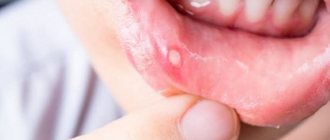
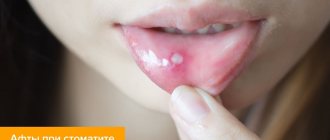
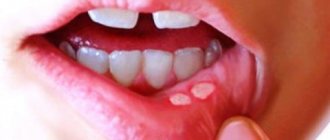
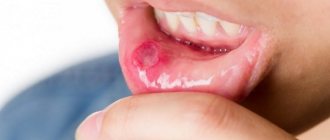
Swelling in the mouth, the presence of painful ulcers and white plaque, inflammation of the gums and fever - all this may indicate the presence of stomatitis. This disease is diagnosed in patients of any age, and the fight against it often becomes difficult and lengthy. Dentists consider miramistin for stomatitis to be one of the best medicines. What is its peculiarity, how is the drug used correctly, and at what age is its use recommended?
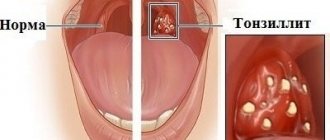
How is stomatitis diagnosed?
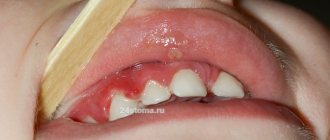
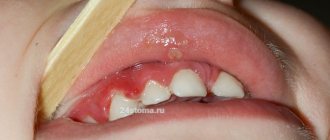
The disease is manifested by the presence of inflammatory processes on the oral mucosa, which is caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Stomatitis has several forms of manifestation. Each of them has different symptoms. It depends on the reason for the development. One or another type of disease can be diagnosed based on the following symptoms.
- When stomatitis is of viral origin, the patient develops a high temperature. The oral mucosa becomes covered with ulcers. The lymph nodes, which are located in the lower jaw area, become enlarged. Very contagious.
- The traumatic origin of the disease is accompanied by swelling and soreness of the oral cavity. The child becomes whiny and refuses to eat. The temperature may rise in rare cases. This type of stomatitis is not contagious.
- With candidal stomatitis, the oral cavity is completely covered with a pronounced white coating. There is pain when eating. The temperature is rising. The disease is contagious.
- The bacterial type of disease is most often provoked by staphylococci and streptococci. At the beginning of its development, it manifests itself as redness and swelling of the gums. Next, the oral cavity becomes covered with ulcers, which cause a painful syndrome. Children may develop a fever. Fever is rare in adults.
- The allergic type begins with swelling and inflammation of the gums. Elevated temperature may not always be present. Easily turns into another form of stomatitis. For development, it will be sufficient for viral or bacterial agents to enter the oral cavity.
In addition to the types described above, so-called symptomatic stomatitis is sometimes diagnosed. It appears as a symptom of another disease.
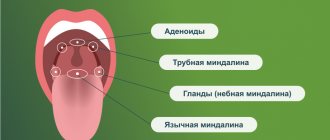
Purulent pathologies
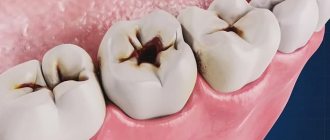
Often, patients come to dental clinics with a fistula, gumboil, purulent cyst, enlarged granuloma, abscess, osteomyelitis, or even phlegmon. All of the listed pathologies, as a rule, are the result of advanced dental diseases (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis). To get rid of them, doctors perform root canal treatment on the diseased unit or remove the tooth. If there are ulcers in the oral cavity, they are opened with surgical instruments and a drainage is installed through which the pus is washed out.
Treatment is also carried out in the presence of a fistula
For better release of purulent masses, experts often prescribe rinsing with Miramistin, since the drug has a drawing property. It also dries wound surfaces, prevents bacteria from entering them, and promotes rapid healing. Plus, it stops the signs of the inflammatory process and allows the patient to return to normal faster.
Dentists prescribe it precisely for its ability1 to activate local immunity, reduce the inflammatory reaction of tissues and help accelerate the process of their regeneration, and stabilize the pathological process. At the same time, there are no allergic reactions, discomfort, taste disturbances, or changes in enamel color to the drug.
Types of stomatitis depending on age
Dentists note a certain pattern between the patient’s age and the type of stomatitis. Children are most often affected by the disease. This is due to the structural features of the child’s mucous membrane, which is formed gradually, and therefore has its own characteristic features.
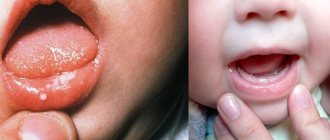
- Children under one year of age often develop the fungal type (thrush). This is due to the slightly acidic or neutral reaction of saliva, which creates favorable conditions for Candida fungi.
- From one year to three years - the viral type. Saliva loses its protective properties. The content of lysozyme, a substance that fights pathogens, decreases.
- Until the age of seven, local immunity declines. The child becomes susceptible to a bacterial type of disease.
- The active development of immunity before the age of fifteen becomes the cause of an allergic type of stomatitis.
Most often, the medicinal antiseptic Miramistin is prescribed to combat stomatitis. Miramistin for stomatitis has proven itself well for patients of any age. The drug is approved for use from the first days of their life and for nursing mothers.
Rubbing with orthopedic and orthodontic devices
Most often, an unpleasant symptom occurs at the stage of getting used to the structures. Out of habit, orthopedic and orthodontic devices interfere, squeeze, rub and even injure the delicate tissues of the oral cavity, causing the appearance of various wounds, ulcers and chafing. During this period, it is very important to prevent pathogenic bacteria that cause an infectious inflammatory process from entering such wounds. It is necessary to promote rapid tissue healing and strengthen local immunity. Miramistin copes well with all its goals.
If the mucous membrane is damaged, Miramistin is also used
However, if you feel severe discomfort one or several months after starting to wear orthopedic and orthodontic devices, this may be due to improper installation, or a discrepancy between the selected and manufactured structures and your anatomical features. Here the drug will not help much, and to eliminate the problems you need to see a doctor.
Is Miramistin effective for stomatitis?
The drug has antimicrobial and bactericidal properties, destroying gram-negative and gram-positive microflora. Under the influence of Miramistin, the proliferation of fungi is inhibited, stopping the development of the disease. The medicine helps to form an adequate and correct immune response. As a result:
- local immunity significantly enhances its protective properties;
- the infection stops spreading to healthy tissue;
- already damaged tissues are restored faster;
- the drug helps to adsorb (collect) pus and remove waste products of pathogenic microorganisms;
- stops inflammatory processes.
Miramistin is available for sale in three forms: as a spray, solution and ointment. This helps the patient choose the most convenient option for using the drug.
A big advantage of the drug is its good compatibility with other antibiotics that are taken to increase tissue regeneration, as well as the taste of the drug. Many medications that are intended for treating the oral cavity are produced with an unpleasant taste. This becomes a problem when using them for children. Reflex vomiting and increased salivation can create a dangerous situation for the child’s health. Miramistin is distinguished by the absence of antipathetic odors and tastes. The solution is more similar in taste to plain water, which greatly simplifies the procedure for using it for children.
The drug is also suitable for preventive purposes when one of the family members already has the problem. To do this, the oral cavity is sprayed with Miramistin solution 2 times a day, but the drug cannot be used for more than 10 days.
The use of the drug does not always guarantee a positive result in treatment. Miramistin will not bring the expected result for allergic stomatitis. Treatment may fail if the disease is caused by dental problems. These include: the presence of periodontal disease or tartar, advanced caries, as well as the presence of other inflammatory processes. First you need to eliminate the original cause. Then just start fighting stomatitis.
Treatment of stomatitis in children
After a medical diagnosis of stomatitis in children under one year of age, a specialist prescribes highly effective drugs to combat the existing type of disease. Experts recommend that parents, at the first suspicion of stomatitis in a child, increase the amount the child drinks to irrigate the oral mucosa and remove toxins from the body. Clean drinking water without gas, fruit drinks or compotes that are not too sweet or sour; herbal teas are perfect for this. During this period, it is worth refusing to drink the child from concentrated juices and drinks with gas in order to avoid irritation of the mucous membrane.
After this, the specialist begins medical manipulations to cure stomatitis in the child.
Anesthesia
The first step is to numb the mucous membranes so that the child can eat and drink properly and generally reduce the child's stress level. Choline preparations with salicylate or lidocaine are commonly used as pain relievers in children. For this purpose, medications to facilitate teething, for example Kamistad or Dentinox gel, are suitable. Gel products are preferable for children because they are almost instantly absorbed into the mucosal tissue. Prepare with lidocaine in the form of a spray should not be used in children under one year of age - this may lead to bronchospasm.
Direct treatment of stomatitis
After anesthesia, you can begin treating your baby’s stomatitis. Firstly, all rashes and wounds must be treated with a special preparation, depending on the type of disease. Antiviral drugs are used for herpetic stomatitis, antibiotics and antiseptic drugs for bacterial stomatitis, antifungal drugs for candidal stomatitis. Not only the affected area, but also adjacent areas must be treated - this will stop the spread of the pathogenic process.
An important condition for eliminating infection is thorough and timely oral hygiene. The surface of the child's tongue and teeth should be brushed twice a day; experts recommend rinsing the mouth after every meal or drink. For young children, hygiene procedures are carried out using a piece of gauze or a silicone fingertip.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis
If a specialist has identified the presence of allergic stomatitis or severe swelling of the oral cavity is observed, then the drugs Fenistil, Suprastin, Diphenhydramine are used.
Treatment of viral stomatitis
For herpetic stomatitis, antiviral agents should be used in the form of ointments containing acyclovir - Gerpevir, Virolex, Acik, Viferon, oxolinic ointment.
For relapses of viral stomatitis, experts recommend a general strengthening of the immune system with the help of Immunal, Interferon, Viferon in suppositories. The duration of treatment and dosage of the drug is determined by the doctor. Often, medical experts recommend using the drug Cholisal in gel form. Perfectly relieves swelling, inflammation, pain, fever, eliminates pathogenic microflora. The drug does not contain sugar, has no taste and has a light anise aroma. To treat stomatitis in a child under one year old, it is necessary to rub a strip of gelatin preparation no more than 0.5 centimeters long into the palate, gums and inner surface of the cheeks, teeth, 2-3 times a day after brushing the teeth.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis
For candidal stomatitis, the doctor uses antifungal drugs in the form of an ointment, for example, Clotrimazole, Candida, Candizol, and often prescribes soda rinses.
This helps create an alkaline environment in the oral cavity, harmful to pathogenic fungal microflora. Procedures with soda are especially effective in the treatment of candidal stomatitis in children under the age of one year, because at this age most drugs are contraindicated. To treat the oral cavity, you need to dilute a teaspoon of soda in a glass of warm boiled water, then wrap a piece of gauze around a clean finger and wipe the palate, inner surface of the cheeks, gums and sublingual space of the child, periodically dipping your finger into the solution. The procedure should be done after every child eats or drinks. Older children can rinse their mouths with baking soda themselves.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
With aphthous stomatitis, the first priority is to unload the affected area and speed up the healing of the poop. An aqueous solution of blue (methylene blue) has long been used for this purpose. It is not recommended to use a blue alcohol solution for this, since the ethyl alcohol in its composition will cause poisoning or burn the baby’s mucous membrane.
Wounds are treated with a blue cotton swab 3-6 times a day.
Treatment of traumatic stomatitis
According to experts, traumatic stomatitis most often occurs in children 1-2 years old. This type of disease is accompanied by bacterial microflora, so the use of medicinal and antiseptic agents will be required. For children under 2 years of age, use Cholisal, Solcoseryl, Actovegin gel, and also wipe the oral cavity with a solution of chlorhexidine or soda.
Treatment of bacterial stomatitis
For the treatment of bacterial stomatitis, drugs such as Tantum Verde, Orasept and Hexoral in the form of a spray, Doctor Theiss and Septolete in the form of lozenges and many others are effective. Experts do not recommend using lozenges to treat children under 6 years of age due to the risk of asphyxia, and sprays are suitable for treating bacterial stomatitis in children over one year of age. Antiseptic rinses and gel preparations with metronidazole are also effective.
Among solutions with an antiseptic effect, the drug Miramistin is especially recommended, as it promotes the regeneration of the affected mucous membrane and eliminates most pathogens. The aerosol can is convenient for treating children under one year of age. To do this, you need to make 3 injections and rinse your mouth with them for several minutes 3-4 times a day. Babies under the age of one year are treated with gauze soaked in the drug.
Side effects and contraindications
Side effects from using the drug include the risk of developing an allergic reaction. It occurs very rarely and most often affects young patients. A burning sensation may occur during use. This phenomenon is considered normal and does not require refusal from further use.
Contraindications include individual intolerance of the body to the components of the drug, which occurs in the presence of certain types of allergies and dermatitis. In any case, Miramistin should be taken under the supervision of a specialist.
Use of the drug for children
Miramistin can be used from the first weeks of a baby’s life, but since a baby at this age will not yet be able to rinse his mouth, a special spray nozzle is used. Using a spray, lesions of the mucous membrane are treated with a single press. The procedure is repeated 4 times/day. Until the child is four years old, you should avoid getting the medicine deep into the neck and onto the tonsils. The effectiveness of the drug can be increased. To do this, you will need to create an alkaline environment in the oral cavity. For these purposes, rinse with a soda solution. The solution is made from a glass of water and a teaspoon of soda.
Miramistin, which is available in gel form, showed good results. Staying on the mucous membrane for a long time, the gel effectively penetrates into the deep layer of the mucous membrane. To apply the drug, you can use a gauze swab and wipe the inflamed areas.
Miramistin ointment is less effective for children. It is quickly washed off by the baby’s saliva and is not able to penetrate into the deeper layers.
Sanitation may be prescribed to a child who can rinse his mouth independently. The product is diluted with boiled, cooled water in a 1:1 ratio. Age dosage:
- less than 6 years – 3..6 ml;
- up to 12 years – 6..10 ml;
- over 14 years old – 15 ml.
The procedure is repeated up to six times a day.
Miramistin for adults
Adults, as well as children over 14 years of age, with stomatitis, choose any suitable option for treating damaged areas of the mucous membrane. This can be either rinsing with a solution or simply irrigating with a spray. For one rinsing procedure, 15 ml of an undiluted solution (0.01%) of Miramistin is used. This solution is commercially available ready-made. Additional manipulations for its dilution or preparation are no longer required.
The course of treatment lasts an average of 7 days, 4 procedures per day. The procedures should be carried out regularly at approximately equal intervals in time. Maintaining time intervals will help achieve more effective results. The drug is quickly washed off by saliva, so a long time without it reduces the therapeutic effect.
During administration, in places where the drug comes into contact with damaged areas of the mucous membrane, a slight burning sensation may be felt. The sensation goes away after a few seconds and is not a reason to discontinue the drug.
Miramistin for gum inflammation
Miramistin is often used for gum inflammation, which manifests itself as a symptom of various dental ailments. The drug has proven itself in complex treatment, where it is used to rinse the mouth. To obtain the most positive result from the rinsing procedure, you need to properly prepare the gums and mucous membranes. This is done as follows:
- The oral cavity is thoroughly cleaned with conventional hygiene products (brush, dental floss and toothpaste). This will make it possible to eliminate plaque and food debris from all hard-to-reach places where the drug should subsequently reach.
- The drug will give a positive effect faster if you increase blood circulation. To do this, you should massage your gums. It is done using the thumb and index finger. The gums are massaged using massage movements for five minutes. For massage, you can use a paste containing medicinal herbs or a drop of essential oil.
- After the massage, the oral cavity is rinsed with water at room temperature (in cases where additional products were used).
Further, all rinsing procedures occur in the order prescribed by the doctor.
In dentistry, Miramistin is also used for the treatment of periodontitis, for hygienic procedures for removable dentures, and also as an effective means for the prevention of microbial complications that may arise after surgical interventions on the oral mucosa.
Sources used:
- “Outpatient surgical dentistry” (Bezrukov V.)
- Miramistin. Collection of works / Ed. Yu. S. Krivosheina. - M., Medical Information Agency, 2004.
- Miramistin. Encyclopedia of medicines and pharmaceutical products. Radar Patent.
Prevention and treatment of postoperative complications
The product promotes rapid tissue regeneration, strengthens local immunity, eliminates symptoms of the inflammatory process, disinfects, and washes pathogenic microbes from wound surfaces. Therefore, it is recommended to use it for oral baths and rinses after tooth extraction as a prevention of complications such as alveolitis, gumboil, phlegmon, and osteomyelitis. They are also prescribed treatment if such complications do arise.
The photo shows alveolitis
A remedy is prescribed for the prevention and treatment of complications after the following surgical procedures in the oral cavity: trimming the frenulum of the tongue, dental implantation, bone grafting, vestibuloplasty.