To understand what allergic stomatitis , it is necessary to clarify two concepts.
Allergy. An excessive protective reaction of the body's immune system to certain external substances foreign to the body, called allergens. These may be substances that are essentially harmless to humans, but for some people (allergy sufferers) they are perceived by the immune system as dangerous to the body. In immunology, there are several types of allergic reactions, but in practical allergology only type I (fast or instant reaction) and type IV (slow or delayed reaction) are relevant. These types of reactions in the body can occur separately, but they can also occur in parallel. In addition, symptoms similar to those of allergies can be caused by other pathologies, for example, pseudoallergic diseases, conditions of intolerance to certain substances.
Autoimmune diseases. A generalized medical term for pathologies that are based on an excessive reaction of the immune system to the body’s own tissue elements (fragments). That is, the immune system recognizes these elements of the body as foreign and triggers a chain of defensive reactions, leading to severe inflammation and pathologies of various internal organs.
Allergic reactions and autoimmune pathologies can manifest themselves on the oral mucosa and the generalized term allergic stomatitis .
Unfortunately, the relative number of patients with symptoms of allergic stomatitis has recently increased. This is due not only to the fact that the ecology of the external environment is deteriorating or new potentially allergenic components appear in food products. It is believed that a significant contribution is made by the emergence of new and diverse materials used in dental treatment - filling materials, materials for dental crowns and dentures, for the manufacture of braces and implants, various mouth rinses, etc. At the same time, new materials often do not go through the research stage for the risk of allergic reactions. allergic stomatitis may appear and children.
Types of stomatitis
Depending on the nature of the disease and its clinical manifestations, experts divide catarrhal, catarrhal-hemorrhagic, as well as bullous, erosive, ulcerative-necrotic and allergic stomatitis.
The latter, in turn, is divided into the following types:
- medicinal;
- contact, for example, as an allergy to dentures, braces, plates;
- catarrhal;
- catarrhal-hemorrhagic;
- ulcerative-necrotic;
- erosive.
From the point of view of etiology and pathogenesis, allergic stomatitis includes medication, contact (including dentures), toxic-allergic, autoimmune dermatostomatitis, chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis and other forms.
Depending on the speed of development of the reaction, doctors distinguish immediate and delayed types of allergic stomatitis. In the first case, angioedema is observed, and in the delayed type, the reaction to a particular irritant usually appears a few days after contact with the allergen.
In rare cases, allergic stomatitis develops while wearing dentures. Sometimes a reaction occurs even after 5–10 years of wearing them, after a long asymptomatic period.
Ask a Question
What it is
Allergies can arise in a person out of nowhere, in the complete absence of any reactions to food, medications, dust, pollen and other irritants in the past. This happens due to failures of the immune system, as well as changes at the genetic level. Blood cells responsible for the formation of antibodies to infections at some point perceive a substance that has entered the body as an “enemy” of the immune system. A response begins, which is accompanied by typical allergy symptoms.
A person can calmly eat honey for half his life, drink chamomile tea, and be treated with penicillin. And at one point, any component of normal life can become a strong allergen, which can lead to a powerful reaction, anaphylactic shock and even death. Approximately a third of the world's population is susceptible to one or another manifestation of allergic reactions, and on average, in 20% of this number, allergies manifest themselves as rashes on the oral mucosa. So if you are faced with stomatitis, allergies may be one of the reasons for its occurrence.
Causes of the disease
As is clear from the name of the disease, a negative reaction of the body develops after contact with various allergens. Most often, allergic stomatitis occurs after contact with plant pollen or mold spores. The disease can also manifest itself against the background of:
- installation of crowns, fillings, prostheses made of low-quality materials;
- consumption of certain types of food (especially in children);
- decreased immunity;
- course of treatment with antibacterial drugs or sulfonamides;
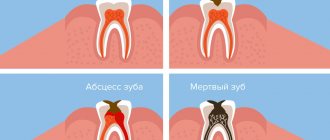
- advanced caries;
- bleeding gums;
- inflammation of the oral cavity;
- proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity.
Sometimes allergic stomatitis manifests itself as a complication of Lyme disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, aphthous stomatitis, hemorrhagic diathesis, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Symptoms
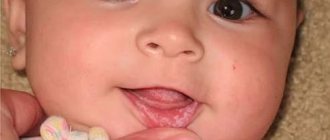
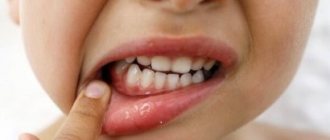
The disease is characterized by general and local symptoms. The first symptoms of a mild form of allergic stomatitis are:
- slight discomfort in the oral cavity during hygiene procedures and eating;
- inflammation and swelling of tissues;
- redness and itching of the affected areas of the mucous membrane;
- excessive salivation.
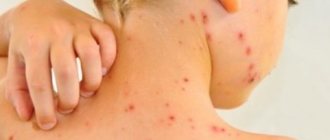
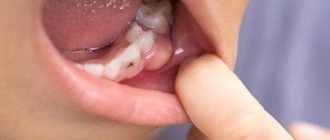
If allergic stomatitis began while taking certain medications, the patient complains of painful blisters filled with liquid. Tick-borne borreliosis is accompanied by redness, blisters on the mucous membranes, as well as bleeding erosions and wounds.
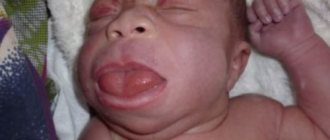
Allergic stomatitis without proper treatment develops very quickly: the patient’s body temperature rises, and bubbles and blisters appear on the skin, mucous membranes of the eyes, and genitals.
If the disease was caused by Lyme disease, red spots with a border appear in different parts of the body and are very painful. Sometimes patients complain of joint pain.
Manifestations of the disease
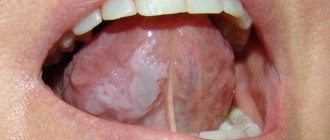
The disease negatively affects the functioning of the entire body. It doesn’t just cause inflammation of the mucous membranes—it also causes migraines, elevated body temperature, and lethargy. Many people notice dry mouth, severe pain when chewing, which is present even when the integrity of the tissues has not yet been compromised.
Saliva thickens, becomes viscous, more like foam. The gums, tongue, and inner surface of the cheeks may swell. All these symptoms deprive the patient of the opportunity to lead a normal lifestyle.
You shouldn’t wait for the disease to clear up. The sooner her treatment is started, the sooner her health will be normalized.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of “allergic stomatitis” is made by a dentist based on an examination of the oral cavity and questioning the patient about underlying diseases and medication use. The dentist clarifies the clinical picture of the disease.
The doctor must conduct a comprehensive examination and diagnosis:
- removable and fixed prostheses;
- braces;
- filling
To clarify the clinical picture of the disease, the specialist refers the patient for a comprehensive blood and urine test and an immunogram to assess the state of the immune system. If necessary, the doctor sends the patient for the following studies:
- determination of the acidity level and composition of saliva;
- identification of the activity of enzymes contained in saliva;
- leukopenic test;
- provocative tests with removal and subsequent installation of prostheses.
An integrated approach to diagnosing allergic stomatitis will allow you to quickly find out the cause of the negative reaction, eliminate it and begin effective treatment.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis in adults
If the dentist confirms the diagnosis, he first prescribes complex therapy. It is important not only to eliminate the painful external manifestations of the disease, but also to adjust drug treatment, change the patient’s lifestyle and, if necessary, discontinue medications that caused irritation.
Folk remedies are excellent aids in treating the disease, but using herbal infusions alone will not completely get rid of the disease. The main thing is to determine the cause of the allergy and eliminate it as soon as possible.
The main directions in the treatment of stomatitis are:
- identification and elimination of allergens;
- selection of suitable orthopedic structures (if an allergy to them is identified);
- replacement of low-quality fillings;
- selection of softer and more gentle medications;
- taking antihistamines and antiallergic drugs;
- use of local antiseptics and painkillers;
- disinfection of mucous membranes by rinsing in order to reduce the risk of infection spreading through the bloodstream throughout the body;
- taking analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis necessarily includes a hypoallergenic diet. In order for the aphthae to heal as soon as possible, and the patient no longer suffers from painful sensations in the oral cavity, the following should be excluded from the diet during treatment:
- sour, spicy and salty foods;
- citrus;
- fried foods;
- peppered dishes.
During treatment, it is recommended to eat soft foods, such as purees or soups. It is important not to injure the affected and swollen mucosa, so that the wounds heal as soon as possible and the swollen mucosa is not injured.
Additional treatment
As prescribed by the dentist and allergist, the patient can use various herbal decoctions and healing oils as additional treatment. The most effective recipes are:
- Aloe juice. The juice of the plant perfectly relieves inflammation, heals ulcers and wounds. You can rinse your mouth with the fresh juice, or you can chew the pulp of the fleshy leaf, peeled.
- Sea buckthorn oil . This oil can treat stomatitis of any form, including allergic ones. You can prepare the oil yourself or buy it at a pharmacy. To supplement the treatment, it is enough to lubricate the affected tissues several times a day. Sea buckthorn will heal wounds, soften the mucous membrane and reduce inflammation.
- Propolis . This beekeeping product perfectly relieves inflammation and heals ulcers and wounds, and also perfectly disinfects the mucous membrane. To treat stomatitis, it is enough to dilute a pharmaceutical tincture of propolis in water in a ratio of 1:10 and rinse your mouth with it.
- Chamomile infusion has excellent anti-inflammatory and wound healing properties. To treat the oral cavity, just pour 2 tablespoons of flowers into a thermos, pour 1 liter of boiling water into them and let it brew for 45 minutes. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with filtered infusion 3-4 times a day. Instead of chamomile, you can use an infusion of sage or calendula, and also prepare a mix, taking a teaspoon of each herb.
Nutritional Features
Due to the fact that painful ulcers appear in the mouth with stomatitis, any meal gives the baby discomfort. Therefore, the diet during the period before recovery should have a number of features.
- All food taken should be warm and at a temperature as close as possible to body temperature. This will prevent unnecessary irritation and will not cause acute pain.
- Since chewing is quite painful, portions should be reduced by about a third, but the frequency of meals should be increased.
- When feeding your baby, you should give preference to dishes with a soft consistency, and it is better to postpone dense and dry foods until complete recovery.
- It is worth giving preference to products with a neutral taste. These are potatoes, bananas, pears, pumpkin.
- Until recovery, spicy, salty and sour foods are completely excluded from the child’s diet.
- To make eating less painful, you can purchase thick straws for cocktails and crush all food so that it can be drunk.
- The emphasis is on healthy foods rich in microelements and vitamins. For example, buckwheat, oatmeal, and rice can be recommended for cereals. It is preferable to give your baby cauliflower and broccoli as vegetables.
Allergic stomatitis in children
In children, the disease occurs more often than in adults, and at the same time, a weak and fragile child’s body reacts more sharply to irritants. The baby begins to be capricious, complain of pain in the mouth and, of course, is afraid to go to the dentist.
In no case should parents let a child’s illness take its course, relying on traditional methods of treatment. If the baby suffers from allergic stomatitis, no ointments or rinses will cure him 100% as long as contact with the allergen continues. Sensitive thin mucous membranes easily crack, bleed, and pathogenic microorganisms quickly penetrate into the ulcers.
It is important to take the child to a specialist as soon as possible, explain to him that the doctor will help him get rid of the pain, and begin the examination.
Prevention of allergic stomatitis
Unfortunately, patients are not always able to prevent the development of allergic stomatitis. It is impossible to predict what the oral cavity's reaction to a foreign substance will be. If an immune reaction is suspected, the dentist may refer the patient to an allergist.
The main measures to prevent allergic stomatitis are timely visits to the dentist and treatment of caries, strengthening the immune system and using suitable products for daily oral hygiene. If detected early, the pathology can be successfully treated.
If you suspect that you or your child have allergic stomatitis, experience pain in the oral cavity, or find ulcers and aphthae on the mucous membrane, do not delay consulting a doctor. Experienced dentists at STOMA clinics will help you determine the source of allergic stomatitis, quickly get rid of the unpleasant manifestations of the disease and return to your normal life.
We will check all structures in the patient’s oral cavity, conduct allergy tests, and, if necessary, refer the patient to trusted allergists and other specialists.
Call and make an appointment by phone. STOMA clinics are open from Monday to Saturday. You can choose a conveniently located clinic; we are open in many districts of St. Petersburg.
Content:
- Description of the disease
- Manifestations of the disease
- How does allergic stomatitis develop?
- Why does it occur
- Establishing diagnosis
- Fighting the disease
- How to reduce the risk of developing the disease
A dental disease in which the integrity of the oral mucosa is damaged - allergic stomatitis - occurs quite often in medical practice. It comes in different forms, so a person cannot always understand what caused the disease and what factors caused its negative symptoms.