Usually, the healing of the hole after tooth extraction occurs painlessly and does not cause any sensations in the patient. It would be good if everyone knew how this process works and how to speed it up.
Proper oral care after tooth extraction and following all the dentist’s recommendations will help speed up the healing of the hole and avoid complications.
Natural processes
Even if the tooth extraction was “simple”, pain in the socket at the site of the extracted tooth is a natural consequence that will bother you for 3-4 days.
This is normal and nothing to worry about, but if the pain causes you severe discomfort, consult your doctor and he will recommend that you take painkillers.
Sometimes regular cold compresses applied to the cheek in the area of the extracted tooth will help relieve pain. This could be a cloth soaked in cold water or ice from the freezer wrapped in a cloth.
Tooth socket
In the case of “complex removal”, in which the gums were cut and sutured, special tools were used to gouge out the root, the pain after the procedure will be felt much longer (the doctor will definitely warn you about this), but will still gradually go away on its own.
If the pain does not go away for more than ten days, consult your doctor: there may be complications in the tooth extraction and you will need dental intervention to eliminate them.
Impacted wisdom tooth
These are usually the hardest eights to remove out of all the others. We have already numbed the surgical field. What's next?
It's under the gum! So, we take a scalpel in our hands and make a delicate incision in the area of the tooth being removed. This creates access to the wisdom tooth being removed. It is isolated from the surrounding tissues using special instruments, and now we can visually assess its position and choose a removal technique.
If the tooth does not erupt, it means that something is preventing it. This “something” will also interfere with its removal, and this “something” could be a neighboring tooth, a bony protrusion, etc. However, you won’t also remove the seven to get to the wisdom tooth, right?
Special surgical tip for removing wisdom teeth. Rotates at the right frequency, provides the right torque, does not burn tissue or inflate emphysema. In surgery, we use only such devices.
Therefore, we divide the tooth into parts. Using a special tip with a cutter speed of 150,000 rpm - this is no longer a simple angle cutter, but not yet a turbine cutter. The latter, by the way, is highly undesirable to use for removing teeth, because at 500,000 rpm it is easy to burn everything with a hellish flame, and with air from the cooling nozzle you can also inflate emphysema over half your face. In general, for removal you need to choose the right tools; there are no trifles or compromises here and cannot be. And you should think a hundred times before removing such problematic teeth in a one-chair dental office at a rural club on the “Half-Empty Bins” collective farm.
Impacted teeth are removed mainly with an elevator, and not with forceps, as many are accustomed to thinking
So, we divide the tooth into 2-3 parts in order to remove it carefully and with little trauma to the surrounding tissues. And teeth are usually removed using an “elevator” (in the picture on the left). Forceps, which everyone associates with removal, are actually used extremely rarely.
Well, the tooth has been removed. Next, we clean the tooth socket from “sawdust” and small tooth fragments that might remain. Using a curette.
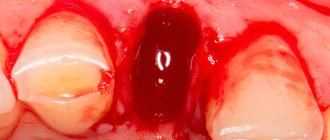
When removing wisdom teeth, no biomaterials are used; the hole is filled with a blood clot on its own, this is quite enough for normal healing.
Moreover, “pushing” biomaterials into the hole can complicate the healing process, so let the regeneration process take place naturally and simply, and not fancy, as some doctors suggest.
After removal, resorbable (absorbable) sutures are placed on the hole; most often they do not need to be removed.
The clot is in place. Next, we bring the edges of the wound together and put stitches so that food doesn’t get stuck in the wound, it doesn’t bleed too much, and it heals faster. But at the same time, the sutures should not be tight, because the wound may bleed significantly during the first 24 hours. And if you don’t create an outflow, edema often develops.
Alveolitis
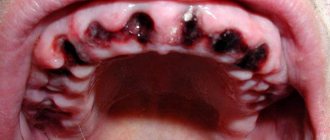
Very often, after the removal of any tooth, the patient develops alveolitis - the tissues in the socket of the extracted tooth become inflamed due to the fact that a protective blood clot has not formed there (or was washed out during brushing or rinsing the teeth).
The main symptom of alveolitis is significant pain in the area around the socket of the extracted tooth. At the same time, the gums swell, the temperature rises and general malaise is observed.
Alveolitis can be cured only by relieving inflammation, for which special anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and sometimes physiotherapy.
You should not try to cure alveolitis yourself based on the recommendations of friends (“I’ve already had this happen”) or information from the Internet (“the best dentists recommend”). Such treatment can lead to more serious consequences, in the worst case - even osteomyelitis: inflammation of the bone tissue of the jaw.
Healing of the socket with gum inflammation
If tooth extraction was carried out against the background of inflammation, or the inflammatory process in the gums developed later, epithelization of the wound begins on the 10th -14th day, bone beams appear only by the 15th day. A significant part of the socket is filled with young osteoid tissue only by the end of the second month.
After a complex tooth extraction, when the gums rupture and the walls of the socket are traumatized, the edges of the gums cannot come together for a long time and the epithelization process slows down. Wound healing can only be completed after 1-1.5 months. In this case, the development of new bone tissue is delayed.
Socket bleeding
Socket bleeding most often appears immediately after surgery, although sometimes several days pass between tooth extraction and the onset of bleeding.
Bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth can occur for several reasons:
- The patient actively disturbs the socket of the extracted tooth - he feels it with his tongue or hands, inaccurately brushes his teeth or aggressively treats the sore spot with an irrigator;
- Physical damage in the socket area - gum injury, fracture of the alveoli, and so on;
- Concomitant diseases of the patient: hypertension, leukemia, etc.
Treatment for alveolar bleeding depends on the cause and source of bleeding.
Healing of the hole
If the gums bleed in the area of the socket, then the problem may be complications after surgery, and the wound will need to be stitched.
If blood comes from the vessels directly in the walls of the socket of the extracted tooth, then it is first cooled, after which the vessels are compressed and a tampon with a hemostatic agent is placed in the socket for 4-5 days.
If local remedies do not give the desired effect, the dentist prescribes the patient to take general hemostatic agents.
How long does it take to remove a front tooth?
The time it takes to remove the upper teeth can vary from a few minutes to an hour. On average, the operation takes 15-20 minutes. Much here depends on the initial situation and the qualifications of the dentist.
Removing front teeth is usually simple. Some difficulties may arise when extracting the upper canine, since it has a long, massive root with an often curved apex.
During surgery to remove a front tooth, the patient sits in a chair with a slightly reclined back and headrest. The doctor is in front of the patient on the right. The procedure looks like this:
- the gum is separated from the edge of the alveolus, and the circular ligament is separated from the neck;
- the forceps are applied to the tooth, moved under the gum and fixed;
- the dentist rocks or rotates the tooth to break the fibers connecting the root to the walls of the socket;
- the front tooth is removed from the socket;
- The surgical site is inspected and broken root fragments are removed from the socket.
How to avoid problems?
First of all, after tooth extraction, you must carefully follow your dentist’s recommendations for the rehabilitation period.
After the operation, the doctor will apply a cotton swab with a hemostatic solution to the wound for 30-40 minutes. You must remove it from the well after the designated time has passed very carefully so as not to damage the clot.
After tooth extraction, you should not eat any food for two hours so that its fragments do not fall into the fresh wound.
For several days, you should not disturb the socket of the extracted tooth - neither with your tongue, nor especially with your hands.
If, after the period indicated by the doctor, the pain in the socket does not go away, moreover, it intensifies, and at the same time there is redness and swelling of the gums, pus from the socket, fever and general malaise - be sure to consult a doctor.
There is no need to hope to fix the problem at home; self-medication will only make it worse for yourself.
Indications for care after removal of the upper tooth
- After removing a front tooth or root tooth, the doctor places a gauze swab into the hole, the purpose of which is to create compression and block small capillaries. This is necessary to stop bleeding. You can keep the tampon in your mouth for no more than half an hour. If it remains in the hole longer, the wound may become infected.
- The blood clot (thrombus) that forms in the hole should not be touched with the tongue, toothpick, hands, or try to rinse it out of the mouth. The blood clot protects the wound from penetration of microbes and promotes its healing.
- For two to three hours after the removal of the upper teeth, you should not eat or drink, so as not to infect the socket. Within three hours, the blood clot will be completely formed, then the likelihood of food getting into the hole will be negligible.
- For several days after surgery, you should refrain from spicy foods and hot drinks.
- On the day of removal of the upper tooth, it is not recommended to perform any hygienic manipulations in the oral cavity. You can brush your teeth the next morning, but avoid the surgical area. In the future, you can return to normal dental care.
We also advise you to read the article about the removal of upper wisdom teeth
Stages of socket regeneration
How long does it take for damaged soft gum tissue to heal? It all depends on the individual characteristics of the human body. Regeneration time varies widely - from several weeks to several months. The healing period depends on the complexity of the dental work performed, the type of unit removed (soft tissue takes a long time to heal after the removal of wisdom teeth and elements with a large number of roots), the presence of chronic and infectious pathologies.
How does the hole heal after tooth extraction? There are several stages of healing:
- Formation of a blood clot (after 2-4 hours). At this time, it is advisable to refrain from rinsing the mouth and eating food. Injury to the clot leads to infection of the soft tissues of the gums and the development of alveolitis.
- The stage of formation of granulation tissue 2-3 days after the intervention. This tissue is the basis for the growth of new epithelium.
- The formation of the epithelium begins on days 7-14 after the intervention.
- Formation of the bone tissue of the socket from the edges to the center - 2-3 weeks.
- Mineralization of osteoid – 21 days from the moment of surgery.
- Calcification of bone trabeculae – after 2-3 months.
Stages of socket healing
How long does it take for gums to heal? The answer to the question depends on the volume of damaged tissue. If the doctor had to apply stitches during the intervention, then gum regeneration can be observed only after a week. Complete tissue restoration is observed only after 3 weeks, at the moment when the formation of new bone tissue begins.
After removing the figure eight, the gums will heal only after a month. This fact must be taken into account so as not to waste time fighting natural symptoms. Stress will only slow down the recovery of the extracted tooth socket.
In normal condition, the wound stops bleeding 3 days after extraction. The clot changes its color from burgundy to light or yellowish. This condition is explained by natural physiological processes: gradually saliva washes away hemoglobin from the clot, leading to its discoloration. Despite the change in color, the clot retains its structure and prevents re-bleeding and infection of the socket.
Do not clean the injured area with a brush or touch it with your hands. Failure to comply with these conditions and the dentist’s recommendations may lead to suppuration of the wound and formation of gumboil in the gums. One of the most common consequences of the removal of multi-rooted teeth is alveolitis, manifested by severe pain and inflammation of the operated area. If timely measures are not taken, the disease can be complicated by phlegmon, sepsis and abscess.
Lightening the hole after tooth extraction by 4-5 days
After 5 days, the wound will regenerate, but the patient will experience discomfort for several more days when eating food. If there is no severe pain, then a repeat visit to the dentist is not required. At this time, it is important to thoroughly clean the oral cavity and try to chew food on the healthy side of the jaw.
How many days does it take for the pain to disappear? This is usually observed on day 7-8. Granulation tissues gradually replace the blood clot. Only in the middle of the wound are epithelial particles observed. If by this time the pain does not subside, you should immediately consult a doctor. It may be necessary to re-open the cavity and rinse it with antiseptics. In practice, complications are rarely observed in patients who follow preventive rules after extraction.
What does the wound healing process depend on? Several factors should be noted:
- Age and immune system of the patient. At a young age, the wound heals faster due to accelerated metabolism. In elderly patients, the socket scars for several weeks longer, which is considered normal.
- Type of element to be removed. The hole after the removal of a wisdom tooth is much larger and deeper than after the extraction of other elements. With complex removal of the figure eight, regeneration of soft tissues is observed only on days 7-8. Gums heal worst after removing elements with crooked roots and crumbled crowns.
- Possibility of infection. The main sign of the pathological process is redness and inflammation of the surgical site. After removing a single-rooted tooth, the sign should disappear on the 5th day, after removing units with numerous roots - on the 13th day.
- Oral care. After the operation, the specialist advises the patient about the features of the rehabilitation period, which include rinsing (from day 3), changing the diet, and careful oral care. It is especially important to adhere to preventive measures after extraction of the lateral elements.
To accelerate the regeneration of soft gum tissue, ordinary and cosmetic sutures are used. In the first case, the patient will need to return to the dentist for suture removal. Cosmetic materials dissolve independently in the oral cavity.