Treatment of herpes in the mouth
Can herpes be in the mouth?
Maybe! Herpes in the mouth requires the same responsible approach and competent treatment as other diseases of the oral cavity. Despite the fact that the infection is often mild and goes away naturally, there are still risks of serious complications, and the possibility of infecting other people remains. Many factors influence the degree of development of the pathology and the presence of possible dangers for the patient. Complete diagnosis and comprehensive treatment can completely stop the manifestations of the infection, although complete elimination of the virus is considered impossible. Herpes, a viral disease known to many as a “cold sore,” is often perceived as a minor problem that does not require treatment. It is characterized by the appearance of a moderately painful blistering rash, but not many people know that this disease is not limited to appearing only on the lips , but can also develop on the oral mucosa . The disease is often accompanied by weakness, general malaise and severe itching, and in some cases can cause complications. During the active phase of the virus, a patient can easily infect others with it through household items, close contact or by airborne droplets.
Types of herpes virus infections
More than 100 representatives of the herpetic family of viruses are known. However, most often a person is affected by 8 of them. Let us consider in detail the features and symptoms of the most common infections.
Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2
The herpes virus type 1 causes blistering rashes on the mucous membranes of the lips and nose. As a rule, infection occurs in childhood. By the age of 5-7 years, more than 50% of children are carriers of the infection. Infection often occurs from sick parents: through kisses, household items.
The incubation period lasts from 2 days to 2 weeks. In addition to the characteristic rashes, the infection may be accompanied by elevated body temperature and enlarged local lymph nodes. After damaging the mucous membranes, the virus reaches the trigeminal nerve, where it can remain latent for a long time.
Herpes simplex virus type 2, or genital herpes, is primarily transmitted through sexual contact. In Russia, the average is 20% among the adult population. In European countries, the incidence rate is even higher. The risk group includes people who have promiscuous sex. Most infections occur during puberty, at the beginning of active sexual life.
Symptoms of the virus include:
- blistering rashes on the genitals;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- painful urination;
- itching in the groin area;
- elevated body temperature.
The disease can occur with frequent relapses (6-12 times a year or more).
Herpes virus type 3
This virus can cause two diseases: chickenpox and herpes zoster. As a rule, chickenpox occurs in childhood and is accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- vesicular rash that lasts about 10 days;
- high body temperature, fever;
- headache;
- itching of the skin;
- symptoms of body intoxication.
Chickenpox in adults occurs rarely and can occur in a more severe form: with damage to the eyes and nervous system. In such a situation, a person requires urgent hospitalization. After the disease, the virus remains in the body for life, remaining latent in the nerve ganglia.
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent the disease in children and adults who did not have chickenpox in childhood and were not vaccinated against it. Vaccination is given to children from one year of age. The immunobiological drug is administered twice with an interval of 6 weeks. Vaccination is also carried out as an emergency measure in the first three days after a person comes into contact with a patient with chickenpox.
Typically, herpes zoster occurs in people over 65 years of age. The disease is severe and is accompanied by severe symptoms:
- severe pain;
- sleep disturbance;
- high temperature;
- vesicular rashes that appear along the nerve endings.
The disease has a rather difficult rehabilitation period. Even after the rash disappears, a person may remain sore for a long time in those areas that were affected by the infection. In all civilized countries of the world, elderly people are vaccinated to prevent herpes zoster.
Epstein–Barr virus
Herpes virus type 4 or Epstein-Barr virus affects the human body in a complex manner, provoking various and sometimes unrelated pathologies. The virus can cause infectious mononucleosis, lymphoma, hepatitis, affect the nervous and immune systems, and the hematopoietic apparatus.
In the human population, infection with the Epstein-Barr virus reaches 75% or higher. Children over two years of age and adults under 30 years of age are at risk. Children under one year of age rarely get sick due to passive immunity received from the mother.
The symptoms of the disease are many-sided and can have various manifestations: from mild discomfort to severe health problems. The most common symptoms of the disease are:
- high temperature, fever;
- sore throat, muscles;
- enlarged lymph nodes, liver, spleen;
- the appearance of rashes, peeling, inflammation, bruising on the skin;
- photophobia;
- nausea.
It is characteristic that the use of antibiotics does not affect the duration of fever.
Herpes virus type 5
Cytomegalovirus infection, caused by herpes virus type 5, occurs in both children and adults. It can occur as a mononucleosis, with high fever, intoxication, purulent sore throat, and damage to the salivary glands. In addition, the infection may be asymptomatic.
There are also congenital forms of the disease, which often lead to the development of hearing loss, microcephaly in the child, cause enlargement of the liver and spleen, and hematological disorders.
Herpes viruses type 6 and 7
The range of diseases caused by these viruses is diverse. Often infections occur in the form of a sudden exanthema. Hepatitis virus type 6 can provoke chronic fatigue syndrome and infectious mononucleosis. It is believed that a consequence of viruses can be a lymphoproliferative process (the formation of tumors of the lymphatic system).
As a rule, sudden exanthema affects children under two years of age. The disease occurs with high fever and intoxication of the body. Febrile convulsions may occur and a rash appears, which goes away on its own after a few days.
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is accompanied by rapid fatigue and decreased performance. Patients are concerned about low-grade fever, enlarged lymph nodes, and the appearance of catarrhal manifestations in the pharynx.
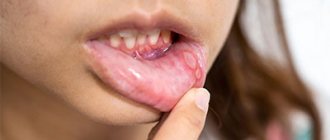
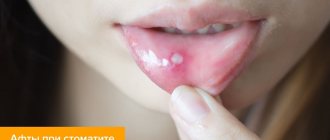
Symptoms of herpes on the oral mucosa
Symptoms of herpes are individual, have varying degrees of manifestation, and can occur in different parts of the oral cavity. For most cases, there are a number of signs that indicate the occurrence of herpes:
- Regular headache;
- Fever;
- A person gets tired quickly;
- Discomfort when eating and drinking;
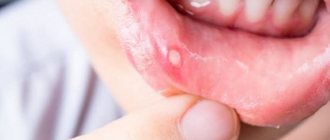
- The appearance of water bubbles filled with transparent white or yellowish exudate, up to 3 mm in diameter;
- The appearance of ulcers at the site of burst blisters;
- Inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, redness, itching, burning, swelling of the lesion.
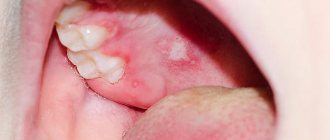
According to clinical studies, blisters in the mouth can form in different areas: on the palate, on the inside of the cheeks, on the tongue, on the gums, on the tonsils.
How is diagnostics carried out?
The appearance of neoplasms on the tongue of an adult or child should at least alert you. If redness, pain and swelling are added to everything else, it’s most likely glossitis. However, to make an accurate diagnosis and choose the appropriate treatment method, you must consult a doctor. Already as part of the initial visual examination, the specialist will be able to draw certain conclusions regarding the clinical picture, and to identify the specific cause of inflammation, it may be necessary to undergo the following types of examination:
- general blood analysis,
- blood chemistry,
- scraping from the damaged area.
Only tests can determine the true cause of the problem.
Only with the results of the studies in hand, the doctor will be able to make a final verdict and prescribe the necessary therapy. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances - such arrogance can lead to a worsening of the situation.
Stages of development of herpes in the oral cavity
The disease develops sequentially, including passing through several distinct stages:
- At first, the patient may experience drowsiness, malaise, and tingling or itching of the mucous membrane. Sometimes body temperature rises slightly;
- Next comes redness and swelling of the lesion, minor pain occurs due to the appearance of herpes on the tongue or lip;
- Blisters appear in the oral cavity, filled with transparent contents. During this period, the patient is most contagious, blood counts change;
- The blisters become cloudy and open, and yellowish, shallow, painful ulcers form in their place;
- A hard, fragmented crust forms on the ulcers, damage to which causes bleeding. After a few days, the crusts disappear.
In the best case, the disease resolves naturally within two weeks and without treatment. All wounds heal quickly and without scars.
But there are also complications that lead to infection of internal organs. Suppuration occurs at the site of the wounds, the temperature rises to 40 C. Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the jaw and neck may begin.
How is the disease treated?
Treatment of herpes on the tongue can be quickly and effectively provided only by a doctor after making an accurate diagnosis and identifying a specific form of pathology. And in each individual case, the treatment method will largely depend on the individual clinical picture. Below are several general principles for combating the disease:
- elimination of all accompanying pathologies of the oral cavity - treatment of carious cavities, removal of plaque and dental deposits,
- rinsing with antiseptic solutions - Miramistin, Laripront, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin. If there is an advanced stage, the doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics,
- compresses - it is recommended to smear the affected areas with products that promote wound healing and eliminate pain. Among such ointments are “Kamistad”, “Vinizol”, “Malavit”, “Solcoseryl” and others1,
- treatment with oils: experts advise treating the affected areas with oil, for example, rosehip or sea buckthorn - they perfectly help in normalizing the microflora of the oral cavity,
- multivitamin complexes: taking healthy vitamins and minerals is necessary to restore the body's defenses.
The recommendations described above are relevant for most forms of glossitis, however, targeted therapy is necessary to effectively eliminate the disease.
Causes of oral herpes infection
Herpes that affects the oral cavity develops when infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1, which not only provokes the appearance of a blistering rash, but can also cause complications in 10% of cases. The second type of herpes virus (genital) also causes a rash in the mouth, but does not cause serious disruption to the body and differs in its mode of transmission (through sexual contact).
Most often, primary infection with a herpes virus occurs in childhood, after which it is introduced into the genome and remains in an inactive form for life.
The main routes of infection with a viral agent are close conversation, skin-to-skin contact, kissing, and the use of shared hygiene products or utensils. However, the entry of viral particles into the body does not guarantee that the disease will develop, since the immune system can suppress the action of the pathogen. In this case, situations that worsen the overall health of the body, on the contrary, provoke a clear manifestation of infection:
- surgical interventions;
- emotional and physical stress;
- lack of sleep, overwork;
- colds;
- chronic pathologies;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- periods of menstruation, pregnancy or lactation;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- AIDS;
- abuse of nicotine or alcohol;
- the appearance of microtraumas from excessive exposure to the sun or frost.
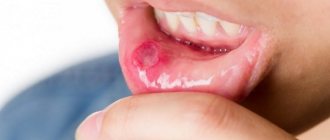
Possible complications
If no attempts are made to cure the disease, over time the lesion will spread further to the mucous membrane and will inevitably lead to serious health problems in general. In the worst case scenario, there may be a threat of an abscess, and it will have to be removed surgically. In this case, the person will experience throbbing painful sensations, and the tongue will increase in size, unevenly.
The photo shows a tongue abscess
Diagnosis and treatment of herpes infection
It is better to start treatment of herpes in the mouth at earlier stages of development to reduce the risk of complications and reduce the likelihood of infecting other people. In order to identify the disease, specialists carry out diagnostic measures:
- collect anamnesis;
- conduct an examination, determine the location of the rash and its nature;
- take a smear to identify the herpes virus and determine its type;
- laboratory tests are prescribed.
Modern methods for identifying the pathogen are a patient’s blood test to detect antibodies to the pathogen and a PCR study of tissues aimed at searching for the DNA of the viral particle. Differential diagnosis is of great importance, since herpetic infection must be distinguished from other similar diseases: stomatitis (not herpetic), tonsillitis, etc.
How to treat herpes on the lip, tongue or gum? Herpes therapy is based on an integrated approach that combines:
- The use of local antiviral agents to stop the process of reproduction and spread of the pathogen;
- Prescribing antiviral medications for internal use (usually indicated for those whose symptoms occur frequently and acutely, or who are immunosuppressed);
- The use of antiseptic drugs for treating blisters and ulcers, rinsing;
- Use of topical anesthetic gels;
- Prescribing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to alleviate general well-being;
- Strengthening the immune system by taking vitamins and immunomodulators.
To eliminate symptoms, advanced technologies such as laser radiation are also used. The technique allows you to quickly and painlessly destroy viral particles without harming mucosal cells and effectively healing damaged tissue. In most cases, several short procedures are sufficient for complete disappearance of symptoms in 2-4 days.
What it is
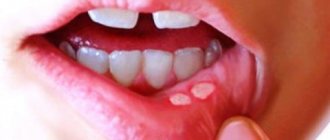
If a pimple appears on the tongue, the main thing to understand is that, in principle, there cannot be pimples on the tongue, since there are no sebaceous glands on it. Those formations that are mistaken for pimples are not actually pimples - they are not filled with purulent exudate. Essentially, these are small swellings and ulcers on the surface of the tongue. They are called "pimples" because they are very similar. They are white, pink, red, yellow, depending on the complexity of the disease and the cause of formation.
Consultation with a dentist: Pimple on tongue after injury
Small pimples are very painful, they interfere with eating, talking and even bother the patient at rest. Let's try to figure out what to do, how to cure it, as well as what they are and why they appear.
White pimple
White pimples most often appear as a result of stomatitis or candidiasis. Since these two diseases are treated completely differently, you should consult a doctor at the first symptoms in order to correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Candidiasis is characterized by white pimples and a coating on the tongue, which in appearance resembles cottage cheese and covers the entire surface of the oral cavity. There are also white pimples on the base, tip and under the tongue. Sometimes the entire surface may be covered with small pimples and a cheesy coating.
Diagnosing candidiasis is not difficult - if you wake up in the morning and find plaque and pimples on your tongue, you have every reason to suspect the presence of candidiasis or thrush. You should consult a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
With stomatitis, small pimples appear on the tongue. There are usually many of them, they can merge with each other. These small white pimples at the tip or root, at the base or underneath are very painful and itchy. The pain intensifies after eating.
Without proper treatment, stomatitis will not go away on its own; you need to see a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. As a rule, it consists of antiseptic treatment of the surface of the oral cavity and lifestyle correction, since the main cause of stomatitis is insufficient oral hygiene.
Red
Red pimples on the tongue are the main sign of glossitis, an inflammatory disease. Outwardly, they look like inflamed red dots that hurt and irritate.
Glossitis can appear for many reasons:
- allergic reaction;
- eating too hot and spicy food;
- alcohol abuse;
- the presence of the herpes virus.
A red pimple on the tip of the tongue can also be the result of a burn from too hot food. The papillae on the surface of the burn become greatly enlarged and swollen, outwardly it looks like a pimple. After a few days everything returns to normal.
With an allergy, many red pimples form on the surface of the tongue, which itch and cause anxiety.
With the herpes virus, a red pimple may not be the only manifestation of the disease; usually the entire surface of the oral cavity is affected.
Yellow
The appearance of yellow pimples on the tongue is usually not an independent disease. Often with stomatitis or candidiasis, the coating on the surface of the tongue takes on a yellowish rather than white tint. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the body. In addition, determining the shade is an individual matter. Therefore, yellow pimples most often also mean either candidiasis or stomatitis. To eliminate any doubts, consult a doctor; he will be able to determine for sure what disease you have encountered.
Pink
Pink pimples on the tongue, like yellow ones, are not an independent disease. Usually they are an early stage of glossitis, when the inflammatory process has not yet reached its peak. At the initial stage of the disease, they have a light pink tint, which after a few hours will turn intense red. Considering the fact that the disease is easier to treat at an early stage, if pink acne appears, you should immediately consult a doctor for advice.
Preventive measures
To avoid the development of such an unpleasant and even dangerous disease as herpetic glossitis, you should adhere to the following tips and recommendations:
- you need to carefully care for your oral cavity, brush your teeth and tongue twice a day, rinse your mouth every time after eating,
- It’s better to stop smoking and drinking alcohol at least for a while,
- it is necessary to carefully control your diet, avoid too salty, spicy and sour foods, cold and hot dishes and drinks,
- it is important to regularly undergo preventive examinations not only with a dentist, but also with a gastroenterologist and immunologist,
- At the first symptoms of pathology, you should immediately seek medical help.
Regular brushing of teeth and tongue will help reduce the risk of disease.
Any form of glossitis, including herpetic, in the vast majority of cases develops against a background of weakened immunity. Therefore, an equally important condition for maintaining complete disease prevention is a healthy lifestyle. Walk outdoors more often, play sports, eat right, and don’t forget to take a responsible approach to oral hygiene.
- Borovsky A.L. Diseases of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and lips, 2001.
How to treat a disease with folk remedies
Treatment of herpetic glossitis at home can only be as a concomitant therapy. To put an end to the problem once and for all, you need competent diagnosis and the help of a specialist. Let us remind you: only a doctor has the right to prescribe medications, and without his consent, you should under no circumstances make any attempts to cure the disease yourself. All this can end not only in vain, but also very disastrously.
If the specialist has given the go-ahead for the use of traditional methods, you should pay attention to medicinal herbs. For example, tea tree oil effectively promotes the restoration of mucosal tissue. Also, in the fight against glossitis, rinsing with a decoction of chamomile and a light solution of hydrogen peroxide have proven themselves to be excellent.
Eppstein-Barr virus
The Epstein-Barr virus predisposes to premature termination of pregnancy, fetal malnutrition, and in newborn children it causes damage to the nervous system, visual organs, recurrent chroniosepsis, hepatopathy and respiratory distress syndrome. However, this virus provokes the listed pathologies only under certain conditions, under which it becomes dangerous during pregnancy. It is very bad if a pregnant woman has not previously encountered the Eppstein-Barr virus, which is why she does not have antibodies to this virus in her body. If there was contact, and antibodies were detected after treatment, then this is a good sign, because in this case there is nothing to be afraid of. This serves as evidence that if a woman’s body becomes infected again, she will cope with this dangerous disease on her own. This means that a pregnant woman will not have to take medications that are heavy and quite dangerous for the development of the fetus.
Herpes during pregnancy
The influence of genital herpes on the course of pregnancy and the condition of the fetus is realized by two mechanisms:
- infection of the fetus, amniotic fluid, placenta and membranes, and varying degrees of spread of infection are observed (generalized infection of the fetus and placenta, local infection of the fetus, teratogenic effects on the embryo and fetus, latent infection of the fetus with clinical manifestations in the postnatal period);
- indirect influences in the form of fever, disturbances in general homeostasis due to severe infection, dysfunction of the fetoplantar complex, disturbances in the immune and hormonal balance.
In case of primary herpes during pregnancy, HSV can enter the fetoplacental link due to maternal viremia (spread of the virus in the mother’s blood).
Herpes during early pregnancy
Herpes during pregnancy in the first trimester causes severe congenital anomalies and spontaneous abortion.
The results of recent studies suggest that primary herpes infection in the second and especially in the third trimester of pregnancy poses an even greater risk to the fetus and newborn.
Perinatal HSV morbidity and mortality occur in 40-50% of fetuses and newborns whose mothers had their first episode of genital herpes during pregnancy.
If the disease recurs during pregnancy, the incidence of the disease in the newborn is much lower, but the risk is still significant - 3-4%.
Treatment of glossitis of the tongue
First of all, the treatment plan depends on the type of inflammation. It is compiled individually, based on clinical and diagnostic data. For acute catarrhal glossitis, it is important to remove the irritating factor: replace the crowns or, conversely, put crowns on the damaged tooth. Change your eating habits, stop chewing nuts, hard candies, and crackers.
For a folded tongue, oral hygiene comes to the fore.
If lumps and papillomas grow during rhomboid glossitis, they are excised. Laser surgery allows you to do this quickly, with virtually no blood.
The main recommendation for black tongue is treatment of somatic diseases and smoking cessation. Liquid nitrogen is used to remove papillae, as well as applications to keratinized areas.
But there is a general approach to treatment:
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- professional teeth cleaning;
- vitamin complexes;
- iron supplements for anemia;
- for pain - light anesthetics in the form of applications;
- for burning - oral baths and irrigation;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- checking for fungal infections.
There are many recommendations on the Internet for treating glossitis with folk remedies. No one disputes the anti-inflammatory properties of chamomile, sage and plantain. When a spot appears on the tongue, applications of sea buckthorn oil and aloe juice can bring relief. But these measures are temporary, they affect the symptoms, but the cause of the disease remains unattended. As a result, it is easy to miss the point when it was not difficult to fix the problem.
Glossitis is closely related to common diseases and psychological causes. Effective treatment is only possible using an integrated approach. How to treat glossitis and what examinations you need to undergo can only be advised by a qualified doctor. Glossitis can be cured quite quickly, but if left untreated, abscesses, tumors, and necrotic tissue changes can form. This is much more serious and the prognosis is not so favorable.
Stomatitis: how to overcome the “language barrier”?
Stomatitis on the tongue is just one of the manifestations of this “popular” disease. There are a huge number of reasons for its appearance, as well as ways to treat it.
There are several types of stomatitis, when it manifests itself specifically on the tongue: glossitis, viral stomatitis, vesicular stomatitis, enteroviral vesicular stomatitis, catarrhal stomatitis, fungal stomatitis, etc.
In general, stomatitis on the tongue is most common. Its notable feature is small ulcers, from which the patient suffers greatly. If inflammation is observed only on the tongue, and, for example, there are no signs of stomatitis on the palate, cheek or gum, then this disease is called glossitis.