensed blood is formed and fixed on the socket, which is necessary to protect against the entry of various elements, including pathogens. If you are very thirsty, you can do this through a straw or in small sips.
On the first day, you can drink non-hot drinks and eat liquid porridge, yogurt, and soups. Over the next few days, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- food must be at a comfortable temperature; hot and too cold food is prohibited, including drinks;
- it is necessary to exclude solid foods that can injure the gums;
- You need to chew food on the side that has not undergone surgery;
- After each dose, you need to rinse your mouth with a warm saline solution;
- If your immune system is weakened, you can take additional multivitamins.
It is better to refuse or limit sweet, spicy foods, alcohol, and carbonated drinks.
Causes of inflammation
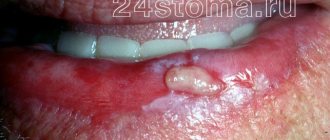
The disease can develop only after tooth extraction. Most often, the hole formed after removal heals within a day after the operation, and the patient feels better. But if the blood clot that covers the open wound moves or becomes deformed, an infection can penetrate into the hole, in which case alveolitis of the gums develops. As a result, the surface of the wound heals for a long time, and the patient suffers from complex discomfort.
Predisposing factors for the development of inflammation:
- Surgical injuries during complex removal. The more complex the operation, the more pronounced the postoperative inflammation of the bone tissue will be, and the more likely the release of direct plasminogen activators.
- Complex extractions associated with tooth segmentation, osteotomy, detachment of the mucoperiosteal flap. Complex operations increase the chance of developing alveolitis 10 times.
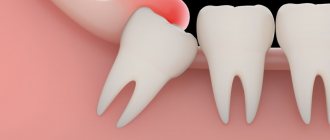
- Removal of wisdom teeth. The denser, less vascularized bone tissue adjacent to the figure eights is prone to the formation of dry sockets.
- General diseases of the patient. Alveolitis often occurs against the background of concomitant diseases. For example, patients with diabetes mellitus or immunocompromised patients are more susceptible to alveolitis due to impaired healing processes in the tissues.
- Taking oral contraceptives. The estrogen contained in these drugs may indirectly enhance the fibrinolytic process, causing the breakdown of the blood clot.
- Smoking. The direct connection between smoking and alveolitis has been repeatedly proven clinically. According to studies, the risk of socket inflammation in smokers increased 4-5 times compared to non-smokers. The incidence increased by more than 20% in patients who smoked 1 pack per day and by 40% in patients who smoked immediately before and after surgery.
- Dislocation of a bunch. If the socket is handled carelessly and there is negative pressure (for example, due to drinking through a straw), alveolitis may develop.
- Bacterial infections. Dentists agree that bacterial infections are the main risk factor for dry socket.
- Poor oral hygiene. The incidence of alveolitis increases significantly with poor oral hygiene.
- Excessive use of local anesthetics. According to some studies, excessive use of an anesthetic with a high concentration of a vasoconstrictor can provoke ischemia and make it difficult for the socket to fill with blood. This condition also increases the risk of alveolitis.
In fact, alveolitis is a fairly rare disease. According to statistics, it affects approximately 3% of patients who have undergone tooth extraction surgery. More often than not, the socket is not formed properly when lower incisors and molars are removed.
But alveolitis is especially common when removing lower wisdom teeth: according to experts, in approximately 20% of cases, the removal of “eights” with difficult eruption is complicated by alveolitis. In addition, it is believed that the risk of developing the disease is inextricably linked with age. This is explained by the fact that metabolism slows down, immunity is weakened, and the regenerative abilities of the body deteriorate.
How to rinse your mouth after wisdom tooth removal
The first few hours after extirpation, rinsing is strictly prohibited. This can lead to the natural plug being washed away, exposing the socket and bone. If bacteria penetrate inside, alveolitis or osteomyelitis will develop.
From the second day, carefully, not intensively, rinse your mouth with various antiseptics:
- chlorhexidine;
- miramestin;
- furatsilin;
- diluted potassium permanganate.
At home, you can prepare a solution with salt, soda, and add a few drops of iodine to the water. Herbal decoctions with sage, eucalyptus, chamomile, calendula, and oak bark perfectly relieve swelling and inflammation.
Types of deletion
Wisdom teeth (eights, third molars) are larger than other dental units in the row. They differ not only in size, but also in the complex anatomy of the root system. Eight has from 2 to 6 roots
, which are often closely intertwined with each other. Given the complex arrangement of wisdom teeth, when they are removed, a significant wound is created.
The risk of complications will directly depend on how difficult the figure eight extraction was. With simple extraction, when the tooth is intact, the roots are not intertwined, and there are no other pathologies (pulpitis, periodontitis, etc.), the risk of complications is minimal. In such a situation, the doctor uses forceps or an elevator to remove the tooth from the socket.
If the wisdom tooth is incorrectly positioned (horizontal eruption, severe curvature), intertwined roots, significant destruction of the coronal part, or the presence of inflammation, a more global surgical intervention may be required. An incision in the gum, cutting a tooth into pieces with a drill, removing root fragments through the jaw bone and other manipulations significantly increase the traumatic nature of the procedure. Aching pain, swelling after removal of the figure eight, increased temperature (up to 37.5℃), hematoma on the cheek - this is a normal reaction to the intervention, which lasts no more than 5-7 days.
How long does it take for gums to heal after wisdom tooth removal?
It is impossible to answer this question unambiguously, since the answer depends on the following factors:
- difficulties of extirpation - with a simple procedure, the tissues are minimally injured, which means the hole will heal within a few days; with incisions in the gums, the tissues heal for several weeks;
- age - faster for young people;
- the presence of complications, inflammatory processes that delay healing indefinitely until the infection is eliminated;
- compliance with doctor's instructions for the rehabilitation period;
- individual characteristics of the body.
Treatment at the dentist
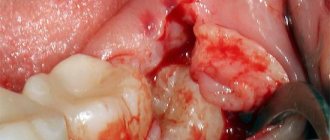
The doctor begins treatment by washing the socket and treating it with antiseptic solutions, and then cleans the socket from the remains of the blood clot using a surgical curette. Then the wound is dried with a gauze swab and treated with an anesthetic and antibacterial agents. The wound is covered with a bandage, which is designed to protect the open surface of the wound from possible biological, chemical or mechanical irritants. To check the possibility of detecting pieces of the extracted tooth in the socket, an x-ray can first be taken.
The procedure for cleaning the hole as a whole is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Local anesthesia is performed;
- The well is washed with an antiseptic solution (hydrogen peroxide solution 3%, chlorhexidine 0.05% or furatsilin 0.02%), and food debris and necrotic masses are removed;
- If there are foreign bodies in the hole (root fragments, cysts and granulomas), they are removed using special instruments;
- After cleaning the hole, it is treated with antiseptic solutions, dried with a sterile gauze swab, and turunda with an antiseptic and an anesthetic is injected into it. With a mild degree of inflammation, a turunda may not be necessary; thorough cleansing of the hole and subsequent care for it is sufficient;
- In case of a pronounced necrotic process in the hole, rinsing and application with trypsin is carried out - this is an enzyme preparation that accelerates the breakdown of dead tissue. Trypsin has anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effects, helps clean the socket from necrotic masses and pus;
- After completing all the manipulations, the patient goes home, the doctor appoints appointment days when he needs to come for antiseptic treatment of the hole and change the turunda, if one has been installed. If necessary, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
For alveolitis, antiseptic baths (not rinsing) with solutions of chlorhexidine 0.05% or miramistin 0.01%, which can be purchased ready-made at the pharmacy, are effective. When performing baths, the solution is taken into the mouth and held for several minutes, then carefully spat out. To relieve pain and reduce the degree of inflammation, nimesulide or ibuprofen are prescribed.
To prevent the turunda from falling out of the socket, during treatment you need to eat soft, pureed food and do not chew on the sore side. If the turunda does fall out, you need to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine solution and immediately consult a doctor.
If this is not possible, you should rinse the hole yourself from food debris: to do this, bite off the sharp tip of the needle from a 5 ml syringe, bend it a little, and disinfect it with pure alcohol. A chlorhexidine solution is drawn into the syringe, the needle is inserted into the hole (not too deep) and the piston is pressed intensely to create a liquid pressure that can remove food debris.
All cases of alveolitis treatment are individual, so it may be necessary to visit the dentist up to several times.
With a favorable course of the healing process, the pain goes away, and the inflammatory process gradually subsides and disappears after a few days.
If the process, despite the procedures performed, progresses, then after antiseptics, gauze tampons soaked in propolis tincture or camvorophenol solution (10%) are inserted into the hole. A tetracycline-prednisolone cone inserted into the well has a good antibacterial effect.
Oral hygiene
It is not carried out on the first day to exclude infection and accidental injury. Chlorhexidine can be used almost immediately after tooth extraction, as it does not cause side effects; the main thing is to rinse carefully and according to the instructions. Further hygienic cleaning can be performed once a day with a soft brush, carefully avoiding the surgical area.
Floss is also used to remove food debris from between teeth and a warm saline solution is used to rinse the mouth after each meal. Do not forget about cleansing your tongue, as plaque also accumulates on it, in which bacteria actively multiply.
Removal of sutures after tooth extraction occurs on the 7th - 10th day. By this time, the wounds have already healed and restrictions on hygiene procedures are lifted. Cleaning is carried out twice: in the morning and in the evening.