Purulent nasal discharge can appear for many reasons and necessarily require treatment. You should not carry out therapy on your own due to the risk of severe complications if treated incorrectly. As soon as purulent discharge from the nose is noticed, you should immediately seek medical help from an otolaryngologist, or, in his absence, a therapist. The fact that pus, and not ordinary snot, began to come out of the nose can be understood by a special, extremely unpleasant odor, which does not occur with a simple runny nose. The yellow-green color of the discharge also differs from the usual one.
The appearance of pus from the nose can be associated with a number of diseases. In order to effectively treat a problem, it is necessary to accurately determine the reason why it occurs. If you seek medical help in a timely manner, the therapy quickly produces positive results and nasal discharge disappears. If for some reason the disease turns out to be advanced, then treatment may take a long time and sometimes require surgical intervention. The appearance of pus from the nose occurs equally in adults and children and requires similar therapy. It is not uncommon for purulent nasal discharge to appear after viral infections as a complication of the disease. In order to prevent this phenomenon, it is necessary to fully treat the primary disease without suffering it on your feet.
When the pus is liquid and white, this is an indicator of the initial stage of the disease. In this case, it is released in large quantities, and also often flows down the back wall of the pharynx. If the particles of pus are viscous and more like lumps, then this is an indicator of severe neglect of the purulent process. Most often, with long-term disturbance, green nasal discharge occurs. The formation of pus is always associated with the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the nasal cavity. If they are absent, then a purulent process cannot occur. Because of this, in the viral form of rhinitis, the appearance of pus always indicates a secondary bacterial infection.
Causes of purulent vaginal discharge
Gynecological infections
With gonorrhea, thick yellow or green pus with an unpleasant putrid odor is released from the vagina. The amount of purulent leucorrhoea may increase after sexual intercourse. Yellow-green discharge from the vagina is accompanied by pain in the perineum with radiation to the sacrum and coccyx. When the infection spreads upward to the overlying genital organs, abundant purulent, creamy discharge with a characteristic odor is observed, sometimes streaks of blood are visible in it. Other infectious pathologies (mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis) may occur with scanty greenish leucorrhoea.
Pathologies of the uterus and appendages
Purulent vaginal discharge is characteristic of severe lesions of the uterus and its appendages - pyometra, pyosalpinx. Women note a constant flow of thick pus from the vagina with a foul odor, in which fragments of necrotic tissue or blood are found. The symptom is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, fever, problems with urination and defecation. Inflammatory causes of the disorder are endometritis (including postpartum) and endocervicitis, in which scanty purulent discharge is observed.
Bartholinitis
When the Bartholin gland is affected (bartholinitis), patients are bothered by the periodic leakage of yellow or greenish pus with a specific odor from the vagina. In the posterior third of the labia majora, the woman feels a lump; when pressing on it, suppuration intensifies. There may be throbbing pain in the perineum, worsening while walking. Lack of timely treatment and other unfavorable reasons provoke the formation of an abscess of the Bartholin gland, which, when spontaneously opened, produces abundant purulent discharge with a pungent odor.
Rare causes
- Staphylococcal infections of the genital tract
: bacterial vaginitis, cervicitis. - Intestinal-vaginal fistulas.
- Boils and carbuncles of the skin of the perineum
.
There may be explicit images of genitals hidden here.
Are you over 18 years of age?
Yes
No
Purulent discharge from gonorrhea
Diagnostics
Purulent vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor is a serious reason to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist to find out the causes of suppuration. The examination of patients involves a physical and instrumental examination of the genitals, various laboratory methods aimed at clarifying the etiological factor. The following have the greatest diagnostic value:
- Gynecological examination
. To obtain a complete picture of the disease, examination of patients with purulent leucorrhoea is carried out without preliminary preparation and toileting of the external genitalia. When examined in speculums, accumulations of thick pus can be detected on the walls of the vagina; hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane are typical. - Ultrasonography
. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs allows you to find out the reasons associated with purulent vaginal discharge. During standard or transvaginal sonography, the condition of the genital organs is assessed, the accumulation of hypoechoic fluid in the uterine cavity is detected, and signs of an inflammatory process are detected. - Endoscopic methods
. To determine the cause of scanty purulent discharge streaked with blood, colposcopy is necessary for a targeted examination of the cervix and cervical canal. The method helps to identify erosive changes and areas of tissue atypia. - Bacteriological method
. In order to identify the causative agent of a gynecological infection, microscopy of a vaginal smear is performed after staining, then the secretions are cultured on nutrient media. Modern methods - ELISA, RSK, PCR - are intended for rapid diagnosis of the cause of suppuration.
To identify laboratory signs of inflammation, general and biochemical blood tests are done. Serological tests help confirm the etiological factor of vaginal leucorrhoea with a pungent putrid odor. To exclude lesions of other pelvic organs, CT or MRI of the pelvic cavity is used. Diagnostic laparoscopy is prescribed if it is impossible to determine the causes of purulent discharge using other methods.
A vaginal smear examination is carried out to identify the causative agent of infection.
Reasons for the problem
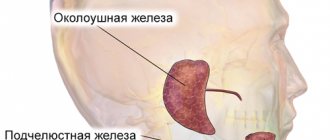
Most often, the appearance of pus from the nose is associated with lesions of the paranasal sinuses, which become inflamed when they are blocked and mucous secretions accumulate in them. In addition, an unpleasant phenomenon can occur as a consequence of injury or the formation of an abscess in the nasal cavity.
Sinusitis
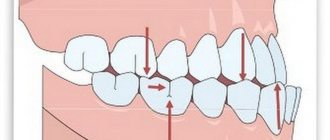
Sinusitis is the most common cause of pus from the nose. The discharge can be not only green, but also brown mixed with blood. With this disease, an inflammatory process develops in the maxillary paranasal sinuses. The disease is often provoked by the presence of carious teeth in the upper jaw. The symptoms of this disorder are as follows:
- temperature rise to 38 degrees and rarely higher;
- headache;
- feeling of heaviness in the head;
- loss of smell;
- a sharp decrease in performance;
- severe weakness;
- sleep disorders.
A problem arises not only because of diseased teeth, but also with insufficiently treated runny nose, nasal injuries and decreased immunity, which can even occur due to significant hypothermia.
Lack of treatment is very dangerous. Sinusitis, more often than other diseases with the discharge of pus from the nose, causes severe complications. After sinusitis has been suffered once, the risk of its reoccurrence becomes quite high.
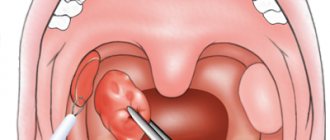
Nasal polyps
Polyps are benign growths and often appear in the nasal cavity. By their nature, polyps are a proliferation of tissues of the nasal mucosa. With this phenomenon, chronic nasal congestion, decreased sense of smell, frequent headaches and a nasal voice occur. Due to the fact that polyps disrupt the outflow of mucus from the paranasal sinuses, a purulent process begins to develop in the latter. As a result, unpleasant nasal discharge appears.
The treatment of this disease is surgical. If the polyps are not removed, the disease will not be cured. However, even after surgery there is no guarantee that polyps in the nasal cavity will not reappear. Sometimes a person can suffer for years as they develop again.
Rhinopharyngitis
With this inflammatory disease, simultaneous inflammation of the nasal and pharyngeal mucosa occurs. The disease most often occurs against the background of viral infections such as influenza, acute respiratory infections and ARVI. The main symptoms of nasopharyngitis are:
- itching and burning in the nasopharynx;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- nasal voice;
- difficult separation of mucus and pus from the nasal cavity, which may also contain blood, causing the discharge to be brown;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the back of the head;
- swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa;
- temperature increase.
Treatment of inflammation requires comprehensive treatment. If it is delayed, damage to the mucous membrane may become irreversible. There is also a risk that there will be a change in the tissue of the pharyngeal tonsils, and then their removal may be necessary for treatment.
Ozena
Fetid runny nose ozena refers to severe lesions of the nasal mucosa that require urgent treatment. The disease is also called atrophic rhinitis. Its main manifestations are:
- purulent nasal discharge with a strong and very pungent rotten odor;
- complete loss of smell, even for very strong odors;
- constant presence of dry crusts in the nasal passages.
Ozena develops if a person has chronic rhinitis for a long time, which is not treated. Its presence at the beginning is indicated by a large volume of transparent watery discharge. As a result of this, gradual atrophy of the mucous membrane occurs, due to which irreversible changes occur in it and a special purulent process develops.
Bacterial lesions
Bacterial lesions of the nasal mucosa also often occur and cause the appearance of pus from the nose. More often, such bacterial infections appear in children, since their immunity is not strong enough. In adults, initial bacterial infection occurs rarely and only in cases of severe weakening of immunity. The pus may be curdled, yellow-orange or dark green.
Complications of injuries and operations
Purulent nasal discharge can also appear if there has been an injury or surgery, and after that a bacterial infection develops as a complication. This phenomenon indicates that after injury or surgery, improper treatment was carried out with infrequent changes of tampons and insufficient use of antibiotics. Also, pus may appear if the surgeon initially violated the sterility during the operation and pathogens were introduced into the nasal cavity. Most often, this complication develops if the operation was extensive, and subsequently the patient himself violated medical recommendations.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
The discharge of pus from the vagina is a symptom of serious disorders of the reproductive system, for which it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible. Self-medication can lead to the spread of the process to other pelvic organs or the peritoneum. Until the reasons for the purulent, foul-smelling discharge are determined, it is permissible to take analgesics to reduce pain. For high febrile fever, antipyretics are used.
Conservative therapy
Medical tactics depend on the prevalence of purulent inflammation, the etiological factor of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathology in the patient. In the acute period, physiotherapy methods are not used; after the main manifestations subside, drug therapy is supplemented with UHF, electrophoresis, and ultraviolet radiation. Local treatment includes instillation of antiseptic solutions (miramistin, chlorhexidine) into the vagina. For sexually transmitted infections, medications are prescribed to both sexual partners. The most commonly indicated medications are:
- Antibiotics
. They are selected taking into account the causative agent of the infection and its antibiotic sensitivity. If severe purulent processes are detected in the uterus and appendages, a combination of 2-3 drugs with a wide spectrum of action is necessary. - Detoxification solutions
. Diseases combined with suppuration are characterized by severe intoxication of the body. To eliminate intoxication, glucose-salt agents are used for parenteral administration. - Immunomodulators
. Medicines increase the overall reactivity of the body, stimulate local immunity, and speed up the healing process. For chronic gonorrhea, a gonococcal vaccine is used for the purpose of immunostimulation.
Pus
Pus is a cloudy liquid that occurs as a result of serous-purulent or purulent inflammation. Essentially, pus is destroyed white blood cells that have completed their life cycle.
Suppuration is the process of formation of pus.
Pus consists of the following components:
- Serum. It contains globulins, albumins, lipolytic and glycolytic enzymes, an admixture of DNA, fats, lecithin, and cholesterol.
- Tissue detritus. It is represented by dead matter.
- Cells of degenerated or living microorganisms, neutrophilic leukocytes. In some cases, the pus may include mononuclear cells and eosinophils .
The color of pus depends on the causes of its occurrence. It can be green, gray, yellow, green-yellow and even bluish. Fresh pus is much thicker than old pus. Most often, the smell of pus is not strong, only slightly specific, but when putrefactive inflammation occurs, its smell can become very strong. The localization of the inflammatory process, the pathogen, the degree of tissue damage, communication with hollow organs determines the consistency, color and smell of pus, which are different for each specific case.
Microorganisms that caused the development of suppuration can almost always be found in pus. Pyogenic bacteria are usually the cause of the development of this process. These bacteria include Escherichia coli , anaerobic clostridia, streptococci, gonococci, staphylococci, meningococci, etc. In this case, the process of formation of pus can be the result of the activity of other bacteria in the tissues and organs, for example, candida, salmonella, pneumococci, mycobacteria , etc. In this case, there may be cases where no microorganisms are found in the pus. This situation is associated either with the destruction of bacteria by enzymes, or with a non-microbial cause of suppuration.
Pus is subject to mandatory examination, like blood, urine and other body fluids, especially when there are large accumulations of it in the cavities. In cases where accumulations of pus are in open cavities, the collection is made from the depths of the lesion, when in closed cavities a puncture . The obtained material is examined immediately after collection in order to prevent possible decomposition of microorganisms by the enzymes that make up the pus, that is, in order to avoid the lysis process.
In the event of purulent wounds, their treatment must be carried out using special methods that avoid sepsis - an extremely serious condition in which microorganisms enter the blood. To prevent complications, drainage of pus from wounds is ensured using various antiseptic methods (catheters, special tampons, etc.). In some cases, wounds are washed with special means.