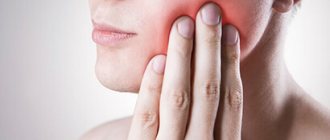
Wisdom or 8 teeth can cause a lot of problems, especially if they grow into the cheek. These teeth have no analogues in the primary occlusion, so they erupt through unprepared periodontal tissue, and their growth is accompanied by discomfort even with proper eruption. The growth of eighth teeth can begin at age 17, but there are cases when these teeth remain impacted (not erupted) throughout life.
Symptoms and signs of abnormal growth
It is extremely rare for eights to appear without any complications. This is due, first of all, to the fact that wisdom teeth grow in adulthood, when the jaw is already formed. Even with proper teething, discomfort may still be present for several weeks or months. If a wisdom tooth grows incorrectly or has an abnormal location, then certain symptoms indicate this.
Let's take a closer look at the types of pathologies and symptoms associated with the growth of wisdom teeth.
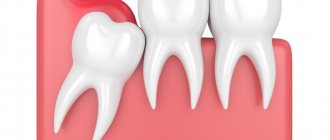
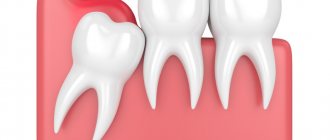
- Retention is a pathology in which the third molar is located under the mucous or bone tissue. The main symptoms are severe pain in the gums, as well as the development of an inflammatory process in the gum pocket.
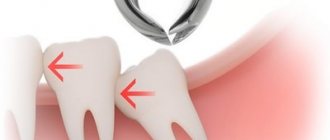
- Dystopia or abnormal position of the tooth. It manifests itself as severe pain, affecting adjacent teeth, and the development of inflammation, including phlegmon or osteomyelitis.
The initial alarming symptoms that a patient may identify when a wisdom tooth grows are:
- Swelling in the cheek area.
- When swallowing, severe pain occurs, radiating to the throat or ear.
- Purulent or bloody discharge.
- Injury to the mucous membrane.
If you detect at least one of the above symptoms during the eruption of figure eights, you must seek the help of a dentist as soon as possible. The doctor will conduct an x-ray and determine whether the wisdom tooth is growing correctly.
Difficulty erupting wisdom teeth
If there are the beginnings of eights, then there are two options: normal eruption of wisdom teeth or difficult. With the first option everything is very clear. But problems during teething may indicate the presence of pathologies - dystopic and impacted wisdom teeth.
What to do with a bothersome wisdom tooth at home
The most important thing is not to cause further harm to yourself before visiting the dentist. It is extremely important to avoid overheating the area of concern. Heat can accelerate the onset of the inflammatory process. Therefore, you should not apply warm compresses or take a hot bath.
What can you do to relieve pain when wisdom teeth erupt:
- follow a gentle diet (do not eat very hard, hot or cold foods);
- after eating, rinse your mouth;
- use local anesthesia, such as gels used during teething in children;
- In case of severe pain, you can take painkillers.
But the most important thing is not to delay your visit to a specialist! Only he will be able to determine the seriousness of the problem and help avoid possible complications.
Features of the structure and eruption of wisdom teeth
Unlike other teeth, the rudiments of “eights” are formed not during intrauterine development, but at 3–5 years, when the child’s body is preparing to change the primary dentition to a permanent one. At this age, you can determine the number of future eights (from one to four). However, it is impossible to detect possible developmental pathologies at this stage.
The crown part of third molars is formed at approximately 12 years of age, but the development of the root part takes several more years and can continue even after tooth eruption. Considering that the most common age for the appearance of third molars is 18–25 years, the eruption of wisdom teeth occurs already in adults. However, approximately 10 - 15% have no eights at all, which is why it is considered normal for an adult to have from 28 to 32 teeth.
Removal of abnormally growing eighth tooth
Very often, if the third molar grows abnormally, it is necessary to resort to its removal. Indications for surgery:
- Repeated cases of pericoronitis (purulent formation in the gum pocket). This problem most often occurs on the lower eights, which have not completely erupted. Pericoronitis is usually treated by removing the overhanging gum, but if the disease recurs, it is recommended to remove the offending tooth.
- The upper eight grows into the cheek, constantly injuring it. To avoid the formation of ulcers and infection of the oral cavity, as well as to prevent pain, wisdom tooth removal is required.
- The development of wisdom tooth dystopia was diagnosed. The tooth grows at an incorrect angle, which can lead to inflammation of the periodontal tissues and the development of caries on the eighth and neighboring teeth.
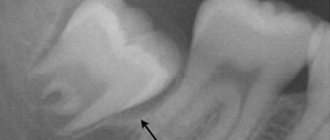
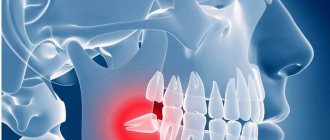
- The wisdom tooth grows to the side and affects the ternary nerve, causing attacks of pain. Most often, this occurs when an unerupted figure eight rests on the roots of neighboring teeth. Such an anomaly can only be diagnosed using an x-ray.
The procedure for performing the manipulation may differ depending on the location of the tooth. The sequence of the procedure during surgery:
- antiseptic treatment of the operating area;
- administration of anesthetic;
- tooth extraction;
- inserting a gauze swab into the hole to eliminate bleeding.
The tampon should be removed from the wound no earlier than after 25 minutes. The tampon must be in the socket to prevent bleeding. After the operation, the dental surgeon gives recommendations that must be strictly followed.
Complications of wisdom teeth eruption
| Type of pathology | Description |
| Dystopia | Incorrect position of the tooth. When a wisdom tooth comes through, it hurts much more than usual. It can push against neighboring teeth, causing them harm. |
| Retention | The tooth is completely or partially hidden in soft tissue or even bone. When a wisdom tooth erupts, the gums hurt and pericoronoritis may develop (inflammation caused by the activity of bacteria that accumulate in the gum hood). |
| Mixed pathology (retention + dystopia) | Incorrect position is complicated by tooth retention. The most severe pathology that provokes the occurrence of phlegmon, abscesses and osteomyelitis. |
Symptoms of the eruption of wisdom teeth in adults with suspected development of pathology:
- when a wisdom tooth erupts, the cheek becomes swollen;
- blood and pus are released when a wisdom tooth erupts;
- severe pain in the gums and jaw when wisdom teeth erupt;
- injury to the cheeks and tongue.
What is dangerous about malocclusion?
Violations of occlusion entail diverse consequences from gastrointestinal disorders to psychological complexes. If you are already thinking about correcting your bite, you are most likely familiar with its consequences firsthand. It is also worth noting that malocclusion often provokes premature tooth decay, as it is often the cause of pathological abrasion of teeth, the development of caries and periodontitis. In addition, the pathology can lead to overload of the temporomandibular joint, when the patient replaces clicks and crunches when opening and closing the mouth.
In order to answer this question, let’s figure out what kind of wisdom teeth they are.
It is not without reason that wisdom teeth received such an interesting name; many beliefs and legends are associated with them. The ancients believed that a person develops these teeth (17 - 25 years old) only when his soul has strengthened, become mature, and life wisdom has appeared. The eruption of all 4 teeth indicated the protection of the clan, so they were practically not removed - because then the person was deprived of protection.
These teeth are also called “eights”, as they are the eighth in the dentition. Wisdom teeth are unique because they are the only group of teeth that do not have a clear anatomy, and for the most part they are all different. It is impossible to be unambiguously sure of the number of root canals and their patency.
Nature has endowed humans with “figure eights” so that the teeth are located closer to each other and to make chewing hard food easier. Now this problem has lost its relevance. In the modern world, we eat softer food, so wisdom teeth began to grow much later than others and not in all people, so “eights” are considered to be rudiments. According to data, 15 - 20% of the population have no wisdom teeth at all, not even the rudiments. The rest have rudiments, but often they prefer to remain in the thickness of the jaw and not rise to the surface. And only some “lucky” ones can experience the beauty of teething already in adulthood.
The unpleasant sensations that wisdom teeth sometimes cause can be safely blamed on the process of evolution. Over the millennia, the human body has transformed, and the jaw is no exception. Gradually it decreased, but the size of the teeth did not change. Because of this, wisdom teeth, which are the last to grow, do not have enough space in the mouth.
Wisdom teeth, indeed, are almost not involved in the chewing process. But you shouldn’t neglect them either, since a fully erupted wisdom tooth in the event of loss of other teeth can “save” a person from removable dentures.
In what cases is it worth fighting to preserve a wisdom tooth?
Arguments for"
A wisdom tooth that has completely erupted and is affected by caries can and should be treated. If the canals are well passable, not curved and can be filled with high quality, even complications of caries (pulpitis, periodontitis) are not a “sentence” for these teeth.
There is one advantage in the “eights”, because of which some patients try to save them. Erupting later than others, wisdom teeth can become a support for a bridge prosthesis - instead of damaged teeth. Without the figure eight, such permanent prosthetics will only be possible with the help of implants.
A wisdom tooth may definitely be required for prosthetics if: the seventh tooth in front is missing, both the sixth and seventh teeth are missing, or the sixth and seventh teeth have not yet been removed, but will soon be removed.
Definitely delete!
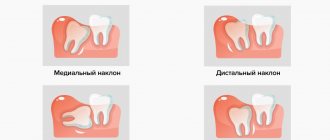
Delayed eruption (retention), incorrect position (dystopia) of the wisdom tooth
As a rule, this is a partially erupted wisdom tooth, lying horizontally or with its crown tilted towards the lingual, buccal, medial (inclined towards the “seventh” tooth), distal (towards the angle of the jaw) sides. The value of such a tooth for prosthetics and chewing food is zero. It happens that the crown of a wisdom tooth has a pronounced slope towards the cheek area. This leads to the person biting his cheek all the time. Chronic injury to the buccal mucosa can even lead to the development of an oncological process in this area. There is no point in preserving such teeth.
2) Destruction of the front (“seventh”) tooth
As mentioned above, wisdom teeth often erupt at an angle. The front cusps of the crown sometimes rest against the seventh tooth in front. Lack of adequate hygiene and constant pressure from the wisdom tooth on the enamel of the nearby tooth can cause its destruction and the occurrence of caries. Preserving the seventh tooth and its full treatment is sometimes not possible without removing the wisdom tooth.
3) Orthodontic indications (bite anomalies).
Previously, to correct the bite, “fourth” teeth (less often “fifth” teeth) were often removed for subsequent orthodontic treatment. These teeth are located in the smile line and from an aesthetic point of view, it is currently more advisable to preserve them. Therefore, removal of wisdom teeth is the right decision, since they can provoke relapse after early orthodontic treatment, due to later eruption. In addition to removing impacted wisdom teeth, orthodontists recommend removing even the rudiments of these teeth.
4) Pericoronitis (inflammation of the mucous hood).
A fully or partially erupted wisdom tooth occupies such a position that part of its crown is covered with an overhanging hood of mucous membrane. In this case, a space is formed between the hood and the tooth in which microbes multiply, which leads to inflammation. In such cases, patients, as a rule, note aching pain in the jaw, discomfort when opening the mouth (sometimes limited mouth opening caused by inflammatory muscle contracture), pain when swallowing, enlarged lymph nodes, and sometimes swelling of the cheek appears. In this case, to stop the inflammatory process, the mucous hood is excised, followed by anti-inflammatory therapy. Such inflammations can happen more than once, so the only correct solution is to remove the wisdom tooth.
There are situations when it is impossible to maintain the “eight”, and inaction is dangerous!
These are inflammatory processes caused by wisdom teeth. Periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum of the jaw). Initially, complaints appear of aching pain in the tooth, which intensifies when biting (a symptom of an “overgrown” tooth). If the patient ignores these pains, the inflammatory process spreads to the periosteum. In such cases, swelling appears and general health worsens. At the same time, pain in the tooth decreases. In case of extensive destructive process on the roots, the tooth is removed with dissection of the periosteum (periostotomy) and subsequent drainage of the lesion.
More serious complications are osteomyelitis (inflammation of the jaw), abscesses and phlegmons (limited and widespread purulent processes of soft tissues), abscessing lymphadenitis (purulent melting of the lymph nodes) and others. These diseases are an indication for the removal of wisdom teeth, followed by serious treatment in a hospital.
Summarizing all of the above, I would like to focus on the fact that everything is very individual, and only after carefully weighing all the pros and cons, having received a comprehensive consultation with a doctor, should you make a decision regarding treatment or removal of a wisdom tooth.
How to understand that wisdom teeth are growing abnormally
Signs or symptoms that indicate problems include the following:
- numbness of the jaw and painful sensations - in this case we can say that the tooth is growing crookedly inside the bone and even injures the jaw nerve,
- sharp pain throughout the jaw, but more so near the base (where the temporomandibular joint is located),
- Above the figure eight, the gum is swollen, moves away from the surface, is red and very painful,
- the lymph nodes become inflamed and increase in size - this indicates the addition of an infectious process,
- the teeth in the row begin to shift - often this may not be noticeable to the person himself, but the doctor will see the changes after performing a panoramic x-ray,
- Due to the lack of space for quality hygiene, a carious cavity appears behind the wisdom teeth or gum disease begins to develop.
Is it necessary to remove a tooth that has not erupted?
If an un-erupted figure eight does not cause a person any discomfort and there are no indications for its removal, then the operation is not necessary. However, if this unit, being in a bud state inside the gum cavity, in any way interferes with the patient’s normal life, the doctor may recommend its removal.
The main indications include: pain over a long period of time, the appearance of cysts, purulent foci of inflammation, for example, osteomyelitis or sinusitis, incorrect direction of growth, partial retention and much more. Also, quite often, an unerupted tooth needs to be removed before starting orthodontic treatment in order to correct a malocclusion.
It is important to understand that if not a single wisdom tooth has erupted and the person does not experience the slightest discomfort, then nothing needs to be done. If the eight does not interfere with the normal development of adjacent units and does not affect the standard of living, then it can be left in its place. However, if unerupted teeth cause pain, the doctor may insist on their urgent extraction.
previous post
Why can all teeth hurt at the same time?
next entry