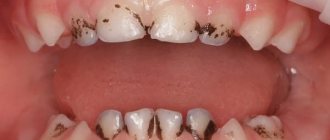
A healthy child's tongue has a soft pink tint , but sometimes a dark gray or black coating appears on the surface of the baby's taste organ.
A change in the color of a child's tongue makes parents seriously worried.
There is no need to panic right away - black coating on the tongue in children is not always pathological .
Why might it appear?
Keep in mind! Most often, a child’s taste organ darkens for the following reasons:
- Eating large amounts of food containing natural or synthetic dyes . Candies, tea, lemonade, dark berries (currants, blackberries, blueberries, mulberries), as well as jams and compotes based on them, can color your tongue dark.
- Taking certain medications. This organ is often colored dark by iron preparations in the form of drops, which are prescribed to the baby to treat anemia. Also, the color of the taste organ often changes during prolonged treatment with antibiotics, or when taking activated carbon.
In rare cases, the tongue darkens for reasons unknown to modern medicine.
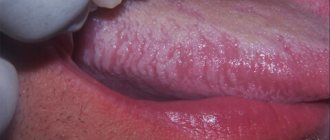
Thus, the surface of the taste organ may darken due to excessive growth of the papillae of the tongue, followed by their keratinization and darkening .
Stay up to date! This phenomenon is called “villous tongue”; in the absence of complaints, special treatment is not required, and the condition of the taste organ is normalized within a few weeks.
Less commonly, the cause of darkening of a child’s tongue is various pathological conditions of organs and body systems:
- gastritis;
- colitis;
- enteritis;
- pathologies of the gallbladder and pancreas;
- acute deficiency of B vitamins and vitamin PP;
- dysbacteriosis;
- stomatitis;
- caries;
- oral candidiasis;
- Crohn's disease;
- lead poisoning;
- immunodeficiency, HIV;
- severe dehydration;
- infectious diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract: sore throat, ARVI, bronchitis.
Note! The cause of dark plaque in a baby can also be acidosis - a shift in the acid-base balance of the body towards increasing acidity.
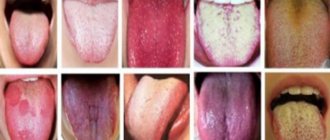
A red or pale tongue is not the norm!
Both options indicate pathological changes occurring in the child’s body:
- A crimson-red tongue always indicates the presence of an infection (viral, bacterial or fungal). Most often it is tonsillitis, scarlet fever, stomatitis or glossitis.
- A red and shiny tongue is a sign of anemia, exhaustion and severe stomach disease;
- A cherry tint is a sign of influenza and measles, as well as general intoxication or kidney dysfunction;
- A bluish color indicates a lack of oxygen; there is reason to suspect disorders in the cardiovascular system or lungs;
- Purple color may indicate blood and lung diseases, heart failure.
- A too pale tongue, being penetrated by blood vessels, a priori cannot be lighter than blood. In most cases, this sign indicates exhaustion, deficiency of folic acid or vitamin B 12.
Let us remind parents that very often there may be a coating on the surface of the tongue, the color of which also has its own characteristics.
Associated symptoms
If a black coating is detected on the child’s organ of taste, you should pay special attention to the child’s accompanying symptoms and complaints.
Possible symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea with particles of undigested food;
- loss or abnormal increase in appetite;
- stomach ache;
- dry or bitter mouth;
- weakness;
- temperature increase;
- headache;
- redness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tonsils;
- pain when swallowing.
It is worth noting! Sometimes, even in the presence of dark gray and black deposits on the tongue, the child voices absolutely no complaints.
The complete absence of accompanying symptoms is characteristic of fungal infection of the mucous membranes of the mouth, as well as when plaque occurs for non-pathological reasons.
White spots on a child's tongue
The easiest way to notice the formation of white areas in the oral cavity of children, which can signal the following problems:
- 1 Candidiasis is an inflammation caused by excessive growth of fungi in the mouth. The spots look like cottage cheese flakes. The problem occurs when the body's defenses are reduced.
- 2 Stomatitis is a common inflammation of the oral cavity in children, accompanied by painful white spots. The cause of infection is bacteria1.
- 3 Leukoplakia is a consequence of frequent minor injuries accompanied by infection.
- 4 Diseases of the digestive system: the tongue is often called an indicator of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, so the presence of white areas in combination with symptoms of digestive dysfunction is a reason to worry about the health of the stomach and intestines2.
In what case should you consult a doctor and undergo an examination?
If the deposits disappear on their own after rinsing your mouth or drinking, there is no need to go to the hospital, since the cause of the darkening of the tongue is most likely food.
If the plaque does not disappear when rinsing, but appears again after cleaning the tongue, you should make an appointment with a pediatrician.
If the blackening of the surface is accompanied by acute abdominal pain, diarrhea or vomiting, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
You should not try to treat your child yourself or try folk remedies without consulting a specialist and finding out the reasons for the blackening of the tongue.
You should know! Self-medication can cause serious harm to the baby's health.
Prevention
Dark spots on the tongue will never bother you if you follow the following rules and recommendations:
- Minimize the consumption of spicy, fatty, carbonated water, coffee.
- Maintain good oral hygiene. In addition to teeth, clean the inside of your cheeks, gums, and tongue. Teach children to this. Use plant extracts for rinsing. Don't skimp on toothpaste.
- Get rid of bad habits: smoking and alcohol abuse.
- When treating with antibacterial compounds, strictly follow medical recommendations.
- Expand the amount of physical activity in accordance with age and health status.
- Add bran, fruits, and vegetables to the menu. Nutritious smoothies are beneficial. Instead of black tea, drink mint, strawberry, linden or other herbal tea.
- If you are prone to sore throat, try not to injure the mucous membrane of the throat, for which purpose eat dishes in the form of puree. Inhalation is carried out using sea buckthorn or fir oil.
- If a child’s tongue turns black, consult a pediatrician to find out what new food triggered such a symptom, so that you can then help the child adapt painlessly. Treatment methods for children do not differ from those for adults. Great care and smaller dosages will be required, as determined by your doctor.
- Baby food should be natural and consist of fresh products. On the recommendation and under the supervision of a pediatrician, vitamin and mineral complexes can be given to the child to strengthen the immune system.
Do not practice self-medication, which rarely ends well. If the condition worsens, immediately contact a doctor. Regularly visit an ENT doctor, dentist and other specialists for preventive purposes. Bitter salt for cleansing the intestines, you can find out at the link.
How is diagnosis carried out?
The doctor begins the diagnosis with a visual examination of the patient , assesses the appearance of the tongue and the nature of the deposits, and interviews the child and mother for complaints and associated symptoms.
Next, the doctor prescribes tests and diagnostic procedures:
- clinical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- blood chemistry;
- culture of microflora from the oral and nasal cavity;
- stool occult blood test;
- Ultrasound of the digestive organs.
If necessary, to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor can give a referral for gastroscopy and colonoscopy .
For your information! A specialist can prescribe all diagnostic procedures in a complex, or several of them separately.
If necessary, the pediatrician gives a referral to see specialists: dentist, otolaryngologist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist.
Belching in toddlers, which provokes a reaction
Belching occurs due to swallowing air while eating.
The normal amount of regurgitation in a toddler is 10 to 15 times a day. A larger number indicates the development of a pathological process. Additional factors that provoke belching:
- Increased activity during feeding or after eating.
- Tight swaddling, rompers or panties.
- Binge eating.
- Violation of feeding technique.
- Aerophagia is the swallowing of air while eating.
- Wrong combination when introducing complementary foods. For example, fruit puree after a cutlet.
- Dad or mom are smokers. The toddler inhales nicotine vapor. This helps weaken the stomach and sphincter muscles.
Treatment
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
In each individual case, the treatment complex is selected individually based on the reasons for the formation of black deposits on the tongue, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Treatment of black plaque:
- If the cause of the formation of black deposits is dental problems , treatment should be performed by a dentist.
- In cases where plaque has formed due to prolonged antibacterial therapy, the doctor cancels it or prescribes another drug.
- For candidiasis, antifungal drugs are prescribed (Fluconazole, Pimafucin)
- If you have stomatitis and fungal infection, rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions (Chlorophyllipt, Hepilor).
- For gastritis, antacids (Maalox) and drugs to enhance the protective properties of the gastric mucosa are prescribed .
- In case of vitamin deficiency, are prescribed .
- If the cause of the black plaque is poisoning, it is recommended to take sorbents (Enterosgel, Polysorb, activated carbon).
If necessary, the doctor prescribes additional medications:
- probiotics (Acipol, Linex, Bifidumbacterin) and prebiotics (Duphalac, Lactusan) to populate the intestines with beneficial microorganisms and stimulate the production of your own healthy microflora;
- interferons to strengthen the immune system (Cycloferon, Kagocel).
Important! The specialist also gives mother and child recommendations on nutrition and oral hygiene, which must be strictly observed during the period of active treatment and after it.
Should I worry?
When conducting an initial diagnosis, the doctor will pay attention to the thickness of the plaque, color intensity and other features. The most important sign of a specific pathology is the localization of layers on different parts of the tongue:
- Damage to the tip
indicates problems with the heart and blood vessels. - Coloration going deep into the organ
indicates breathing pathologies. - Spots on the central part
towards the root indicate diseases of the digestive canal. - On the sides
- about dysfunction of the spleen and liver.
The coating also varies in consistency. It can be greasy, curdled, wet or dry. In terms of area of distribution, it sometimes looks like clear spots, small inclusions, or completely covers the tongue. It is also important how the plaque is removed:
- Painless, but difficult.
- In the form of film.
- It is difficult and accompanied by severe pain.
Black deposits also appear against the background of other symptoms, such as:
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Thirst.
- Bad breath.
- Pain in different parts of the body.
- Fever.
- Yellowness, pallor or bluishness of the skin.
- Losing weight.
- Diarrhea or constipation.
- Heartburn, belching.
Such symptoms are only part of the overall picture. It will differ for a particular patient with a certain pathology. A black coating on the tongue can be a temporary phenomenon, caused by the influence of food pigments, both chemical and natural. There are many of the latter in blueberries, black currants, and mulberries. In such cases, there is definitely no reason to worry.
A similar situation develops after taking liquid iron-containing drugs or activated carbon. Slight darkening of the surface of the tongue occurs in those who like sweets with dark dyes, coffee or tea. It is not difficult to eliminate such plaque; just rinse your mouth several times or exclude the corresponding foods from your diet. It’s another matter when the nature of the symptom is related to the source of the pathological property.
conclusions
- there are both pathological and non-pathological causes of darkening of the tongue in a young child;
- plaque formation may be accompanied by alarming symptoms, such as vomiting and fever, or may occur without the appearance of additional symptoms and complaints;
- if the plaque does not disappear on its own, but appears again after cleaning the tongue, you should make an appointment for the child to see a doctor;
- Treatment can be prescribed only after a comprehensive examination and clarification of the causes of darkening of the tongue;
- the appearance of the taste organ will return to normal when the causes of the formation of black plaque are eliminated.
Is plaque after taking antibiotics normal?
When taking antibiotics, it is normal for .
The symptom disappears within two weeks and does not require specific treatment.
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe antifungal drugs or drugs to strengthen the immune system of a small patient.
The reaction in the form of a black tongue occurs due to the active reproduction of certain types of pathogenic microorganisms.
This effect is provoked by numerous types of medications from the antibiotic category.