What is
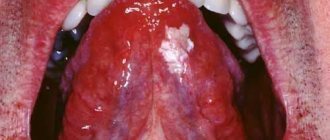
A lump is a formation of varying size, formed from the upper layers of the mucous membrane. The neoplasm may be white or red, as well as a bluish tint. Inside the cavity there is content consisting of lymph, blood clots, pus or pathologically altered cells.
A lump under the tongue often indicates a disease. The cause is identified based on external signs, examination of the tumor, and histological examination.
Treatment depends on the provoking factor and type of formation. Antibiotics and antiseptics are prescribed. Sometimes surgery is required.
There may be several reasons for the formation of a tumor. Most often this is damage to the mucous membrane or the development of other diseases. That is why it is important to promptly establish the cause of its occurrence, before the pathological process spreads to other tissues of the oral cavity.
Sometimes a lump in the area of the hyoid frenulum may indicate a mandibular ridge (torus).
Bone hyperplasia is in most cases benign and requires treatment only if it interferes with the installation of prostheses.
Dentist
Novikova Olga Alexandrovna
8 years of experience
Treatment is carried out after diagnostic testing and exclusion of malignancy, since a lump in the sublingual area may appear as a result of the development of oncology.
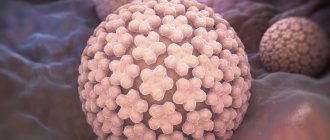
How and why we become infected with HPV:
- In most cases, HPV is transmitted through sexual contact.
- Infection is possible through household means, through touch, while staying in public places, such as baths, saunas, swimming pools, toilets or gyms.
- Self-infection, such as when you accidentally cut yourself while shaving.
- There are known cases of infection of a newborn during passage through the birth canal.
The danger of HPV lies in the fact that, once it enters the human body, it can remain in an inactive state for a long time, but then suddenly (during stress, a cold or other immune system failure) make itself felt in the form of the appearance of tumors on the body and growths on the tongue.
Classification
Cysts, lipomas, papillomas, and lymphangiomas usually form under the tongue. The most common types of formations that form on the oral mucosa include:
- Sialadenitis.
- Salivary gland cyst.
- Lipoma.
- Papilloma.
- Hemangioma.
- Lymphangioma.
Each type of neoplasm is characterized by certain symptoms that appear as the lump grows. They also have different causes.
Sialadenitis
Appears against the background of inflammation of the salivary glands. The causes are usually viruses, infections and pathogenic microorganisms. They penetrate into the oral cavity not only with food, but also from inside the body.
In medicine, the disease is called salivary stone disease, in which a white lump forms. A stone formed in the cavity of the formation clogs the duct and causes stagnation.
Symptoms of the disease include:
- Painful sensations in the area of the salivary glands.
- Decreased salivation and constant dry mouth.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Enlarged gland.
You may also feel pressure and tension in the area of the duct. Treatment for salivary stone disease occurs surgically.
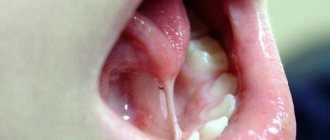
Cyst
A cyst under the tongue is rare. The disease is characterized by the formation of a tumor in the maxillofacial area. The cavity of the neoplasm is filled with secretion. There are several types of cysts:
- Dermoid. This is a small cone of white or gray color. At the initial stage, there are no symptoms other than mild discomfort. Over time, difficulty swallowing and chewing food appears. This type is a congenital disease and is removed surgically.
- Mucous. The cone does not reach 1 cm in diameter and has a bluish tint. It disappears upon spontaneous rupture.
- Ranula. It looks like a mucous cyst and is considered a type of cyst. It has the ability to grow up to five centimeters. After the break it appears again. The tumor can be completely removed surgically.
A ranula is a white lump with liquid inside. The reason for its appearance is the inability of the secretion to pass through the duct due to its blockage or inflammatory process.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the type of cyst. Some of them may go away on their own, while others require surgical removal. Only a doctor can diagnose the type of tumor.
Lipoma
It is formed from adipose tissue located under the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. The tumor has a benign course. Rarely diagnosed. The cone itself is always located towards the capsule and is separated by bridges.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Removal of the tumor is carried out in cases where it has reached a large size and becomes a cause of discomfort.
Papilloma
Formed from the epithelium of the mucous membrane. The cone is round or oval in shape and has a pale pink color. Papilloma can be single or multiple. In some cases it develops into a malignant formation. In medical practice, cases of spontaneous resorption are known.
Hemangioma
The lump begins to form from blood vessels as a result of embryogenesis pathology. Tissue changes are already noticeable in newborns. Has two types:
- Capillary. In appearance it resembles a small pink spot. It differs in shape, size and shade. Does not rise above the surface of the mucous membrane.
- Cavernous. When pressed, it decreases, but once again takes its previous shape. The tumor is convex and has a blue or purple tint.
Hemangioma is a congenital disease characterized by benignity and rapid growth. It may be located under the mucosa or have a part formed on the surface of the membrane.
Lymphangioma
Looks like a wart with blisters. Characterized by frequent inflammation after mechanical damage during eating. Appears more often in children of the first year of life.
In adults, according to experts, lymphangioma is formed against the background of bad habits or inflammation in harmful conditions. May have a malignant course.
When diagnosing, it is important to establish what type of neoplasm the formed lump belongs to. In certain cases, special research methods are required to establish the nature of the flow. Only after an accurate diagnosis is made, treatment is prescribed.
How to get rid of papillomas?
If the growths on your tongue are present in small quantities and are small in size, then the process of removing such growths is quite simple. But this does not mean that you can remove the papilloma yourself, using such “effective folk remedies” as cauterization, cutting the “leg” of the tumor with scissors, etc. To remove the growth, you should contact a professional medical institution.
Methods for removing tumors:
- Excision of papillomas with a scalpel or electric knife. This affects not only the growth itself along with the stem, but also part of the healthy tissue around it.
- Laser removal of tumors.
- By using a tool such as a conchotome, shaped like a wire cutter. After removing the papilloma with such a device, galvanoacoustics is performed (cauterization of the localization of the growth using a platinum wire).
Causes of a lump under the tongue
A tumor can occur for various reasons. Usually this is mechanical damage to the mucous membrane and inflammation during chewing of hard foods. In this case, the lump will disappear on its own after some time.
Other reasons for the formation of tumors under the tongue include:
- Wearing low-quality dentures. Sharp edges can injure the surface of the mucous membrane.
- Infections. They get into microcracks formed as a result of injury and become the cause of inflammation. If left untreated, the process affects the deep layers of the mucosa, and a tumor begins to form.
- Salivary stone disease. The lump occurs in the area where the stone is formed.
- Genetic predisposition.
- The first stage of syphilis. A ball forms under the tongue, which causes pain when pressed or during conversation. After a while he disappears.
A tumor under the tongue can form against the background of the development of oncological pathologies. That is why it is important to promptly contact a specialist who will determine the cause and nature of the disease.
Polyp
A benign neoplasm of a flat or convex shape that grows over the mucous membrane of the root of the tongue. Formed from areas of ectopic gastric mucosa.
Unlike other tumors, tongue polyps are quite rare and appear as a lump on the base of the tongue. The polyp itself is painless. Discomfort occurs only in the event of an accidental injury or when a polyp grows.
The formation of such a lump does not exclude its ability to develop into a malignant tumor. As a rule, surgery is used to remove a polyp.
Diagnostics
In the early stages, the disease is difficult to detect, since the lump is small and does not show symptoms. A preliminary diagnosis is established based on the patient's complaints and visible signs. The doctor carefully examines the tumor to determine its characteristics.
For confirmation, a histological examination is prescribed. To do this, cells from the tissue of the cone are collected with a special instrument, and then the sample is sent to the laboratory.
In some cases, consultation with other specialists, such as an oncologist, may be necessary.
Sialadenitis
Sialadenitis is an inflammation of the salivary gland that affects the sublingual glands. The main reason for the development of the disease is the penetration of infection.
Various microorganisms act as pathogens. Harmful bacteria that cause disease include:
- tuberculosis bacillus;
- virus ;
- causative agent of syphilis;
- various other infectious diseases.
The causes of the disease can be:
- weak immunity;
- infections;
- oncological diseases.
The acute form of sialadenitis is manifested by tissue swelling. After this, compaction occurs, suppuration and, as a final result, necrosis. Sometimes the disease process is inhibited at the initial stage.
In case of illness, symptoms are observed:
- general malaise;
- increased temperature ;
- a characteristic taste in the mouth ;
- pain in the form of attacks in the gland area;
- discomfort and pain while eating;
- swelling of the affected area.
When treating sialadenitis, both traditional medicine and folk methods are allowed. All therapeutic measures are carried out as prescribed and under the supervision of a doctor.
Treatment
The treatment regimen depends on the type of tumor and the reasons why it appeared. Lumps in the sublingual area resulting from mechanical trauma are strictly prohibited from piercing.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Once the contents are released, the wound may become infected. It is also not recommended to consume sour, spicy, hot foods, or alcoholic drinks, as they irritate the mucous membranes and provoke inflammation.
All oral diseases are associated with poor hygiene or lack thereof. Over time, plaque accumulates on the teeth and gums, creating a favorable environment for bacteria and microorganisms. As they multiply, they cause inflammation and many pathologies. To eliminate the problem, rinses with special antiseptic solutions are prescribed.
In cases of diagnosing sialolithiasis, antibiotics and mouth rinsing are indicated. It is also recommended to eat foods that promote saliva production. With sialadenitis, the neoplasm may not go away for a long time, even after the cause is eliminated.
In case of cyst formation, surgical intervention and disinfection of the oral cavity with antibiotics are indicated. Lipoma does not pose a threat to human health. During its formation, observation by a dentist is indicated.
For a malignant tumor, radiation therapy, chemotherapy or surgical removal is prescribed, depending on the extent and form of the disease.
Cyst (wound)
A cyst under the tongue appears as a growth in the form of a ball with liquid inside. It is localized on the tip of the tongue, in the sublingual area and on the root. Most often, a cyst forms in the area of the frenulum of the tongue.
The cyst progresses slowly, but as its size increases, it causes a sensation of a foreign body in the oral cavity; there is no pain. A large growth is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the lower jaw;
- rupture of the growth shell.
In case of the first manifestations, it is necessary to seek the help of a doctor, since ranula can become infected and cause complications of the following nature:
- displacement ;
- disorder ;
- breathing and swallowing problems
- development of an abscess.
The cyst itself is not dangerous, but additional research is required to establish a diagnosis.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of any oral disease, you should follow the rules of hygiene. It is also important to choose the right toothbrush, since bristles that are too hard can injure the mucous membrane.
If an infectious disease develops, you should undergo the entire course of treatment, since the inflammatory process can spread throughout the body, reducing immunity and causing the formation of a lump.
A tumor under the tongue may indicate the development of serious diseases, such as oncology, or appear as a result of improper oral hygiene. When the first symptoms occur, you should contact your dentist, who will determine the cause and extent of the disease.
Papillomas
A benign tumor of the tongue is caused by the human papillomavirus. Favorable conditions intensify and activate the disease. Such conditions include: stress, weak immunity, lack of vitamins and minerals in the body. The shoots are formed mainly in places prone to injury.
Most often they are located:
- under the tongue;
- on the side of the tongue;
- at the root of the tongue.
There are two types of papillomas: flat and pointed.
Flat
Pronounced round growths with clear boundaries. They do not cause any particular problems to humans.
Pointed
The nipple-shaped tubercles at the base of the tongue are pinkish in color. They cause some inconvenience, especially during eating and talking.
In cases of the appearance and growth of papillomas, their removal is prescribed, as well as treatment with antiviral drugs, since the presence of infection can cause re-formation of growths. Therapy at home with folk remedies is excluded.
Lymphangioma
Lymphangioma is a congenital benign tumor localized in the lymph nodes. The tumor can affect either one side or the entire tongue. In this case, the organ takes on an enlarged shape, which makes it difficult to close the mouth.
Such a disorder causes the formation of small bubbles on the cavity of the tongue, which can grow at high speed.
The main causes are considered to be:
- congenital pathology;
- infectious diseases;
- hereditary factor;
- previous surgical operations;
- the presence of other neoplasms of any form.
Signs of the disease:
- bubbles of different sizes with a glassy surface;
- opening and bleeding due to injury;
- white coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue;
- malocclusion ;
- disorder .
The presence of signs indicates immediate treatment, which involves complete removal of the tumor. Minimally invasive methods are considered effective removal methods.
Special Recommendations
When treating a bubble under the tongue, all rules of oral hygiene are strictly observed. For this we recommend:
- brush your teeth after every meal;
- rinse your mouth with special solutions or boiled water, to which you can add soda or a decoction of chamomile and calendula;
- purchase a special antibacterial toothpaste that relieves pain and blocks the spread of infection.
During the period of illness, it is worth completely reconsidering your diet, excluding from the daily diet:
- any alcoholic drinks;
- spicy;
- smoked;
- sour;
- salty;
- canned.
It is recommended to periodically change your toothbrush and allocate personal utensils for eating. Smoking negatively affects the treatment process, so it is best to get rid of this bad habit.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the pathology depend on the reason for which it arose.
With injuries in the tongue area, blisters may appear not only under the tongue, but also on the side. It is mainly pink in color or engorged with blood, which is visible to the naked eye.
If any blood manifestations are absent, then this indicates the superficial nature of the pathology; most often, such a bubble goes away on its own and does not cause noticeable harm to health. When a blood clot appears, the hematoma is very deep and can become a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria, most often this leads to an inflammatory process.
A small bubble that has popped up may be the cause of vitamin deficiency. In this case, the patient feels almost no discomfort. Such manifestations disappear within a few days. To prevent the bubble from appearing again, you need to reconsider your diet and enrich your diet with vegetables, fruits, meat and dairy products. It is also recommended to undergo a course of treatment with vitamins.
If bloody inclusions are noticed in the bubble, then this is most likely a rune, which can only be removed through surgery.
Malignant tumor
Tongue cancer is a dangerous form of oral pathology. The tumor varies according to location:
- on the tip of the tongue;
- on the side parts;
- in the root zone;
- under the tongue;
- in the area of the floor of the oral cavity.
Malignant tumors come in several types.
Ulcerative
The first sign is the formation of a compaction, which subsequently turns into an ulcer. Located below on the tongue. It often hurts and bleeds.
Infiltrative
A lump on the tip of the tongue or at the back of it, covered with a white coating. The tumor itself resembles a dense tubercle, which is accompanied by constant and severe pain.