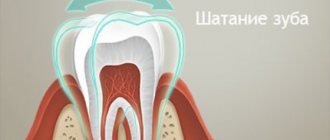
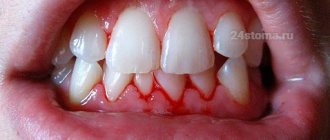
Healthy gums contain a healthy tooth
Each tooth is surrounded by soft tissue. They carefully protect its vulnerable spots from bacteria, the mechanical effects of food and acidity surges. The collection of these tissues around each tooth is called the gum.
Let's imagine that:
- The oral cavity is a huge house in which teeth “live”.
- Each tooth has its own “apartment” - the gums.
A person feels better in a well-kept and renovated apartment. Let's make an analogy: teeth need healthy gums.
Let’s figure out what you need to be wary of and what to do if your fears become reality. Let's talk about the health of our gums.
How inflammation begins
All about dental health
How to maintain beautiful healthy teeth? We tell you in detail: - how to brush your teeth correctly, - how to choose a toothbrush, - how to choose other devices for cleaning your teeth, - how to choose toothpaste, - how to preserve tooth enamel, - how to care for your first teeth, - how to use calcium for dental health. , - how sugar and other foods affect dental health, - how to use chewing gum correctly, - what are the misconceptions about dental health.
Gum inflammation, or
gingivitis
, is caused by bacteria that grow in plaque.
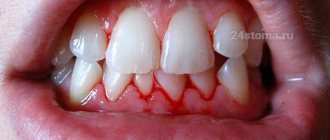
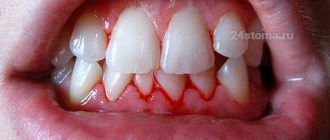
They penetrate under the gums and release enzymes and toxins. At the same time, the gums change color. It turns red if the inflammation is acute, or becomes bluish if the process has entered a chronic stage - and swells. However, the first sign of inflammation that you will notice on your own is bleeding gums
when brushing your teeth or eating solid foods.
What causes gum pain?
Diseases are classified according to several criteria:
- According to the size of the focus of the disease (local process or large-scale).
- Based on the type of disease, the most convenient classification is:
- Gingivitis;
- Periodontitis;
- Periodontal disease;
- A separate point should be made about microtrauma of the gums and the consequences of other oral diseases (stomatitis, cyst, periodontitis).
Let us consider the etiology and clinical manifestations of each of these pathological conditions.
Gingivitis
This is a disease of the gum margin and interdental papillae. The reason for this is food debris that is not removed from the source of inflammation, rots and provokes the abundant proliferation of opportunistic microorganisms. Typical for adults and children.
The enamel near the gums begins to darken and is covered first with a soft coating, then with hard stone.
The more plaque, the higher the likelihood that the gums will begin to bleed.
With a long process, the gums grow and turn red.
In the photo above: healthy gums, below: the initial stage of gingivitis - tartar
Periodontitis
Untreated gingivitis causes inflammation to spread to nearby tissues. Periodontal and bone tissue suffer.
Over time, the tissue between the tooth and gum is destroyed, leaving the tooth exposed. This is how periodontal pockets form. Pus accumulates in them.
Symptoms: discharge of pus from the pockets, crimson-red mucous membrane, bad breath.
Gingivitis and periodontitis are 2 stages of the same process, starting with plaque and ending with tooth loss. These diseases are not age related.
Before visiting a doctor, we recommend rinsing your mouth with decoctions of chamomile and calendula.
Stages of periodontitis:
Periodontal disease
Attention! In this variant of gum disease, pockets do not form! And gum inflammation does not occur here.
The nature of the disease is dystrophic in nature.
This condition is associated with age and is caused by hardening of the blood vessels that supply the gums. Every year the disease occurs earlier and earlier: today people over 35 years of age suffer from periodontal disease. The process is treatable only in the early stages. At a later stage, it remains possible to control the rate of degeneration. Periodontal disease is associated with systemic diseases of the body (disruption of the endocrine system, atherosclerosis). Its treatment is aimed at ridding a person of systemic diseases and maintaining or restoring blood supply to the gums. For this purpose, nutritional pastes and microbial additives are used. It is necessary to care for the oral mucosa and enamel to avoid inflammatory complications.
Stages of development of periodontal disease:
Stomatitis
This is an inflammation of the oral cavity, localized on the surface of the gums, cheeks, and tongue. Unlike stomatitis and injuries, the rest of the listed diseases are characteristic exclusively of the gums.
There are several types of stomatitis. One of them is typical for older people - this is denture stomatitis. The rest can affect children and adults.
Home treatment for stomatitis is replacement of dentures, antihistamines and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions. For the viral variant, ointments containing acyclovir salts are used.
Features of stomatitis are transparent blisters, in place of which pink sores remain.
Microtraumas and gum cysts
Frequent causes of injury are foreign bodies and wisdom teeth.
The risk group is children who transport into their mouths everything that can fit there.
At the site of microtrauma, a purulent sac may form - a gum cyst.
Wisdom teeth are of particular interest. Their growth is accompanied by high fever and throbbing pain.
You can try rinsing your mouth with antiseptic solutions (chamomile, calendula, chlorophyllite). If you have a cyst, be sure to see your dentist.
Periodontitis
With advanced caries, there is a possibility of infection from the carious canal entering the periodontium. From the periodontium, a microbial agent can rise to the surface of the gums, causing inflammation. If the infection is deep, a cyst or abscess may form on the surface of the gum.
The pain is strictly local in nature. The pain is throbbing. Treatment: local use of antiseptics, systemic antibiotic therapy and surgery.
We do not recommend self-medication.
Results of periodontal treatment
Doctors at a French dental clinic will help you get rid of all the listed symptoms, as well as keep your own teeth in place. The most common periodontal diseases are gingivitis and periodontitis. Periodontitis, for example, if it is severely neglected, can lead to the loss of a tooth or several teeth (and at first they will be very loose).
In very severe (advanced) cases, even intoxication of the body, destruction and degradation of bone tissue are possible. Modern methods of diagnosis, prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases used in our center, as well as a good knowledge of periodontics itself by our dentists, specialists from France, allow us to avoid all of the above dangers.
We promise that periodontal treatment at FDC
it will take a minimum of time, will be carried out completely painlessly and will definitely bring the best result.
How modern clinics save gums
The treatment is carried out by a periodontist. It can be found in any dental clinic. We recommend visiting the dentist once a year. Treatment consists of several stages:
- Elimination of the cause of the disease,
- Anti-inflammatory therapy,
- Dental fixation, removal,
- Further prevention.
The cause of inflammation is eliminated by cleaning the oral cavity using various methods.
Previously, doctors practiced the instrumental method of removing plaque. Now – sandblasting and ultrasonic cleaning. These 2 methods are used together. First, stronger ultrasonic cleaning occurs, then cleaning with compressed air moistened with solutions of special salts. In severe cases, it is recommended to carry out procedures once a quarter.
Air Flow Treatment
This is a modern version of sandblasting the oral cavity. Suitable for removing soft plaque. More durable deposits are resistant to this cleaning method. Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) is used as salt in combination with other substances. The mixture is under enormous pressure, so the output is a powerful stream that dissolves and washes away plaque.
Ultrasonic cleaning of the oral cavity
This is the best method of all time. The principle of the method: dental stone and plaque are destroyed by ultrasound. The nozzle of the device is generously moistened with a stream of antiseptic solution or purified water to wash off the crushed plaque.
Then each tooth is ground with a special attachment.
As an example, let's talk about the drug Vector. This is a German technology for ultrasonic cleaning of plaque. A special feature of the device is the direction of the sound wave along the tooth. With the help of Vector, plaque is removed faster and more efficiently than using non-directional ultrasonic vibrations.
Anti-inflammatory therapy
It consists of using gels and special pastes. The most common method is the complex use of cholisal dental gel (pain relief), an antiseptic solution (chlorhexidine or chlorophyllite), and paste to maintain healthy gums (lacalut, paradontax). It is recommended to use this treatment tactic for 21 days after the procedure.
In the case of gingivitis, treatment ends at this stage.
Be sure to read our article about periodontal mouthguards “New in gum treatment”
Surgical intervention, splinting, prosthetics
In case of periodontitis, further therapeutic measures are required: the patient is prepared for prosthetics or splinting (loose teeth are attached to a healthy dental mass using a splint).
Treatment should be accompanied by taking antibacterial drugs!
Surgical cleaning of periodontal pockets is the main method of treating periodontitis.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia and lasts less than an hour. The most common method of cleaning pockets is the “flap operation.” The gum is cut into flaps, which are sewn back after cleaning. Hence the name of the manipulation.
Modern anesthesia allows invasive interventions to be performed absolutely without pain.
Why you can’t self-medicate
Home treatment – eliminating symptoms! The cause of the disease remains, but the pathological process will remind itself again and again and develop further. It is necessary to eliminate the cause, which cannot be done at home.
Bibliography
- Oral health // World Health Organization. — 2022. — URL: https://www.who.int/ru/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/oral-health (date accessed 04/29/2021)
- Goncharik P.V., Kravchenko A.V., Panasyuk G.D. Periodontal diseases // Practical guide for doctors. - Gomel: State Institution "RSPC RMiECH", 2022. - 37 p.
- Analysis of the clinical effectiveness of complex treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis of moderate severity Vanchenko N.B., Seiranidou Z.A., Abdulakhova D.A., Karakov K.G., Khachaturyan E.E. Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "Stavropol State Medical University" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation #2 2018
- Trezubov V.N., Arutyunov S.D. Clinical dentistry // Textbook. — Moscow: Practical Medicine. - 2015. - 788 p. URL: https://books.google.by/books?id=USeNCgAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&hl=ru&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed 04/29/2021)
- Ulitovsky S. B. Basics of prevention of periodontal diseases // Medical Council. — 2014. — No. 1. — P. 68-71
- Fyatkulin R.R., Dmitriev S.A., Kerimov N.D. Gingivitis in children and adolescents // Bulletin of medical Internet conferences. - 2014. - T. 4. - No. 12. - P. 1382-1383
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of gingivitis // Approved by Resolution No. 15 of the Council of the Association of Public Associations “Dental Association of Russia” dated September 30, 2014
- Latysheva S.V., Brundukova O.N. Target directions for the prevention of periodontal diseases // Modern dentistry. — 2014. — No. 1. — P. 59-61
- Borovsky E.V. et al. Therapeutic dentistry // Textbook. — Moscow: Medicine. - 2001. URL: https://www.rulit.me/books/terapevticheskaya-stomatologiya-uchebnik-read-301411-1.html (access date 04/30/2021)
- Usova N. F. Inflammatory periodontal diseases: pathogenesis, principles of complex treatment // Siberian Medical Journal. — 2013. — No. 1. — P. 141-144
- Dental gel for gums “Metrogil Denta®” in the treatment of periodontal diseases and oral mucosa // Practical Medicine. - 2009. - No. 1 (33). — P. 105-106
- Instructions for the medical use of the drug Metrogyl Denta® Dental gel // Registration number P N015982/01 // State Register of the Russian Federation. – URL: https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=9bc9a05c-d28b-473d-b8d4-60e8b8323762&t
- Orekhova L.Yu. et al. Results of clinical studies to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and preventive programs with toothpastes and dental gels in patients with periodontal diseases // PERIODONTOLOGY. — 2022. — No. 21 (1.82)
- Suvorova M.N. et al. Individual oral hygiene // educational manual. - Penza. — 2022. — 32 p.
- Suvorova M. G., Medvedeva L. S. Microbial landscape of major dental diseases // International Student Scientific Bulletin. – 2022. – No. 6
- Nelovko T.V., Oganova K.M., Fedorov S.A. Nutritional hygiene in the prevention of dental diseases // Bulletin of medical Internet conferences 2014. Volume 4. No. 5
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of periodontitis // Approved by the Decision of the Council of the Association of Public Associations "Dental Association of Russia" on April 23, 2013 with amendments and additions based on Resolution No. 15 of the Council of the Association of Public Associations "Dental Association of Russia" dated September 30, 2014
- Great Medical Encyclopedia (BME), edited by Petrovsky B.V., 3rd edition. Volume 7. https://xn--90aw5c.xn--c1avg/index.php/%D0%94%D0%95%D0%A1%D0%9D%D0%90
Preventive measures for gum disease
Remember simple rules for oral health:
- Visit your periodontist (or dental therapist) once a year.
- Brush your teeth twice a day.
- Use dental floss!
- Use special pastes.
- Rinse your mouth after any meal.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, watch your diet.
You need to train yourself to take care of your oral cavity from childhood. This habit should become a regular way of your life. Believe me, it is better to follow all the rules than to undergo treatment later!
You need to visit a doctor once a year, at least. In 100% of cases, you will be prescribed a dental cleaning, and this is the only way to remove plaque and tartar. No plaque – no problems with gums.
Oral hygiene is another important point. This includes brushing your teeth. You need to clean it 2 times a day consistently. Select the brush individually - the cleaning process should not cause discomfort. It is better to use soft electric brushes. They thoroughly clean the surface of the enamel and gums.
You cannot clean the interdental space with a brush. So use dental floss. How often – decide for yourself. If food clogs up after every meal, floss every time you eat. If everything is in order, then once every 1-2 days, but clean all the gaps.
If you have large interdental gaps, use simple wooden or special toothpicks.
People with bleeding gums need to use special pastes. The composition of the pastes allows you to speed up the healing of wounds and stop bleeding.
Rinsing your mouth is a good habit. Teach your children to this from early childhood.
Why do gums recede with crowns and veneers?
Veneers or crowns also sometimes cause gum recession.
The issue may be the quality of the restorations themselves. For example, if the edge of the prosthesis adjacent to the mucous membrane is more massive than necessary and literally does not fit under the gum. Normally, veneers and crowns are created with a beveled edge, that is, they are thinner in the area adjacent to the gum. It also plays a role how carefully the orthopedist worked and polished the edge of the restoration near the mucosa, and whether he removed the remnants of the fixing cement. The slightest roughness near the neck of the tooth can irritate the soft tissues.
And, of course, the problem arises due to improper care of veneers and crowns: aggressive cleaning with a hard brush or the use of dental floss, which is prohibited after restoration. In addition to the fact that the thread causes cuts to the mucous membrane, it can get caught on the veneer and partially peel it off from the tooth. Then its open edge can injure the gums.
We will answer your questions
I experience pain when I brush my teeth, and blood flows from my gums. What could it be?
Contact a periodontist. You have gum disease caused by poor oral hygiene (or gingivitis).
How can you tell if your gums are unhealthy?
Pay attention to the color of the gums, bleeding, pain when brushing and the size of the visible part of the tooth, the presence of plaque. These are the main criteria in this case.
Does smoking affect your gums?
Yes, tobacco smoke negatively affects the color of teeth and destroys enamel. Accordingly, the gums will also suffer.
Can I die from periodontitis?
Theoretically yes. You can die, for example, from sepsis or from infection entering the brain. In practice, in the modern world, this is very difficult to achieve, only if you wait until the disease goes away on its own.
I'm pregnant, is gum disease dangerous for me and my baby?
Yes, in your case there may be a miscarriage or premature birth. Remember that a chronic source of infection in your body is a threat to the child. A microbial agent can enter the fetus’s body and cause irreversible processes. There is also a danger to your teeth. During pregnancy, the mother's bone tissue is very vulnerable.
Is this even curable?
Gum disease can almost always be cured. The only question is how many teeth you will have left by then. Joke. But, if the disease starts, the loss of some teeth is inevitable.
How much does gum prevention cost?
The ultrasonic cleaning procedure costs from 5 to 15 thousand rubles per procedure.
If I take care of my gums, what is the likelihood that they will always be healthy?
Probability 99%
Are there any contraindications for dental implantation?
There are several contraindications: osteoporosis (which has not been treated), diabetes and smoking. The implant may not take root.
My mother has periodontitis. Will I suffer from this too?
Gum disease is not inherited.
Once a year, the gums around the wisdom teeth become very painful and swollen, what should I do?
When there is another inflammation, contact your dentist. There is a high probability of surgical intervention. Use Cholisal when pain worsens.
Periodontitis or Periodontal disease
Despite the fact that the names are very similar, periodontitis and periodontal disease are two completely different diseases that are connected by only one thing - they develop in periodontal tissues.
The periodontium is the gums, the cement of the tooth root, the bone tissue surrounding the tooth, the periodontium (the ligament connecting the tooth and the bone), nerve fibers, blood and lymphatic vessels that supply this area.
The difference between the diseases is that periodontitis is an infectious inflammatory process, and periodontal disease is a non-inflammatory process of destruction of periodontal tissue caused by insufficient blood supply.