Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
More than 300 varieties of microorganisms live in the oral cavity (streptococci, lactobacilli, fungi of the genus Candida, staphylococci, etc.), which make up its microflora, or microbiota. Constant humidity, optimal temperature and pH values, the presence of food residues - all this creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of various types of microbes.
The composition of the oral microbiota is individual for each person, so the concept of “normal microflora” is also individual. Many opportunistic microorganisms that make up the normal microflora of the oral cavity play an important role in the etiology and pathogenesis of caries, diseases of the mucous membrane and periodontal tissue. The microbiota of the oral cavity is involved in the primary processes of food digestion and absorption of nutrients, in the synthesis of vitamins, and in maintaining the proper functioning of the immune system.
The qualitative and quantitative composition of microflora usually changes little throughout a person’s life, but under certain factors this is possible. In this case, they speak of an imbalance of microflora, that is, dysbacteriosis, when the proportion of normal microflora decreases, and the growth of pathogenic microorganisms increases.
The ailment itself, designated by the term “dysbacteriosis,” is not a disease and is not included in the official international classifications of diseases. It should be considered as a set of symptoms indicating the presence of pathological processes in various body systems. Occurs in adults and children. Let's talk about oral dysbiosis: how it manifests itself, why it is dangerous, how to treat it.
Stages of development of dysbiosis in the oral cavity
Some researchers identify several stages in the formation of oral dysbiosis:
- Stage 1 - dysbiotic shift (compensated dysbiosis). Characterized by an increase in the number of one type or several types of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity. At this stage there are no manifestations;
- Stage 2 - subcompensated dysbacteriosis. There are fewer lactobacilli, and barely noticeable manifestations appear;
- Stage 3. The lactobacilli needed by the body are replaced by pathogenic microorganisms;
- Stage 4. Yeast-like fungi begin to actively multiply in an unnatural niche for them.
At stages 3 and 4 (decompensated dysbacteriosis), inflammatory elements, ulcers, and excessive keratinization of the oral epithelium may occur.
All this can lead to the development of stomatitis, periodontitis, and periodontal disease. An infection of the nasopharynx may occur.
Symptoms of oral dysbiosis
Symptoms designated by the term “oral dysbiosis” occur in many different diseases and syndromes, so the disease is difficult to diagnose. Let's name the signs of an imbalance in the oral microflora:
- bad breath (halitosis);
- metallic taste, burning sensation in the mouth;
- the development of candidiasis, or thrush - a white coating on the tongue and mucous membranes of the cheeks;
- inflammation of the mucous membranes and gums;
- swelling, redness and soreness of the tongue;
- The appearance of so-called jams in the corners of the mouth is characteristic.
The pathology of normal microflora in the mouth is fraught with the danger of endogenous infections.
The listed manifestations are due to the following changes:
- colonization resistance (local immunity) of the mucous membrane is disrupted - yeast-like fungi easily adhere to the surface of the epithelium, where there are optimal conditions for reproduction;
- the bacterial antagonism of normal microflora changes significantly - normally, antagonistic microbes do not allow pathogenic fungi to actively multiply, but with dysbiosis, the former are destroyed, which provokes rapid proliferation of Candida fungi;
- In patients, a significant shift in local protective factors is detected - the weakened defense does not cope with its function, so the volume of pathogenic microflora increases unhindered.
How do probiotics work?
Dysbacteriosis and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity very often cause not only local discomfort, but also discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract and bad breath. Antibiotics, along with pathogenic microorganisms, begin to destroy the beneficial bacteria necessary for humans.
Probiotics are live strains of “friendly” bacteria and bring invaluable benefits to the body:
- help destroy pathogenic microorganisms;
- promote the regeneration of damaged tissues;
- activate the immune system;
- normalize cell metabolism;
- prevent cells from degenerating into malignant formations;
- restore the balance of fluid and beneficial microorganisms;
- prevent allergies;
- removes unpleasant odors from the mouth;
- eliminate toxins produced by pathogenic microorganisms.
Reasons for the formation of oral dysbiosis
The reasons that lead to disturbances in microbiocenosis in the mouth are, for the most part, the same as for dysbacteriosis in other areas of the gastrointestinal tract. These include:
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
- use of antibacterial and antiseptic agents for mouth rinsing. Long-term use of bactericidal rinses, antimicrobial toothpastes, and local antiseptics like chlorhexidine leads to the destruction of not only harmful, but also beneficial bacteria in the oral cavity. At the same time, the resistance of pathogenic flora to antibiotics increases;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases, intoxication and weakening of the macroorganism against their background;
- hypovitaminosis - lack of vitamins.
Often the cause of dysbiosis in the mouth is incorrect or insufficient oral hygiene. A factor that provokes a violation of the microflora of the oral cavity is smoking.
Acylact. Diseases of the oral mucosa and
Acylact. Diseases of the oral mucosa and teeth in children.
The occurrence of stomatitis and dental caries in children always causes a lot of problems for themselves and their parents. Of course, any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. But if this happens, you need to act quickly and competently. It is important to understand that behind oral diseases (OD) lie other health problems that led to its occurrence.
The 21st century was marked by the discovery of the most important role of the normal microflora of the human body in the regulation of all vital processes of the entire organism. There is not a single function of the body that is not directly or indirectly affected by human microbiocenosis.
The main cause of PR diseases is a violation of one’s own defense, i.e. immunodeficiency. The protection of the oral mucosa is formed by its own eco-biosystem, which consists of a set of beneficial bacteria that tighten the mucous membrane in the form of a protective biofilm. The destruction of harmful factors: pathogens, chemical components of food, allergens, household dirt is ensured by colonies of living beneficial bacteria that form the basis of the biofilm.
What is microbiocenosis?
The surfaces of the human body in contact with the external environment (skin and mucous membranes) are covered with a biofilm of a wide variety of “useful” microorganisms. Due to the presence of specific receptors on the mucous membrane, beneficial bacteria attach (adhere) to them, then begin to multiply, form colonies, become saturated with mucin (viscous secretion of the salivary glands) and tighten the mucous membranes and skin in the form of a protective biofilm.
The entire set of microbiocenoses belongs to the normal microflora - human microbiota. The leading microbiocenoses are intestinal (total area 200-300 m2), urogenital tract, lungs (80 m2) and skin (2 m2).
There are up to 600 species of microorganisms in the oral cavity.
The total mass of all microorganisms colonizing human organs and tissues is 3-5 kg (about 5% of body weight). The skin is colonized with 1 mm square. about 1012 microorganisms, the oral cavity - about 1010, in the gastrointestinal tract the total number of microbial bodies reaches 1014-1015. The last figure is approximately 10 times the total number of cells in the human body!
What are lactobacilli?
The totality of lactobacilli is one of the most important components of human mycobiocenosis.
Lactobacilli (lat. Lactobacillus) are a genus of gram-positive anaerobic non-spore-forming lactic acid bacteria. They are also called lactobacilli .
Lactobacilli usually have a regular long “rod” shape, sometimes coccoid, located in short chains or singly.
Lactobacilli are the very first living microorganisms that a baby encounters in his life, already during the birth process, then he receives them with mother’s milk. These microbes begin to shape the health of a newborn baby.
Lactobacilli are representatives of the normal human microflora and its main functions.
By creating an acidic environment in the cavities of the body, lactoflora prevents the development of pathogenic and putrefactive microflora. Representatives of the normal microflora of the PR prevent the contamination of the mucous membrane by pathogenic microbes. This antagonism is achieved due to the fact that lactobacilli produce strong antiseptics and antibiotics in the human body: reuterin, plantaricin, lactocidin, lactolin, brivin; lactic acid, bacteriocins, hydrogen peroxide, lysozyme, interferons, cytokines and substances with antibiotic activity. Some of them can also produce acetic acid and carbon dioxide as final products. In addition, representatives of natural flora reduce the synthesis of histamine, and therefore reduce allergic potential. One of the important functions of normal microflora is its immunomodulatory effect. Lactobacilli actively stimulate the lymphoid apparatus and the synthesis of immunoglobulins. (Grudyanov A.I. Prof. Fomenko E.V. Ph.D.).
Lactobacilli (as well as bifidobacteria):
– stimulate the human body’s defense mechanisms,
- provide regeneration of the mucous membrane,
- influence the synthesis of antibodies to pathogenic microorganisms,
- activate phagocytosis - absorption of pathogenic microorganisms by phagocytes (blood cells),
- stimulate the production of secretions of the digestive organs - gastric juice, enzymes and saliva,
- produce a number of hydrolytic enzymes, in particular lactase, which breaks down lactose (milk sugar) and prevents the development of lactase deficiency,
- trigger a mechanism that allows the body to fight cancer cells on its own,
- take part in the formation of “oral tolerance”. This means that lactocultures help the body fight allergies caused by certain foods,
- stimulate the contractile function of the intestine and, accordingly, the removal of waste digestive products,
— lactobacilli (lactobacillus) are the predominant type of normal microflora of the vulva and vagina. The main functions of lactobacilli in the vagina are to maintain an acidic environment and suppress the growth of opportunistic microorganisms. Previously, all lactobacilli found in the vagina were called Doderlein's bacilli (in honor of the German gynecologist A. Doderlein, 1860–1941).
In terms of its general biological significance, normal microflora can be considered as a kind of extracorporeal organ.
The permanent microflora of the PR serves as a kind of shield, a “biological barrier” that prevents the proliferation of random flora. This is an evolutionarily developed, physiologically necessary means of protection against infection.
Thus, beneficial lactobacilli have a comprehensive positive effect on the human body.
Currently, the term “dysbacteriosis” refers to qualitative and/or quantitative changes in normal microflora that arise as a result of exposure to various factors of an exogenous or endogenous nature on the body, entailing pronounced clinical manifestations on the part of the macroorganism (Rabinovich I.M., 2001). The concept of dysbiosis was introduced into medicine in 1916 by the German scientist A. Nissle.
“Dysbacteriosis is a social disease of the planet, the result of the era of antibiotics and the source of 90% of all human diseases” - conclusions of the international congress on dysbacteriosis, Morocco, 1999.
«Unfavorable environmental conditions, increased stress, and irrational antibiotic therapy create conditions for the widespread spread of dysbiosis of the gastrointestinal tract, the activation of chronic bacterial infections, and allergization of the body of adults and children.
Dysbacteriosis and immunodeficiency significantly affect the duration and severity of acute and chronic diseases of the oral cavity, complicate and increase the cost of their diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, the development and use of agents that promote the restoration of normal oral microflora during the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity is considered as a necessary condition for increasing the effectiveness of treatment.
One of the promising directions in this regard is the use of biological products (probiotics), the active principle of which is representatives of the normal microflora of the oral cavity.” (Grudyanov A.I., MD, prof., head of the Russian Center for Periodontology and co-authors).
According to WHO, “probiotics” are bacterial preparations containing live beneficial microorganisms , when used in appropriate quantities, exhibit beneficial effects on human health.”
Probiotics (from lat .) “for life.”
“Ignoring the role of microflora and dysbacteriosis means slowing down the further development of medicine” - President of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Academician V.I. Pokrovsky.
As inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity develop, the composition of the microflora of various biotopes that make up the oral cavity changes. At the onset of the disease, replacement of normal microflora by opportunistic bacteria is observed. Then comes the abundant proliferation of pathogenic microbes, including those that cause putrefactive processes (Legler., 1965).
There is no doubt that the origin and maintenance of life is possible only with the close and joint work of the human genome and the microorganism. (Tkachenko E.I. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., co-author, St. Petersburg)
According to E.O. Kravtsova (1995) in environmentally unfavorable areas in the microflora of the oral cavity, compared to the norm, the amount of lactobacilli decreases and the concentration of staphylococci and fungi of the genus Candida increases.
Thus, the severity of PR diseases increases in proportion to dysbiotic disorders. It is important to note that the increase in the concentration of opportunistic microflora contributed to the exacerbation of the disease precisely against the background of lactobacilli deficiency.
Currently, the role of changes in the composition and activity of microbiocenoses, i.e. dysbacteriosis in the pathogenesis of a wide range of human diseases.
“Relatively recently, intestinal microflora, in particular bacteria of the colon, began to be regarded as the main determinant of health and disease in people” (Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences A.I. Ugolev).
It is gratifying to note that priority in the formation of classical ideas about the role and nature of the relationship between the macroorganism and the microbiocenosis belongs to our compatriots. Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov, Nobel laureate in 1908, discovered and described intracellular digestion (phagocytosis), was the first to point out the most important role of the intestinal endoecological system in maintaining human health, and created the world's first probiotic preparation (Mechnikov's curdled milk) containing cultures of lactic acid bacteria.
“ This is all the more important because in the country that gave the world I.I. Mechnikov and A.M. Ugolev, as well as a number of living researchers (V.M. Bondarenko, B.A. Shenderov, etc.), unfortunately, there are some specialists who deny the colossal experience accumulated in this area. And in this case we are not talking about a scientific discussion, without which no development is possible, but about minimizing the capabilities of a practical doctor in the strategically important matter of maintaining and strengthening the health of the nation" (E.I. Tkachenko, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Uspensky V N., Doctor of Medical Sciences).
Oral diseases – stomatitis and caries in children.
Diseases of PR, as is known, are a consequence of disruption of its ecosystem (weakening of normal flora).
Treatment, first of all, should be aimed at restoring the natural protective factors and barrier functions of the body - restoring the PR ecosystem (protective biofilm), consisting of representatives of human normal flora, the basis of which in the oral cavity is lactobacilli (lactobacillus). By creating an acidic environment and releasing natural antibiotics, lactobacilli prevent the development of pathogenic and putrefactive flora and restore local and general immunity.
According to modern concepts, the mechanism of the positive action of a probiotic is based on the biological capabilities of physiological microflora.
Inflammation of the oral mucosa, or stomatitis, remains one of the most common childhood dental diseases. There are many factors contributing to the development of pathology. But the main thing is not compliance with basic hygiene rules, which include oral care and prevention of “dirty hands.” Children, especially young children, tend to put various objects in their mouths and lick their fingers.
The cause of the development of this disease is dysbiosis of the oral cavity, caused by intestinal dysbiosis and a decrease in one’s own immunity, due to which there is an uncontrolled proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the child’s oral cavity due to a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria;
Unfavorable factors of the environmental and internal microbial environment, aggravating dysbiosis of the oral cavity, contribute to the occurrence of stomatitis and dental caries in children:
- infectious diseases:
- household aggressive toothpastes with antiseptics contribute to the weakening of the PR ecosystem;
- unbalanced diet. Eating large amounts of foods containing refined sugar. Of course, dental health largely depends on a proper diet. And first of all, it must be balanced in all components. An excess of carbohydrates in the diet increases acidity and thereby contributes to the occurrence of caries;
- chronic diseases: diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (chronic gastritis, enteritis), diabetes, anemia, leukemia and many other diseases systemically affect the body;
- taking heavy medications: iron supplements, antibiotics, hormones, cytostatics, chemotherapy drugs that suppress normal flora;
- mucosal injury;
- insufficient oral hygiene.
This is what happens:
- poor absorption of calcium by the body,
- formation of dental plaque. With a deficiency of fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals, the composition and quality of saliva may be impaired, which in turn leads to the appearance of plaque on the enamel and its darkening,
- metabolic disorder and fluoride metabolism disorder. Endemic fluorosis is a systemic disease associated with an excess of fluoride in the body. As a rule, it occurs when consuming water in a certain area that contains large amounts of fluoride. Clinically manifested by dark spots and stripes on the enamel.
Also affects:
- heredity. There is no doubt that heredity affects the structure of the enamel and the composition of saliva, and therefore predetermines the tendency to dental diseases,
- genetic predisposition and disruption of the formation of tooth enamel during fetal development under the influence of smoking and medications taken by the mother during pregnancy,
- early childhood caries, which appears before the age of 2, can be caused by the child taking medications that negatively affect the enamel, as well as a lack of fluoride and calcium in food,
- dental trauma (trauma, blows)
- night feeding. A child who is used to falling asleep with bottled milk or juice in his mouth is at high risk of developing caries. Saliva maintains a neutral environment in the oral cavity; at night, salivation decreases, which leads to the fact that saliva does not wash away acids fermented by microorganisms from tooth enamel. These acids cause the release of calcium from the tooth enamel and thereby destroy them.
A healthy oral mucosa, covered with a protective biofilm, is pink, moist, without cracks or crusts. Only a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria in the oral cavity and damage to the protective biofilm lead to the fixation of pathogens to the mucous membrane and the formation of inflammatory lesions in it.
We remind you that a key role in protecting the oral mucosa is played by lactobacilli, with which the child comes into contact at birth and passing through the mother’s birth canal.
Types of stomatitis:
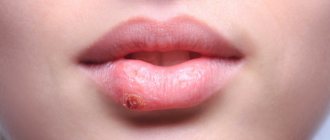
If a small child begins to be capricious, refuses to eat, body temperature rises to high levels, older children complain of pain in the mouth, and upon examination the mother discovers redness or ulcers on the cheeks, palate, tongue or the inside of the lip - this is stomatitis. In children, the treatment of this disease depends on the causes that caused it, since there are several types of pathogens that provoke the development of inflammation in the oral cavity - common bacteria, herpes viruses, Candida fungi, and stomatitis can also be toxic-allergic.
Catarrhal stomatitis (allergic)
The mildest form is catarrhal stomatitis. In this case, the mucous membrane is inflamed, has a red tint, is swollen and painful. The pain manifests itself especially when talking and eating. In later stages, bad breath, increased salivation and general fatigue appear.
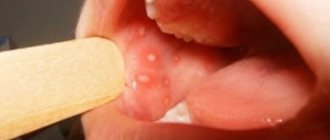
Aphthous stomatitis
Its course is very difficult. It is accompanied by high body temperature and enlargement of nearby lymph nodes. Specific morphological elements - aphthae - are found in the mouth. They have a rounded shape, with a whitish coating in the middle and a bordered hyperemic border.
Ulcerative stomatitis
It is more often formed in weakened children who have problems with the gastrointestinal tract and immunity. The ulcers are quite deep and painful.
Vincent's stomatitis can be considered as a type of ulcerative lesion of the oral mucosa. The disease does not affect infants, but older children: aged 6-8 years, 13-17 years. Occurs against the background of reduced immunity and severe chronic diseases. It is characterized by the formation of deep necrotic ulcers. They are localized on the inner surfaces of the cheeks, lips, gums, hard and soft palate. In this case, the bone tissue is not affected in the process. The disease is quite severe and is accompanied by a sharp disturbance in the general condition of the body. The main symptoms of stomatitis in children are as follows:
- strong sweetish-putrid odor from the mouth;
- high fever, chills, severe headaches;
- gums are loose and hyperemic;
- heavy salivation;
- a constant increase in the number of ulcers. Moreover, the primary lesions do not disappear, but become covered with necrotic plaque, and when you try to remove it, a bleeding wound is formed;
- In the absence of treatment, the process spreads to the tonsils and severe ulcerative tonsillitis occurs.
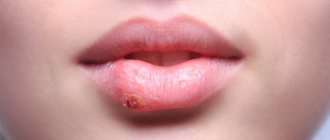
Infectious stomatitis
It is usually caused by a herpes, influenza, or chickenpox virus. More often these are herpes viruses. The first signs of the disease: severe itching of the mucous membranes of the lips, cheeks, gums and palate. Acute herpetic stomatitis in children is severe, with complications.
Within a few hours, multiple bubbles filled with clear liquid appear. At this time, the body temperature rises sharply, numbers up to 40-41 degrees are possible. The child is restless, capricious, refuses to eat and even drink. When body temperature rises, headaches and joint aches appear. Thermal cramps are common. On day 2, the bubbles begin to burst. The liquid they contain spreads, and the resulting erosive areas become covered with a gray coating. In severe cases, shallow ulcers may appear in place of the blisters.
After opening the bubbles, the general condition may improve slightly. The temperature drops, headaches and sweating decrease. But pain in the oral cavity persists.
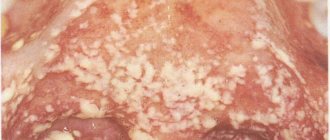
Candidal stomatitis
More commonly known as oral candidiasis. Symptoms may appear suddenly and bother the child for a long time. The main symptom is a curd coating on the mucous membrane, a feeling of a foreign body in the mouth, soreness, loss of taste, easy bleeding, even with a mild injury. Stomatitis occurs more often in both newborns and children under 1 year of age. But manifestations of the disease in adulthood are not excluded.
All activities are prescribed by the doctor. In severe conditions, in cases of stomatitis, bed rest and, if necessary, hospitalization are indicated.
Is it possible to bathe a child with stomatitis?
It all depends on the cause of the disease and the general condition of the body. If a child has an elevated body temperature, then water procedures should be postponed until it normalizes.
How is stomatitis transmitted in children?
For example, viral stomatitis can be transmitted through toys and cutlery used by a sick baby. For prevention, they should be washed thoroughly under running water.
Is it possible to walk with a child with stomatitis?
You can go for a walk if the general condition of the body allows. But if inflammation of the mucous membrane occurs due to a viral infection, it is not advisable to do this, since the infection can be transmitted to other children.
Childhood early caries and causes of teeth darkening
The biggest misconception of parents is that if you do not eat sweets, then your child’s baby teeth will not be at risk of caries. As is known, dental caries is caused by a violation of the ecology of the oral cavity - oral dysbiosis.
Types of caries in children
There are several classifications of the carious process in children, which reflect its location, depth and intensity.
Depending on which teeth are affected, caries occurs:
- Milk teeth - can appear even in infants immediately after teething.
- Permanent teeth - occurs in children over 5 years old, after the change of temporary teeth has begun.
Depending on the depth of caries spread:
- The spot - initial caries, represents the first stage of development of the pathological process, which has not yet affected the anatomical structures of the tooth enamel. It can be treated with minimal interventions and can be easily reversed.
- Superficial enamel caries - damage to dental tissues does not extend beyond the enamel.
- Medium caries is the destruction of not only the entire enamel layer, but also part of the dentin tissue.
- Deep caries is the most complex variant of the disease, when the pathological process affects the entire thickness of the tooth and almost reaches the pulp.
Despite the fact that the signs of the disease are very specific, parents do not always know what caries looks like and how to recognize it in children.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the depth of damage to dental tissues.
- With initial caries, white spots of various shapes and sizes appear on the enamel surface, which do not cause any unpleasant sensations in the child. Over time, such formations begin to change their color - they become brown, brown or even black. This indicates the progression of the disease.
- With superficial caries, the cavity does not extend beyond the enamel and may be light or dark in color. Already at this stage, children notice the appearance of pain when eating sweets or sour foods.
- With average caries, as the pathological cavity deepens, the early symptoms are joined by pain when the teeth come into contact with cold or hot food. A deep cavity is identified on the tooth surface in which food debris can accumulate. Often there is an unpleasant odor from the child's mouth.
- With a deep process and the addition of pulpitis, the child will complain of intense pain, aggravated by eating. At this stage, the baby’s general condition may suffer with the appearance of weakness, nausea or a rise in temperature. The tooth undergoes significant destruction and cannot perform its chewing functions.
General principles of treatment of diseases of PR (stomatitis, caries)
Self-medication is unacceptable! You need to contact your pediatrician or dentist.
One of the promising areas of modern microbiology and medicine is the creation and introduction into clinical practice of drugs based on living cells of physiological microorganisms - probiotics.
It is predicted that in the 21st century, probiotics will replace a significant part of traditional pharmacological drugs and will take their rightful place among effective and safe ways to improve public health.
Improvement of technological processes for the production of microbial biological products has opened up opportunities for the development of another, very promising medicinal form in the form of tablets . The advantage of the tablet form of probiotics is that they can be used without prior dissolution with liquid, which eliminates the need for the patient to prepare the drug for administration and increases the accuracy of dosing. Exposure of lactobacilli in the mouth (resorption) allows their rapid attachment to the oral mucosa and dispersal, forming a protective biofilm .
The Russian probiotic drug Acylact in the form of tablets contains 3 strains of live acidophilic lactobacilli.
Practical recommendations of the Russian Center of Periodontology:
- “Inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, as a rule, are accompanied by dysbiosis of the oral cavity, the severity of which corresponds to the degree of damage. Antimicrobial and antiseptic drugs used in dental practice have a total effect on all parts of the microbiocenosis of the oral cavity. At the same time, against the background of a strong increase in the concentration of pathogenic species of microorganisms, the amount of normal microflora sharply decreases.
- During the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, the use of drugs that help restore the normal microflora of the oral cavity - Acylacta - is considered as a necessary condition for increasing the effectiveness of treatment. One of the important directions in this regard is the use of biological products (probiotics), the active principle of which is representatives of the normal microflora of the gastrointestinal tract.
- It is advisable to prescribe Acylact in the form of lozenges. The required dosage is 3-10 doses per day (i.e. 3-10 tablets per day). The tablets must be kept in the mouth until completely dissolved. They should be taken in 3-4 doses during the day before meals. The course of treatment is 15-30 days. The most effective period for using bacterial drugs in complex treatment is their early use from the first day of illness, if necessary, in parallel with antibacterial, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs.”
(A.I. Grudyanov, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor and co-authors, Central Research Institute of Information Sciences.)
It is important to note that the use of bacterial preparations allowed not only to normalize clinical parameters and oral microflora, but also had several positive side effects.
In addition to taking Acylact, you need to drink plenty of fluids. The more liquid a child drinks, the more he will excrete it, which means that various bacteria and viruses will be removed from the body. Large fluid intake increases the secretion of the salivary glands. This helps to better wash away pathogenic bacteria from the mucous membrane.
With stomatitis, a diet is required, hard, coarse foods, too hot or cold are excluded, the amount of carbohydrate foods, spices, confectionery, and sweets in the diet is reduced.
For mild forms of stomatitis, you can get by with topical agents. Treatment includes local procedures and the use of general therapeutic agents. To provide an anti-inflammatory effect, it is best for children to treat the affected areas with decoctions of medicinal herbs 3-4 times a day - sage, chamomile, Kalanchoe juice, for this you should use cotton pads soaked in the decoction. In pharmacies there are ready-made herbal mixtures, such as Ingafitol, Evcarom, which can also be used to treat ulcers or rinse the mouth in older children. For pain relief for children over 4 years old, you can use the drug Stomatidin, an antiseptic for topical use that has an antimicrobial and mild analgesic effect on mucous membrane in the mouth. Treating ulcers with propolis (Propolis spray) is very effective and has a restorative effect on any skin damage, ulcers, and herpes. The use of antiherpetic ointments is also indicated for local treatment; Zovirax and Acyclovir ointments are used. Bonafton ointment, an antiviral drug used to treat herpetic stomatitis, may be recommended. Carotolin - an oil solution with vitamin A, sea buckthorn oil and rosehip oil promote wound healing. Vinilin for stomatitis, also known as Shostakovsky's balm, is able to cleanse wounds, also has an anti-inflammatory effect, accelerates the process of healing, epithelization and tissue regeneration. Lugol and Rotokan are used as antiseptics. For frequent relapses of herpetic stomatitis, the doctor may prescribe antiviral drugs orally, that is, in tablets, such as Valtrex, Acyclovir, etc.
A high therapeutic effect of vinylin has been established for stomatitis in children; gauze napkins soaked in the solution are applied to the affected areas. The procedure is carried out 1 hour before meals. During the day you can carry out 5-6 procedures. Sodium tetraborate solution for stomatitis in children is used as an antimicrobial and antiseptic agent. Along with antiseptics, healing drugs are prescribed on day 5. Solcoseryl has this property. The wound is first dried with a sterile cotton-gauze pad. Then a thin layer of ointment is applied to the bandage strip and applied to the affected areas. Solcoseryl will not only help wound healing, but also relieve pain. Cholisal ointment gives an excellent effect. It has local anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effects.
For candidal stomatitis, local procedures consist of creating a more alkaline environment in the oral cavity, since an acidic environment has a very beneficial effect on the progression of the process. Local treatment of fungal stomatitis in children is as follows: treatment of the oral cavity 3-6 times a day with a solution of soda - 1 glass of water, 2 teaspoons of soda, as well as special aniline dyes - methylene blue. At high temperatures above 38C, of course, you should take antipyretic drugs for children.
To strengthen the immune system during and after stomatitis, vitamin therapy and restoratives are prescribed.
Why do you need to treat baby teeth?
It is very important to realize the importance of ensuring the health of the oral ecobiosystem by eliminating dysbiosis in order to prevent dental disease. Baby teeth fall out over several years (from 5-6 years to 12-13 years) and throughout this period, diseased teeth can cause discomfort to the child. And most importantly, long-term absence of teeth can cause malocclusion and uneven teeth.
Treatment for darkening of teeth.
If a child’s teeth have darkened or dark spots have appeared, first, you need to consult a dentist and eliminate oral dysbiosis using probiotic preparations. You will need to review the child’s diet, gradually eliminate night feeding or reduce it to a minimum. If the cause of darkening is caries, then treatment will depend on the stage of the disease. If the damage is minor, the altered tissues are removed and the tooth is filled, using the method of silvering the teeth. If there is significant damage to the crown of the tooth, it is removed, since caries can spread to neighboring teeth and to avoid damage to the rudiments of permanent teeth.
Prevention of diseases PR
Prevention of this problem includes several points:
- prevention and treatment of dysbacteriosis
- In an infant 1 year of age, the best prevention of caries is a healthy microbiocenosis of the oral cavity and breastfeeding. It is with mother's milk that beneficial bacteria, protective antibodies, amino acids, protein, calcium and other minerals necessary for the proper formation of a healthy child and his teeth come.
- Prevention of caries in primary teeth begins long before the child is born.
The main condition is the elimination of dysbiosis in the mother. Since the formation of tooth germs begins quite early, the expectant mother’s diet should contain a sufficient amount of calcium, vitamin D and protein from the earliest stages.
- timely treatment of chronic diseases.
- A balanced diet is important. Consumption of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals and limited consumption of refined sugar.
- proper oral hygiene. When a child’s first teeth appear, they need to be carefully cleaned with boiled water or chamomile decoction. In the future, you should choose a special toothpaste appropriate for the baby’s age.
Keep an eye on your baby's teeth and seek help from dentists in a timely manner.
Influence of the state of the oral microflora on other organs and systems
The connection between the general condition of the body and dental health is known. Thus, those patients who have oral diseases are more likely to develop cardiovascular diseases. Clinical studies confirm the presence of oral bacterial microflora in the blood and atherosclerotic plaques. Periodontopathogenic microflora is the main source of local and systemic chronic inflammatory process. Acts as a risk factor for the development of coronary heart disease.
In addition, scientists have discovered a connection between bacteria living in the mouth and the occurrence of migraines.
Another dangerous consequence of disruption of the oral microflora is the aggravation of intestinal and esophageal cancer. One study found that bacteria living in the mouth can trigger the development of colon cancer.
Diagnosis and treatment of oral dysbiosis
Oral cavity dysbiosis syndrome in the initial stages of development is detected during laboratory tests. To diagnose oral dysbiosis, microbiological examination of a smear from the oral mucosa or saliva is used. When diagnosing, the number of opportunistic microorganisms in the test material is determined.
Important: it is necessary to accurately establish the root cause of the disease, which a comprehensive examination of the body will help with, and treat the primary disease.
For pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract that affect the condition of the oral cavity, they are first treated.
If the balance of the oral microflora is disturbed, treatment is mainly used in the form of sanitation and taking medications to normalize the microflora in the mouth. However, all drugs that are used to treat oral dysbiosis are considered drugs with unproven effectiveness. The following is used as therapy for this condition:
- eubiotics - needed to increase the number of beneficial bacteria in the mouth;
- immunomodulators - increase local immunity and prevent the growth of pathogenic microorganisms;
- antimicrobial and antifungal agents.
Oral probiotics (oral probiotics)
Probiotics are live microorganisms that promote the growth of friendly microbiota. Most often, such substances are used to improve intestinal microflora, but not many people know that there are probiotics for the oral cavity.
It is important to understand that probiotics for the oral cavity are represented by one group of substances, and probiotics for the intestines are a completely different one. Scientific research regarding these drugs is very controversial, so dentists recommend using them only as an addition to the prescribed treatment for dysbiosis.
Prevention of dysbiosis in the mouth
Prevention of oral dysbiosis includes the following measures:
- use of antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor in the recommended course;
- use of alcohol-free and antiseptic rinses for daily oral hygiene, for example, ASEPTA Parodontal Fresh with plant extracts and microelements;
- smoking cessation: it is advisable to eliminate smoking altogether;
- strengthening local immunity: timely sanitation of the oral cavity, maintaining oral hygiene. You also need to strengthen your general immunity.
The main advice for normalizing the microflora of the oral cavity: do not feed the bad microbiota and do not destroy the good one.
Let's summarize: we have given a definition of oral dysbiosis, which is understood as a violation of the ratio between normal and pathogenic microflora in the direction of increasing the latter. They indicated that this condition is not an independent disease, but only a complex of symptoms. The stages of formation of oral dysbiosis, symptoms and causes of disturbances in the microflora of the oral cavity were named. Also from this article you learned how to treat oral dysbiosis and how to prevent its occurrence.
Types of Oral Probiotics
Biologists call the most common types of probiotics:
- Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium (Lactobacillus and bifidobacteria), obtained mainly from dairy products. However, it is important to normalize the population of these bacteria, but not to “overdo it” with them, since their excessive quantity provokes the formation of caries.
- Bacterial strains Bacillus subtilis, L. salivarius WB21, L. casei Shirota, L. brevis, L. reuteri, L. acidophilus may be useful in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
- Candidiasis, the most common cause of oral dysbiosis, can be treated with L. rhamnosus strains (GG and LC705) as well as Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp. shermanii JS. This type of oral probiotic can be obtained from cheese or other fortified dairy products.
- To treat halitosis (bad breath), probiotics E. coli Nisle 1917 and S. salivarius K12 can be used.
Experts' opinion
Asept products have proven effectiveness. For example, multiple clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on clinical trials to determine/confirm the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: mouth rinse "ASEPTA PARODONTAL" - Solution for irrigator." Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Head. Department of Preventive Dentistry S.B. Ulitovsky, doctor-researcher A.A. Leontiev First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after academician I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry.
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.