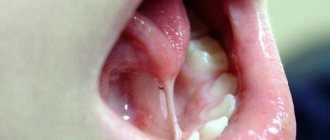
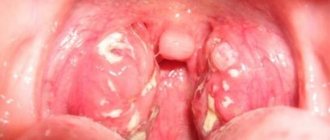
If the pain is associated with damage to the frenulum
The hyoid frenulum is a mucous membrane that connects the tongue to the base of the mouth. Inflammation can be caused by:
- Diseases occurring in the oral cavity - stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis;
- Using incorrect hygiene products: toothpaste, toothbrush, mouthwash;
- Allergies caused by taking medications.
Inflammation of the frenulum under the tongue can also occur as a result of injury to it during brushing teeth, eating (too hot or cold foods), talking loudly, sharply biting the tongue, or careless handling of cutlery.
The reason why it hurts under the tongue may also be a physiological feature. In cases where the frenulum is short from birth, the likelihood of damage increases significantly, and discomfort can occur even while eating.
What can you do
A visit to the dentist cannot be avoided if the frenulum under the tongue hurts. The doctor will examine the damage and prescribe treatment. At home, especially if you can’t immediately visit a specialist, in order to relieve pain, you can rinse your mouth:
- Soda solution (a teaspoon per glass of chilled boiling water);
- Chamomile or sage decoction;
- Preparations: Stomatofit, Rotokan, Chorophyllipt.
Also, if the frenulum under the tongue is inflamed, it is recommended to treat the affected area with Iodinol or place a cotton swab dipped in sea buckthorn oil at the damaged area. Such measures can only be used in cases where you know for sure that the cause of the pain under the tongue is an inflamed frenulum.
Which doctor should I contact?
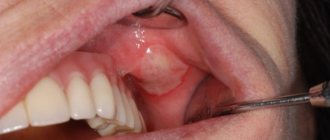
If a lump appears under the tongue on the frenulum, you need to find out what factors provoked its formation. Only a doctor can correctly determine the cause. After all, the ball can be filled with liquid or consist of epithelial cells. The degree of discomfort depends on the size of the formation. When papillomas are soft, the patient may not feel them, but large inflammatory growths interfere and begin to hurt. Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- The mucous tissues of the oral cavity constantly dry out;
- The deficiency of saliva and its composition is clearly expressed;
- The taste sensations have changed a lot;
- Increasing pain appeared;
- Swelling on the face increases;
The affected tissue around the lesion may become red and begin to bleed. First of all, you should consult with your local therapist. To confirm the suspected diagnosis, it is most often necessary to visit a dermatologist, dentist, otolaryngologist, venereologist, or gastroenterologist. If the need arises, the patient is referred to a surgeon or oncologist. During the examination, the doctor collects anamnesis, conducts a thorough examination, and performs laboratory diagnostics and histology. In complex cases with abscesses, patients are referred for ultrasound examination, as well as computed tomography. The pathogen is detected using a cytological analysis of saliva.
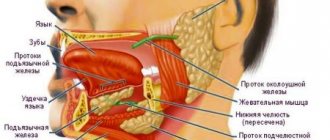
Pain due to inflammation of the salivary glands
In cases where a person feels pain on both sides of the tongue, the cause may be inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland. It arises as a result of:
- Complications of another disease (inflammation of the tonsils, acute respiratory viral infections, anemia, vitamin deficiency, dental diseases);
- Insufficient hygiene;
- Obstruction of salivary flow caused by stones or pathogens.
The main symptoms indicating inflammation of the salivary gland:
- Dry mouth – it always seems like there is not enough saliva;
- Pain that is observed not only under the tongue, but also in the ear area;
- Redness of the mucous membrane, thickening or swelling under the tongue;
- Putrid taste.
If you observe such signs in yourself, you should immediately go to the dentist and undergo a course of therapy. Otherwise, an abscess may develop or the disease may become chronic.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Symptoms and signs
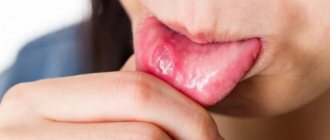
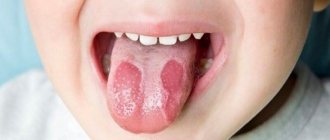
The most common cause of sores and ulcers is sublingual stomatitis, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a whitish or yellowish coating on the tongue;
- swelling;
- ulcers and abscesses in the sublingual area.
In especially severe cases, ulcerations heal poorly, fester, and subsequently leave a scar.
With herpetiform stomatitis, the ulcers are located at the bottom of the tongue. In appearance, they resemble herpes - small blisters filled with liquid.
With tuberculosis of the oral cavity, the sores initially look like small tubercles, the ulcers are round, their edges are undermined. Often the formations may bleed. Over time, they become very painful, the patient's condition worsens sharply, and pain occurs when eating and talking.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
With tongue cancer, the patient observes lumps. Mouth ulcers are a sign of metastatic disease. They can reach from 1 to 4 cm. The color of the affected area can vary from dark red to dark gray or yellow.
Tongue cyst is a rare disease. A small, painful white growth forms under the tongue. The patient has difficulty breathing and swallowing.
Treatment
Having established the causes of inflammation of the tongue, the specialist prescribes treatment. In case of inflammation of the salivary glands, the purulent contents are initially removed, then antibacterial agents are injected into the ducts, and the patient is also prescribed antibiotics or sulfonamide drugs orally.
As a rule, therapy is accompanied by rinsing (in each case the doctor selects the optimal solution) and physiotherapy: UHF, Sollux and others. For fever and general malaise, paracetamol or ibuprofen is prescribed.
Surgical treatment methods are used extremely rarely. The operation is performed if there are stones in the duct and they cannot be removed in any other way.
If you experience unpleasant symptoms or discover inflammation or swelling under your tongue, do not look for what it might be. Go to a qualified dentist, he will examine the oral cavity, make a diagnosis, and prescribe adequate therapy. Perhaps pain in the sublingual space is a symptom of another serious disease and consultation with an appropriate specialist will be required.
Monitor the condition of your teeth and mucous membranes, visit the dentist regularly, promptly treat inflammation of the ENT organs and ARVI - such preventive measures will minimize the possibility of inflammation and pain.
Treatment and removal methods
The treatment regimen is drawn up depending on what factors caused the anomaly. But treatment is necessary so that the acute stage of the disease does not develop into the chronic phase. If this happens, the exacerbation will recur from time to time. This form of the disease is more difficult to treat. If necessary, laser treatment of gums should be carried out on time. A healthy oral cavity is the key to the overall well-being of the body.
- The doctor selects medications based on the underlying pathology. The initial manifestations of the disease are successfully eliminated with medications and local applications. According to indications, medications are recommended that stimulate saliva production. This may be Galantamine, Pilocarpine, Potassium Iodide. To maintain general condition, the doctor selects means to stimulate the immune system.
- Serious blockage of the salivary glands is eliminated by mechanical cleaning of the ducts. Today, sialoscopy, a minimally invasive procedure for grinding mineral deposits, is widely used.
- Purulent papules are opened, after which the exudate is removed. Surgical technologies such as galvanocaustics, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser beams, and radio waves are used.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity to accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissue includes rinsing with Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Rotokan, Miramistin.
To prevent pathology, you need to regularly carry out hygiene procedures with a brush and toothpaste. In addition, floss and irrigator should be used. It is necessary to visit the dentist every six months, and other doctors when the initial symptoms of the disease appear.
Growth under the tongue
Growth under the tongue: types, consequences
It happens that a growth appears on the root of the tongue, which can cause discomfort and anxiety due to the reasons for its occurrence.
Growths should be divided by origin and properties. Let's look at the main types.
Growths under the tongue should be divided into:
- Papillomas;
- Polyps;
- Lipomas;
- Cysts;
- Sialadenitis;
- Hemangiomas;
- Lymphangiomas;
- Tumors of a malignant nature.
Human papillomavirus can cause a benign tumor under the tongue. Due to stress, poor immune defense, lack of minerals and vitamins, this disease can become more active. Typically, papillomas are located on the root of the tongue, under the tongue, or on the side of the tongue.
Papillomas can be pointed or flat.
Pointed papillomas
They are tubercles in the form of papillae at the base of the tongue and are pinkish in color. Because of them, unpleasant sensations may arise when eating or communicating.
Flat papillomas
This type of papillomas does not cause a person much discomfort. They are round, flat in shape and have clearly defined boundaries.
If papillomas appear and begin to grow, then they can be removed and treated with antiviral drugs. There is no need to self-medicate and resort to traditional therapy.
This formation is benign, has a flat or convex appearance, and grows above the mucous membrane of the lingual root. A polyp is formed from the gastric mucosa, which has been ectopic.
Lingual polyps are a rare occurrence. They usually look like a bump on the back of the tongue. They do not cause pain, but can cause discomfort if they grow or become injured.
A polyp can develop into cancer. The polyp is removed promptly.
The formation is a benign wen located on the lingual mucosa.
Lipoma can be patchy and vulgar. Flap lipoma has a flat shape and is capable of growing into the tissue. Wen vulgaris is a bulge on the tongue of a simple type.
Lipoma is painless, has a soft consistency, grows slowly, and is usually small in size.
The reasons why a lipoma is formed include heredity, bad habits, poor metabolism, injury, and poor ecology.
To diagnose the disease, you will need to see a dentist.
This growth under the tongue looks like a ball with liquid inside. It occurs under the tongue and on the root of the tongue. It happens that a new growth occurs at the lingual frenulum.
The cyst does not grow quickly, but it can create unpleasant sensations; there is no pain. The symptoms will be as follows:
- The lower jaw is swollen;
- A rupture occurs at the growth shell.
To avoid infection, you need to seek help from a doctor, otherwise an abscess may occur, swallowing will be impaired, speech and breathing may be impaired, and the tongue may become displaced.
The cyst is not dangerous.
The disease is a disease of the salivary gland and sublingual glands. The cause of the disease is infection. The causative agents of infection are harmful bacteria, such as the mumps virus, tuberculosis bacillus, and the causative agents of diseases such as syphilis.
Poor immunity, the presence of oncology, and the presence of infection can be cited as the reasons for the appearance of this disease.
In the acute form of the disease, swelling appears, due to which the tissue thickens, festers, and then a necrotic process occurs.
Symptoms of this disease will be as follows:
- Weakness;
- Temperature,
- Taste in my mouth
- Paroxysmal pain localized in the gland area;
- Swelling;
- Pain and discomfort while eating.
This disease is treated under the supervision of a doctor.
This disease is a benign tumor formed due to disorders of the blood vessels. The tumor grows slowly, but can behave unpredictably. Externally it has a purple or red tint. It is divided into capillary and cavernous.
Hemangioma may occur due to hormonal imbalances, weak immunity, metabolic disorders, or due to injuries to the oral cavity.
The disease must be treated immediately to avoid complications and degeneration into cancer.
The disease is a benign tumor that is located in the lymph nodes. It can affect the entire tongue or one side of it. An enlarged tongue may make it difficult to close your mouth. Many small blisters appear in the oral cavity, growing very quickly.
The causes of lymphangioma are:
- Previously undergone surgical operation;
- Infections;
- Other neoplasias in the body;
- Congenital pathologies;
- Heredity.
Signs of lymphangioma will be the following:
- Glassy small bubbles;
- Plaque on the lingual mucosa;
- Bleeding of vesicles when injured;
- Bite problems;
- Speech problems.
The disease must be treated immediately by removing the tumor in a minimally invasive manner.
Lump on penis
The most dangerous pathology of the oral cavity is cancer. It can be located under the tongue, at its tip, on the side, at the root of the tongue, at the bottom of the mouth. The tumor is of the following types.
Ulcerative tumor
The lump can develop into an ulcer; it hurts, bleeds, and is located at the bottom of the tongue.
Infiltrative tumor
A thickening with a white coating appears on the tip or back of the tongue. It looks like a dense tubercle that constantly and severely hurts.
Papillary tumor
The tumor is a pedunculated growth located on the lateral parts of the tongue. Grows moderately. It develops into malignant due to mechanical injuries, viruses, inflammation, bad habits and poor heredity. It has distinct features:
- Severe pain throughout the mouth;
- A lump or ulcer in the tongue area;
- Swelling of the tongue, neck and face;
- Difficulty swallowing, speaking, closing the mouth;
- Smell from the mouth.
If such symptoms occur, you should contact an oncologist. Next, treatment is carried out. The method of treatment is selected individually and depends on many factors.
Modern diagnostics and new techniques used in the Onco.Rehab clinic treat tumors of any kind, contact our clinic to avoid the dangerous consequences of the disease.
Stomatitis: what kind of disease is it, the mechanism of appearance of stomatitis ulcers
Scientists have not yet fully studied the mechanism by which stomatitis occurs on the mucous membrane in a person’s mouth. The manifestation of symptoms of the disease is associated with the specific reaction of a person’s immune system, which he exhibits in relation to irritants present on the mucous membrane of the mouth.
Bacteria, fungi, viruses and other microorganisms act as irritants. Normally, they are always present on human mucous membranes in one quantity or another. But when a person’s immunity is weakened, or other reasons provoke an increase in the number of microorganisms and the development of infectious diseases in the mouth (staphylococcal, streptococcal, candidal, etc.), this fact can trigger a stomatitis reaction.
Ulcers on the human mucosa, which are stomatitis in nature, are formed as a result of the fact that lymphocytes (white blood cells of the human immune system) begin to attack molecules that they cannot recognize. This reaction of the body is similar to that which occurs in the case of organ transplantation. As a result of such a lymphatic attack, stomatitis ulcers are formed on the oral mucosa, which usually go away on their own in one to two weeks without scarring.
Prevention
To avoid consequences, you should regularly visit a dentist, observe the rules of oral hygiene, do fluorography in a timely manner, avoid mechanical and chemical injuries to the tongue, avoid alcohol and smoking, and adhere to a diet.
Nutrition should be balanced, rich in microelements and B vitamins. A mandatory condition for maintaining health is taking medications that stimulate the body’s protective functions.
Sores under the tongue can be a signal of a serious disease, therefore, if discomfort and pain appear in the oral cavity, as well as in the presence of lumps and small wounds, the patient should consult a doctor in order to begin timely treatment and avoid negative consequences.
Which people are at risk for stomatitis?
As already noted, children are primarily susceptible to stomatitis, since their immune system is just learning to fight infections and diseases and respond to irritants appropriately. Therefore, if, with timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment, your baby still chronically develops stomatitis in the mouth, then perhaps the reason is due to age, and over time these problems will disappear.
But besides age, there are other factors that increase the risk of stomatitis ulcers in a person’s mouth. They are associated with various reasons, some of which we have already named when characterizing the types of stomatitis, but now we will try to specify each factor separately.
Those at risk for possible development of stomatitis include:
- People with a hereditary predisposition to the disease. Scientists have proven that the likelihood that stomatitis will develop in a person’s mouth (on the palate, mucous membrane, throat or tongue) increases if one or both parents have ever encountered similar problems. The best way out in this situation is to follow the rules of oral hygiene and take vitamin and immunomodulatory complexes as prescribed by your doctor.
- People with current somatic diseases. Quite often situations arise when stomatitis chronically develops in a person’s mouth without any obvious reason. During a complete examination of the body of such a person, any diseases are usually revealed, in particular, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (giardiasis or helminthic infestations). Parasites, while in the body, may not manifest themselves in any way and not bother a person for years, but they reduce his immunity and prevent resistance to infections and other diseases. In this case, in order to get rid of stomatitis in the oral cavity, a person should undergo a course of treatment that will allow him to get rid of other concomitant diseases.
- People with reduced immunity. Human immunity is reduced not only by somatic diseases, but also, for example, by factors such as stress. Therefore, if you have a hard job or tense family relationships, this can cause chronic stomatitis, localized on the oral mucosa. In addition, frequent occurrence of ulcers in a person's mouth may indicate more serious problems with the immune system caused by a disease such as AIDS. Therefore, in this situation, a person is recommended to get tested, undergo a full examination of the body and get plenty of rest.
- People with bad habits. Bad habits such as alcohol, smoking and drug use can cause stomatitis and the formation of painful ulcers in the mouth. The fact is that such a lifestyle weakens the immune system and undermines human health. In addition, cigarette smoke and alcohol create favorable conditions in the oral cavity for the development of bacteria, viruses and fungal infections, which provoke the appearance of stomatitis ulcers on the human mucosa.
If you have seen photographs of people with stomatitis in the mouth, then you have probably noticed how unattractive this disease looks, not to mention how much discomfort it causes to a person. Therefore, if you are at risk for the possibility of developing stomatitis ulcers on the mucous membrane, palate, throat or tongue, then you should take measures to reduce the chances of getting stomatitis: quit bad habits, undergo a course of treatment for somatic diseases, increase your immunity and take vitamin complexes. But these measures should be taken only after consulting a doctor.