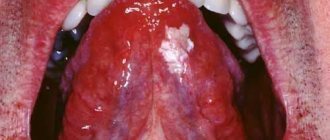
What is it and why do we need it?
Such anatomical formations are the thinnest folds of the mucous membrane that connect the mobile lips and tongue with the fixed parts of the oral cavity: the gums and the sublingual space.
In total, there are three frenulums in the baby’s mouth:
- Tongue - located under the tongue.
- Upper lip - localized between the upper lip and the gum mucosa above the level of the central incisors.
- Lower lip - connects the inner surface of the lower lip with the gums at the level of the middle of the alveolar process on the lower jaw.
Despite their small size, such mucous folds are of great importance in human life. In a newborn, they are responsible for proper attachment to the mother's nipple. In older children, the frenulum is involved in the correct pronunciation of sounds and in the formation of a normal bite.
Contraindications
Tongue frenuloplasty in newborns does not involve major surgical intervention, so the operation is considered safe. In addition, the procedure is painless and does not require anesthesia. However, given that after cutting a short fold of mucosa, a small wound still forms, there are temporary restrictions on manipulation related to the child’s health condition.
Temporary contraindications:
- inflammatory diseases;
- infectious diseases;
- immunodeficiency pathologies;
- acute respiratory viral or bacterial infections.
If there are contraindications for health reasons, it is advisable to postpone the operation until complete recovery.
Short frenulum and why it is dangerous
Shortening of the frenulum is understood as a decrease in its absolute length or its incorrect location, which makes it relatively short (i.e., the length remains normal, but its incorrect localization causes all the symptoms characteristic of shortening).
A short frenulum of the upper or lower lip in a baby can negatively affect the process of breastfeeding. In this case, the child cannot correctly position the nipple in the oral cavity and create a sufficient vacuum necessary for sucking and swallowing. Therefore, in order to get enough, the baby has to make significant efforts. The baby quickly gets tired and stops breastfeeding without being properly satisfied. Such children behave restlessly, require frequent breastfeeding, but do not gain weight well.
In children over 3 years old, a shortened upper frenulum can cause an increase in the interdental spaces between the upper incisors and their advancement sharply anteriorly. A short lower labial frenulum sometimes causes malocclusion.
Also, a decrease in size or incorrect location of any of them can have an extremely negative impact on speech function. Children 2 years of age who have not had this pathology diagnosed or corrected in time often do not pronounce individual sounds. Such speech defects are difficult to correct.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
Indications:
- Restoring sucking function in infants.
- Speech defects.
- Delayed development of the lower jaw.
- Not chewing food thoroughly.
- Malocclusion.
- Too dense arrangement of teeth or presence of gaps between them.
- Difficulties during orthodontic treatment.
- Preparation for implantation.
Contraindications:
- Poor blood clotting.
- Presence of cancerous tumors.
- Infectious diseases.
- Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
- The presence of carious lesions and inflammation of the dental nerve.
If there are problems with breastfeeding, surgery is often performed in the maternity hospital. In older children, the procedure is performed if there are discomfort or problems with diction.
How to check a child's frenulum?
A shortened frenulum between the lip and gum is diagnosed quite simply even in infants. To do this, you need to carefully pull back the child’s lips and see how pronounced the fold of the mucous membrane is and where it is attached. If it is short, then it will have a thick appearance and its attachment point will be at the very base of the incisors.
The hyoid frenulum normally has a length of at least 8 mm and is attached approximately halfway between the root and tip of the tongue. A small frenulum usually looks like a fold on the mucous membrane, attached along its entire length to the tongue or sublingual space.
Consequences of a short frenulum of the upper lip
Defects in the structure of the frenulum of the upper lip entail a number of negative consequences:
- During the neonatal period or in infancy, the child may have problems with sucking. In such cases, plastic surgery is performed as early as possible to restore breastfeeding.
- A shortened frenulum makes it difficult to pronounce certain words and impairs diction. Many speech therapists recommend frenuloplasty to correct the pronunciation of sounds in children.
- Impaired chewing due to a short frenulum can lead to problems with the digestive system.
- A short frenulum stretches the mucous membrane of the gums, which over time leads to the appearance of an interdental gap - a diastema, which is a cosmetic defect and can lead to malocclusion.
- Due to the retraction of the gums, a gum pocket appears in which plaque and tartar accumulate, which contributes to the development of caries and other inflammatory processes.
- A wide frenulum is a cosmetic defect and also contributes to excessive accumulation of plaque.
- Improper fastening of the bridle in some cases leads to increased sensitivity of the teeth.
Frenum trimming surgery is also an important part of preventing periodontal disease.
How to stretch
It is necessary to immediately make a reservation that, due to anatomical features, only the frenulum under the tongue can be stretched without surgery. This technique is usually taught by a speech therapist and is effective only if all recommendations are carefully followed over the course of several months.
Before performing any exercises, it is recommended to do a special massage to stretch the soft tissues. To do this, you need to carefully take your tongue by the very tip and with gentle movements move it upward, then to the sides and pull it forward a little. Gentle stroking from bottom to top along the frenulum using the thumb and index finger has a good effect.
The exercises themselves are performed sequentially twice a day:
- Relax your tongue as much as possible and place it on your lower lip. Hold for 10 seconds in 3 sets.
- Stick your tongue out of your mouth as far as possible. Fix in this position for 10 seconds. Repeat 3 times.
- Extend your tongue and circle your lips with it.
- Click your tongue for 10 seconds, imitating the clatter of horse hooves.
- Open your mouth wide. Slowly run the tip of your tongue across the roof of your mouth, moving from your teeth to your throat.
- Place your tongue on the roof of your mouth just behind your teeth. Holding it in this position, open your mouth as wide as possible.
Such fairly simple exercises help both stretch the frenulum on the tongue and correct some speech defects.
Symptoms of incorrect placement of the frenulum of the tongue
With significant pathology of the frenulum, the following symptoms may be observed:
- It is impossible to stick the tongue out of the mouth due to the short length of the frenulum.
- When trying to stretch the tongue, it bends and takes an arched shape.
- When you try to reach the palate with your tongue, the tip of the organ expands, as there is a strong tension.
- When at rest, the tongue has the shape of a groove.
If you have such symptoms and discomfort, you should consult a specialist. Perhaps the doctor will conduct a more thorough diagnosis and make a diagnosis.
Surgical correction
If a short frenulum is detected in the maternity hospital, then its trimming is carried out immediately. This is done so that the baby can properly take the nipple and eat properly. If shortening is diagnosed at an older age and is not corrected by speech therapy techniques, then three options for surgical treatment are possible:
- Frenotomy is cutting to increase its length.
- Frenectomy is a circumcision when it is almost completely excised.
- Frenuloplasty is a plastic surgery during which the place of its attachment in the mouth is changed.
Despite the fact that frenulum surgery itself is quite common, most parents have a lot of questions about this procedure. We will consider the main ones below.
Why trim?
A too small size of such a fold of the mucous membrane can cause difficulty sucking at the breast in infants, and problems with the pronunciation of certain sounds and with the arrangement of teeth in the permanent dentition in older children. To avoid such problems, pruning is required.
Do I need to prune?
Most doctors, including the famous Dr. Komarovsky, are of the opinion that a short frenulum should be trimmed if it adversely affects the child’s ability to suck milk or pronounce certain sounds.
When a short frenulum does not negatively affect the processes of sound production and bite formation, then in such cases surgical intervention is not required.
What kind of doctor cuts?
Typically, frenulum correction operations are the responsibility of a dentist.
At what age is it best to have surgery?
When the frenulum should be trimmed is decided individually for each child. If we are talking about a fold on the upper lip, then correction is done no earlier than 6 years. Typically, the operation is performed only after the eruption of the permanent upper incisors. If correction is required on the lower lip, this is done more often after the 4th year of life.
In most cases, the hyoid frenulum is cut before 1 year of age (most often this is done in the maternity hospital). But correction is possible at any age.
How do they prune?
The frenulum trimming operation is performed on an outpatient basis in the surgical office of a dental clinic. The doctor carefully stretches the fold of the mucous membrane and makes a small incision with a sharp scalpel. After that, small sutures made of threads are applied to the edges, which after some time dissolve on their own and do not need to be removed.
A more modern technique is laser dissection, which eliminates the need for stitches, which speeds up the child’s recovery process.
Does it hurt to prune?
The dissection procedure is performed under local anesthesia, which eliminates the possibility of any pain.
«
Features of the procedure
Plastic surgery of the frenulum of the tongue involves cutting it with a scalpel or surgical scissors. After cutting the fold of the mucous membrane in a newborn, the tissue immediately stretches and lengthens after healing. When the operation is performed at the age of 3–5 years, the process of stretching the frenulum is more complex. To increase the length of the fold and prevent the formation of scars, the child will need to perform special exercises.
In Martinka dentistry, plastic surgery of the frenulum of the tongue and lip is performed not only by the classical, but also by the modern method using a laser. The use of laser equipment eliminates the risk of infection and bleeding. The laser has an antiseptic effect and instantly seals the vessels; moreover, during the operation there is no contact of the instrument with the tissues of the oral cavity. Laser surgery involves contraindications and is only allowed for children over 1 year of age.
For newborn children, tongue frenuloplasty can be performed without anesthesia. In children from 3 months of age, the folds of the mucous membrane thicken, which suggests discomfort and minor pain during the operation, so cutting the frenulum is done with local anesthesia. Sedation is used only in extreme cases, if the child has complex illnesses or increased anxiety.
What to do if a child breaks the frenulum
Children at any age are quite active and mobile. Therefore, injuries are inevitable. Quite often, parents turn to the dentist with the following problem: the baby fell unsuccessfully and tore the frenulum above the upper lip or under the tongue. At the same time, damage to the lower lip is extremely rare due to the fact that normally it is almost not expressed.
If a child cuts the frenulum, then the following signs will be characteristic of such an injury:
- Swelling of the soft tissues in the mouth and above the lip (if the child has torn the upper lip).
- Quite profuse bleeding.
- Pain in the mouth when talking or eating.
In any case, if the baby has torn the mucous fold under the upper lip or under the tongue, you should immediately consult a doctor. It is he who will decide whether such a gap needs to be sutured and will carry out the necessary procedures. Self-treatment can lead to negative consequences: the tissues will not heal properly with the formation of rough scars, which will subsequently lead to an incorrect bite and unclear pronunciation of sounds.
After operation
As a rule, there are no complications after trimming the frenulum of the upper, lower lip or tongue, and recovery takes only a few days. When the operation is performed, it is best to feed the baby immediately, since mother's milk acts as a pain reliever. Adult patients should temporarily avoid hard and sticky foods. If there are problems with speech, then special sessions with a speech therapist are necessary. The slight discomfort caused by the sutures will go away on its own after they are absorbed, that is, after 4-5 days, maximum in a couple of weeks.