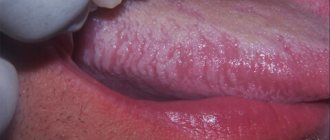
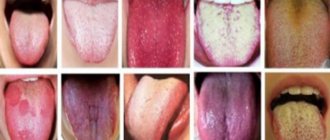
What kind of coating on the tongue indicates health problems?
If there is a thickening of the plaque, a change in its color and the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth , this is already the result of the activity of bacteria and fungi. Of course, the body is not a sterile substance and microorganisms are always present in it, but the immunity of a healthy child controls their numbers. When immunity decreases or any disease occurs, there is a significant increase in pathogenic bacteria and fungi, which is accompanied by the formation of plaque on the child’s tongue.
How is plaque formed?
Epithelial cells on the surface of the tongue are constantly exposed to fairly aggressive factors: acidic foods, temperature changes, bacteria. That is why their lifespan is not long and after they are exfoliated, young cells appear. If the processes of changing cellular layers are excessively active, then the upper layers do not have time to peel off and remain on the surface of the mucosa in the form of plaque.
Another factor in the formation of plaque can be microorganisms. Children often do not pay enough attention to oral hygiene, as a result of which microscopic particles of food can remain between the lingual papillae, which become a place for active reproduction of bacteria. Taking antibacterial drugs often provokes the growth of pathogenic microflora in the mouth (fungi), some varieties of which are quite brightly colored.
Causes of plaque on the tongue
There are many reasons why various plaques may appear on the tongue: from the banal consumption of foods that can change the color of the tongue, to serious health problems that require immediate medical attention.
Read also: Computer anesthesia STA – dentistry WITHOUT PAIN!
The very first thing you need to do when you discover strange coatings on a child’s tongue is to remember what the baby ate in the last 24 hours. Very often, sweet carbonated drinks, caramels or other sweets contain active dyes that can give the oral mucosa the most exotic shades: crimson, purple, green, orange and others. Even natural berries and fruits can radically change the color of the tongue. Therefore, there is no need to panic right away. You should ask the child to brush his teeth and tongue, and then evaluate their condition and color. If the plaque has not changed or has reappeared without connection with food intake, then this is a reason to urgently visit your pediatrician.
What to do if your tongue changes color?
If you notice a plaque of a specific tone in a child that does not go away for a long period of time, you should contact your pediatrician. Self-administration of medications is unacceptable. After the examination, the pediatrician will recommend an additional consultation with specialized specialists: a dermatologist, an infectious disease specialist, a gastroenterologist, a toxicologist, and a dentist.
Only after the examination, all doctors have the opportunity to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. Typically, when a child has a purple tongue, the following therapeutic intervention is recommended:
- Problems with the digestive system - antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antispasmodics are prescribed;
- If there is a lack of vitamins in the body, the pediatrician will prescribe the required fortified complexes that will replenish the lack of nutrients in the internal organs;
- If a fungal infection is detected, antifungal drugs or antibacterial substances are required for treatment.
You should definitely make sure that your baby cleans his mouth with toothpaste that contains antibacterial ingredients. During therapy, as well as after the treatment process, it is recommended to rinse the mouth for a long period of time with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, soda-saline solution or Furacillin.
In addition to medications, you can use infusions of medicinal herbs to irrigate the oral cavity: a collection of cinnamon and cloves, calendula and medicinal chamomile.
The doctor will develop a special therapeutic diet for the baby that will prevent the condition from worsening and prevent the possibility of such a dangerous symptom from appearing in the future. It is required to give up fast food products, not to consume smoked meats, pickles and other heavy foods, as well as concentrated juices and carbonated drinks.
White coating on the tongue
White plaque can be found in the oral cavity of a baby most often.
This phenomenon also happens normally when, after a night’s sleep, a thin white coating without an unpleasant odor is found on the tongue, disappearing after hygiene procedures and not causing any discomfort or unpleasant sensations.
The appearance of a dense whitish plaque, which is extremely difficult to remove from the surface of the tongue and does not disappear after brushing your teeth, may indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, enteritis or dysbacteriosis). This phenomenon is often accompanied by bad breath. In addition, children may present complaints that may indicate gastrointestinal pathology:
- abdominal pain of various localizations;
- bloating;
- stool disorders;
- change in appetite
In order to get rid of such white plaque, it is necessary, first of all, to examine the digestive system and eliminate even the most minor disturbances in its functioning.
Read also: Drilling teeth? NO thanks, we use ICON!
In infants up to 2 months of life, thrush or oral candidiasis is a common occurrence in a nursing mother, especially after taking antibiotics or an error in diet. With this pathology, abundant cheesy white deposits appear on the tongue and cheeks, which are easily removed, and small ulcers are found underneath them. After starting treatment for thrush with antifungal agents and treating the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions, the tongue and other mucous membranes quickly cleanse and regain their previous appearance.
What parents should pay attention to and be wary of
- Breathing through the mouth if the child does not have a runny nose.
- No gaps between teeth by 4-5 years.
Baby teeth are small and there is usually always room for them, even if the jaw has not developed enough. As the child grows up and prepares for a mixed dentition, so-called trema should appear between the baby teeth - small but distinct distances. When baby teeth fall out, permanent teeth will erupt, which are much wider than baby teeth, and they should have enough space for normal growth and the formation of an even, beautiful dentition.
- Observe the child’s swallowing of saliva; normally, swallowing occurs imperceptibly, without tension in the facial muscles.
Usually, during an appointment, a pediatric dentist draws the attention of parents to the emerging problems of forming a correct bite and refers such children to an orthodontist.
If this does not happen, it is necessary to show the child at the age of 4-5 years to a pediatric orthodontist, preferably one who takes into account the functional approach in his work.
Gray coating on the tongue
A gray coating on the tongue can be a sign of some infectious diseases.
For example, with scarlet fever, on the very first day the mucous membranes become covered with a dirty gray coating, which, starting from the tip of the tongue, gradually disappears and reveals a “raspberry tongue” - enlarged papillae on a bright red background, which is very reminiscent of raspberries.
With diphtheria, gray filmy deposits can be found on the root of the tongue, which are difficult to separate. Such plaques spread to the mucous membranes of the throat, palatine arches and are accompanied by coughing and attacks of suffocation.
Treatment of such infectious diseases is carried out only in a hospital setting. After healing, all plaque on the tongue disappears.
Dehydration in a child can also lead to the formation of a gray coating on the surface of the tongue. At the same time, the mucous membranes look dry and dull. Replenishing the required volume of fluid quickly eliminates this symptom.
Bald
Normally, the lingual surface is covered with a large number of small taste buds, which give it a velvety appearance. If such papillae die or atrophy for any reason, “bald” spots appear. They are pink in color, irregular in shape and do not spread to the mucous membranes of the cheeks, lips or gums.
Reasons that can cause the appearance of such pink “bald” spots:
- Inflammatory diseases (glossitis, stomatitis).
- Tongue injuries.
- Burns from heat or chemicals.
“Bald” spots do not cause any inconvenience to children, but may slightly change the taste sensations. It is impossible to cure such formations, since the taste buds cannot be restored.
If you find that your one-year-old or older child’s tongue has become spotted, you should not panic and try to treat it yourself. Also, the appearance of spots on the tongue should not be ignored, as they may indicate the presence of serious diseases. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will find out the exact cause of such changes and, if necessary, select appropriate treatment for the child.
Yellow coating on the tongue
A dense yellow coating on the tongue indicates pathology of the liver or biliary tract.
Often in children, diseases of the biliary system occur without a clear clinical picture, and the presence of bile stagnation can only be suspected by a change in the color of deposits on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
If a child has a yellow coating on the tongue , it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and have an examination of the internal organs and the biochemical composition of the blood.
Read also: Medication sleep - WHAT? For what? HOW?
Geographical
If red spots and a white coating along their edges appear on the tongue, then this is a sign of a geographic tongue - desquamative glossitis. The disease is not inflammatory in nature and may indicate some hormonal disorders, worms and problems in the digestive system. Such spots do not have smooth outlines, they quickly change their location and do not bother the child in any way. They can be oval, round or have fancy shapes.
This disease lasts a long time and often goes away on its own after some time, even without specific therapy. Sometimes antiseptics, vitamins and drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration processes are used to treat geographic tongue. But most experts (for example, Dr. Komarovsky) believe that there is no need to treat geographic spots.
Green coating on the tongue
The appearance of a green coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue often frightens parents, especially if it is found in a newborn or infant.
The most common cause of this phenomenon is candidiasis - a fungal infection of the oral cavity that occurs due to imperfect immune defense in the body of a 1-year-old baby or while taking strong antibacterial drugs.
This plaque has varying color intensities and can spread to other parts of the oral cavity, found on the cheeks, palate and lips. After removing it, you can see the red surface of the tongue with small blisters or ulcers, which cause discomfort to the child.
You should start treating green plaque only after consulting a doctor. Therapeutic measures will consist of taking special drugs with antifungal action and local antiseptics to treat thrush and prevent bacterial complications.
Read also: How bite affects posture and spinal health
What are the symptoms in babies?
Symptoms may range from mild to severe. This depends on the level of bilirubin in the blood and the duration of the disease. The causes and consequences of jaundice in newborns can vary, but there is one common characteristic - jaundice of the skin and sclera. It is worth noting that the eyes show symptoms faster. The baby may experience increased drowsiness with a decreased sucking reflex. Convulsions may occur. Without treatment, advanced jaundice can cause deafness, mental retardation and paralysis.
Does your newborn have symptoms of jaundice?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Brown coating on the tongue
A brown tongue in a child is not such a rare occurrence. There can be many reasons for this:
- Severe diseases of the digestive system , accompanied by inflammatory changes, stagnation of bile in the bile ducts, and disruption of the digestive processes.
- Constant dehydration of the child's body due to high ambient temperatures or insufficient fluid intake.
- Insufficient intake of B
- Taking certain medications : antibiotics, antiseptic solutions, concentrated herbal decoctions.
It is very difficult to establish the exact root cause of the appearance of such a dark plaque. This can only be done by an experienced doctor, who, after additional examinations, will be able to prescribe the optimal treatment.
Black coating on the tongue
The presence of a black coating on a child’s tongue looks quite scary, and there may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
Bacterial sore throat is often accompanied by the appearance of dark plaques on the mucous membranes, even black. In this case, the child will have signs of inflammation in the tonsils: red throat, high fever, pain when swallowing, weakness.
Hidden forms of diabetes mellitus, which lead to persistent disruption of the acid-base balance in the body. Excess acid or acidosis will cause darkening of the tongue.
Taking some antibiotics causes the growth of pathogenic microflora in the mouth, which causes the mucous membranes to become permanently stained black.
Treatment of such plaque will consist of eliminating the causes that caused its appearance. After a sore throat is treated, medications are stopped, or diabetes is identified and compensated for, this symptom will most likely go away on its own.
Dark
Dark spots on the tongue often occur when eating food that contains dark pigments that color the plaque on the surface of the mucous membranes. Such spots do not pose any danger to the child and disappear after hygiene procedures. But there are a number of conditions that manifest as dark spots in the mouth and which can have very serious consequences.
Black
Black spots on the tongue in children most often appear during a long course of antibiotic therapy as a result of the active proliferation of microorganisms and fungi. Blackening of the tongue develops gradually and can last up to 2-3 weeks. The main treatment for this condition is to restore normal microflora in the child’s intestines and oral cavity. For this purpose, eubiotic drugs are prescribed (for example, Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin).
It is extremely rare that black spots on the tongue appear as a result of deep degenerative processes accompanied by necrosis of areas of the mucous membrane. This condition is very dangerous and requires emergency medical attention. The treatment of such spots is often surgical.
Blue
Blue spots in a child's mouth are a rare occurrence. They may appear in the following situations:
- The presence of severe heart failure due to heart disease and defects. Spots on the tongue appear due to stagnation of blood in the venous bed and are accompanied by blue discoloration of the lips and limbs. Their treatment consists of eliminating cardiac pathology and normalizing blood microcirculation in the vessels.
- With the growth of a benign vascular tumor - hemangiomas. This blue spot is most often single. Treatment is only possible through surgery.
Blue coating on the tongue
A blue tongue is a sign of blood stagnation.
Very often, various diseases of the cardiovascular (congenital heart defects, arrhythmias, heart failure) and nervous system (hemorrhages, cysts, epilepsy) lead to the fact that blood flows through the tissues more slowly than it should - cyanosis or cyanosis appears on the limbs, lips and language. Therefore, if you notice such a symptom in your child, you should urgently contact your doctor for advice.
Read also: Now the beauty and health of your child is completely in your hands
Prevention
In order to prevent the appearance of plaque on a child’s tongue, there are a number of preventive measures that many experts focus on:
- The room in which the child lives should always be clean, well ventilated and humidified.
- You should not prescribe antibiotics to your child yourself. The use of such medications must be strictly justified.
- It is necessary to closely monitor the baby's health. If the slightest symptoms appear that indicate a possible disease from the internal organs, you should urgently seek medical help.
- Limit your child's consumption of sweets containing synthetic coloring pigments: sweet carbonated drinks, candies, chewing gum. This will not only prevent the appearance of active staining of the tongue, but will also preserve the health of delicate children's teeth.
If plaque does appear on the tongue, there is no need to try to remove or treat it yourself. Consult your doctor about the possible causes of this phenomenon and the necessary treatment for it.
Posted in For parents by biglamed
What diseases does a red tongue hide?
A red tongue can be a symptom of diseases of various etiologies, including:
- angina;
- flu;
- chickenpox,
- scarlet fever;
- stomatitis;
- glossitis;
- pneumonia;
- Kawasaki disease;
- gastritis;
- severe poisoning;
- renal failure;
- vitamin deficiency (vitamin B deficiency).
As you can see, the list of diseases is quite wide and requires visiting not only an otolaryngologist, but also, if necessary, other specialized specialists: dentist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, etc.