Small wounds, cuts and abrasions are all common and quite common. You often encounter such troubles in everyday life. Most often, children encounter such problems, but adults are by no means immune from minor injuries.
Small wounds, cuts and abrasions are all common and quite common. You often encounter such troubles in everyday life. Most often, children encounter such problems, but adults are by no means immune from minor injuries.
On the one hand, the majority are sure that they probably know what to do - iodine, alcohol, a plaster or a bandage are the main helpers in trouble. However, everything is somewhat more complicated, because if the wound is treated incorrectly, you can get complications that will lead to infection, prolonged healing or an unsightly scar.
Types of abrasions and wounds
We encounter cuts and all kinds of abrasions in everyday life. An abrasion is damage caused by mechanical friction against a rough and rough surface, often hard. This may be the result of a fall on asphalt or gravel.
The abrasion may be superficial, in which case only the epidermis is affected. The area turns red and swells a little. If the injury is deeper, then not only the epidermis is damaged, but also the capillaries, which leads to pinpoint bleeding, droplets of blood are released, but most importantly, the person experiences severe pain.
A cut is a shallow cut wound. With such an injury, either only the skin is damaged, or the layer of fatty tissue is affected. In such cases, bleeding occurs, the intensity of which will be determined by the depth of the cut and the number of damaged vessels.
Wounds can be superficial or deep, and large vessels can even be damaged. In this case, severe bleeding occurs. Wounds may be accompanied by bruises and bruises. In addition, dirt, various objects, earth, etc. often get into the wound.
Medicines for treating injuries and wounds
Injuries and wounds, unfortunately, do not happen as rarely as we would like. In summer, the most common injuries are burns, bruises and minor injuries such as scratches and abrasions. But it should be remembered that any wound or injury requires serious treatment . Under certain conditions, even minor damage can cause serious consequences.
Burns
We mainly encounter household burns of the 1st (redness of the skin) and 2nd (formation of blisters) degrees.
Most often these are thermal burns - i.e. received as a result of contact with fire, heated objects, liquids, steam. Burns can also occur from exposure to the sun. The first thing to do is cool the burn area with cold water or a hypothermic pack. This will reduce pain. If you need to take painkillers, a good choice would be drugs based on ibuprofen: Next, Ibuprofen Medisorb
in capsule form, or a drug based on naproxen Theraliv 275, which is safe for patients with cardiovascular problems.
MestaMidin-sense Home
is
suitable as an antiseptic - it effectively fights germs without causing pain or irritation;
Chlorhexidine
or
ramistin
may also be used .
2nd degree burns can cause scarring. To prevent the appearance of scars and restore the skin, you need to regularly apply healing products. Usually these are drugs based on dexpanthenol
, because
it increases collagen production. This can be a spray, aerosol or foam, for example Panthenol
,
Librederm Panthenol
AfaPlast
liquid patch . They do not cause pain or discomfort when applied.
Children's Pan tenol BC foam spray
.
If you are more comfortable using drugs in the form of ointments and creams, you can use Romalen cream, Panthenol 6%, Dexpanthenol Vertex
.
For buyers who trust products with herbal composition, it would be advisable to offer Cikaderma
, which promotes healing and relieves the inflammatory process.
The treatment of sunburn is not much different from the treatment of thermal burns, but it is quite possible to prevent their occurrence. In addition to sunscreen, offer the buyer a course of beta arotine
, which will help prepare for sunbathing by improving the condition of the skin and protecting against ultraviolet radiation due to increased antioxidant activity.
It is worth giving preference to such dietary supplements as the Complex of hyaluronic acid, vitamins and collagen
;
Solgar Beta Carotene
;
Nature's Bounty Beta Carotene. Bruises and contusions
Summer is a time for outdoor activities, which are very often accompanied by falls and bruises and, as a result, hematomas (bruises).
Initially, it is recommended to cool the site of the bruise; AfaFrost
is a freezing spray that instantly relieves pain and prevents the formation of a hematoma, as well as a hypothermic package.
Ketoprofen gel 5%
or
Diclogen 5%
is suitable as a local anesthetic , depending on purchasing power.
The release form (gel) allows the drugs to be easily distributed on the skin and quickly absorbed, which ensures a faster onset of the therapeutic effect. For removal, we recommend Arnigel gel
- thanks to its natural composition, it is suitable for the smallest (1+), and a large tube (120 g) will be indispensable in a family where fidgets live.
As a budget option, suggest Troxerutin DS
,
gel with badyagi “Simple recipe”
.
The combined use of external and internal agents will be more effective; for this we recommend using Arnica Montana granules (0+)
. Mountain arnica helps strengthen the walls of blood vessels and capillaries, due to the rupture of which the hematoma appeared.
Minor damage: abrasions, scratches, cuts
Since abrasions and scratches are considered accidental injuries, they are always contaminated with microbes to one degree or another.
Wounds contaminated with soil and caused by rusty nails are especially dangerous because of the possible development of tetanus. The first thing you should do is wash the wound with clean warm water and treat it antiseptic solution
, such as
MestaMidinsense Daily
in a convenient spray bottle - it does not sting and is suitable for pregnant women and children (0+).
Miramistin
or
Furacilin
tablets for preparing a solution
are also suitable hydrogen peroxide 3%; chlorhexidine bigluconate. After treatment, the damaged area is carefully dried by blotting with a sterile gauze pad. Then the wound must be treated with antibacterial agents to prevent the development of purulent-septic complications. It is best to use drugs in powder form, such as Baneocin, which can be used from birth. To speed up healing, use Cikaderma
, which has an antiseptic effect, and its herbal components relieve inflammation and reduce pain;
it is suitable for children from the first year of life. -
based products: Stellanin
,
Solcoseryl or
Emalan collagen hydrogel
.
If necessary, the wound can be sealed with a plaster or BF-6 glue
, which is suitable for shallow cuts.
Afa Plast (liquid patch)
has become a competitor to the regular patch : it creates a protective film and does not peel off like a traditional patch.
For mothers of active children, we recommend that you always carry disinfectants with you, such as Lekker hydrogen peroxide 3%
in the form of a spray - it does not take up much space in your bag and is easy to use.
Large wounds with bleeding bodies included
Such wounds require immediate medical intervention.
As first aid for heavy bleeding, you should raise the affected area above chest level and firmly press the edges of the wound with a sterile cloth until the bleeding stops. Next, you need to treat the edges of the wound with antiseptic agents, such as MestaMidin-sense Home
, hydrogen peroxide, and a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
The wound should be isolated from the environment using a gauze pad, and for fastening it is better to use a self- fixing Hartmann bandage
— unlike gauze bandages, it does not weaken and does not “crumple.” If blood leaks through the first bandage, you need to apply a second pressure bandage without removing the previous one. If you can see fat, muscle, or bone in the wound, or, for example, if the cut is very wide and has jagged edges, you will likely need stitches.
It is also important to remember that no objects should be removed from a wound containing foreign bodies (for example, glass fragments)! Wounds and injuries, whether we like it or not, will happen in our lives from time to time. Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely protect yourself and your family from receiving them. But you can and should be ready to provide first aid when it is especially needed.
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, YOU MUST READ THE INSTRUCTIONS OR CONSULT WITH A SPECIALIST. Dietary supplement NOT A MEDICINE.
Treatment of wounds and abrasions
First of all, it is necessary to disinfect the resulting wound. This must be done before treatment. Otherwise, an infection may enter the wound and tissue, causing inflammation.
For cuts, wounds and abrasions, proceed according to the following algorithm:
- Washing - the wound is washed under running water, preferably with laundry soap. You can dissolve soap in a bottle of water and wash the wound with the solution. This way, dirt and sand are washed away, and bleeding, if it is small, also stops.
DON'T : Do not use water from open bodies of water (river, lake, pond), as microorganisms live in them that can cause contamination and infection.
If you get a wound in nature and there is no clean water at hand, then you need to wash the wound with any water-based antiseptic - hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, miramistin, a solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin. All or any of these products should always be kept in your first aid kit.
- Removing foreign matter and objects. At this stage, foreign bodies are removed from the wound. This is done using tweezers, very carefully.
DO NOT: widen the wound, dig into it, etc. It is better to seek help from specialists.
- Stopping bleeding - if the bleeding does not stop after washing the wound, then it is necessary to press the wound with a napkin or cotton swab, which must first be moistened in hydrogen peroxide. In cases where the wound is deep, accompanied by severe bleeding, peroxide will not help. In such cases, you need to put a clean napkin on the wound and go to the emergency room.
- Treatment of the wound - any antiseptic can be used for treatment. It is desirable that it be water-based.
DO NOT : pour alcohol solutions on wounds and abrasions (iodine, brilliant green, vodka, etc.), as they can lead to burns rather than treatment. Such solutions can only lubricate the tissues surrounding the wound.
- Healing ointments - these compositions must be used to help wounds heal faster. These can be sprays, gels, ointments, jellies. For example, solcoseryl, panthenol, argosulfan, eplan, etc. After the wound is treated, wipe it with a dry, clean cloth and apply ointment.
DO NOT: use bactericidal powders on fresh wounds because they interfere with the process of tightening the edges.
- Applying a bandage - if the injury is small, then a bandage is not required. If small injuries are left open, they heal much faster. In addition, napkins and bandages stick to the scabs, and when the bandage is removed, the scabs come off along with the bandages, and this is not only accompanied by pain, but also interferes with the healing of the wound. For large wounds, bandages are indispensable. This is necessary for protection and application of healing agents, but bandages are applied after the crust has formed and dried. For deep wounds, a bandage is applied so that the edges of the wound are tightened as much as possible.
Swelling of the labia.
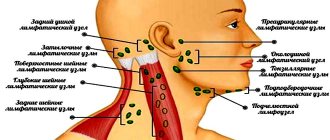
In women, swelling is often combined with itching and burning, discomfort, redness of the mucous membranes, the appearance of erosions, pathological watery discharge mixed with pus or blood, and inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes. Pain may occur when walking, playing sports, or having sexual intercourse.
Swelling often occurs as a result of abrasions or wearing synthetic underwear, due to insufficient hygiene, allergies and sexual intercourse. But there are also more serious problems.
Why do the labia swell? Causes of swelling of the genital organs.
Various factors can cause swelling of the labia:
Candidiasis (thrush).
A characteristic symptom of the disease is white curd-like discharge, a sour smell, possible itching and burning, swelling, pain during urination and sexual intercourse. Yeast infections most often occur when the immune system is weakened and during pregnancy.
Bacterial vaginosis.
The result of an imbalance in the vagina. Green or gray discharge often appears, a fishy odor is felt, and swelling is possible. But asymptomatic progression of the disease also occurs.
Genital infections. Quite often, the labia become swollen due to irritation from pathological vaginal discharge caused by sexually transmitted diseases (trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea). Other signs may appear: itching, irritation, unpleasant odor, painful urination.
Vulvodynia.
Accompanied by pain of varying intensity in the vulva area. It occurs suddenly, worries for a long time and often goes away just as abruptly. May sometimes cause swelling.
Vulvitis.
The main symptoms are swelling of the genitals, redness of the skin and burning. Inflammation of the vulva can occur due to poor hygiene and frequent changes of sexual partners, as a result of allergies, long-term use of medications and certain diseases.
Vulvovaginitis.
The main symptoms are skin flushing, abnormal discharge, pain when urinating, severe itching, causing the desire to scratch, which can lead to swelling. Often, inflammation of the labia develops due to poor hygiene and active masturbation, as a result of allergies or infections.
Bartholinitis.
Bartholin's glands are located in the vestibule of the vagina. When infected, they become inflamed, which is accompanied by redness and swelling of the genitals. If the gland duct is blocked, pus accumulates inside, which contributes to the formation of a cyst. In this case, discomfort and pain occur, which intensifies with movement.
Allergic reactions.
An allergy to fragrances contained in soap or intimate hygiene gel, components of washing powder, spermicides, latex condoms, tampons, low-quality pads, linen fabric, certain foods or medications can cause irritation. In addition to swelling, rashes are often found.
Contact and atopic dermatitis.
It develops with hypothermia, severe depilation of the bikini area, wearing tight synthetic underwear, and exposure to allergens. In the acute form, edema appears unexpectedly and grows rapidly, while in the chronic form it can periodically disappear and then reappear.
Sexual contact.
As a result of rough friction during sexual intercourse due to lack of lubrication (natural or artificial), damage to the labia and vagina is possible, which is accompanied by discomfort and swelling. In some cases, wounds and hematomas may form.
Stressful state.
Sometimes severe stress can cause itching of varying intensity and swelling in the genital area, which makes a woman distracted from the problems that have arisen.
Phthiriasis. (Pubic lice, lice)
You can become infected with lice not only through sexual intercourse, but also through everyday contact. The problem can be diagnosed quite easily by identifying bite marks or parasites. Lice cause severe itching, causing scratching, which causes swelling of the labia and pubis.
In addition to lice, swelling can be caused by mosquito bites, wasps, and bed bugs. In this case, bite marks are clearly visible, and the skin color may be red or bluish.
Hormonal disorders.
During the premenopausal period, the synthesis of estrogen decreases, which is why the woman feels dryness and burning, and possibly swelling of the genitals.
During pregnancy and the premenstrual period, blood flow to the tissues increases, which can lead to increased sensitivity of the mucous membrane. As a result, even the usual gel causes itching, burning and swelling.
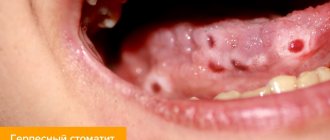
Genital herpes.
The virus may not manifest itself in any way until favorable conditions arise (hypothermia, colds, vitamin deficiency, weakened immunity). The main signs are watery blisters, erosions, itching, swelling, twitching.
Tumor.
Quite often, in the initial stages, malignant neoplasms do not cause any symptoms. Occasionally, mild itching and slight swelling may occur, to which women do not attach much importance.
Additional factors.
With dermatological diseases, various parts of the body itch. The genitals are no exception. The woman begins to itch, causing swelling.
Diabetes mellitus causes increased dryness of the labia, which causes cracks and swelling. The wounds are irritated by urine, increasing the itching.
In rare cases, edema can occur due to diseases of the internal organs (heart, kidneys, liver, intestinal dysbiosis).
Treatment methods.
If swelling does not decrease within 24 hours and other symptoms become noticeable, you should visit a gynecologist. He will conduct a diagnosis, determine the cause of the pathology and select an effective treatment method. If necessary, he can refer you for consultation to other specialists (endocrinologist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist, nephrologist, allergist, venereologist).
Most often, local antiseptic treatment is carried out, and antibacterial or antifungal medications are prescribed. For candidiasis, suppositories containing antifungal substances, immunostimulating drugs, and a special diet are used.
For allergies, antihistamines will be helpful. For vulvitis, analgesics are used, and sometimes antihistamines and antidepressants may be needed. Herpes is treated with antiherpetic and immunomodulatory medications.
Timely consultation with a doctor helps to quickly get rid of problems. Self-medication can aggravate the situation, leading to the development of serious diseases and infertility.
Reasons for visiting a doctor
You should consult a doctor if the wound or abrasion is accompanied by problems. In the following cases, you should definitely visit a specialist:
- The wound was caused by a rusty object - it could be a simple nail, but in such cases a tetanus vaccine may be required.
- If the edges of the wound diverge greatly and require suturing. If stitches are not applied, the result will be a strong and deep scar, and healing will be slow.
- If the wound is accompanied by severe bleeding that cannot be stopped within 20-30 minutes. In such cases, either blood clotting may be impaired or a large and important vessel may be damaged.
- If the area around the wound is very swollen, swelling and suppuration appear, all this is accompanied by twitching pain and fever. In such cases, surgical debridement and, probably, drug therapy are necessary, since the symptoms indicate infection of the wound.
IMPORTANT : even the smallest and most insignificant wound is a violation of the skin, which pathogenic microbes and bacteria can use as an entrance gate. Tetanus bacteria are especially dangerous. Be sure to treat everything, even minor abrasions and cuts.
Damage to teeth and soft tissues of the face
Example No. 25. Tooth dislocation
Option for recording local changes:
Complaints of bleeding from the socket of a knocked out tooth and pain in the upper lip, difficulty eating.
History of the disease. While playing hockey 3 hours ago, the patient was hit in the upper lip by a puck. The central incisor of the upper jaw was “knocked out”. Bleeding appeared from the socket of an extracted tooth. The patient took the fallen tooth and went to the doctor.
Previous illnesses: practically healthy.
Local changes. An external examination reveals swelling of the upper lip due to edema and hematoma. The skin of the lip is bluish in color. The submandibular lymph nodes are not enlarged. Mouth opening freely. On palpation of the upper lip, pain is detected; on the mucous membrane of the upper lip there is a lacerated and bruised wound 2.5 cm long with uneven and bluish edges. Well 11 is filled with a blood clot, the mucous membrane of the gums in the area 11.21 is hyperemic, with areas of hemorrhage, palpation of the alveolar process in this area is painful, the outer wall of the alveolus 11 is preserved. Stored by patient 11 is intact.
Dental formula: (specify).
Diagnosis: “Complete dislocation 11, laceration and bruise of the upper lip.”
Option for recording the operation of tooth replantation and primary surgical treatment of a wound of the upper lip:
Under infraorbital (infiltration) and incisive anesthesia (specify anesthetic), a blood clot was removed from hole 11 with a curettage spoon. Delivered to the patient, 11 was washed with an antibiotic solution, its apex was resected, the pulp was extirpated, the canal was medicated and retrogradely filled with amalgam (phosphate cement). by 1/5 of the length. The tooth is inserted into its own socket, removed from occlusion and fixed with a plastic splint to the adjacent teeth. The wound in the area of the upper lip is treated with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide (or another antiseptic - indicate which one) and tightly sutured with interrupted catgut sutures.
The patient is incapacitated from _______ to ________________________________, sick leave No. ________________ has been issued. Drug therapy prescribed
(specify which one). PSS introduced, series__________________________________________________________________________, No.__________________________________________________________________________,
2002 Turnout___________________________ (specify date) for dressing.
Journaling option after surgery
tooth replantation and postsurgical surgical treatment of upper lip wounds:
The condition is satisfactory. Body temperature 37.2°C. I slept intermittently throughout the night and was bothered by pain in the upper lip area. On examination: the wound is well fixed with sutures. The mouth opens freely. In the oral cavity: the tooth is well fixed with a splint. The suture area is treated with 1% tincture of iodine.
Continue previously prescribed medication. Appearance (specify date) for dressing.
Example No. 26. Bilateral dislocation of the lower jaw
Option for recording local changes:
Complaints of the inability to close the mouth and pain in the parotid areas.
History of the disease. In the morning, while eating and trying to bite off a large piece of an apple, the patient felt pain in the parotid areas and the inability to close his mouth. I went to the dentist, who diagnosed a dislocation of the lower jaw and tried to realign it, which ended in failure. Subsequently, the patient was sent by the ambulance team to the maxillofacial department.
Past diseases: polyarthritis.
Local changes . An external examination reveals a change in the configuration of the face due to the lengthening of its lower third and the displacement of the chin anteriorly. There is drooling due to the inability to close the mouth. Upon palpation, the tension of the masticatory muscles itself is determined, in the form of rollers. The tissues in front of the tragus of the ear on the right and left are sunken. Under the zygomatic arch, the displaced heads of the condylar processes are palpated on both sides. It is not possible to palpate them through the external auditory canal. When a forceful attempt is made to close the mouth, the lower jaw exhibits springy resistance, which is accompanied by pain. In the oral cavity, upon palpation of the anterior edge of the lower jaw, the coronoid processes have shifted anteriorly. The bite is open, there is contact on the molars.
On radiographs of the lower jaw in lateral projections, the heads of the lower jaw are determined, located anterior to the articular tubercle.
Dental formula: (specify).
Diagnosis: “Bilateral anterior dislocation of the lower jaw.”
Option for recording the operation of lower jaw reduction:
Under bilateral anesthesia according to Berche (specify the anesthetic), it was not possible to reduce the lower jaw. Under general mask anesthesia, the lower jaw was adjusted downwards, backwards and upwards. The heads of the lower jaw moved into place into the articular sockets, and the bite was restored. The patient is advised not to open his mouth, take semi-liquid food, and wear a Pomerantzova-Urbanskaya sling bandage for a week.
The patient is incapacitated from _______ to ________________________________, sick leave No. ________________ has been issued. Drug therapy prescribed
(specify which one). Appearance__________________________________________ „(specify date) for control inspection.
Example No. 27. Fracture of the zygomatic bone
Option for recording local changes:
Complaints of limited mouth opening, numbness of the skin in the left infraorbital region and upper lip, double vision, retraction of tissue in the area of the zygomatic bone and arch.
History of the disease . A day ago I hit a trolley bus stand with the left side of my face. I did not lose consciousness, there was no nausea or vomiting. He noted short-term nosebleeds.
Past diseases: pneumonia, chronic cholecystitis. Examined by a neurologist: there is no evidence of a concussion.
Local changes . An external examination reveals hemorrhage in the infraorbital region, lower eyelid and conjunctiva of the left eye, and retraction of the tissues of the zygomatic region on the left. Upon palpation, a bone step is identified in the region of the lower orbital margin on the left and the upper-outer part of the orbit, as well as the temporal process of the zygomatic bone on the left. Mouth opening is somewhat limited. In the oral cavity, hemorrhage is noted in the mucous membrane of the upper fornix of the vestibule, respectively 25,26,27. A bony step is palpated in the area of the zygomaticalveolar ridge on the left. A semi-axial radiograph reveals a decrease in the transparency of the maxillary sinus on the left, a violation of the continuity of the lower and outer edges of the orbit, the temporal process of the zygomatic bone and the zygomatic alveolar crest on the left.
Dental formula: (specify).
Diagnosis: “Fracture of the zygomatic bone on the left with displacement.”
Option for recording the zygomatic reposition operation
Bones on the left
Under general anesthesia in the analgesic stage, the place of insertion of the hook into the tissue is determined (at the point of intersection of a horizontal line drawn along the lower edge of the zygomatic bone and a vertical line drawn along the outer edge of the orbit). At this point, the skin is cut for 1 cm. The end of the hook is inserted into the wound, which is immersed deeper than the displaced fragment of the zygomatic bone and brought under it. The fragment is pulled upward with a hook - outward and anteriorly. The zygomatic bone was fixed in the correct position, the hook was removed, and an interrupted polyamide thread suture was applied to the wound. An aseptic dressing is applied.
The patient is incapacitated from _______________ to ______________________, sick leave No. ________________________ has been issued. Prescribed: vasoconstrictors
drops in the left half of the nose and drug therapy (specify which). Appearance________________________________________________ (specify date) for dressing.
Journaling option after surgery
repositioning of the zygomatic bone:
The condition is satisfactory. Body temperature 36.7°C. I slept peacefully that night. The mouth opens freely. The cheek bone is positioned correctly. Continue previously prescribed medication. Turnout
(specify number) for dressing.
Example No. 28. Cyst of the nasopalatine (incisive) canal
Options for recording local changes:
Complaints of swelling in the area of the hard palate corresponding to the front teeth, periodic occurrence of pain in this area.
History of the disease . I first noticed these phenomena 6 months ago. After rinsing the mouth with a soda solution, the swelling decreased and the pain did not bother me. Four days ago I noticed the reappearance of the above symptoms.
Previous illnesses: practically healthy.
Local changes . No changes are detected during external examination. An enlarged lymph node is palpated in the submental area. The mouth opens freely. In the oral cavity: crowns 11 and 21 are converged, the teeth are intact, their percussion is painless. In the anterior part of the hard palate, a bulging of soft tissues measuring 2 cm in diameter is determined; upon palpation, it has a dense consistency and is somewhat pliable. During puncture, the needle penetrated into the cavity, and 1.5 ml of dark-straw-colored liquid containing cholesterol crystals was aspirated with a syringe.
An x-ray of the hard palate reveals a rarefaction of bone tissue with clear contours in the area of roots 11 and 21. The periodontal gap of these teeth is clearly visible. EDI 11-3 microamps, 21-2 microamps.
Dental formula: (specify).
Diagnosis: Cyst of the nasopalatine (incisive) canal.
Option to record a cystectomy operation for
nasopalatine canal cysts:
Under extraoral incisal and infiltration anesthesia (specify anesthetic), an incision was made in the mucous membrane of the hard palate in the area 13-23 parallel to the gingival margin and spaced 1 cm. Additionally, incisions were made in the projection of the roots of the canines 2 cm long.
The mucoperiosteal flap was separated. An area of thinned bone tissue in the anterior part of the hard palate is exposed. A bone window has been formed and expanded. It was discovered that the cyst shell is located in the area of the incisive canal; it was completely enucleated and removed. The bone wound was washed with chlorhexidine solution, the flap was put in place, and the wound was sutured with interrupted catgut sutures.
The patient is incapacitated from_____________________ to_________________, a sick leave certificate has been issued No. Drug therapy has been prescribed (specify which). Appearance__________________________________________________________ (specify date) for dressing.
Example No. 29. Perforation of the maxillary floor
Sinuses
Option for recording local changes:
Complaints of liquid food getting into the nose from the mouth while eating, lack of tightness of the oral cavity (cannot be inhaled while smoking).
History of the disease . Two days ago, previously treated 26 was removed due to exacerbation of chronic periodontitis using bayonet forceps, but without using an elevator and drill. The bleeding from the hole stopped after 15-20 minutes. A day later, while brushing my teeth, I noticed water getting into my nose from my mouth. These phenomena were repeated during breakfast: tea came out of the nose. I turned to the dental surgeon again.
Past diseases: pneumonia, chronic cholecystitis.
Local changes . No changes were found during external examination. Nasal breathing is not difficult, there is no purulent mucous discharge from the nose. The mouth opens freely, the submandibular lymph nodes are slightly enlarged on the left, painless on palpation. The removed socket 26 is partially filled with a blood clot. The alveolus of the anterior buccal root is gaping. When performing a nasal-oral test, air from the maxillary sinus whistles into the mouth. An attempt to puff out the cheeks fails.
On the radiograph of the paranasal sinuses, the transparency of the paranasal sinuses is not changed.
Dental formula: (specify).
Diagnosis: Perforation of the maxillary sinus on the left in the area of the removed socket 26.
Option to record the operation of plastic closure of the perforation hole in the bottom of the maxillary sinus:
Under tuberal (or infiltration) and palatal anesthesia (specify anesthetic), a strip of tissue was excised to the bone, about 2 mm wide, around the perimeter of the removed socket 26. Next, a trapezoidal incision was made from socket 26 towards the transitional fold and slightly above the border of the mobile and immobile mucosa shells. The mucoperiosteal flap, with its base facing the upper fornix of the vestibule of the mouth, is peeled off using a raspatory. At the border of the upper and middle third of the flap, the periosteum is cut horizontally across the entire width of the flap. The elongated flap is transferred to the palatal side, as a result of which the hole of the removed 26 is covered with this flap, which is fixed to the mucous membrane of the hard palate with interrupted catgut sutures. Several (specify how many) interrupted sutures with catgut were applied to the wound on the vestibular surface of the alveolar process. A pressure bandage is applied to the left cheek.
The patient is incapacitated from _______ to ________________________________, sick leave No. ________________ has been issued. Drug therapy prescribed
(specify which one). Appearance ___________________________________ (specify date) for dressing.
An option for recording a diary after plastic closure of the perforation hole in the bottom of the maxillary sinus:
The condition is satisfactory. In the buccal area there is swelling of the soft tissues. Body temperature 37.3°C. The mouth opens with slight restriction. In the oral cavity: the flap covering the perforation hole is slightly hyperemic, imbibed with blood, well fixed with catgut sutures. The area of the seams is shaded with 1% tincture of iodine. A bandage with Vaseline is applied to the skin of the cheek. Continue previously prescribed medication. Turnout to indicate the number for dressing.
Example No. 30. Lipoma of the buccal area
Option for recording local changes:
Complaints of swelling in the left cheek area, an aesthetic defect.
History of the disease . I first noticed a swelling in the thickness of my cheek 3 years ago. I didn't see a doctor. Over time, the swelling has increased in size approximately 3 times. I repeatedly applied compresses to the cheek area, which did not lead to improvement. No pain noted. I went to the doctor.
Previous illnesses: practically healthy.
Local changes . Upon external examination, swelling is visible in the lower buccal region on the left. The skin over the swelling is not changed in color and folds well. Upon palpation, a formation in the thickness of the cheek is determined to be about 5 cm in size, soft-elastic consistency with a smooth surface, painless, well displaced in relation to the surrounding tissues. According to bimanual palpation, the formation is located lateral to the buccal muscle. The submandibular lymph nodes on the right and left are not enlarged, the mouth opens freely. In the oral cavity: the mucous membrane is pale pink in color and is normally moisturized.
A diagnostic puncture of the mass was performed; the results of the cytological diagnosis were in favor of a lipoma.
Dental formula: (specify).
Diagnosis: Lipoma of the buccal area on the left.
Recording option for buccal lipoma removal surgery
areas:
Under buccal and infiltration anesthesia (specify anesthetic), a 7 cm long incision was made in the mucous membrane of the cheek on the left in the projection of the neoplasm parallel to the line of closure of the teeth. The tissues are dissected layer by layer down to the membrane of the neoplasm. The tumor is isolated from surrounding tissues using a hemostatic clamp, then removed and sent for pathomorphological examination. The wound is sutured in layers with interrupted catgut sutures, and a rubber graduate is inserted into it.
The patient is incapacitated from ___________________________________ to ____, sick leave No.________________ has been issued. Drug therapy prescribed
(specify which one). Appearance ___________________________________ (specify date) for dressing.
Journaling option after surgery
removal of buccal lipoma:
The condition is satisfactory. Notes soreness in the cheek area and slight pain when opening the mouth. Body temperature 36.9 degrees. S. Slept peacefully that night. Opening the mouth is somewhat difficult. In the oral cavity: after removing the drainage from the wound, some blood was obtained. The sutures secure the edges of the wound well. The area of the seams is shaded with 1% tincture of iodine.
Continue previously prescribed medication. Appearance (specify date) for dressing.
Part II. Hospital
Example No. 31. Submandibular phlegmon
Regions
Option for recording local changes:
Complaints of pain and swelling in the left submandibular region, moderate pain when swallowing, elevated body temperature up to 37.9°C, general poor health, sleep and appetite disturbances.
History of the disease. She fell ill 4 days ago, when spontaneous pain and pain when biting appeared in area 36. In the evening, she noticed a slight swelling in the submandibular region on the left. I didn’t go to the doctor, I took analgin tablets and made alcohol compresses on the submandibular area. There was no improvement; the swelling in the soft tissues increased in size. On the fourth day from the onset of the disease, the pain in the perimaxillary tissues intensified significantly, the skin over the swelling turned red, moderate pain when swallowing appeared, the patient went to the dentist at the district clinic, after whose examination she was hospitalized in the maxillofacial department.
Previous illnesses: practically healthy. Notes an allergic reaction to novocaine.
Local changes. An external examination reveals a violation of the facial configuration due to swelling in the submandibular, lower buccal and parotid-masticatory areas on the left. The skin above the swelling within the boundaries of the submandibular region is hyperemic, does not form a fold, and is shiny. Upon palpation in the submandibular region, a dense painful infiltrate is determined, in the depth of which fluctuation is felt. The submandibular lymph nodes on the left cannot be palpated due to the dense infiltrate. The mouth opens 3 cm. The mucous membrane of the vestibule of the oral cavity is pale pink, somewhat swollen in the area 36, well moisturized. The mucous membrane of the maxillo-lingual groove on the left is hyperemic, edematous, and palpation reveals a moderately painful infiltrate in the underlying tissues. Crown 36 is significantly destroyed, there is a lingual wall, percussion of the tooth is painful.
Dental formula: (specify).
Diagnosis: “Phlegmon of the submandibular region on the left.”
Option for recording the operation of opening phlegmon
submandibular region:
Under infiltration (or general anesthesia) anesthesia (specify the anesthetic), a 6 cm long incision was made parallel to the base of the lower jaw and 2 cm down from it. The skin, subcutaneous fat, superficial fascia of the neck, and subcutaneous muscle (platysma) are dissected in layers. The outer layer of the own fascia is cut, the mandibular salivary gland in its own capsule is exposed, and a lot of pus is obtained. Having freed the lower pole of the gland from adjacent tissues, tissue revision was carried out in the area of the lower part of the submandibular triangle and behind the gland. Focusing on the anterior edge of the masticatory muscle itself and the base of the lower jaw, the facial vein and facial artery are isolated, ligated and crossed, after which the fascial sheath of the submandibular salivary gland is cut off from the base of the lower jaw. The gland was moved downwards and the tissues in the upper part of the submandibular triangle were inspected. The wound is washed with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide (or another antiseptic - indicate which one) and drained with rubber drainers. A bandage with a hypertonic solution (levomikol ointment or other medications - please indicate which) is applied.
Prescribed ________________________________________ (specify medication
therapy).
An option for recording a diary after the operation of opening phlegmon of the submandibular region:
The condition is satisfactory. Complains about (specify complaints). After removing the bandage and drainage, a small amount of pus was obtained from the wound.
The wound is washed with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide (or other antiseptic - specify) and drained with rubber drainers. An aseptic dressing is applied. Continue previously prescribed medication.
Example No. 32. Adenophlegmon of the submandibular
Regions
Option for recording local changes:
Complaints of pain and swelling in the submandibular region on the right, poor health, slight increase in body temperature to 37.4°C, sleep disturbance.
History of the disease . I fell ill 8 days ago when I discovered a “ball” in the right submandibular region after suffering from a sore throat. This “ball,” at first mobile and painless, gradually became less mobile, and slight pain appeared when touching it. In recent days, a dense, slightly painful infiltrate has formed under the lower jaw, and the contours of the “ball” have ceased to be defined. I did not go to the doctor, I was treated with warm compresses and took antibiotics orally (1 tablet x 3 times a day). Since there was no improvement, the patient was forced to see a dentist, who referred him to the maxillofacial department.
Past illnesses: stage 2 hypertension, frequent colds.
Local changes. An external examination reveals a violation of the facial configuration due to swelling in the right submandibular and parotid regions. The skin above the swelling within the submandibular region is tense and does not form a fold. Upon palpation in the right submandibular region, a dense and painful infiltrate is determined, in the center of which it is difficult to identify signs of fluctuation. The mouth opens freely. In the oral cavity: the mucous membrane is not changed in color, well moisturized. All teeth are intact, tonsils are enlarged, and there are signs of chronic tonsillitis.
Dental formula: (specify).
Diagnosis: “Adenophlegmon of the right submandibular region.”
Option for recording the operation of opening adenophlegmon of the submandibular region:
Under infiltration (or general anesthesia) anesthesia (specify the anesthetic), a 6 cm long incision was made in the right submandibular region, 2 cm away from the base of the lower jaw and parallel to it. The skin, subcutaneous fat, superficial fascia of the neck, platysma, and the outer layer of the proper fascia of the neck were dissected. A creamy, odorless pus was obtained. When examining the wound with a finger, a cavity was discovered from which pus and tissue of a melted lymph node were released. The wound is washed with antiseptics and drained with a rubber tube. An aseptic bandage with a hypertonic solution (or other medicinal substances - indicate which) is applied to the wound. Prescribed (specify drug therapy).
An option for recording a diary after the operation of opening phlegmon of the submandibular region:
The condition is satisfactory. Complains about
(indicate complaints). After removing the bandage and drainage, a small amount of pus was obtained from the wound.
The wound is washed with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide (or other antiseptic - specify) and drained with rubber drainers. An aseptic dressing is applied. Continue previously prescribed medication.
Example No. 33. Cellulitis of the chewing area
Muscles
Option for recording local changes:
Complaints of swelling in the left parotid-masticatory area and pain that intensifies when trying to open the mouth or clench teeth, difficulty opening the mouth, high body temperature up to 38.5°C, general poor health, lack of sleep and appetite.
History of the disease. Five days ago, 38 fell ill, having previously repeatedly bothered the patient. Rinse your mouth with a warm solution of potassium permanganate. The pain did not disappear, soft tissue swelling and limited mouth opening appeared. On the 3rd day from the onset of the disease, he consulted a dentist, who removed 38. However, the patient’s condition did not improve, the swelling in the parotid region on the left increased, the pain in the jaw intensified, and mouth opening worsened. The patient was hospitalized by ambulance to the maxillofacial department.
Past diseases: childhood infections, pneumonia.
Local changes. An external examination reveals a violation of the facial configuration due to swelling of soft tissues in the parotid-masticatory, submandibular, buccal areas, the lower part of the temporal region on the left, in the lower eyelid area. A sharply painful inflammatory infiltrate is palpated within the boundaries of the masticatory muscle itself. Above other anatomical areas in the area of swelling there are signs of tissue edema. The skin over the infiltrate is slightly hyperemic and difficult to fold. The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged on the left, mobile, slightly painful. Mouth opening is limited to 0.5 cm between the incisors. When trying to open the mouth, there is an increase in pain in the area of the masticatory muscle on the left. In the oral cavity: 38 has been removed, its socket is partially filled with a disintegrated blood clot. In the area of the remote hole 38
on the vestibular side the mucous membrane is torn, hyperemic and edematous. Palpation of the anterior edge of the masseter muscle itself is painless.
Dental formula: (specify).
Diagnosis: “Phlegmon of the masticatory muscle area.”
Option to record an autopsy operation regarding
phlegmon of the masseter muscle area:
Under general anesthesia, an 8 cm long incision was made, bordering the angle of the lower jaw on the left and moving 2 cm down from it. The skin, subcutaneous fat, superficial fascia of the neck, platysma are dissected, the lower pole of the masseter muscle itself is exposed. The masticatory muscle was dissected along the lower edge of the base of the lower jaw and peeled off with a raspatory along its entire length from the branch of the lower jaw. Pus was obtained. The wound is washed with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide (or another antiseptic - indicate which one) and drained with rubber tubes. An aseptic dressing with hypertonic solution (or other medications (specify which) is applied to the wound). Drug therapy is prescribed (specify which).
Journaling option after surgery
opening of phlegmon in the area of the masticatory muscle:
The condition is satisfactory. Complains about_______________________________________________________________________________ (specify complaints). After removing the bandage and drainage, a small amount of pus was obtained from the wound.
The wound is washed with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide (or other antiseptic - specify) and drained with rubber drainers. An aseptic dressing is applied. Continue previously prescribed medication.
Example No. 34. Phlegmon of the pterygoid