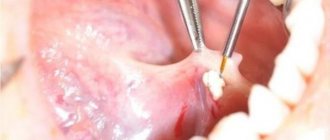
The importance of oral hygiene
The health of our teeth and gums directly depends on proper oral hygiene. The importance of daily hygiene procedures is difficult to overestimate, but it is often easy to underestimate and pay with the loss of teeth even at a young age. So the statement of dentists that one of the most effective and at the same time simple ways to prevent dental diseases is proper and regular dental and oral hygiene in children and adults is more relevant than ever. We should not forget that hygiene procedures should not be limited to just brushing your teeth at home.
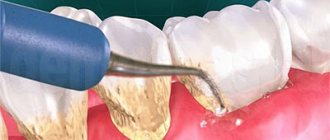
Preventive oral hygiene is a comprehensive measure that includes daily brushing of teeth and visiting a hygienist at least once a year. The fact is that in order to maintain teeth and gums in a healthy condition, it is necessary to promptly and efficiently remove dental plaque, as well as thick plaque on the tongue. Food debris and soft plaque can be removed with a toothbrush and toothpaste. But the removal of tartar (mineralized dental deposits) is carried out by a dentist using special means and instruments, for example, Air Flow. In this regard, comprehensive oral care implies individual and professional hygiene.
How to brush your teeth correctly
To ensure proper oral hygiene, it is not enough to choose the right toothbrush, toothpaste and other products. Proper cleaning technique must be followed to completely remove plaque and tartar from the enamel surface. The basic rules of this procedure are as follows:
- making rotational movements, trying to remove food debris from the interdental space, move it from the gum to the tooth;
- Using gentle back-and-forth movements, clean the entire tooth: outer, inner and chewing surfaces. The procedure should take about 3 minutes;
- clean the surface of your tongue to freshen your breath and rid your mouth of bacteria as much as possible;
- use dental floss;
- Rinse your mouth with mouthwash for 30 seconds.
Dentists distinguish several methods of brushing teeth. The appropriate one is determined individually; it is better to consult a dentist about this. What all methods have in common is that they are performed for at least three minutes and at the same pace.
On average, instead of the allotted three minutes, people spend 46 seconds brushing their teeth.
Universal cleaning suits everyone. With it, two teeth are cleaned in turn in the direction from the gums to the cutting part of the tooth. The outer side of the teeth is cleaned first, and only then the inner side. If there are no gum diseases, you can complement the procedure with a massage using circular movements of the gums.
During standard brushing, the brush should be held at a 45-degree angle to the gum.
Brushing harshly will help remove plaque effectively, but is not suitable for people with painful gums. The brush is positioned perpendicular to the buccal surface and moves in a circle from the internal surfaces to the chewing surfaces.
Gentle brushing will not harm sensitive gums. Vertical movements from the gums down are made with the teeth closed when cleaning the front surface and with the jaw open when cleaning the inner surface.
The technique of using dental floss also implies several rules. First, the floss should be about 45 cm long. For each brushing, use a new section 3-5 cm long. The interdental spaces should be cleaned with gentle movements, following the contours of the gums. Go to the surface of the teeth below the gum line, but do it carefully, avoiding sudden movements.
Individual oral hygiene
Individual oral hygiene is most effective if you follow certain rules on how to brush your teeth. As you know, there are many ways - each of them is correct and complete, it all depends only on our personal preferences. But it is still advisable to listen to the following recommendations from dentists:
- Always start brushing your teeth with the same row of teeth;
- adhere to a certain sequence of teeth cleaning so as not to miss any area;
- Carry out cleaning at the same pace in order to maintain the required duration of cleansing.
Of course, you need to pay attention to your teeth brushing technique. If, for example, you brush your teeth across the dentition, the enamel will wear off over time. Therefore, individual oral hygiene must be carried out in compliance with the technique of brushing teeth (you cannot even make circular movements - they must be perfectly round). But in our version they are more oval. Therefore, due to non-compliance with this important rule, the enamel by about 35 years of age is severely damaged, if not completely erased. However, if you use an ultrasonic brush, all of the above is not relevant for you. In addition, do not forget that cleaning the tongue with special scrapers is a necessary component of oral hygiene.
Dental floss
Flosses are used to remove soft plaque from the side surfaces of teeth and from between teeth. Dental floss helps clean hard-to-reach areas that a brush cannot reach. If your teeth and gums are healthy, you can use floss after every meal, as well as after brushing your teeth.
Dental floss is made from natural silk or synthetic fibers (nylon, nylon, acetate). It is better to use artificial materials - they have a fixed thickness, clean the interdental spaces well, do not delaminate, and do not tear.
The surface of the threads can additionally be treated with wax. In this case, it is smoother, penetrates the interdental spaces more easily, and is more convenient to use. Unwaxed dental flosses are not as convenient, but they clean the enamel surface better (such flosses are “rougher”, can separate into fibers, and remove plaque better). The cross-section of the floss can be round, flat, voluminous, or ribbon. The larger the thread, the better it cleans the enamel surface. The flatter the section, the easier the floss penetrates into the interdental spaces. Additionally, the thread can be impregnated with sodium fluoride, chlorhexidine or menthol. Such impregnations generally do not affect the cleaning efficiency. The exception is the antiseptic chlorhexidine, which provides an anti-inflammatory effect.
Floss can only be used if the gums are healthy, not bleeding, and not inflamed. When cleaning teeth with their help, it is important to act correctly: do not press too hard on the side surface of the crown, do not injure the gingival margin.
Basic personal oral hygiene products:
- toothpastes, gels, tooth powders;
- toothbrushes;
- chewing gum (therapeutic and prophylactic).
It is recommended to choose toothpastes depending on the presence of certain problems or specific tasks. If you have had dental implants, your best choice would be toothpaste for implants. To lighten the enamel surface, you should pay attention to whitening pastes. But to strengthen teeth, restorative products are suitable, for example, Theodent or Swiss Smile Crystal toothpaste with theobromine.
When it comes to a single, free-standing crown , there is practically no difference in hygiene procedures in the oral cavity with healthy teeth and gums, with a single crown, except for some nuances. Firstly, if it is a metal crown, steel or gold, then it should extend into the periodontal sulcus by 1 mm. This is a theory.
In practice, quite often we see, especially in the distal areas, that the contact surfaces of the molars are not completely processed and, as a result, the contact sides of the crowns hang over the gum or cut into the remaining protrusion of the root, which leads to the crown hanging above the gum. Ideally, such work should be redone, since this is an open marriage, but how often does this happen? The fact is that such situations exist; they also echo the situations that arise against the background of periodontal diseases, when, due to pathological resorption of the alveolar process, the gums sag and the crown hangs over it from all sides.
In these cases, food and liquids accumulate especially intensively under the artificial crown, which contributes to faster destruction of the tooth underneath, especially since the hardest tissues have already been removed. In these cases, you should resort to particularly intensive cleaning of the interdental spaces and spaces under the overhanging edges of the crown. If we consider that we already use floss all the time, then we need to add superfloss, ultrafloss, satinfloss and a brush to them.
When using dental floss inserted under the overhanging edge of the crown, it is necessary to make circular movements with the floss, which helps to better remove food debris. Just be careful not to cut the thread. It is much more effective to use superfloss and brushes.
After this, it is imperative to take baths with rinse aid. Irrigators in jet mode are good for cleaning subcoronal spaces.
With metal-ceramic crowns, when the junction of the crown with the tooth stump occurs due to a specially formed step, the transition from the artificial crown to the natural root becomes smoother, but this does not mean that this fact can be ignored.
On the contrary, any accumulation of plaque at the interface leads to faster destruction of the fixing material, against the background of more intense formation of dental plaque. Therefore, it is necessary to use superfloss especially carefully, circling it around the root with an artificial crown and making pulling-back movements. Then, due to the loosened part of the thread, all gingival surfaces of both the tooth and the artificial crown are better cleaned.
The next option is the presence of intermediate defects, where the defect with missing teeth is limited by healthy natural teeth at both ends. In these cases, bridge-like fixed dentures are used.
There will be no significant difference in the implementation of IGPR by persons with bridge-like fixed dentures (FND), metal, combined, metal-ceramic, or having any special features in the form of the design of the prosthesis.
In any case, it will consist of the following stages:
Cleaning the outer part of the MHSP
- cleansing the actual crowns of the MNZP;
- cleansing the body of the bridge.
Cleaning the inside of the MHSP
- cleansing the internal (hidden) spaces around the MNZP crowns and the hidden parts of the actual artificial MNZP crowns covered with soft tissue;
- cleaning the inner surface of the body of the bridge prosthesis, the rinsing space, in order to avoid the formation of bedsores under them.
Table 1. Basic individual oral hygiene products used in the presence of bridge-like fixed dentures in the oral cavity and features of their use (S.B. Ulitovsky)
| Individual oral hygiene products | Indications and features of use |
| Preventive manual toothbrush | The most effective and appropriate in its use is a brush with a multi-level brush field, a power protrusion, medium-hard bristles and an indication of the degree of wear. |
| Therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes | The most acceptable paste is a paste of medium abrasiveness, which has mild anti-inflammatory and astringent properties (due to extracts and/or oils of herbs and/or plants) and moderate antimicrobial properties (due to fluoride compounds, the action of which is aimed exclusively at pathogenic microflora, but not saprophytic ). |
| Hygienic dental elixirs | Can be used, but they are ineffective |
| Therapeutic and prophylactic dental elixirs | You can use them, their effectiveness is slightly higher than the previous position |
| Hygienic mouth rinses | Can be used, not much different from elixirs |
| Therapeutic and prophylactic rinses | The most optimal option, especially non-alcoholic, containing extracts and/or oils of herbs and/or plants and having anticaries, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, astringent, deodorizing effect. Use at the end of the hygiene procedure. |
| Floss Tape Satinfloss Satintape Flossette | They clean the interdental spaces of teeth without MNZP, as well as interdental spaces or any spaces near teeth covered with artificial crowns, as well as the mesial surfaces of the anterior abutment crowns and the distal surfaces behind the abutment crowns. |
| Superfloss Ultrafloss | An integral component of a hygiene kit for persons with MNPD. Due to the rigid guide, the superfloss is introduced into the rinsing space, and the loosened part most effectively collects and then removes plaque from the inner surface of the body of the MNSP. |
| Brush-brush | If the interdental spaces allow, then with its help they can be cleaned well, but it is even better to use it to clean the rinsing gap. |
| Mono-beam and small-beam toothbrushes for special purposes | Used to cleanse cervical areas. |
| Electric toothbrushes | Provide excellent quality oral hygiene. |
| Irrigators | Very effective for washing away food residues in the “jet” mode and for massaging the gums in the “shower” mode. Jet - before starting hygiene procedures; shower at the end. |
Table 2. Basic individual oral hygiene products used in the presence of partial and complete removable dentures in the oral cavity, and features of their use (S.B. Ulitovsky)
| Individual oral hygiene products | Indications and features of use |
| Preventive manual toothbrush | If there is an incomplete set of teeth in the oral cavity, the number of teeth requiring individual hygienic care is reduced. However, this does not mean that you can continue to ignore individual hygiene measures in the oral cavity. The brush should be sized according to the size of the mouth and the size of the teeth. Preference is given to medium-hard bristles. In any case, it should have rounded and polished bristle tips, a multi-level brush field consisting of a power protrusion and an active recess, micro-textured bristles and an indication of the degree of wear. These are the main parameters that can significantly increase the cleaning efficiency of a toothbrush and transfer it from hygienic to preventive. |
| Therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes | First of all, preference is given to “herbal” pastes. Fluoride components play the role of antimicrobial substances, and their presence in the paste is not significant for people belonging to this group. |
| Therapeutic and prophylactic mouth rinses | If previously a person did not have the opportunity to properly care for his own oral cavity, at least having lost most of them, it is necessary to make every effort to preserve the remaining teeth. It is necessary to understand that no, even the best dentures, are able to fully compensate and perform the functions of natural teeth. Therefore, it is necessary to use rinses that have mild anti-inflammatory, astringent and pronounced deodorizing and moderate antimicrobial properties. |
| Floss Tape Satinfloss Satintape Flossettes | Any of them should be used to clean the spaces between the remaining teeth. Their choice is determined by the size of the gap. Satin floss is much more tensile and does not fibble like other dental floss. |
| Superfloss Ultrafloss brush | If the interdental spaces allow, then it is imperative to clean them with one of the indicated types of interdental agents. |
| Preventive electric toothbrushes with round head | They can be used just as successfully as manual preventive ones; it is preferable that they have two-level bristles, an indication of the degree of wear of the bristles, two types of bristle hardness, rounded and polished bristle tips. |
| Mono-beam and small-beam toothbrushes for special purposes | One type of these brushes must be used, since only with their help can plaque be removed as much as possible from the cervical area, especially from the lingual and palatal surfaces of the teeth. |
| Irrigators | When there are not many natural teeth left, you should still fight for them, and irrigators can be used an unlimited number of times a day. If after each meal you remove food debris with a stream and lightly massage the adjacent gums, then the oral cavity will regain its former youth and freshness. |
Recently, a lot of products have appeared for partial and complete removable dentures , which have antiseptic, deodorizing properties and are intended not only for the treatment of dentures, but also for their storage.
Therefore, oral hygiene for persons with partial dentures (PRD) and complete dentures (CRD) should be considered in two ways: for persons with RDPR, it is individual hygienic care of the remaining teeth and gums, tongue and oral mucosa, and individual hygienic care for emergency patients; for persons with PSLD - this is individual hygienic care for the oral mucosa and tongue, and individual hygienic care for PSLD.
We have analyzed the main trends existing in individual oral hygiene . In each specific case, the dentist-prosthetist, together with the dental hygienist or, in his absence, with the periodontist, draws up an individual hygienic program for the care of dental prosthetics and dentures and periodically monitors its implementation. Therefore, it is so important to know which of the available personal oral hygiene products can and should be used.
Source Hygiene in the presence of orthopedic structures in the mouth
There are also additional oral hygiene products. These include:
- floss (dental floss), toothpicks;
- oral irrigators (before choosing the best irrigator, be sure to study the main characteristics of the models);
- means for cleaning the tongue: scrapers, scraper brushes;
- Mouth rinses, oral deodorants, teeth whiteners;
- denture treatment powders/denture treatment tablets;
- foam for oral hygiene (foam dissolves plaque well and is indispensable where it is not possible to use standard oral hygiene products; just hold the foam in your mouth for 20–30 seconds and spit).
The unique, multifunctional device JETPIK JP200-Elite combines an electric sonic toothbrush, irrigator and dental floss. The components and the device itself are stored in a convenient plastic container, which is ideal for traveling or storing in a small bathroom.
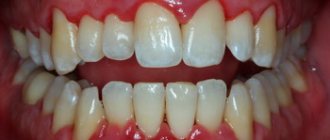
Oral hygiene is important not only for the prevention of caries, but also for free, comfortable communication with others. Stained yellow teeth and bad breath will not make anyone attractive. Aesthetic dentistry procedures such as veneers and expensive laser teeth whitening will not make sense without basic hygiene procedures.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
What happens if you don't maintain hygiene?
If you neglect the process of oral hygiene care, it can ultimately lead to many unpleasant consequences. Among them:
- Caries;
- Gingivitis (gum inflammation);
- Candidiasis (infection caused by bacteria of the genus Candida. Manifests itself in the form of a yellowish and grayish coating);
- Periodontitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the gums, characterized by tissue atrophy;
- Stomatitis (inflammation of the oral mucosa).
Free webinars on anti-aging medicine Learn about the features of the Anti-Age Expert International School, as well as the opportunities for improving your medical practice every day. The webinar program also includes fascinating reviews of innovations in anti-aging medicine and analyzes of the most complex clinical cases with recommendations that really work
Find out more
Results and discussion
The initial value of the Silness-Loe index in the group was 1.2±0.27, the average value of the Navy-Rustogi index was 0.7±0.11. At the beginning of the study, the differences in the average index values between the quadrants were not statistically significant: the ANOVA criterion value was 0.151 for the Silness-Loe index and 0.162 for the Navi-Rustogi index.
Within 4 weeks, a statistically significant decrease in the average values of the studied indices was noted in all quadrants (Tables 1, 2). The average value of the Silness-Loe index was 0.7±0.28, the average value of the Navy-Rustogi index was 0.5±0.16. At the same time, using the ANOVA test, differences in the average index values between the quadrants were determined, which indicates the unequal effectiveness of the hygiene products under study.
The T-test was used to compare mean index values between quadrants and identify the most effective hygiene products. A statistically significant difference in mean values was found between quadrants 1 and 2 (interdental brushes and floss), 1 and 3 (interdental brushes and a monotuft brush), 1 and 4 (interdental brushes and control), 2 and 4 (floss and control), 3 and 4 (mono-tuft brush and control). However, there was no statistically significant difference between quadrants 2 and 3, indicating the same effectiveness of floss and mono-tuft brush.
The results of the study suggest that training in the correct technique for brushing teeth and the use of additional hygiene products can increase the effectiveness of individual oral hygiene, as evidenced by a decrease in the values of hygiene indices. Note that the average values of the studied indices decreased even in the control quadrant, which we associate with increased motivation and improved manual skills. However, by comparing the average index values in different quadrants, it can be concluded that interdental brushes provide maximum effectiveness of oral hygiene. There was no significant difference in the effectiveness of floss and a single-tuft toothbrush in this study.
The data obtained generally coincide with the results of previous studies. According to the results of a meta-analysis of 22 studies conducted by G. Kotsakis et al. (2018), irrigators and interdental brushes are recognized as the most effective means of interdental hygiene [9]. According to D. Bourgeois et al. (2016), interdental brushes in combination with a manual toothbrush can significantly reduce bleeding of the interdental papilla when brushing teeth [10]. At the same time, researchers note that brushes are more effective than floss both in terms of plaque and bleeding [11, 12]. However, to ensure high-quality removal of biofilm in the interdental space, it is necessary to first determine the individual size of the brush [13].
Material and methods
The study was conducted at the Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of the Perm State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov. A non-randomized controlled trial with a split-mouth design was conducted.
At the first stage, 76 patients were screened and a study group of 25 people (10 men and 15 women) was formed.
Inclusion criteria: written informed consent of the patient to participate in the study; age from 18 to 35 years; intact periodontium.
Non-inclusion criteria: presence of non-removable orthopedic and orthodontic structures in the oral cavity; partial edentia; presence of implants; the presence of carious cavities; presence of inadequate restorations according to class II; supragingival calculus.
Criteria for excluding patients from the study: patient refusal to further participate in the study; failure to comply with study recommendations.
All patients were recommended a Curaprox 5460 toothbrush (Curaprox, Switzerland) as the main hygiene product; in the 1st quadrant, individually selected CPS Prime brushes (Curaprox, Switzerland) were additionally used; in the second, Curaprox floss (Curaprox) , Switzerland), in the third - monobeam brush Curaprox 1006 (Curaprox, Switzerland), in the fourth quadrant no additional products were used.
The hygienic state of the oral cavity was assessed using the Silness-Loe and Navy-Rustogi indices immediately before the start of the study and after 4 weeks.
The study was approved by the Local Ethics Committee of the Perm State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov (Sechenov University): Order No. 470 R dated October 19, 2012 “On the creation of a local ethics committee”, minutes No. 05−17 of the meeting of the Local Ethics Committee dated 06/14/17.