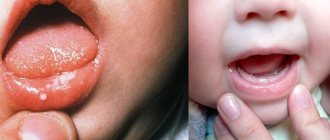
The yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida is always present in the human body, but under certain factors it begins to multiply faster. The consequence of this process can be inflammation. Unpleasant white spots and plaque form on the tongue and oral mucosa - the main manifestation of candidal stomatitis.
Infants are often susceptible to the disease, as their immune system has not yet fully developed. It can appear from the first weeks of life. Moreover, it occurs in children under 10 years of age and in older people, especially if they suffer from dry mouth.
Cause of candidal stomatitis
We have already said above that the main reason is the increase in the concentration of Candida fungus in the body. Let us emphasize once again that normally in the human body, including the oral cavity, these microorganisms are always present and do not cause harm.
We can distinguish two groups of factors that provoke this process: endogenous (internal) and exogenous (external).
Endogenous (internal) factors:
- metabolic disorders, gastrointestinal problems, diabetes and other diseases;
- lack of vitamins;
- acute and chronic infectious and non-infectious general diseases;
- weakened immune system;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics.
Among the exogenous (external) causes: various damage to the mucous membrane (for example, due to dentures), thermal or chemical burns, poor personal hygiene.
Causes of candidal stomatitis
The most common cause of candidiasis stomatitis is a fungus of the Candida albicans group. It is worth noting that these fungi are always present on the mucous membranes of the mouth, and do not cause any harm to the body until they begin to multiply.
The causes of the development of candidal stomatitis are the following factors and diseases:
- Weak immunity;
- People with Sjögren's syndrome;
- Neglect of general rules of oral hygiene;
- Constant stress;
- Various diseases of the oral cavity;
- Taking antibiotics or corticosteroids;
- Having a disease such as diabetes. This is all due to the fact that the blood contains a large amount of sugar, and this serves as an excellent environment for the development of fungus of the genus Candida.
It is also worth noting that adults who suffer from excessive dry mouth can get candidal stomatitis. The most common cause of such dryness is the abuse of dental elixirs.
Another factor that can cause the development of candidal stomatitis is pregnancy. After all, it’s no secret that it is during this period that significant hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body, which, in turn, greatly affect the bacterial balance in the mouth.
Types of disease
Pseudomembranous. One of the most common types, which has several forms. To a mild extent, a white coating appears on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and tongue. In the middle, it becomes denser and begins to grow into the mucous membrane, erosion and bleeding appear, and regional lymph nodes enlarge. In severe form, weakness appears, body temperature rises, ulcers form under a white coating, and local lymph nodes enlarge.
Atrophic. It can develop independently or after the pseudomembranous form. Its manifestation is dry mouth, burning or pain when eating, and spots form on the surface of the tongue. The mucous membrane turns red, swells, and tongue movements become limited. Inflammation begins in the corners of the mouth.
Chronic. Candidomycosis stomatitis develops into this form if treatment is not carried out at the initial stage. In this case, changes begin in the mucous membrane (thinning, drying, redness), it becomes difficult to swallow, and a burning sensation is felt in the mouth. If left untreated, there is a risk of damage to the larynx, esophagus and intestines.
It can also be classified by location: candidal stomatitis of the corners of the mouth, yeast glossitis (appears on the surface of the tongue), thrush (plaque covers the mucous membrane of the cheeks and gums).
What is oral candidiasis?
Oral candidiasis (also called oral thrush) is an infection of the mouth caused by the yeast-like fungus Candida. These microorganisms are part of a healthy microflora, but under certain circumstances their reproduction disrupts the favorable environment and becomes a source of disease processes. Inflammation and plaque on the tongue, ulcers on the mucous membrane and discomfort in the mouth - this disease is called oral candidiasis.
Infants are most susceptible to this disease, but at this age it is treated faster and is tolerated almost painlessly. Oral thrush is often observed in adults after 50 years of age, when the immune system is already weakened. Oral candidiasis is less common in men than in women. Recently, the percentage of cases has increased significantly, which is associated with uncontrolled use of medications: weakening of cellular immunity increases the risk of oral candidiasis after antibiotics, or rather their improper use. Microbiology, the science of microorganisms, studies the essence of oral candidiasis. And she successfully copes with her task, at the moment this disease has been studied in detail, and doctors know all the methods of treating and preventing infection.
Symptoms of candidal stomatitis
Clinical manifestations of oral candidiasis are varied. As a rule, a milky-white cheesy coating forms on the back of the tongue, palate, and cheeks. When it is removed, the eroded bleeding surface of the mucous membrane is exposed, and painful sensations appear when swallowing. A common symptom is dry mouth and an unpleasant metallic taste.
In the earliest stages, a small number of white spots form. As the disease progresses, their number increases and they turn into ulcers. In severe forms, the white plaque cannot be removed and it completely covers the oral cavity.
If left untreated, the fungus can invade the area of the larynx, esophagus and even the intestines. The pain intensifies and the red border of the lips and corners are affected. When the lips are affected, candidal cheilitis begins to develop, due to which cracks and erosions form, thin films and crusts grow. Seizures may also appear in the corners of the mouth, which bleed and cause pain when opened.
Symptoms
A number of symptoms are characteristic of candidal stomatitis:
- The appearance of a white or yellowish coating on the tongue, cheeks or palate. When trying to eliminate it, bleeding wounds may appear on the mucous membrane.
- Constant metallic taste.
- Feeling of heartburn on the tongue.
- Painful sensations from touching plaque.
- Later, as plaque spreads, difficulty swallowing occurs.
- Deterioration of tongue sensitivity and poor taste perception.
Diagnosis of the disease
Before starting treatment for stomatitis, you should consult a dentist. The doctor will listen to complaints, conduct a visual examination of the oral cavity and skin, and also take scrapings from the affected areas. In some cases, consultation with a therapist, dermatologist, allergist and endocrinologist may be required.
Remember that timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment and easy progression of the disease. Also, regardless of the causes and form of the disease, treatment in newborns should be carried out under the supervision of doctors.
Prevention of stomatitis in children
Irritative stomatitis can be prevented with good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups and proper nutrition. Because many adults and children carry the herpes virus and can transmit it even without symptoms, there is no practical way to prevent herpetic stomatitis. However, parents may discourage their child from kissing, eating, or playing in close contact with people who have an active herpes infection.
Ulcers can be minimized by teaching children to avoid injury, even minor trauma to the mouth. If our doctor determines that a child has a nutritional deficiency, parents can make sure the child is taking appropriate supplements and eating recommended foods. It won’t hurt to visit the dentist once every six months if we have previously discovered stomatitis in the child. Regular visits to our clinic will help prevent serious complications and detect the disease in time.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis
The course of treatment depends on the type and severity. Often the complex includes local and general methods:
- rinsing with antiseptic, antimycotic and analgesic drugs;
- use of antifungal ointments, aerosols, gels;
- when it spreads to other body systems, systemic antimycotics are prescribed.
With properly selected therapy, its duration is two weeks. If stomatitis has become chronic, then courses of treatment must be repeated to avoid relapses. In the most advanced cases, this is from 1 to 3 months.
With a mild degree of the disease, candidiasis can be eliminated forever. In other cases, there is a possibility of relapses, and even the development of candidal sepsis, so prevention is of great importance.
Treatment of oral thrush
The treatment of this disease is carried out by the dentist, although he may seek advice from a therapist, immunologist or endocrinologist. To get rid of this disease, there are many medications, from which a specialist will choose the one that is right for you. Do not forget that different medications are used to treat oral candidiasis in adults and children. Also, to speed up recovery, you should follow a special diet that your doctor will prescribe; it is important for restoring the mucous membranes after candidiasis of the mouth and throat. Many patients neglect visiting a specialist and prefer advice from those who have already encountered this infection, as well as traditional methods. Such behavior is extremely dangerous; oral candidiasis cannot be treated based on reviews on forums or recommendations from friends. This can provoke unforeseen complications and cause serious harm to health. The doctor will accurately determine the cause of your disease and prescribe a drug that is suitable for your physiological characteristics. Read more about the treatment of oral candidiasis in the article.
Prevention
To prevent the manifestation of candidal stomatitis, you must adhere to the following rules:
- learn to brush your teeth so as not to injure the mucous membrane;
- use mouth rinses to cleanse the mouth;
- change your toothbrush every 2 months and rinse thoroughly after use;
- if you wear a denture, you must wash it thoroughly using special products, and also follow the storage rules;
- get rid of bad habits;
- if you are taking antibiotics, you must use antifungal drugs and probiotics as prescribed by your doctor;
- wash and treat with boiling water accessories that small children come into contact with;
- Nursing mothers are advised to maintain breast hygiene;
- hardening, physical education in the fresh air;
- visit the dentist regularly.
Treatment
First of all, when treating candidal stomatitis, you need to determine and eliminate the cause, adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and strengthen the body's immune system. And, of course, it is necessary to monitor oral hygiene. In most cases, this is quite enough for recovery.
If the disease is in a moderate or severe stage, the doctor often prescribes special medications for oral administration and antifungal ointments. Taking medications continues until the symptoms in the oral cavity are completely eliminated, in order to exclude possible relapses.
Treatment of mild forms of candidal stomatitis is carried out at home and does not require special conditions. Antifungal elixirs and lozenges are used. On average, the treatment course takes no more than two weeks.
More severe forms are characterized by the fact that the infection enters the digestive tract. Antifungal drugs are used to combat the disease. The course of treatment lasts from 2 to 4 weeks.
Recurrent forms of candidal stomatitis require much more time and money. Treatment is carried out until all symptoms disappear completely. Various antifungal agents are used.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis must be combined with a special diet. First of all, you should stop eating foods that are rich in starch and various confectionery products, minimize the consumption of cereals, baked goods, potatoes, etc.
When treating candidal stomatitis, other concomitant diseases should be eliminated, in particular:
- Caries;
- Periodontal disease;
- Chronic diseases of internal organs.
Traumatic stomatitis
Traumatic stomatitis develops as a result of mechanical, thermal or physical trauma. This type of stomatitis occurs:
- superficial (burn of the mucous membrane by hot tea)
- deep (burn with a strong alkali or acid, strong biting of the mucous membrane)
Acute mechanical stomatitis: rare, it can be caused by trauma to the mucous membrane when biting the cheek, tongue, lip while eating, an attack of epilepsy, a blow, trauma during dental treatment and other traumatic factors.
It is manifested by pain, hyperemia, swelling at the site of injury, erosion. With secondary infection, the wound can develop into long-term non-healing ulcers. Most often, traumatic stomatitis is acute, but can also be chronic, for example, constant biting of the cheeks under stress, chronic injury from braces, a sharp tooth edge, or a bad crown. As a result of trauma, painful erosions or ulcers with jagged edges form on the mucous membrane, which can become infected.
The cause of physical injury is most often a thermal burn due to contact with hot liquid, inhalation of steam, or exposure to fire, the latter, as a rule, accompanied by damage to the respiratory tract. The lesion is most often located on the tip of the tongue, lips, and the front of the palate. The mucous membrane becomes swollen, red, painful, and blisters may form, which then burst. With deep damage, the mucous membrane dies, and the damage involves muscles and even bone.
Chemical stomatitis occurs when burned with acid or alkali. In everyday life, this is most often acetic acid; also at a dental appointment, burns can occur with various drugs (phenol, formaldehyde, alcohol, hydrofluoric acid, etc.). The depth of damage depends on the damaging substance and its concentration, and the duration of exposure. First, the mucous membrane becomes bright red and painful, and with severe lesions, foci of necrosis then appear within a few hours.
In case of burns with acids, alkalis, or thermal burns, it is recommended to call an ambulance!
Types of stomatitis
Stomatitis comes in different forms: it depends on the causative agent of the disease. So, it can have a viral, microbial or mycotic etiology. Accordingly, the symptoms, description and principles of treatment of the disease will be different.
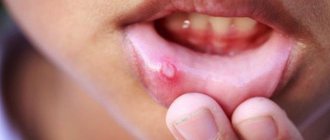
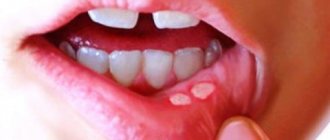
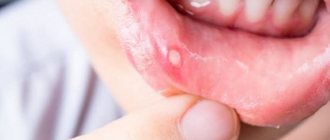
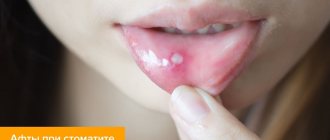
Aphthous stomatitis: treatment
The exact reasons why this type of stomatitis occurs have not yet been established. Some experts consider staphylococci and adenoviruses to be the source of ulcers, while others attribute the disease to a viral disease. Some doctors equate aphthous stomatitis with herpetic stomatitis, with the only difference being that in the first case, instead of ulcers, aphthae appear - round white or yellow plaques with a red frame. Aphthae are concentrated on the cheeks, lips, and tongue.
The disease occurs against a background of decreased immunity and can transform into an ulcerative-necrotic form.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis in adults is as follows:
1. Local treatment, including treatment of aphthae and rinsing the oral cavity with disinfectants and antiphlogistic agents, such as hydrogen peroxide (diluted 1:1 with water), furatsilin tablet, boric acid, sea buckthorn oil.
2. Drug therapy aimed at detoxification and desensitization.
3. Vitamin therapy.
4. Use of sedatives and antihistamines.
5. Physiotherapy.
6. Diet, which consists of excluding spicy, allergenic and rough foods from the diet.
Aphthous stomatitis in adults often occurs against the background of exacerbation of pathologies of the nervous, endocrine systems and diseases of the gastrointestinal system. Therefore, its prevention will be the treatment of concomitant diseases.
Since aphthous stomatitis is often caused by staphylococcus, a pathogen that multiplies in dental plaque and teeth affected by caries, a thorough improvement of the oral cavity is necessary. With surgical dental treatment and removal of dental plaque, the problem of aphthous stomatitis in adults is minimized.
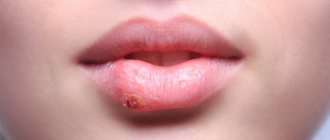
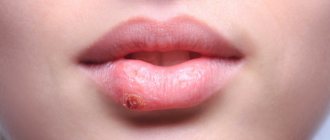
Herpetic stomatitis: symptoms
Herpetic or herpes stomatitis is the most common form of manifestation of the disease. Almost 90% of the adult population are carriers of the herpes virus, which in itself does not cause any discomfort. But with a decrease in immunity, exacerbation of chronic pathologies or trauma to the oral cavity, it can intensify and manifest itself in the form of herpetic stomatitis.
This type of stomatitis most often affects the cheeks, tongue, and palate. The clinical description of the oral cavity will be as follows: the mucous membrane becomes swollen and red. Against this background, small rashes appear.
The disease lasts about ten days, during which the adult usually does not experience any acute reaction to the appearance of ulcers. Body temperature remains normal, no symptoms of intoxication are observed, and the person feels relatively well. In case of reduced immunity or in a child, general intoxication, malaise and high fever are possible.
Discomfort is caused only by the process occurring in the mouth, consisting of:
• formation of bubbles;
• merging them into a group;
• bursting of ulcers and the formation of painful erosion (it hurts a person to drink, eat, talk).
The disease is also often accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes.
Sometimes herpetic stomatitis can develop into gingivitis, characterized by sharp redness of the gums around the teeth. Also, with gingivitis, rashes can affect the red border of the lips. Treatment for gingivitis is problematic, so it is better to prevent herpes from developing into gingivitis.
Treatment of stomatitis consists of taking medicinal anti-inflammatory, anesthetic and antiviral drugs. It should be remembered that herpes is not sensitive to conventional disinfecting infusions, so herbs and chlorhexidine are not a help here.
Local treatment and vitamin therapy also help. It should also be borne in mind that this form of the disease is contagious, therefore, during the period of illness, close contacts associated with kissing, drinking from the same cup, etc. should be limited. This especially applies to people whose disease has progressed to gingivitis.
Candidal stomatitis: treatment
This is already a fungal manifestation of a disease that is characteristic only of people with a very weakened immune system, suffering from chronic diseases or taking steroid hormones.
The causative agent of the disease is the Candida fungus, which is always present in the oral cavity. Its reproduction and manifestation in the form of a cheesy coating and white spots begins only in the presence of provoking factors.
The treatment regimen for stomatitis in adults consists of the following measures:
• taking antifungal medications;
• treatment of lesions with antifungal gels and ointments;
• if you have dentures, treat them with antiseptic solutions;
• rinsing the mouth;
• exclusion of easily digestible carbohydrates from food;
• visiting a gastroenterologist and endocrinologist, since the disease is often caused by pathologies characteristic of these medical areas.
Catarrhal stomatitis: causes of occurrence
This is the mildest and most common form of stomatitis. Often this is where other types of disease begin. With timely rinsing of the mouth, the disease will subside within a couple of days. Otherwise, it may develop into a more severe form. The patient only has to follow one simple rule: you need to rinse your mouth for at least a minute.
Externally, the disease looks like a light coating on the mucous membrane and is accompanied by slight swelling and redness. You may also experience bad breath, increased salivation, and a severe burning sensation in the mouth.
The main reason why catarrhal stomatitis occurs is oral candidiasis, which occurs against the background of a general inhibition of the body's defenses. The causes of the disease also include:
• inadequate oral care;
• diseases in the gastrointestinal tract of a chronic nature;
• damage to the body by worms;
• dental problems – untreated caries, periodontitis, dental plaque.
Regular visits to the dentist will help eliminate the problem of the development of catarrhal stomatitis and its transition to another form of the disease.
Allergic stomatitis
Allergic stomatitis in adults is not an autonomous disease: it can accompany any allergic reaction in a person. Particularly susceptible to illness are individuals who react with allergies to food or medications when there is direct contact of the allergen with the oral mucosa. People also often react to dentures with allergic stomatitis.
Allergic stomatitis comes in several types:
• viral;
• bacterial.
It depends on the causative agent of the infection. Often, due to allergies, aphthous stomatitis can occur, which is called aphthous allergic stomatitis.
Signs of stomatitis are manifested by the appearance of white spots or small blisters in the mouth. The mucous membrane turns slightly red and becomes covered with pinpoint hemorrhages. The person may experience pain, burning, severe itching, or dry mouth.
Treatment of stomatitis comes down to taking medicinal antihistamines and eliminating the main cause of the allergy.
Prosthetic stomatitis: causes
Prosthetic stomatitis in adults manifests itself in two types: allergic and bacterial. In both cases, the clinical picture is manifested by a sharp reddening of the mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed. And with the allergic type, redness also occurs in all areas of the mucous membrane that are in one way or another in contact with plastic.
The causes of prosthetic stomatitis depend on its type:
1. Allergic
This is a common allergic reaction to dentures. The main reason for this is the monomer included in the structure of acrylic plastic, which is used in the manufacture of prostheses. Also, the reason for the body’s reaction to dentures may not be the competence of the dental technician, who committed a violation in the selection of the proportion of components in the manufacture of plastic.
Replacing a low-quality prosthesis can solve the problem.
2. Bacterial
In this case, the “owner” of the prostheses himself becomes the culprit of the disease. It must be remembered that removable dentures require the same care as teeth. They must be constantly cleaned after eating. Otherwise, pathogenic elements may form on the surface of the product, which, in addition to the proliferation of bacteria, become a source of unpleasant odor.
Therapy for denture stomatitis consists of disinfecting rinsing of the oral cavity and treating the inner surface of the denture and the mucous membrane underneath it. It is enough to apply a small layer of antiseptic to relieve the painful condition.
Vincent's ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis
The main difference between ulcerative stomatitis is the presence of large, small-sized ulcers in the oral cavity coupled with the death (necrosis) of gum tissue. The disease is quite rare and may be a consequence of untreated catarrhal stomatitis.
Favor the development of Vincent's stomatitis:
• bacterial growth due to poor oral hygiene;
• weakened immunity;
• smoking;
• previous viral diseases.
The cause of the disease is often gastric ulcers and various poisonings.
The development of pathology occurs according to the following scheme:
1. Changes in the oral cavity
The patient notices dryness of the mucous membrane, bleeding gums, the appearance of ulcers on the hills between the teeth, which are later covered with plaque. Inflammation affects the inside of the cheeks, palate, and tongue, making eating and talking painful.
2. General health
The disease is accompanied by fever, weakness, and loss of appetite. The lymph nodes may become enlarged and tender to the touch.
To treat ulcerative stomatitis, the help of a specialist is necessary. Under anesthesia, he will remove dead tissue, bacterial plaque and tartar. Otherwise, you can get exposure of the roots of the teeth and massive necrosis of the gums.
Further therapy consists of the use of antibiotics and antihistamines, disinfectant rinsing and local treatment of the mucous membrane. If necessary, antipyretic and painkillers help. A course of vitamins also has a therapeutic effect.
Stomatitis acute and chronic
Stomatitis in adults differs not only in the form of manifestation. There are also differences in the nature of the disease. So, it can be acute and chronic. The first is characterized by the following description:
• swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane;
• formation of ulcers, erosions and plaque.
Stomatitis transforms into a chronic form if it becomes acute. And if a person’s immunity is weak, then the causative agent of the disease remains in the oral cavity constantly even after treatment. As a result, inflammation takes on a chronic form, characterized by a sluggish course with relapses.
The most common chronic form of the disease is characteristic of herpetic stomatitis. The herpes virus, even despite complete recovery, continues to constantly remain in the nerve endings of cells and is activated at the slightest weakening of the immune system.
Microbial carious stomatitis
There is another type of major stomatitis, which is an accompanying disease and manifests itself during the development of infectious diseases - microbial carious stomatitis. The origin of the disease in this case may be related to:
1. With any dental problems that are a source of infectious processes
Tartar, caries, dental plaque - all this is a place where carious bacteria - streptococci and staphylococci - are concentrated. At the slightest trauma to the mucous membrane, carious infection leads to the development of stomatitis.
2. With scarlet fever or sore throat
Scarlet fever is accompanied by a strong white coating on the tongue, which after a few days is replaced by a bare, bright red surface of the mucous membrane. In this case, they also talk about bacterial microbial stomatitis. A white coating on the tongue also accompanies a purulent sore throat. In the case of stomatitis, inflammation spreads not only to the mucous membrane and throat, but also to the gums, which look reddened, swell and hurt.
Therapy for microbial carious stomatitis consists of antiseptic rinsing and diet.
What it is
Most often, this disease affects young children who are breastfed. The fact is that constant consumption of milk creates the most comfortable conditions for the active development of the fungus, which is why another name that fungal stomatitis received among the people is thrush.
The mucous membrane in children is even thinner than in adults, the immune system is not formed to the proper level of resistance to pathogenic infections, anything can damage the mucous membrane and soft tissues, from a toy taken into the mouth to a teething tooth. In this regard, the likelihood of stomatitis in children is much higher than in their parents, even if both are infected with candidiasis.
The name for this type of stomatitis was given by the Candida fungus that provokes it. Of course, not only children encounter it. Adults, especially women, are also highly susceptible to its effects. However, in them it more often affects not the oral cavity, but the genitals. Newborn children receive the disease from an infected mother at birth. Older people are also often susceptible to fungal stomatitis.
Viral stomatitis
Herpetic stomatitis
Caused by the herpes virus of the first, less often the second type.
It accounts for 80% of all stomatitis and occurs mainly in children, less often in adults. The prevalence of herpes simplex virus ranges from 65% to 90%8. Infection occurs through airborne droplets and household contact. More common is recurrent herpetic stomatitis, which is manifested by itching, burning, slight soreness in the oral cavity, then vesicles (bubbles) appear, which burst and heal after 7-10 days.
During primary infection, acute herpetic stomatitis occurs; it is characterized by general symptoms such as fever, weakness, aches in the muscles and joints, the degree of these manifestations depends on the severity of the disease. As a rule, the acute form occurs in children.
Varicella zoster virus infection
The mildest form, in which the mucous membrane of the tonsils is affected. The palatine tonsils are not very enlarged, the mucous membrane of the throat is red, there is no plaque or pus.
Stomatitis with measles
Measles is an acute viral, highly contagious disease that is caused by the Polinisa virus and is transmitted by airborne droplets. The disease is extremely contagious. It is characterized by a rise in temperature, symptoms of ARVI, a rash on the face, neck, and then the whole body. In the oral cavity, Filatov-Koplik spots and stomatitis occur, which is characterized by hyperemia, swelling of the mucous membrane and white plaque. Nowadays, thanks to vaccination, this disease practically does not occur.
Bacterial stomatitis
Vincent's ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis
It manifests itself as ulcerations of the mucous membrane, strong odor from the mouth, fever, weakness, pain when eating. In severe forms, ulcerations can occupy almost the entire oral cavity, and the temperature rises above 38°C.
Gonorrheal stomatitis
Caused by Neisser's gonococcus. The mucous membranes of the lips, gums, lateral and lower surfaces of the tongue are mainly affected. The mucous membrane has a brightly hyperemic color and a large amount of gray purulent plaque with an unpleasant odor. But, as a rule, there are no complaints.
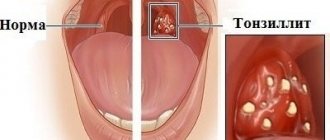
Acute streptococcal gingivostomatitis
It is characterized by general damage to the gums, severe pain, fever, enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes. The mucous membrane of the mouth and tonsils is hyperemic, abscesses may form.
Prevention of oral candidiasis
The occurrence of this disease is a very unpleasant and painful phenomenon, fortunately, it is quite easy to avoid by following the recommendations. One of the main causes of infection is weakened immunity, so the basic rule for preventing the disease is to treat any disease at the right time and take medications strictly as prescribed by the doctor. To avoid candidiasis of the oral cavity, pharynx and larynx, hygiene, visiting a good dentist, professional ultrasonic cleaning and other preventive measures will help. Oral candidiasis in women is often due to hormonal imbalance; if you have symptoms of the disease, you should pay attention not only to the affected area, but also to the condition of the body as a whole.