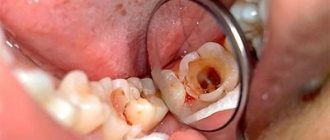
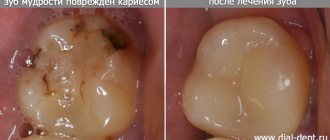
Gangrenous pulpitis is a putrefactive inflammation of the pulp in the crown and root parts of the tooth, which is accompanied by the death of its tissues. This form is considered one of the most dangerous and neglected, and its characteristic feature is the destruction of the pulp.
Gangrenous pulpitis of the tooth
is a late stage of chronic pulpitis, resulting from the lack of treatment for a disease such as caries. It is characterized by such unpleasant manifestations as darkening of the tooth, the development of halitosis (bad breath), and aching pain symptoms. Most often, this form of pulpitis affects the chewing teeth of the lower jaw.
Filling made of light-curing material for classes I and V - 2,000 rubles.
Filling made of light-curing material in classes II, III, IV - 3,000 rubles.
Placing a temporary filling - 400 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (frontal group) - 6,500 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (chewing group) - RUB 9,000.
Mechanical and medicinal treatment of canals for periodontitis (1 canal) - 1,100 rubles.
Closing perforations (MTA) - RUB 6,500.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a dental consultation is 1,000
- The cost of an orthodontist consultation is 2,000
Make an appointment
Gangrenous pulpitis: etiology
Gangrenous pulpitis occurs due to the penetration of putrefactive anaerobic bacteria into the pulp. At the same time, the routes of penetration can be different:
- A carious cavity that requires treatment;
- Incorrectly carried out treatment, in which the affected tissues reached the nerve of the tooth (pulpitis develops under the filling);
- Violations of the technique of preparing a tooth for a crown;
- Deep periodontal pockets;
- Destruction of the tooth to soft tissues with severe abrasion;
- Periodontitis of the adjacent tooth;
- Various tooth injuries;
- Diseases of an infectious nature in which microorganisms are transferred to dental tissues through blood and lymph.
Another reason for the development is exacerbation of gangrenous pulpitis
, which was not cured and over time developed into a chronic form.
Pulp anatomy
In the depths of the tooth, under the dentin layer, there is a pulp, which consists of soft, loose, fibrous connective tissue, dotted with blood and lymphatic vessels, as well as nerve endings running from the jaw along the root canal through the apical foramen.
Pulp (lat. pulpis dentis) is the “heart” of the tooth, reliably protected by powerful dental walls of bone tissue from the effects of external factors, nourishing the tooth with minerals, ensuring its growth, restoration, and vitality. It is important to note that the pulp is not only a space of soft tissue (pulp chamber), but also the dental canal connected to it. The pulp chamber is a loose, amorphous colloidal system containing loose, fibrous connective tissue, as well as a large number of elastin and collagen fibers. The cellular composition of this system contains histocyotes, mast cells, macrophages, as well as fibroblasts that produce collagen and provide intercellular communication. The surface layers of the fibrous structure of the pulp contain odontoblasts - cells with long processes located in the dentinal canals. These processes make dentin sensitive to any irritants. Stellate cells are located a little deeper, and the central layer contains collagen and nerve fibers and blood vessels. If an inflammatory process begins in the pulp, then leukocytes appear in the structure, lymphocytes and plasma cells are activated.
In addition to providing the tooth with nutrition, the pulp performs several other important functions. Plastic, responsible for the delivery of “building” proteins, is ensured by the activity of odontoblasts involved in the formation of dentin: before the eruption of the primary tooth, after eruption - the secondary one. The protective function of the pulp is carried out thanks to macrophages, lymphocytes and fibroblasts. Macrophages “recycle” dead cells and, together with lymphocytes, are responsible for immune reactions, and fibroblasts produce and maintain the necessary balance of the intercellular substance of the pulp, which is responsible for metabolic processes in it. In general, the protective function of the pulp is to create a barrier for the penetration of pathogenic bacteria that have entered through the dentin further, along the root canal into the periodontium, and then to the soft tissues surrounding the tooth. In addition, the protective function includes the regeneration of the so-called replacement (tertiary) dentin: when caries occurs, this dentin prevents its spread deep into the tooth. The trophic function of the pulp, which affects the metabolism and nutrition of the tooth, supporting the vital activity of tooth enamel, is ensured by the activity of a developed vascular system, characterized by thin vessel walls, high blood flow speed and, accordingly, higher pressure than in other organs. The sensory function of the pulp is carried out due to the activity of a large number of nerve fibers, which, like a fan, diverge from the apical foramen to the periphery of the pulp.
Very often the pulp is called the “dental nerve” because its sensitivity to any irritants is so high that inflammation, as a response to a bacterial, viral, or infectious attack, occurs almost immediately. Such inflammation in medical terminology is called pulpitis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of gangrenous pulpitis depend on the form in which it occurs:
- Acute gangrenous pulpitis is characterized by the presence of deep ulcers that cover the entire pulp. Due to the destruction of the septum between the carious cavity and the pulp, the infection penetrates inside. The acute form is characterized by severe pain that occurs for no reason or as a result of a reaction to irritants in the form of hot or cold food;
- Chronic gangrenous pulpitis is characterized by a dirty-gray tint of the upper layers of the pulp and the tooth itself, and the presence of a large carious cavity. There is no bleeding. There are practically no symptoms of pain, but sometimes aching pain may occur, especially when exposed to irritants. There is a putrid odor from the mouth.
The course of the disease depends on the following factors:
- pathogenicity of microorganisms;
- pulp resistance;
- the patient's general health status;
- periodontal condition;
- body resistance;
- the presence of concomitant pathologies.
This means that the process of development of the disease directly depends on how healthy the patient’s body is: the stronger it is, the more time it takes for bacteria to have a negative effect. Taking into account the above, we can conclude that the disease is especially severe in children, since the resistance of the child’s body is much lower than that of an adult. Clinic of gangrenous pulpitis
may vary depending on whether the tooth cavity is open or closed. So, with an open cavity, the following symptoms are observed:
| Symptoms of an open cavity | Symptoms with a closed cavity |
|
|
Historical reference
In ancient times, humanity did not yet know the term “pulpitis,” but they were familiar with toothache in different parts of the world. The main means of getting rid of it was tooth extraction. In some countries, conspiracies and rituals with sacrifices were used “for medicinal purposes.” In ancient Egypt, according to information found in ancient papyri, doctors looked for ways to help the patient using anti-inflammatory ointments containing the juice of various plants, and pastes made from myrrh, ash, pumice and eggshells.
In the 1st century AD The personal physician of the Roman Emperor Trajan, the surgeon Archigenes, drilled a tooth for medicinal purposes. Around 150-160's. the famous physician and philosopher of antiquity, Claudius Galen, described in his works the differences between pulpitis and periodontitis, but this knowledge was forgotten for a long time. In the 9th century in the Middle East, the physician and pharmacist Muhammad al Rashid advised using arsenic to destroy the dental nerve that was causing pain to the patient. But in European countries this method became known much later.
In the 11th century, in some European countries, caries and the pulpitis caused by it were “treated” with laxatives and enemas, and if this did not help, the pulp was burned with a hot iron with “anesthesia” in the form of using alcohol-containing compounds before manipulation or even hitting the head with a board. , the so-called Rausch anesthesia. In the 15th century, a professor at the University of Bologna repeated the experiment described by Archigen - he removed the affected dental tissue by drilling, after which he cauterized the pulp and filled the tooth cavity with gold.
Pierre Fauchard, a French doctor who lived in the 18th century, learned to identify 102 types of toothache, studied and practiced various methods of eliminating it, and became the founder of the “dental” patient position. Before him, the patient was placed on a table or seated on the floor, pressing his head between his knees, and P. Fauchard insisted that the patient in this position experiences unwanted nervousness and it is necessary that he sit in a chair, and the doctor stands next to him.
After 1871, when James Morrison patented the dental drill, therapeutic dentistry began to develop rapidly. Tools, equipment, drugs for pain relief, technologies began to appear, some of which are still actively used by dentists. Today, modern dentistry has effective methods, modernized instruments, and improved technologies with the help of which dental diseases, including pulpitis, can be effectively treated.
Gangrenous pulpitis in children
Children are much less susceptible to this disease... However, if it occurs, its treatment requires considerable effort. Most often, young patients suffer from chronic pulpitis due to the fact that they cannot correctly explain the essence of the problem and the nature of the pain. This leads to the disease becoming chronic. According to dentists, gangrenous pulpitis in childhood develops as a result of fibrous and purulent forms of pulpitis, occurring in a chronic or acute form, respectively. Necrosis of the tooth nerve begins as a result of the penetration of anaerobic microflora into it, while pain symptoms are determined by the peculiarities of the baby’s nervous system. During the examination, the dentist identifies large carious cavities and dead pulp tissue. Painful symptoms occur when probing the canal openings. For treatment, it is most often necessary to use a devital method of removing the nerve of the tooth.
Age restrictions
Pulpitis can occur in anyone at any age. The conservative method of treating this disease has no age restrictions. When choosing a surgical method in patients over 45 years of age, it is necessary to take into account the condition of periodontal tissues.
Treatment of pulpitis in children with baby teeth has its own characteristics. Thus, the inflammatory process in baby teeth arises and spreads rapidly and does not always depend on the depth of carious lesions and visible tissues affected by caries. In this case, it is extremely important to stop the spread of infection to the periodontal tissue, since the rudiments of molar teeth are formed in this tissue. However, removal of teeth affected by pulpitis is used only in rare cases, since the absence of each dental unit has a negative impact on the formation of the bite. In the treatment of pulpitis of baby teeth, filling pastes are used that do not affect the rudiments of the molars, but are absorbed along with the “milk” roots when teeth change begins. Anesthesia must be carried out taking into account possible allergic reactions.
Diagnosis of the disease
Treatment of gangrenous pulpitis is prescribed only after the dentist makes the correct diagnosis. It is very important to be able to distinguish this disease from:
- deep caries;
- chronic fibrous pulpitis;
- apical periodontitis.
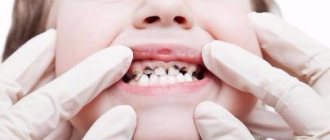
A visual examination of the oral cavity by a dentist reveals the following:
- deep carious cavity with softened dentin;
- open dental cavity;
- grayish coating on the upper layers of the pulp;
- change in the color of the tooth crown.
Probing the pulp can be painful, in contrast to percussion, in which there are practically no pain symptoms.
In addition to a visual examination, the doctor will prescribe:
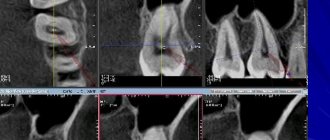
- X-ray diagnostics;
- electroodontodiagnostics.
Price
The cost of treating pulpitis is influenced by many factors. First of all, these include the form and stage of pulpitis, diagnostic measures that make it possible to establish an accurate diagnosis and choose the most appropriate treatment method. In addition, the medications, materials, equipment and instruments used during treatment are important. Not the least important role is played by the qualifications of the doctor, additional consultations with specialists, as well as medical measures accompanying the main treatment, if necessary.
Many patients think that toothache is a temporary “little thing in life” that can be overcome with the use of modern painkillers. But this illusion quickly dissipates as soon as a person experiences unbearable pain... Remember that the sudden appearance of toothache is in all cases a serious signal warning of the presence of some kind of pathology in the maxillofacial system. In many cases, this pathology turns out to be pulpitis - a disease that, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to many complications, including tooth loss. But only a qualified doctor can determine the exact cause after conducting a thorough diagnostic examination. Therefore, visit the dental office as soon as possible. Your efficiency, combined with modern treatment methods and the professionalism of the doctor, is a guarantee that the disease that caused the pain will be completely cured and will not deprive you of the beauty of a full smile.
According to antiplagiat.ru, the uniqueness of the text as of October 16, 2018 is 97.5%.
Key words, tags: caries, periodontitis, periodontitis, deep caries, tooth extraction
1 Therapeutic dentistry. Dental diseases: textbook: in 3 hours / ed. E.A. Volkova, O.O. Yanushevich. - 2013. - Part 1.). 2 https://mkb-10.com * Images: - Domenico Ricucci, Jose Siqueira, “Endodontics. Clinical and biological aspects”, Publishing house “Azbuka”, Moscow, 2015. A book for dentists and endodontists. Edition in Russian, translated from English, 415 pages, 1682 illustrations, hardcover. The original edition of the book “Endodontology: An Integrated Biological and Clinical View (Ricucci, Domenico and Siqueira Jr, Jose)” was published in 2013. — Database of clinical photo protocols of the Dental Clinic Dr. Edranov; Personal archive of S.S. Edranova.
Reviews about our doctors
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
I am very grateful to Evgeniy Borisovich Antiukhin for removing my three eights. Especially considering that the lower tooth was not the simplest (it was located in an embrace with a nerve). The removal took place in 2 stages, one tooth under local anesthesia, two under general anesthesia. I had no idea that wisdom teeth could be... Read full review
Sofia
28.12.2020
Treatment of gangrenous pulpitis
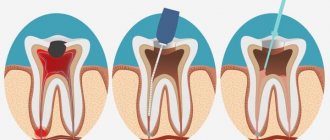
Unfortunately, treatment of acute and chronic gangrenous pulpitis
It is carried out only by surgical techniques. They involve removing the nerve of the tooth, since the process of its damage is irreversible. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and requires complete removal of the pulp from the root and crown parts of the tooth. In order for it to proceed correctly, it is necessary to exclude bleeding. To do this, the dentist performs cauterization of the vessels. Once the pulp has been removed, one of two solutions is used:
- the canals are cleaned and sealed, and a permanent filling is applied;
- obturation is performed using calcium hydroxide and temporary filling.
Since the disease is often accompanied by severe destruction of the crown part of the tooth, it may require the installation of an artificial crown to restore it.
Treatment prognosis and disease prevention
Dentists at the CELT clinic give favorable prognoses for treatment that was carried out efficiently and on time. In any case, they take all measures to save the tooth.
In order to avoid this disease and keep the tooth healthy, it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations at the dentist every six months and not try to endure toothache. The earlier the disease is detected, the easier and faster it can be cured. Prevention measures also include maintaining oral hygiene. The dental department of the CELT clinic offers services for the treatment of the most complex cases of gangrenous pulpitis. Contact us and be healthy!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Is it possible to cure pulpitis and how are nerves removed: types of anesthesia
As mentioned earlier, pulp inflammation is an extremely painful pathology, which primarily affects the nerve endings inside the oral cavity. The process of its treatment necessarily includes an operation to select a high-quality antiseptic that is suitable for a particular person. Moreover, the drug is applied to the desired places using various methods:
- application;
- infiltration;
- conductive;
- stem
The anesthetics used are traditional pairs of lidocaine and novocaine, as well as more advanced and modern formulations: Ultracaine, Ubistezin, Septanest, and so on.