- Published by: Laima Jansons
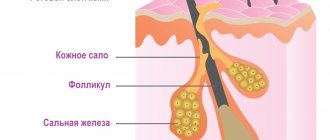
The oral mucosa performs a protective function and is a kind of mechanical barrier that prevents the penetration of microorganisms and bacteria into the body.
The plastic function ensures rapid tissue regeneration .
Due to the location of tactile and taste receptors in the mouth, the lining of the oral cavity is responsible for sensitivity.
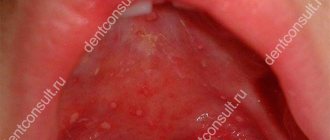
Often, pimples, ulcers and blisters form on the inside of the lips, which have different origins and differ in pain. Such pathological formations cause discomfort and pain while eating . In order to prescribe effective treatment, it is necessary to identify the causes of the disease.
Factors contributing to the formation of bubbles:
- Oral diseases: caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, stomatitis;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Allergy to toothpaste or mouthwash;
- Injuries;
- Poor hygiene;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Immunity impairment;
- Alcohol and nicotine addiction.
Watery blisters on the mucous membrane in some cases can indicate the occurrence of serious diseases. Such manifestations occur with tuberculosis, syphilis or diabetes. Therefore, if such a pathology occurs, it is recommended to immediately make an appointment with a doctor and undergo the necessary examination. The first sign is the sensation of a strange object in the mouth that is in the way.
Reasons for appearance
- Mechanical damage to the mucous membrane - injury to the lips by teeth or due to a blow, burn or piercing, ingestion of solid food (caramel, sugar, salt). Bubble formations filled with liquid appear.
- Failure to maintain oral hygiene , the presence of dental plaque, the proliferation of harmful bacteria in damaged teeth, oral dysbiosis, microtrauma during prosthetics and fillings. These factors are the cause of the development of stomatitis .
- The contact of viral particles on the mucous membrane , intrauterine infection of the fetus (acne in newborns) contributes to the disease of herpes .
- Decreased immune defense of the body , consumption of unwashed food, use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, malignant tumors, treatment with glucocorticosteroids. A concomitant disease of the oral cavity is candidiasis .
- Allergic reaction to medications or food.
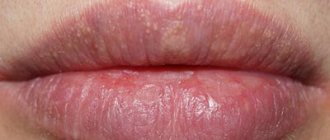
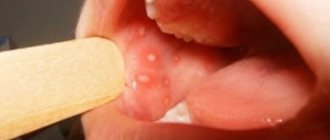
White pimples on the inside of the lips
Photo 1: The appearance of white rashes in the oral cavity is usually accompanied by painful sensations that intensify while eating food, sour drinks, tea or coffee.
Source: flickr (Joseph Doyle). Repeated appearance of white pimples indicates various pathological diseases of internal organs.
Causes of white pimples on lips:
- allergic reaction to decorative cosmetics;
- dermatitis;
- colds;
- disturbances in the body's hormonal system;
- smoking;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules.
White rashes can appear due to a combination of several factors . Depressive states, stress, and congenital anomalies of the gallbladder can aggravate the pathology
The appearance of white pimples during pregnancy indicates the development of the following pathologies:
- disturbances in liver function;
- disruption of the adrenal glands;
- chloasma - hyperpigmentation of the skin.
Symptoms
- Painful sensations when eating occur if a bubble has formed in the gum area or on the tongue;
- Pain when talking or smiling appears when a formation occurs on the inner surface of the lip;
- Pain in the throat area occurs if the bubble is located at the root of the tongue.
Transparent and bloody blisters can be not only inflammatory in nature. If the formation does not cause pain and is not accompanied by swelling, then you should consult a dermatologist. It is not recommended to treat yourself in such a situation, as it can be dangerous to health.
Is it possible for acne to appear on the lips?
Acne is a disease of the sebaceous glands. Since there are very few of them on the red border of the lips, the likelihood of acne forming in this area is low. But acne can form in the area around the lips. If a dermatologist has diagnosed acne, he may prescribe azelaic acid preparations for treatment9. Azelik® belongs to this group of drugs. This is a 15% azelaic acid gel with the following properties5:
- the ability to normalize keratinization processes in follicles;
- anti-inflammatory effect exerted by reducing the metabolism of neutrophils and the free radical forms of oxygen they produce;
- reduction of free fatty acids in skin lipids;
- antimicrobial activity against propionibacteria and Staphylococcus epidermidis.
The results from the action of Azelik®, as a rule, become noticeable after 4 weeks of using the drug5.
Treatment methods depending on the cause:
- If the formation occurs due to a viral infection, then treatment will be based on the use of antiviral drugs;
- If the cause is injury, then it is necessary to eliminate the consequences and rinse the mouth with antiseptics;
- If an allergic reaction provokes an illness, then you should find out what the irritant is and not use it anymore. The doctor will also prescribe antihistamines;
- If a large bloody bubble has formed, then surgery is performed. After this, the doctor prescribes medications for rapid tissue regeneration and restoration.
Homeopathic treatment for acne of all types
Along with traditional medications, homeopathy is considered more effective and faster in the treatment of pimples on the mucous membranes of various etiologies. The exceptional advantage of homeopathic medicines is the complete absence of side reactions , which often occur when using chemical medicines.
- Borax. Symptoms: burning pain, hot mouth, bleeding of the mucous membrane .
- Kalium bichromicum. Symptoms: deep aphthae, inflammation of the oral mucosa .
- Kalium muriaticum. Symptoms: acne, ulcers on the mucous membrane .
- Arsenicum. Symptoms: pimples that cause pain and discomfort .
- Apis mellifica. Symptoms: blistering acne .
- Rhus toxicodendron or poison sumac. Symptoms: herpes, blistering rashes .
- Thuja occidentalis or Western Thuja. Symptoms: herpes, white pimples .
When a symptom appears, you should not self-medicate , especially if it occurs frequently. For a complete cure, you should undergo a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment .
Classification of rashes on the labia
Before answering the question of why acne appeared on the labia, for a correct assessment of the pathology process, it is important to be able to differentiate the elements that make up the rash.
According to dermatological terminology, primary ones are distinguished, appearing on unchanged skin.
And secondary elements, developing from primary ones.
Actually, in most situations, various types of acne on the labia belong specifically to the primary forms.
They are divided into cavity and cavityless.
Sometimes the transition from primary to secondary forms occurs very quickly.
In such a situation, knowledge of the specifics and patterns of transformation makes it possible to determine the type of previous education.
Primary elements include:
- A spot (artificial, non-inflammatory and inflammatory vascular, pigmented) is a limited change in skin color without cavities or elevations. Vascular formations of an inflammatory nature up to a centimeter in size are called roseola, from one to five centimeters - erythema. Examples include roseola syphilitica, erythematous variants of dermatitis, and toxicoderma. Possible secondary forms are secondary pigment spot, scale.
- A blister is a raised, cavity-free formation, the result of edema with acute inflammation in the papillary skin layer, which quickly appears/disappears. It can form due to urticaria, insect bites, and toxicoderma. Such itchy pimples on the labia are usually pink, less often whitish in the central zone, and may be accompanied by a burning sensation.
- Papules, otherwise known as nodules, are hollow, raised elements that usually pass without a trace. Such formations vary in size, depth, and can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory in nature. They may transform into cracks, scales, secondary pigment spots, lichenification (thickening, pigmentation disorders, deepening of the skin pattern). In some diseases, papules merge to form plaques.
- A tubercle is a hollow, raised, dense element up to a centimeter in size, which usually leads to the formation of scars and cicatricial atrophy. It can also develop into ulcers, growths, scales, and crusts. The formation lies deep in the skin and is observed in cases of tuberculosis, leishmaniasis, leprosy, and tertiary syphilis.
- A node is a hollow, raised element measuring over a centimeter (up to 10 cm). It may end without a trace or with the formation of a scar, ulcer, secondary pigment spot, or crust. Formed in the subcutaneous tissue. A subcutaneous pimple on the labia of inflammatory nature may turn out to be syphilitic gumma, a typical manifestation of tertiary syphilis. Non-inflammatory is formed due to the deposition of metabolic products (“pimple wen” on the labia) or as a result of neoplasms (lymphoma).
- A vesicle, otherwise known as a vesicle, is a cavitary single- or multi-chambered elevated formation, up to 5 mm in diameter, with a tire and a bottom. On the labia with genital herpes, watery pimples with serous contents appear on erythematous skin. Also, blisters on the labia are filled with serous-hemorrhagic contents (blood pimples). When the vesicles are opened, weeping erosions, scales, crusts, and secondary pigment spots may appear, but usually in the end there are no traces left on the skin.
- Bubble, bulla - differs in size from the bubble (its radius exceeds a quarter of a centimeter, and can even reach several centimeters). Resolves without a trace or with scarring. It is also possible to form erosions, scales, crusts, growths and age spots.
- Pustule, abscess - a cavitary deep or superficial raised formation with purulent contents (a pimple with pus is found on the labia). There are follicular, predominantly staphylococcal in nature, and non-follicular (superficial - phlyctena, deep - ecthyma), usually streptococcal. They can develop into crusts, erosions, spots, scars, ulcers, and growths. Follicular pustules form in the hair follicle, appearing on the labia as characteristic yellow pimples.
Secondary elements:
- scale – loosened horn cells in the form of a layer
- crust – drying contents of primary formations
- crack - a violation of the integrity of the skin that occurs due to a decrease in elastic properties
- abrasion - mechanical damage to the surface layer of skin
- erosion - a defect within the surface layer that appears when formations with a cavity are opened
- ulcer – deep skin defect
- scar - the formation of new connective tissue during the healing of skin defects
- cicatricial atrophy - cicatricial transformation without previous skin damage
- lichenification – thickening, dryness, compaction, staining, deepening of the skin pattern
- vegetation - growth of a skin area in an area of prolonged inflammation
- hyper- and hypopigmentation – weakening/increasing coloration of a skin area
Blisters on the labia
Blisters appear at the sites of insect bites (fleas, lice, etc.).
They are characterized by itchy rashes, the severity of which depends on the type of insect and the sensitivity of the bitten person.
Scratching the elements can lead to infection.
Spontaneous urticaria appears as itchy, sometimes burning, blisters.
The state is called:
- taking certain medications
- eating certain foods
- concomitant diseases (chronic gastrointestinal pathologies, diabetes, leukemia, etc.)
- pathological pregnancy, menopause, etc.
The elements first have a pale pink color, which becomes white as the swelling increases.
Usually such blisters disappear within 24 hours.
Genital warts on the labia
Anogenital warts, also called condylomas acuminata, are caused by the human papillomavirus.
They are formations of a characteristic appearance: their lobed structure makes them look like a cauliflower stalk.
Such a pimple forms inside the labia, near the vestibule of the vagina, anus.
There are also varieties with a smooth surface and the color of raw meat (papular warts).
Separately, there is a giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma, which can form during pregnancy or in people with reduced immunity.
It is important to differentiate genital warts from broad ones, manifestations of secondary syphilis.
The latter are a dense purple, red dark pimple with a wide base on the labia.
Bowenoid papulosis is a relatively rare disease.
It also occurs when infected during sexual contact with the human papillomavirus (type 16, high cancer risk group).
The main complaint of patients is that a flesh-colored, brown or red pimple has appeared in the pubic area, inguinal folds, perianal area, and on the labia.
Gradually, such papules merge into plaques with a warty surface.
Approximately 3% of cases of the disease result in malignancy.
Pustules on the labia
Usually a pustule, otherwise a purulent pimple on the labia, does not exist for a very long period and may not even be noticed by the patient.
Superficial pustules quickly turn into crusts, while deep ones can form ulcers/erosions.
A group of dermatoses based on purulent inflammation of the skin is called pyoderma.
Pustular lesions are characteristic of:
- folliculitis
- impetigo
- hidradenitis
- syphiloid Sevestra-Jacquet and others.
Impetigo is a small superficial abscess with a convex red border.
The most common causes of the condition are staphylococci (80% of episodes) and streptococci.
A type of streptococcal impetigo in infants is post-erosive syphiloid Sevestra-Jaquet.
A problem arises with poor hygienic care for well-fed children as a result of the irritating effect of urine and feces.
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicle caused by bacteria, fungi, etc.
Deep folliculitis is called a boil.
Boils are inflamed, swollen pimples on the labia, cone-shaped with a necrotic core.
After the rod is separated, an ulcerative lesion develops in its place.
The recurrent appearance of numerous boils occurs with furunculosis.
A conglomerate of boils is called a carbuncle; it is a dense, up to 10 cm in diameter, node with pus.
Hidradenitis is a purulent inflammatory lesion of the apocrine glands that develops in the genital area, navel, anus, nipples, and axillary area.
In an infant, papulo-erosive streptoderma may appear on the labia, skin of the perineum, buttocks, and thighs - dense bluish-red pimples.
Other lesions on the labia
Bulla
A bulla is a huge pimple on the labia, a blister with a diameter of more than 5 mm.
Such formations in most situations are a symptom of serious skin lesions - bullous dermatoses.
For example, bullous pemphigoid is an autoimmune skin disease.
With it, itchy spots and papules first appear, and in their place blisters later develop, gradually turning into erosions.
tubercles
Tuberous dermatoses are rare.
Tend to progress to ulcerative formations with subsequent scarring.
They can be detected in cutaneous tuberculosis, pyogenic granuloma and tertiary forms of syphilis.
Nodes
Nodes are deeply located formations of dense consistency.
They do not exceed five centimeters in diameter and are rarely localized in the genital area.
Diseases manifested by the formation of nodes include:
- lymphangioma is a benign tumor that arises from the lymphatic vessels
- hidradenoma – benign tumor of the sweat gland
- lipoma – benign tumor of adipose tissue
- tertiary syphilis, etc.
A separate problem is pathologies in the area of the Bartholin glands.
They are located symmetrically at the base of the labia majora.
When the lumen of the gland is blocked, secretions accumulate in it and a cyst forms.
If infectious agents penetrate into the lumen, the development of bartholinitis (inflammation of the gland) and abscess (painful node with a purulent cavity) is possible.
Diagnosis and treatment
First, a smear is given to analyze the infection, a conclusion is made from the blood whether there is inflammation in the body, and according to indications, a pelvic ultrasound is performed to eliminate the risk of any neoplasms. If you have conditions such as fever, pain in the lower abdomen or pain when urinating, immediately make an appointment with a specialist.
Depending on the appearance of the rash, treatment methods are selected individually. Before visiting a doctor, it is better if you treat the affected area yourself with an antiseptic (alcohol, brilliant green, iodine, chlorhexidine) and start taking multivitamins to increase immune resistance. For local therapy the following will be prescribed:
- cream for children, chamomile or powder with zinc;
- soda or herbal baths, which should be taken on a daily basis.
The systematic approach consists of applying:
- Vitamins and immunostimulating drugs.
- Drugs that fight allergies.
- Antifungal ointments.
- Preparations based on acyclovir.
- Tablets that normalize the activity of the central nervous system (Vitamin B, mint, valerian).
- Antibiotics of the penicillin group if the infection has entered the circulatory system.
- Surgical method. It is used to eliminate fatty cysts, papillomas, and dubious rashes that grow abnormally.