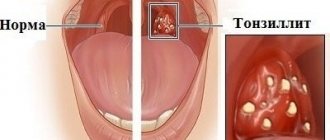
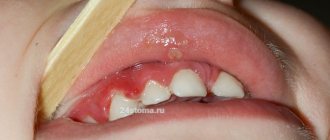
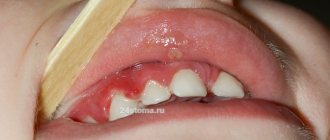
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of areas of lymphoid tissue (tonsils) located on the back wall of the pharynx. They protect the body from the penetration of potentially dangerous viruses or bacteria, but in some cases they themselves can become infected. In many acute cases, the disease is viral in nature, so tonsillitis can be treated without the use of antibiotics. The chronic form of the disease is associated with the long-term existence of bacteria in the tonsil tissue. It requires complex therapy, and in some cases, surgical intervention. Tonsillitis most often affects children, but it can develop in people of any age.
Exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis: symptoms
Often, for a long time, chronic tonsillitis occurs without symptoms or has scanty symptoms (in a simple form). There may be discomfort when swallowing food and liquids, a sensation of a foreign body in the throat, dry mouth, halitosis (bad odor) and tingling. Externally, the tonsils increase in size and there are signs of inflammation. The disease is characterized by exacerbations of sore throats up to three times a year, long periods of recovery, with general symptoms of asthenia and prolonged low-grade fever.
For the toxic-allergic form, more frequent exacerbations are typical, often with complications in the area of neighboring tissues (pharyngitis, peritonsillar abscesses), and the almost constant presence of asthenia and prolonged fever are typical.
The clinical picture of chronic tonsillitis during an exacerbation is as follows:
- sore throat that gets worse when swallowing;
- redness of the throat and tonsils;
- characteristic plaque;
- purulent discharge from the tonsils;
- bad breath;
- swelling of the nasopharynx;
- temperature increase;
- weakness;
- headache;
- fast fatiguability;
- arrhythmia;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- dyspnea.
Reviews
Andrey
For most of my life I was tormented by constant exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis. Every spring and autumn I consistently lost two weeks for treatment. Surgery to remove tonsils has bothered me since childhood. My wife almost forcibly brought me to the clinic. I didn’t even imagine that new techniques can eliminate the problem absolutely painlessly. I have been living without constant exacerbations for a year now, and I am very grateful to the hospital specialists for this.
Natalia
Not long ago I had to bring my child to have his tonsils removed. From my own experience I remember how unpleasant and painful this procedure is. I was more worried than my son. However, the clinic doctors were able to find an approach to the child and calm him down. The operation was performed without pain or blood. Now I know for sure that your clinic employs super specialists and kind, sympathetic people.
Causes, main risk factors
Up to 30 different colonies of pathogenic microbes can be sown on the surface of the tonsils of patients suffering from chronic tonsillitis. But in crypts and lacunae staphylo- or streptococcus is usually determined. A key role in the pathogenesis of chronic tonsillitis is played by beta-hemolytic strains of streptococcus (type A). Other flora - gram-negative coccal, fungal, viral - have an impact on local immunity, they support inflammation.
There are a number of factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease:
- hypothermia;
- decreased immunity;
- microtrauma of the tonsils;
- foci of inflammation in the mouth and in the head area (caries, sinusitis, adenoids, etc.);
- smoking;
- poor nutrition;
- allergy.
Viruses and bacteria that cause tonsillitis can come from the external environment.
Anatomy of the throat
In the pharynx, on the sides and along the back wall, as well as on the border of the oral and nasal cavities, there are accumulations of lymphoid tissue - the so-called lymphoid-pharyngeal ring. It performs a protective function, and each of the tonsils of this ring is an important organ of our immunity.
The largest accumulations of lymphoid tissue are called tonsils (they are also called tonsils ) and there are several of them: two palatine, two tubal, one pharyngeal (aka adenoid) and one lingual.
Inflammation of the palatine tonsils (in everyday life they are called tonsils) is called acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis .
Classification
Doctors distinguish various clinical forms of chronic tonsillitis, differing in clinical manifestations, severity of the condition and prognosis, risk of complications, as well as treatment tactics.
The simple form of chronic tonsillitis is characterized by a predominance of local symptoms. If general manifestations and lymphadenitis occur, this is referred to as a toxic-allergic form of tonsillitis. It comes in two versions:
Toxic-allergic chronic tonsillitis 1st degree . Sore throats are typical for him, which can worsen after ARVI, combined with general symptoms.
Toxic-allergic chronic tonsillitis of the 2nd degree - the symptoms are more pronounced, associated with diseases that have common factors of etiology and pathogenesis.
According to the degree of compensation of the process, the disease is divided into two options:
- chronic tonsillitis, compensated form - the source of infection is in a dormant state, there are no reactions from the body, repeated sore throats do not occur; The function of the tonsils and general reactivity are not impaired.
- chronic tonsillitis is a decompensated form - relapses of sore throat occur, complications of the heart, damage to the paranasal sinuses, middle ear, and renal complications are possible.
According to pathomorphological criteria, the process is divided into the following options:
- lacunar tonsillitis with predominant damage to the area of the lacunae;
- parenchymal-lacunar, involving in addition to the lacunae also the area of the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils themselves;
- phlegmonous - inflammation is predominantly localized in the area of lymphoid tissue;
- sclerotic with abundant growth of connective tissue fibers in the area of the tonsils and surrounding tissue.
Complications of chronic tonsillitis
Against the background of a chronic inflammatory process in the tonsil area, various complications are possible. Therefore, it is important to know why chronic tonsillitis is dangerous. Thus, the tonsils themselves, losing their function as a barrier to infection, become its breeding ground. Inside them are pathogens with the products of their metabolism. The infection can spread throughout organs and tissues, affecting the renal parenchyma, joint and heart tissue, and liver. In addition, tonsillitis adversely affects the functioning of the immune system and can be a provocateur of collagen diseases - lupus, scleroderma, dermatomyositis, periarteritis. The skin and peripheral nerve fibers may also be affected. With prolonged intoxication against the background of the disease, damage to blood vessels (vasculitis) and platelets (purpura) is possible.
Complications of tonsillitis
Tonsillitis, both acute and chronic, can cause local and general complications.
The first group includes damage to the tissues of the pharynx: paratonsillar abscess, parapharyngitis, laryngitis. Local complications also include acute otitis media and cervical lymphadenitis.
Common complications associated with damage to internal organs:
- diseases of the joints and connective tissue: rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, infectious polyarthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- damage to the heart and mediastinum: myocarditis with the development of dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure, mediastinitis;
- inflammation of the lungs, kidneys, appendix, sepsis and others.
To avoid the development of such complications, if there are symptoms of tonsillitis, it is necessary to carry out its full treatment.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis occurs on the basis of complaints, examination of the patient, and questioning of the patient. Objective signs, manifestations of chronic tonsillitis, and the general condition of the tonsils are important; the doctor determines the stages of the process and the form.
The following diagnostic procedures are also carried out:
- throat swab for flora;
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood test for antibodies to streptococcus.
This helps determine treatments for chronic tonsillitis.
How to treat acute tonsillitis
Treatment of acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis depends on the pathogen and the severity of the disease.
1. If we are talking about bacterial infection, then it is necessary to prescribe antibacterial drugs of different groups.
Only a doctor can prescribe an effective antibiotic!
Antibiotics are not effective against viral tonsillitis.
2. Symptomatic treatment:
Includes taking antipyretics, painkillers, as well as the use of local anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs in the form of solutions, lozenges, tablets.
3. A gentle diet. Namely, the exclusion of spicy, fried, and sour foods will help reduce irritation to the inflamed tissues of the throat.
4. If treatment is ineffective or complications occur, hospitalization is indicated. In the hospital, the patient will be under the close attention of doctors, blood tests will be monitored, and hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs may be administered. It is possible to use systemic antibiotics in the form of tablets or intravenously or intramuscularly.
If necessary, surgical intervention is performed.
Regardless of the severity of the disease, pathogen and form, treatment must be comprehensive, that is, have an antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Uncontrolled treatment with folk remedies can only do harm.
Treatment methods in adults
In most cases, they resort to conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis. Source: Modern methods of treating chronic tonsillitis. Ryazantsev S.V., Eremina N.V., Shcherban K.Yu. Medical Council, 2022. p. 68-72:
- therapy for inflammation in the head and oral cavity;
- procedures that increase immunity (hardening, taking vitamins, physical education, etc.);
- hyposensitizing drugs (to suppress allergic reactions);
- immunomodulators (normalize the immune system);
- means of reflex action (acupuncture, manual therapy);
- washing the tonsils with antiseptics;
- administration of drugs to the tonsils.
The treatment plan is complemented by physical therapy for chronic tonsillitis.
A radical method of treating chronic tonsillitis is surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy). The operation is performed in cases where inflammation occurs more than five times a year and does not respond to complex conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis. Source: Choosing an antibiotic for exacerbation of tonsillitis. Karpishchenko S.A., Kolesnikova O.M. Medical Council, 2015. p. 40-43.
Survey
In the department of otorhinolaryngology (ENT) of the hospital, patients with a chronic form of the disease are examined using:
- pharyngoscopy (visual method);
- PCR diagnostics - a high-precision method of molecular genetic diagnosis of infectious diseases;
- bacteriological tests - diagnosis of the main agent of infection and its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- antigen tests - diagnosis of immune system activity;
- general blood tests.
Prevention of chronic tonsillitis in adults
Preventive measures to prevent chronic tonsillitis include:
- proper hygiene;
- hardening;
- balanced diet;
- maintaining cleanliness in the home and workplace, eliminating dust;
- timely treatment of inflammationSource: Treatment and prevention of chronic tonsillitis. Atagulova G. Zh. Medicine and ecology, 2012.
Chronic tonsillitis is a very common disease that causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient. But is it possible to cure chronic tonsillitis? If your tonsils often become inflamed, then do not self-medicate, but consult a doctor who will select the optimal treatment regimen for you and determine how to get rid of chronic tonsillitis. You can make an appointment with a medical specialist in St. Petersburg by calling the phone number listed on the website.
Article sources:
- Treatment and prevention of chronic tonsillitis. Atagulova G. Zh. Medicine and ecology, 2012
- Chronic tonsillitis in the practice of an otolaryngologist and cardiologist. Yalymova D.L., Kostyuk V.N., Vishnyakov V.V., Yalymov A.A., Shekhyan G.G., Zadionchenko V.S. Cardio Somatics, 2014. p. 60-65
- Choice of antibiotic for exacerbation of tonsillitis. Karpishchenko S.A., Kolesnikova O.M. Medical Council, 2015. p. 40-43
- Modern methods of treating chronic tonsillitis. Ryazantsev S.V., Eremina N.V., Shcherban K.Yu. Medical Council, 2022. p. 68-72