In general, the condition of the front teeth greatly affects the aesthetics of your smile. Darkening of the front tooth makes patients want to solve the problem of darkening as quickly as possible - this is a good motivation to visit an endodontist. Especially if you are going to correct your bite using aligners or braces. If a patient’s tooth has darkened, this is a unique and timely motivation to take care of the health of their teeth.
Agree, when even one front tooth has darkened, this is a serious aesthetic problem that affects the eyes of others!
We asked our colleague, chief physician of the German Implantology Center Magomed Dakhkilgov, to talk about the problem of darkened teeth and ways to solve it.
For reference:
Magomed Dakhgilkov - maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist, orthopedist.
The total work experience is more than 20 years, more than 5 thousand dental surgeries have been performed. The doctor who created the German implantology clinics, which today are the best in ratings both in Moscow and in Russia. In his clinics, doctors work exclusively using a microscope and use an analytical approach to dental treatment with maximum preservation of nerve endings. The doctor’s motto is “ The tooth must live
.”
Main reasons
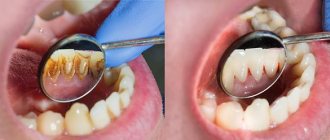
Why can one or more teeth turn blue? There may be several reasons for this; sometimes there is nothing dangerous to health in this process, and sometimes this is a reason to urgently seek advice from a dentist. A change in shade is possible due to poor quality nutrition or adherence to a strict diet. This can also happen if you eat a lot of fresh berries, such as blueberries, blueberries or blackberries.
Newly installed fillings may differ in color from natural tissues. A pulpless, that is, dead tooth can also change its color. This is explained by the fact that when the pulp is removed, nutrients stop flowing to the tissues.
If a seemingly healthy tooth begins to turn blue, this may indicate that there are problems with the root system. This is usually preceded by serious dental diseases. In addition, the cause of blue enamel may lie in the patient’s body; this phenomenon may be caused by the presence of chronic diseases or problems with the digestive system. Another common reason is the use of low-quality water with high levels of iron.
Causes of darkening of tooth enamel
The cause of tooth discoloration can be not only staining of the enamel, but also darkening of the hard tissue underneath. While the first may simply be the result of eating habits, the second indicates the presence of an internal problem.
Dark enamel in all or most of the teeth may appear due to the following reasons:
- Excessive consumption of coffee and strong tea,
- Smoking
- Metabolic disease
- Long-term use of certain medications, such as tetracycline-based antibiotics
- Reaction to filling material
- thinning of the enamel after nerve removal.
From smoking, tobacco tars accumulate on the teeth, which are not completely removed during normal hygiene procedures. Food dyes from some foods, as well as tea, coffee and other drinks, also tend to “eat” into the enamel over time.
Improper metabolism leads to an imbalance in the acid-base balance in the mouth, which causes bacteria to multiply more actively and plaque to form more actively. That is, a patient whose enamel of all teeth has darkened should pay attention to the condition of the gastrointestinal tract.
Some medications have the ability to change the pigmentation of enamel, for example, antibiotics from the tetracycline group or iron-containing drugs taken in liquid form.
Darkening can also occur when using outdated filling materials containing metals (silver or even tin). But even modern materials, under incorrect storage conditions, change their properties and adversely affect the color of the enamel.
The “wear and tear” factor cannot be ignored. If the tooth has been depulped for a long time, then it is not supplied with useful substances. This means that all mechanical actions lead to abrasion of the enamel and gradual destruction. Careful care slows down this process, but does not completely eliminate it.
Often the patient cannot understand why dark teeth appeared in a row against the background of others that were still light. This may mean that a pathological process has occurred under the still intact tooth crown, which has changed the color of the hard tissue - dentin.
Darkening of dentin can be due to the following reasons:
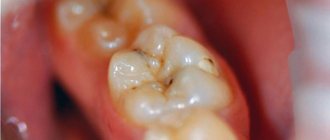
- untreated caries or its relapse
- advanced stage of pulpitis
- poor quality pulp removal
- injury from a strong blow
Caries destroys part of the protective layer of tooth enamel and gets underneath it. As the infection continues to develop, it affects the internal tissues, causing them to turn black. The affected dentin shows through the enamel, so the tooth can stand out noticeably among its white “neighbors.”
Pulpitis is often accompanied by pain, which brings the patient to the dentist even before the pulp dies. But if treatment was not carried out at the acute stage, then the chronic stage begins. At this stage, the pulp (nerve) begins to die, which changes the color of the tooth.
After removal of the nerve, if the operation was performed poorly, the color may also change. Insufficiently thorough cleaning of the canals will cause further decomposition of the remaining pulp. If not all cavities are filled with filling material, then microbes will again penetrate into the remaining voids. All this will again cause darkening of the dentin. Less commonly, the cause of darkening may be the paste used to seal the root after cleaning the canals. Sometimes its composition changes the shade of hard tissues.
Trauma to a tooth causes it to darken due to blood entering the bone tissue.
Sometimes, if a tooth has been restored, the pins may be visible through the filling compound. In this case, repeated restoration may be required.
Treatment of blue teeth
If during diagnostics it is determined that the cause of blueness of all teeth is the use of special products, the dentist or hygienist may prescribe a professional cleaning of the oral cavity. Quite often the patient requires enamel polishing; this allows for the best results.
If after such manipulations the blue discoloration does not disappear, you can try other methods.
First of all, the doctor should send the person for an X-ray examination of the jaw, this will make it possible to make a correct diagnosis, as a result of which the treatment will be as effective as possible. It may also be necessary to remove previously installed fillings and caries-infected hard tissues. If necessary, treatment of the annals and root system of the tooth will be prescribed.
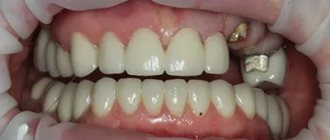
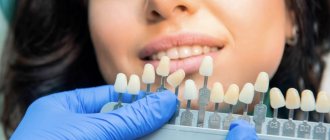
There are several methods to restore the original whiteness of your teeth. One of the most common options is the installation of a composite filling, that is, direct artistic restoration of a row. A more expensive procedure is the production of an artificial crown or special onlays - veneers (indirect restoration).
How to eliminate darkening of a tooth
If your tooth has darkened, a very effective method of solving the problem is the method of internal whitening of the darkened tooth.
With this method, the old filling is removed, the tooth canal is cleaned using a microscope, and a whitening substance is placed inside the tooth. After a couple of days, this substance is removed and a filling is placed on the tooth. The tooth is lightened - the problem is solved! As a rule, I re-treat the root canal of a darkened tooth under a microscope, then whiten the tooth from the inside, strengthen it and restore it with a filling. If the outer surface of the enamel is not damaged, the filling can be installed on the inside of the tooth.
Why does such a tooth need to be treated first? If you leave the infection in the tooth canal, the darkening process will continue, and the inflammation will spread to the bone around the root. As a result, the patient may be left without a tooth altogether.
It is the treatment of the tooth under a microscope that is aimed at completely removing the infection from the tooth cavity and root.
Blue gums
Another common phenomenon, especially in young children, is blue discoloration of the gum tissue. It often occurs during the eruption of the first, baby teeth. During this process, inevitable damage occurs to tissues penetrated by a huge number of blood vessels of different sizes. As a result, blood can enter the soft tissue, leading to the formation of a small hematoma.
That is why, if a baby has a hematoma or bruise in a place where a new tooth is expected to appear soon, there is no cause for concern. However, in all other cases it is recommended to show the child to the dentist. The cause of blueness may be an inflammatory process. It is usually preceded by diseases such as gingivitis or stomatitis.
It is important that such complications usually occur in children with weakened immune systems. Also, the health of teeth and gums is greatly influenced by compliance with the rules of daily care. Due to the abundant accumulation of plaque and stone, most ailments appear; this is especially dangerous at an early age, when the enamel is not yet strong enough.
What to do with a darkened tooth
If a tooth has darkened, the first thing to do is to determine the cause of the problem. The situation with coffee lovers and smokers is clear - they should have their teeth professionally cleaned by a specialist and adjust their habits. In the future, you can sign up for whitening, but first you will have to prepare yourself mentally, because after it, smoking and drinking coloring drinks are strictly prohibited for some time.
If the enamel of your teeth has darkened due to medications, then you need to either limit their intake or switch to other medications if the attending physician approves. To reduce your exposure to liquid coloring medications, drink them through a straw. If it is impossible to change the therapy, and the pigmentation causes severe discomfort, then installing veneers will help - plates that replace the top layer of enamel.
Only a qualified dentist can make a correct diagnosis. Therefore, the best thing to do if a tooth has darkened is to go to see a doctor. It will determine the presence or absence of a pathological process. There is no need to postpone your visit. If the cause of the color change is inflammation, then an assessment of the situation by a specialist is necessary. Internal inflammatory processes are not always accompanied by acute pain. If you neglect other signs, then you may subsequently encounter not only chronic pulpitis, but also other unpleasant pathologies, such as granuloma, periodontitis, and radicular cyst.
Granuloma and cyst are formations with purulent or serous fluid inside. Their development can proceed practically asymptomatically for some time, making itself known only by a change in color. But then you cannot do without serious interventions: cutting tissue, removing part of the root, or even the entire tooth. Purulent inflammation can even damage the jaw bone. In this case, you cannot do without tooth extraction.
Removal is necessary in the following situations:
- the inflammation spread to the area around the tooth and affected the jawbone;
- the tooth is loosened and the gums are bleeding due to internal injury;
- the crown is too destroyed, less than 30% of hard tissue remains;
- the tooth is split, and the split continues inside the gum.
In the latter case, it is possible to preserve the roots of the tooth, but the cracked upper part will still be removed and replaced with a prosthesis.
It is clear that if a tooth suddenly darkens, an examination should be done immediately. To save a tooth, you need to see a dentist immediately. If there is inflammation, the doctor will remove the infected tissue and fill the voids. After treatment, it may be necessary to bleach not the outer part, but the inner part of the crown, since it was this part that darkened due to the death of the pulp or its remains. Often after this, the teeth return to their former whiteness and natural appearance. In other cases, when lightening and restoration with filling materials are impractical, but removal is not required, partial or complete “artificial enamel” is created for the tooth - veneers or crowns are installed.
To whiten a pulpless, darkened tooth, the doctor brightens it from the inside. To do this, he opens the canals, cleans them and fills them with a bleaching compound. Until the composition lightens the tissue, the patient will have a temporary filling. This procedure is called endobleaching. In some cases, it may take several sessions.
If the tooth walls are too thin, or there are other contraindications for whitening, then, depending on the situation, the dentist will select alternative methods: direct restoration with composite material, installation of veneers, lumineers or crowns. Positive aspects of restoration with composite material:
- ease of implementation - the tooth is covered with a composite composition, forming one large filling on its surface;
- speed of implementation - can be done in one visit to the doctor;
- affordable price.
Disadvantages of such restoration:
- composite material is easy to paint, you will have to change your eating habits;
- fragility - average service life is about 5 years;
- During repeated restoration, the integrity of the tooth walls suffers.
Associated symptoms
Gums can turn blue not only in the youngest patients, but also in adults. As a rule, this pathology is accompanied by many other symptoms. Most often, a person experiences noticeable pain, especially with accidental contact with tissue or with solid food, and the gums may swell and bleed.
If the cause of darkening or the appearance of age spots lies in the inflammatory process, the following symptoms can be diagnosed: severe fever and chills, itching and burning, the appearance of blood or purulent discharge, and others. In this case, immediate treatment is required in a dental clinic; traditional methods will not be effective.
If the cause of darkening of the gum or tooth is the incorrect installation of a prosthesis or crown, the patient may complain of pain even at rest, as well as slight tingling and numbness of the tissue (a sensation similar to what happens after the end of anesthesia).
previous post
How is a general examination at the dentist performed?
next entry
Prevention of complications after treatment
Regardless of the color of the gums, every person when caring for them must adhere to the following rules:
- brush your teeth every day after breakfast and before bed;
- the brush should be directed from top to bottom on the upper jaw and from bottom to top on the lower jaw;
- the procedure should be completed with circular movements from the molars to the anteriors;
- horizontal movements of the brush can injure the mucous membrane, as can very hard bristles.
Following these recommendations will help keep your gums healthy under any circumstances.
What to do if the gums near the crown become inflamed
Inflammation of the gums near the tooth under the crown is treated based on the original cause that caused it. So, if swelling of the soft tissues appears as a result of trauma to the gums with a brush or due to the chemical components included in the rinses, it is enough to replace oral hygiene products with more suitable ones, and treat the gums themselves with antiseptics.
If swelling of the gums is caused by the development of dental pathology - gingivitis, periodontitis, etc., complex treatment is necessary - professional cleaning, curettage of periodontal pockets, application of anti-inflammatory and wound-healing ointments, injection of vitamins and sometimes antibiotics into the gums.
When flux forms, it is opened and the wound is drained.
If the flux has opened on its own and a fistulous tract has formed, endodontic treatment is carried out (if a crown covers a living tooth or not all root canals are filled) or resection of the apex of the root on which inflammation has formed. If it is presented late, it is not always possible to save the tooth under the crown and then it is removed. To the list of posts
Complications: ways to fix the problem
Many Patients mistakenly consider the appearance of pain to be a normal situation and refuse to visit a doctor. But the condition worsens, and other problems are likely to develop that can lead to tooth loss. Sometimes the cause of complications is poor-quality glue or inflammation of the pulp. In such cases, a visit to the dentist is mandatory; he will perform the following procedures:
- visual inspection, determination of the degree of sensitivity;
- diagnostics, identification of the cause of pain;
- removing the cover, cleaning the surface from glue residues;
- elimination of plaque, food particles;
- opening the coronal part, removing affected tissues and pulp (only if necessary);
- treatment with antiseptic solutions, canal filling;
- installation of a temporary lining to protect tissue.
Next, a short break is required for healing. After the discomfort and other unpleasant sensations disappear, it is possible to manufacture and install a new plate.
Secondary and recurrent caries: is there a difference?
Dentists of the Soviet school for a long time considered these concepts identical, because there really is a lot in common between them. Currently, dentists interpret them differently.
- In secondary caries, the pathological process continues to develop after filling the tooth due to the insufficiently tight fit of the filling to the walls of the carious cavity.
- Saliva, which contains enzymes produced by the body, as well as pathogenic bacteria and acids that are products of their vital activity, penetrates into the resulting marginal microgap.
- They have a destructive effect on all types of filling compounds: they increase the moisture absorption of dental cements, activate the corrosion of amalgam fillings and disrupt the mechanism of adhesion of composite materials to the dental surface.
But recurrent caries affects a tooth under a filling in cases where, during treatment, the affected necrotic dentin was not completely removed from the walls of the treated carious cavity or the cavity was poorly treated with an antiseptic. Recurrent caries is, as a rule, a consequence of the dentist’s lack of proper experience or mistakes made by him.
In addition, both processes can develop in parallel, which significantly complicates and increases the cost of treatment.
When to see a doctor
There are situations in which it becomes impossible to visit your doctor. In such cases, you should remember about the serious causes of blue gums that require urgent treatment:
- cyanosis does not subside within 4–5 days;
- in addition to changes in gum color, there are signs of local inflammation (hyperemia, swelling of soft tissues, bleeding gums);
- I am concerned about acute pain that is not relieved by painkillers;
- a sharp increase in body temperature to 38–39 degrees;
- deterioration of the general condition of the body, weakness.
Ignoring a dental problem is fraught with the development of serious consequences. Severe complications include: the formation of a benign or malignant tumor, as well as the occurrence of an intraoral cyst.
What determines the result of filling?
A tooth after filling can be destroyed by secondary caries for several reasons.
- When consuming cold and hot food and drinks at the same time (for example, cold ice cream and hot coffee or hot kebab and cold beer). In such cases, under the influence of a significant temperature difference, microcracks form in the tooth enamel and in the places of contact of dental tissues with the filling material.
- The seal may shift slightly when chewing on too hard, tough foods. This will be enough for a microcrack to appear.
- Malocclusion and pathology such as bruxism are accompanied by excessive friction of teeth against each other and cause accelerated abrasion of the filling composition and dental tissues.
- An insufficient level of hygiene leads to the settling of food particles and the formation of a significant amount of soft plaque in the fissures (tubercles on the chewing surface of the teeth) and in the interdental spaces. This accelerates the development of a bacterial infection.