29.11.2019
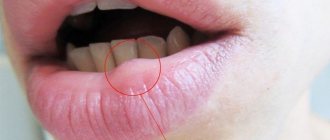
A growth on the mucous membrane of the mouth, located on the upper palate, causes discomfort to the wearer, sometimes accompanied by pain. A lump on the roof of the mouth occurs due to several completely different diseases. Each disease has its own characteristics and causes, but their clinical characteristics are similar. Without the qualified help of a doctor, it is impossible to determine an accurate diagnosis and effective method of therapy.
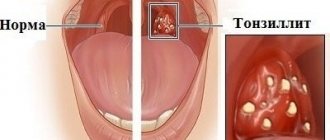
Bumps in the mouth: what they are, their causes and treatment
Any neoplasms in the oral cavity require careful study of the clinical picture. This can be either a harmless growth or an alarming signal from the body. Thus, a lump on the roof of the mouth often occurs as a result of a cold or infection. This formation does not cause discomfort and resolves on its own after strengthening the immune system. If the growth is accompanied by pain and other unpleasant symptoms, this may indicate a serious pathology. Only a doctor can determine the cause of the lump and tell you what to do.
In what case and which doctor should I contact?
A lump has appeared on the roof of your mouth and it hurts - this is not yet a reason to visit a doctor.
You can contact the clinic if other symptoms appear:
- Increasing pain when chewing and swallowing.
- Increase in volume of the tubercle.
- The appearance of bad breath.
- The thickening does not go away within several weeks.
First of all, you should contact your dentist. Subsequent examinations can be carried out by doctors: a surgeon, a therapist, an otolaryngologist.
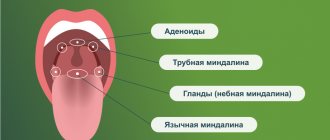
Why do bumps appear in the sky?
A growth in the mouth appears as a result of blockage of blood vessels and stagnation of organic fluids, which causes inflammation in the mucosal tissues. Among the most common causes of pathology are the following:
- bad habits – alcohol abuse and smoking;
- chronic diseases – sore throat, sinusitis;
- constant exposure to traumatic factors - incorrectly fitted crowns that become infected, eating too hot food, sucking on lollipops, etc.;
- insufficient oral hygiene - food remains behind the teeth become a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic microflora;
- inflammation of the salivary glands;
- colds and infectious diseases;
- Doctor’s mistakes – incorrect filling or tooth extraction.
A child can also develop a lump in the mouth. In most cases, the pathology occurs due to bruises, which are quite common in childhood.
Bumps also form in the mouth due to cancer (leukoplakia and papillomatosis), which pose a great danger to human health and life.
Classification of palate cancer
Based on location, cancerous tumors are divided into 2 types of malignant tumors of the palate. In case of cancer of the hard palate, the malignant neoplasm is located at the border of the nasopharynx and the oral cavity, affects the bone structures and spreads to all layers of the oral mucosa. In the case of cancer of the soft palate, the tumor is localized in the mucous layer and muscles of the vault of the oral cavity.
Based on the histological structure of the tumor, there are 3 types of malignant neoplasms of the palate:
- Cylinder;
- Adenocarcinoma;
- Squamous cell carcinoma.
Cylindroma (adenocystic carcinoma) is formed from glandular tissue. It is characterized by rapid, uncontrolled growth of pathologically altered cells and quickly metastasizes. Adenocarcinoma develops from the epithelium of the oral cavity. The tumor can be localized in all parts of the hard and soft palate. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of oral malignancy. The tumor affects the mucous membrane.
General symptoms
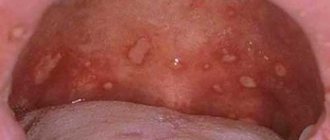
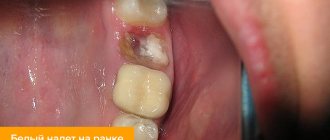
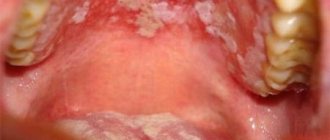
A tumor formed in the oral cavity can be of different colors: white, dark red, blue, transparent yellow. Sometimes it is soft, in other cases it is dense. A lump that appears against the background of one pathology may differ depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body: age, general condition of his body, bad habits, etc.
The lump appears in the form of a bubble, growth, ball, compaction, tumor with faint edges. Spots (change in color of the mucous membrane) may also form in the affected area. In some cases, numbness is felt in a certain part of the oral cavity, difficulties appear when swallowing, and the voice changes. In advanced forms of the disease, the cones may be damaged, which provokes bleeding with an unpleasant taste and odor.
Painful lumps indicate inflammation and suppuration. General health worsens, body temperature may rise. Purulent intoxication of the body occurs. In this case, the lump grows, it becomes hard and hot, and the regional lymph nodes enlarge.
Types of growth
New growths on the gums vary in shape, size, and method of formation.
- Angiomatous growth. A soft, bumpy, pink growth that grows very quickly. Often reappears after removal. This growth is diagnosed in children aged 10-12 years; as a rule, it does not occur in adults.
- A fibrous growth is a gum-colored lump. It grows slowly and does not cause pain, so patients are in no hurry to see a doctor.
- Giant cell growth. A rapidly growing neoplasm of red-blue color, from which serous fluid is secreted. The lump is easy to injure.
Diagnosis of diseases accompanied by the formation of lumps in the mouth
Tumors have appeared in the mouth, and the question is, which doctor should I contact? This symptom is a prerequisite for visiting the dentist. To diagnose the disease, the doctor will first conduct a visual examination and palpation, and collect an anamnesis. A puncture is taken from the resulting lump and a bacteriological examination is carried out, which makes it possible to determine the cause of its occurrence.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor determines the need to use other diagnostic methods:
- general tests;
- X-ray;
- Ultrasound;
- biopsy.
If the cause of the formation of a lump on the upper palate is beyond the scope of the dentist’s competence, the patient is prescribed consultations with other specialists (pediatrician, therapist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, hepatologist). Only after making a diagnosis will the doctor determine how to treat the disease.
Folk remedies
A lump has appeared on the roof of the mouth and it hurts - this is the reason for many people to turn to traditional medicine. It should be borne in mind that in the presence of malignant tumors, traditional methods should only complement the main therapy. Before resorting to home remedies, you should consult an oncologist.
Bumps on the roof of your mouth that are not cause for concern can be treated at home. For this, plant components are used; spotted hemlock, celandine, borax or aconite. After undergoing chemotherapy sessions, the following will help restore strength: lady's slipper, cat's claw root. Tinctures are prepared from these herbs and taken over a long period of time.
- Daily 1 tsp. cat's claw is poured into a glass of boiling water, infused and taken for 3 months, 3 glasses a day.
- The same infusion is made from the herb spotted slipper.
- Tincture of fragrant laurel leaves is taken 1 tbsp. l. 5 times a day, in small sips. To do this, take 250 g of leaves, add 0.5 liters of alcohol and infuse for 2 weeks in a dark place.
Aloe juice helps a lot. The pulp from the leaves can be applied in the form of applications to the thickening or rinsed with juice in the mouth. A soda solution prepared with warm water helps speed up healing if you rinse your mouth with it 2-3 times a day.
You can make a paste from baking soda:
- Mix 1 tsp. soda with a small amount of water, bring to a paste.
- Apply the mixture to the thickening of the mouth and leave for a few minutes.
Honey procedures performed 3-4 times a day will help get rid of the growth. To do this, you need to lubricate the palatal cone with warm honey.
To reduce pain and relieve inflammation, mouth rinses based on witch hazel are used.
A tubercle that appears on the roof of the mouth does not cause many problems if there are no alarming accompanying symptoms. To prevent infections, you should follow basic hygiene rules, and in case of severe pain, seek help from a doctor.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Dental diseases
At an advanced stage of periodontitis, a fistula forms near the tooth involved in the painful process. If periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum) develops, flux may appear. At first the lump is hard, but over time it becomes softer and filled with pus.
In case of periodontitis, the tooth is unfilled and the root canals are cleaned. After removing the exudate, oral baths are prescribed using special solutions. In case of periostitis, the dentist opens the tooth, places medications in the cavity, and closes it with a temporary filling. If this treatment does not help, the tooth is removed.
Forecast
If the disease is diagnosed in a timely manner, treatment will allow you to quickly and completely get rid of the pathology. Fortunately, angioma is not prone to recurrence and malignancy. However, in the absence of adequate therapy, the likelihood of developing dangerous consequences increases significantly.
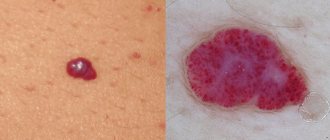
Angioma on the palate is a benign tumor that forms due to the proliferation of blood vessels or lymph nodes. If the tumor is small, it does not manifest itself in any way, but large pathological defects can cause a lot of discomfort to the patient, so it is better not to delay a visit to the otolaryngologist.
Angioma
It is a benign formation, which in most cases is a congenital pathology in children. It consists of blood vessels and is dark red in color. Sometimes it looks like a small ball on a leg. Lymphangioma, formed from lymphatic vessels, most often appears on the soft palate. It looks like a small bump with a bubbly surface. First, the tumor grows inside, then a swelling appears that hurts.
The choice of treatment method depends on the type of vessels. The angioma is removed or reduced by sclerotherapy, alcohol injection, or radiation therapy. If there is a risk of severe swelling, the formation is excised with a scalpel. The ball-shaped angioma is removed using a galvanoacoustic loop.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of cancer is difficult in the initial period of tumor appearance. It is during this period that a thorough examination of the oral cavity and tissue biopsy are necessary.
| Type of seal | State Definition | Type of study | Symptoms |
| Hemangioma | palpation of the tubercle, during which the lump is first reduced in size and then restored to its original shape | taking a smear for bacteriological analysis | turns pale when pressed and may bleed |
| Myxoma | visual | smear for histology, general blood analysis, X-ray (if necessary), puncture | difficult to see, especially during the initial stage, myxoma grows slowly |
| Cyst | visual | clinical blood test, biopsy sample, x-ray | no pain is felt, the growth does not interfere with eating or talking |
| Pemphigus | visual | clinical blood test, test for Nikolsky syndrome | caries as a concomitant symptom |
| Angioma | oral examination | blood test, smear | healing is long-term, bleeds, interferes with eating and talking. |
A lump has appeared on the palate and the pain may be a hemangioma.
In most cases, when making a diagnosis, two main types of examination are implied: examination of the mucous membrane and examination using X-rays. In cases where the doctor is in doubt, a puncture is prescribed.
Preventive measures
To reduce the risk of developing pathologies in the oral cavity, you should follow a number of recommendations:
- quit smoking and alcohol;
- normalize nutrition - do not eat hot, salty and spicy foods, introduce fermented milk and plant products into the diet;
- carefully and regularly observe oral hygiene;
- start treatment of any pathologies in a timely manner;
- Take vitamin complexes periodically (after consultation with your doctor).
If you experience the slightest discomfort in the palate, you should see a dentist. Paying attention to your health prevents the development of complications.
Clinical picture
Small tumors do not affect the patient’s quality of life. As it increases, the person begins to suffer from the following symptoms:
- Pain syndrome, discomfort when swallowing.
- Bleeding after palpation of the defect.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the mouth.
- The taste of blood.
- Irritating cough.
If a large tumor has reached the vocal cords, then hoarseness appears. Angioma is a fragile neoplasm, so the slightest contact with the surface of this growth can lead to heavy bleeding.