The nose is the first to encounter pathogenic microbes coming from the external environment, therefore it is there that inflammatory processes quite often develop - local “battles” of the immune system with pathogenic flora.
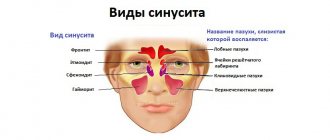
Sinusitis is the general name for inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (from the Latin sinus - sinus, the names of inflammatory diseases end in “it”). Possible inflammation of the maxillary sinus (sinusitis), frontal sinus (frontitis), ethmoid sinus (ethmoiditis), sphenoid sinus (sphenoiditis). Sphenoiditis is extremely rare, almost always together with ethmoiditis.
Signs of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (if you find two or more of the symptoms listed, you need to consult a specialist):
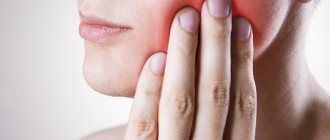
- Headache and/or pain in the teeth, eyes, cheekbones, cheeks
- Feeling of fullness in the nose, eyes, forehead, jaw
- Increased sensitivity of a part of the face
- Redness of the face or part of it
- Pain points in the face
- Nasal congestion and/or runny nose
- Increased body temperature
Damage to the maxillary sinuses - studying the causes
Most often, injury occurs in the area of the bottom of the sinus, since the roots of the molars and premolars are located quite close to it, and in some people they are located directly in the maxillary sinus, protected from them only by the mucous membrane. In some cases, the cause of bone thinning is the presence of acute and chronic diseases, such as cysts, periodontitis, periodontitis. All this can cause injury, even if the doctor did not violate any rules of dental treatment and did not apply traumatic pressure.
Damage to the maxillary sinuses is always associated with some of the dental interventions:
- removal of a cyst on the root of a tooth;
- dental implantation;
- endodontic treatment;
- removal of a tooth.
Perforation of the maxillary sinus during cyst removal occurs due to medical errors - ignorance of the exact size of the bone plate that separates its bottom from the walls of the resulting cyst, as well as in cases of a large volume of jaw bone tissue. The same reason for perforation is observed in the case of installing an implant, filling canals or inserting pins.
When carrying out endodontic treatment, in the case of greater than necessary expansion of the canals, as well as the use of brute force when installing pins, filling materials may penetrate into the maxillary cavity. When a tooth is removed, the cause of perforation can be both the anatomical features of the patient and the forceful pressure of the doctor.
Treatment of bleeding
If snot with blood appears, you should definitely consult a doctor, take a general blood test and identify the cause of the disease.
An increased content of granulocytes and high ESR values indicate acute sinusitis. With severe bleeding, the sinuses can be damaged, mucus accumulates in them and interferes with the normal functioning of the respiratory system. In addition, blood may occur due to burst capillaries. In this case, to improve blood circulation and restore the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels, you need walks in the fresh air, jogging, and playing sports.
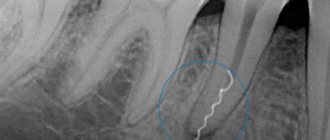
An x-ray of the parasinus sinuses shows areas affected by sinusitis.
To determine the cause of sinusitis, an x-ray of the parasinus sinuses is taken. If an inflammatory process is detected, the patient needs hospitalization. Treatment consists of taking medications, antibiotics, injections and IVs. Physiotherapy is prescribed.
It is recommended to rinse the nasal passages with saline solutions, a decoction of plantain, chamomile or calendula. They have healing properties. Peach oil has a good effect.
One of the causes of bloody snot may be an allergic reaction. In such cases, it is necessary to take an allergen test. With allergies, the snot is clear and does not go away for a long time.
Our team of doctors
Maxillofacial surgeon, Implantologist
Bocharov Maxim Viktorovich
Experience: 11 years
Dental surgeon, Implantologist
Chernov Dmitry Anatolievich
Experience: 29 years
Orthopedist, Neuromuscular dentist
Stepanov Andrey Vasilievich
Experience: 22 years
Endodontist, Therapist
Skalet Yana Alexandrovna
Experience: 22 years
Orthopedic dentist
Tsoi Sergey Konstantinovich
Experience: 19 years
Dentist-orthodontist
Enikeeva Anna Stanislavovna
Experience: 3 years
How is sphenoiditis treated?
There are two treatment options for sphenoiditis:
- Medication.
- Surgical.
Drug treatment
Painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen are suitable for treating acute pain.
Decongestants such as xylometazoline, pseudoephedrine, or phenylephrine in the form of nasal drops or nasal sprays help drain secretions from the paranasal and sphenoid sinuses.
Corticosteroids (cortisone), such as mometasone or fluticasone, may be used as a nasal spray.
If symptoms do not go away for more than 10 days, and they intensify, or a high temperature is observed, this indicates a bacterial infection. Then the doctor prescribes antibiotic therapy.
Symptoms of perforation of the maxillary sinuses
Damage to the maxillary sinuses during tooth extraction can be diagnosed if the patient has:
- blood with air bubbles released from the tooth socket;
- the appearance of blood from the nose on the side of removal;
- the appearance of “nasality” in the voice.
If this damage occurred during endodontic treatment or implantation, the doctor can diagnose it based on the following signs:
- failure of an instrument or implant into a tooth socket;
- the appearance of air bubbles in the blood;
- changing the position of the instrument when working in a wound.
General blood analysis
For sinusitis, you need not only to undergo basic functional examinations, but also to undergo a whole series of tests. First of all, the doctor will have to assess the erythrocyte sedimentation rate . This indicator indicates the level of the inflammatory process. The accuracy of the conclusions made on the basis of a general blood test will help confirm the level of C-reactive protein.
- Why does the nose bleed when you blow your nose - the main reasons for children and adults
However, these tests are not specific and provide information only about the presence of some kind of inflammation in the human body. Elevated levels do not necessarily indicate a disease of the maxillary sinuses. Therefore, along with general laboratory tests, the patient needs to undergo a series of functional examinations.
In acute form of sinusitis, the patient needs to undergo immunodeficiency testing.
An analysis to study the state of the immune system is prescribed only in the case of a chronic form of the disease. Also, the doctor may insist on performing this procedure if inflammation of the paranasal tract occurs frequently, at least three times a year.
The study for immunodeficiency includes the following series of tests:
- for HIV;
- serological studies;
- for immunoglobulins.
After receiving the test results, the patient is referred for a cytological examination. This procedure will help specialists determine the contents of the mucous secretion.
We also recommend that you study information about parietal sinusitis at this link.
What the indicators say
A clinical blood test allows a specialist to determine inflammation in the early stages of development. Thanks to the results of this study, the patient is prescribed a number of diagnostic and preventive procedures . Blood is the best reflection of any changes in health. Any disorder, be it an allergic or inflammatory process, will certainly be reflected in the general blood test in the form of deviations from the norm in monocytes and leukocytes.
Find out what contributes to the manifestation of allergic sinusitis here.
You should donate blood for laboratory testing as soon as possible. Such an examination allows you to eliminate the risk of developing complications, as well as to respond in a timely manner to the inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses.
With sinusitis, you can see the following indicators of a general blood test:
- How to deal with unpleasant odors in the home of a seriously ill person
- Increased ESR - in men the indicator can be within 9 mm/h, and in women it is slightly higher than normal at 7-14 mm/h.
- Leukocytosis is a significant increase in the level of leukocytes compared to the norm of 5-9x109l.
- Monocytosis - the rate exceeds 11%, which indicates the development of an inflammatory process in the mucosa.
Along with these changes, pay attention to the level of neutrophils, which will tell you about the degree of inflammation:
- 1-5% initial level.
- 1-5% are rod-shaped.
- 40-70% segmented.
When these indicators increase above the permissible norm, conclusions can be drawn about the development of bacterial sinusitis.
A general blood test cannot indicate a specific disease, since changes in the composition of physiological fluids indicate only a deviation of the state of health from the norm. However, the result of a clinical study serves as a direct indication for additional functional examinations.
Can there be good indicators for sinusitis?
A laboratory blood test gives the specialist a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s condition. Body fluids are the first to react to inflammation , therefore they allow you to react in time to the development of the disease even before the first symptoms of sinusitis appear. You can’t count on good results from clinical blood tests for acute or chronic sinusitis.
When visiting a doctor with complaints of deterioration in health, the specialist will first refer the patient for a general blood test. This study allows you to detect inflammation at the earliest stages.
Consequences and prevention of injury
This complication, if left untreated, can lead to:
- inflammation of the maxillary sinus;
- infection of surrounding bone tissues with transition to other sinuses of the skull;
- formation of foci of osteomyelitis in the upper jaw;
- suppuration of foci of infection;
- loss of healthy teeth in the affected area.
If the perforation was not identified and treated in time, this can lead to the development of sinusitis or acute sinusitis, which is characterized by acute pain, swelling of the nasal mucosa - with difficulty breathing and purulent discharge.
To avoid such unpleasant consequences of dental treatment for the patient, specialists at the Implantmaster clinic conduct a comprehensive study of the patient’s anatomical features using X-ray and computed tomography images and strictly observe the accuracy of medical manipulations.
Paranasal sinus puncture
One of the most reliable methods for diagnosing sinusitis is puncture of the paranasal sinuses. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, which ensures that risks are minimized and the puncture is painless . Due to the administration of the drug, anemia of the mucous membrane also occurs, which improves the outflow of fluid through the natural sinus anastomosis. After the puncture, the physiological fluids contained in the nasal cavity are suctioned or the paranasal sinuses are washed from the consequences of exudative sinusitis.
Treatment of damage to the maxillary sinuses
Treatment is determined by the degree of damage, the presence of foreign bodies in the cavity, as well as the speed of diagnosis and initiation of treatment. The only non-surgical treatment is one that was diagnosed at the time of tooth extraction and does not have signs of infection or the presence of foreign bodies in the sinus. In this case, the doctor does everything to keep the blood clot that closes it in the tooth socket and prevent it from becoming infected. For this purpose, a gauze swab soaked in iodine solution or a special plastic plate is placed in the hole; in rare cases, sutures are required.
These dental procedures are performed in combination with a course of antibiotics, drops with a vasoconstrictor effect and anti-inflammatory drugs. If a foreign object gets inside the maxillary cavity, treatment is carried out surgically through opening and removal of the foreign object and non-viable tissue. The specialists of the Implantmaster clinic not only effectively treat such injuries, but also do everything possible so that their patients know about them only by hearsay.
Author:
First aid for nosebleeds
- When bleeding from the nose due to sinusitis, the patient should be seated and his head tilted slightly forward.
- With two fingers: with your thumb and forefinger, pinch us and hold in this position for 5 minutes.
- If the bleeding does not stop, take a gauze pad and roll it into a gauze swab that will fit into the nasal cavity.
- Moisten it with hydrogen peroxide or cool water and insert it into the nasal passages.
- You can put ice on the bridge of the nose and hold it for 15 minutes.
- Sometimes the bleeding becomes so severe that blood may leak into the mouth. To make sure that this does not happen, you need to ask the patient to spit.
- If, despite all efforts, the bleeding does not stop, you must seek help from a medical facility.
Treatment with modern methods
Treatment of sinusitis depends on the severity of the disease, the general condition of the patient, the structural features of the nose and other factors. Treatment of sinusitis can be divided into:
- conservative;
- puncture;
- punctureless;
- surgical.
Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and local treatment are also used in combination. Our clinic’s specialists will select individual treatment for each patient, because our priority is an individual approach to each client.
Causes of the disease
The most common cause of sinusitis, of course, is infection. As for chronic sinusitis, in this case a relapse is possible due to untreated acute sinusitis or a history of acute respiratory viral infection, against the background of a weakened immune system.
The main causes of chronic sinusitis can be:
- Deviated nasal septum and/or vasomotor, allergic rhinitis;
- Deep caries.
The complexity of the disease lies in the fact that it can manifest itself only several days, and possibly weeks after the acute symptoms of a cold have passed. In the autumn-winter period, when the weakened immune system is most likely, the risk of sinusitis is very high.