What is flux and its types
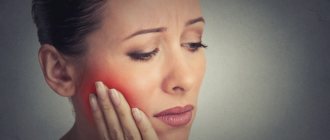
Flux is an inflammatory process of the soft tissues of the periodontium and periosteum.
The scientific name of the disease is periostitis. It can occur on the gum under any tooth (or above it, if we are talking about the upper jaw). Caused by infection of dental tissues. The process of progression of periostitis goes through four stages (if you do not consult a dentist in a timely manner). The first is characterized by slight pain in the gums, “radiating” to the tooth. The second is the appearance of swelling and redness at the site of tissue infection (the tumor visually resembles a small sac). The third is an increase in body temperature, discharge of pus and swelling of the cheek due to inflammation. The fourth is manifested by severe throbbing pain and increased swelling. Types of flux:
- ordinary - the inflammatory process does not affect the periosteum;
- fibrous – inflammation spreads to the periosteum;
- orthodogenic – infection of bone tissue occurs (osteomyelitis);
- albuminous - a chronic form with a slight increase in temperature and periodic suppuration.
How to recognize periostitis?
Adults suffer from flux much more often than children. Note that such inflammation is accompanied by a number of symptoms, so it immediately makes itself felt.
Signs of classic purulent flux:
- the mucous membrane hurts a lot
- soft periodontal tissues become inflamed and swell. The cheek swells on the side of the localization of the pathological process
- lymph nodes increase in size
- body temperature rises to +38 degrees
It is worth understanding that periostitis does not go away on its own. Some patients are sure that after the purulent contents flow out of the burst lump, there is no need to treat the inflammation. They say it went away by itself. However, this is a misconception and in this case a dental clinic will definitely be required. After all, it is possible to completely get rid of pus only by installing a special drainage and carrying out certain therapeutic measures prescribed by the doctor. If flux treatment is started on time and carried out correctly, then the pathology can be eliminated in 12-14 days. If the form is advanced, recovery will take more than a month.
Causes and mechanism of flux occurrence
As already mentioned, the cause of periostitis is infection. It may be caused by the following factors:
- the presence of carious lesions on the teeth;
- injury;
- infection during treatment;
- poor oral hygiene.
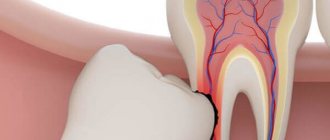
And yet the most common cause of the disease is caries. If a person does not go to the dental clinic, pathogenic microflora destroys tooth enamel and then penetrates inside the tooth. Then pulpitis develops, accompanied by acute pain. If left untreated, the pain gradually stops as the nerve endings die. But the spread of infection does not stop, it reaches the tooth root, causes inflammation of the gum tissue, in which the pathological process begins with the formation of pus. Flux is formed.
Causes
Inflammatory (infectious-inflammatory) diseases of the maxillofacial area are caused by microbial microorganisms, which are usually part of the normal microflora of the oral cavity. Microbial pathogens are staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, diplococci, gram-positive and gram-negative bacilli (intestinal, protea, etc.). In addition, during flux, fungi, mycoplasmas, treponema, and protozoa from the Trichomonas family are found in foci of odontogenic infection. According to various authors who analyzed the microbial flora in foci of odontogenic infection (flux), the microflora is represented by a monoculture of staphylococcus (aurus and epidermal) or streptococcus of groups D, F and G. Associations of the above microorganisms are often identified.
The question arises of how non-pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms trigger the initiation of an infectious-inflammatory process (flux). For the occurrence of a disease, the presence of only non-pathogenic or pathogenic microorganisms is not enough. The answer to this question is given by the so-called Arthus-Sakharov phenomenon. According to the infectious-allergic theory, its essence boils down to the following: under the influence of a foreign serum protein, which has antigenic properties, antibodies are produced, which leads to sensitization of the body. Sensitization of the body is the acquisition by the body of increased sensitivity to foreign substances (proteins) - allergens. Against this background, repeated introduction of the protein into the vascular bed causes the formation of antigen + antibody complexes, which are fixed on the membranes of blood vessels and turn into target cells. Then the cell membrane is damaged, enzymes are released, mediators (from the Latin mediator - mediator) of inflammation are released. This is accompanied by activation of the third platelet factor and can cause intravascular coagulation, which leads to impaired microcirculation and necrosis (death) of tissue. This immunopathological reaction is also involved in odontogenic infection, leading to the occurrence of gumboil. The waste products of microbes participate in the role of antigen. This explains why in many patients non-pathogenic microorganisms are found at the site of inflammation.
The dynamic balance between the focus of chronic odontogenic infection and the body is ensured by the connective tissue capsule surrounding the focus. It limits the penetration of microbes into the tissues and vascular bed adjacent to the lesion, and limits the effect of immune factors on the infectious focus. The balance is also maintained by the fact that part of the waste products of microorganisms and tissue decay through the root canal of the tooth, fistula or periodontal fissure is released from the infectious focus into the oral cavity.
An imbalance can be caused by a disruption in the outflow of exudate from the lesion through the root canal due to food masses entering the carious cavity or when filling a carious cavity by a dentist. In the infectious focus, the concentration of microbes, their toxins, and waste products, which penetrate through the connective tissue capsule into the surrounding tissues, increases. Here their direct damaging effect on tissue can occur, and upon penetration into the vascular bed, the mechanism of the Arthus-Sakharov phenomenon is triggered. Clinically, this is manifested by an exacerbation of a chronic focus of odontogenic infection and the occurrence of gumboil.
Another mechanism of imbalance between the focus of chronic infection and the human body is associated with damage to the connective tissue capsule itself. This can happen when a tooth is removed, when there is increased load on the tooth while chewing hard food, etc. Damage to the capsule leads to the spread of microorganisms (their toxins, waste products) beyond the infectious focus, which in a sensitized organism leads to the occurrence of the Arthus-Sakharov phenomenon. These are the reasons and the main mechanism of exacerbation of odontogenic infection, leading to the development of gumboil.
Symptoms
- The formation of a small lump on the gum under (above) the tooth
- Throbbing pain radiating to the back of the head, chin, temple
- Redness of the gums
- Swelling of the cheek due to inflammation
- Increased pain when touching a tooth next to a lump
- Deterioration of general condition caused by intoxication
- Temperature increase (low to high)
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck
Note: sometimes swelling on the cheek occurs without any apparent reason or pain. But nevertheless, if this symptom appears, you need to consult a dentist as soon as possible. The doctors in our network of clinics have extensive experience in treating flux, regardless of its type and complexity of the clinical case.
Content:
- Gums gumboil - what is it?
- What causes gumboil to appear?
- Signs of dental flux
- How long does it take
- What to do in case of flux
- Is it necessary to remove a tooth during periostitis?
- Danger of violation
- Prevention
Almost everyone knows what flux is. The disease is quite common. Both children and adults encounter it. The tooth begins to hurt, as a convex lump appears at its base. Then a person has to look for ways to cure the disease.
There are many traditional ways to remove flux. However, it is unwise to use them. How to get rid of the problem, you need to find out from a qualified doctor. Otherwise, the disease may not be eliminated, but rather transformed into a chronic, sluggish form, which is very dangerous.
What happens if flux is not treated?
Many patients, when symptoms of periostitis appear, hope that everything will “resolve” on its own, as people say. This is an erroneous and dangerous opinion, following which can have dire consequences. This situation can have a particularly serious impact on the child’s health, because the protective immunity at an early age is not well developed. If left untreated, the infection remains in the body, causing the emergence of new diseases, some of which can result in sepsis and death. What is most likely to happen? We list them according to the severity of the problem.
How long does it take
There is no point in waiting for periostitis to pass. Some people think that if the lump bursts and pus flows out of it, then nothing more can be done. This is not entirely true. To ensure that the wound is completely clean, dental drainage must be installed. Only a doctor can do this.
If therapy is carried out correctly, recovery occurs in one to two weeks. It is very important that the patient follows all medical prescriptions. In advanced cases, the rehabilitation period can last for a whole month.
Consequences of untreated flux:
- abscess (abscess) - the formation of a purulent sac;
- phlegmon - an extensive inflammatory process after the rupture of an abscess;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw - inflammation of the tissues of the jaw bone;
- inflammation of the sinuses of the skull - the sphenoid, maxillary and frontal sinuses are involved in the pathological process. Sometimes the infection penetrates into the brain tissue.
Important: specialists from the “Smile” clinic network recommend starting treatment as early as possible. The faster the inflammation is stopped, the less effort will be required to eliminate the problem and restore the patient’s health.
Removal of a tooth
After examining the patient, the doctor outlines the treatment path, first of all, deciding whether the tooth can be saved or whether it will have to be removed. If the tooth is damaged, the canals cannot be cured, the tissue between the tooth and the gum is infected, then the tooth must be removed, for which the following procedure is performed:
- the doctor cuts the periosteum;
- examines and treats the wound with antiseptic agents;
- removes tissue damaged by inflammation and removes the tooth;
- puts sutures, installs drainage, at the second visit the drainage is removed, the sutures are changed to self-absorbing ones.
When performing all actions, hygiene rules are carefully observed so as not to introduce a second infection, which will lead to blood poisoning. The operation is not painful as it is performed under local anesthesia.
Treatment algorithm
The treatment protocol for periostitis involves a combination of surgical, medicinal and physiotherapeutic methods:
- taking (or a course of injections) antibiotics to destroy pathogenic microflora;
- opening the purulent sac (using local anesthesia), and in difficult cases, installing temporary drainage to drain the pus;
- eliminating the cause that caused the formation of flux: treating a tooth or extracting it if therapeutic measures are inappropriate, cleaning periodontal pockets;
- treating the wound with an antiseptic (gel, rinsing) until it is completely healed;
- course of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Expert advice: after opening a purulent sac, you should not apply warm compresses or take antibiotics that have not been approved by the doctor. If pain continues more than 8 hours after surgery, you should contact the clinic immediately.
When does flux require tooth extraction?
The appearance of flux does not require tooth extraction at all. If the primary stage of the disease occurs, treatment with conservative methods becomes quite successful. The inflammation is eliminated by antibiotics, and it is quite possible to save the tooth: removing it is not at all necessary. If periostitis is advanced, it is extremely rare to leave the tooth intact and remove the inflammation. When deciding whether to remove or preserve a tooth, the doctor takes into account the condition of the tooth canal and the possibility of endodontic treatment to eliminate harmful microbes in the inflamed area.
Recommendations from prevention experts
- Timely treatment of caries
- Thorough hygienic care of teeth and gums at least 2 times a day
- Rinsing your mouth after every meal and sugary drinks
- Visiting the dentist for a preventive examination twice a year
- Have it professionally cleaned at least once a year
- Eating firm, raw fruits and vegetables daily
The network of dental clinics “Smile” offers services for the treatment of dental flux in adults and children. Contacting our centers has a number of important advantages:
- highly qualified specialists;
- compliance with examination and treatment protocols in accordance with international standards;
- system of family and cumulative discounts;
- stable price of treatment, depending on the severity of the clinical case.
You can contact any of the branches of our clinic in Moscow, located within walking distance from metro stations:
- Art. Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Art. Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, address: building 34, building 1.
Do not delay your visit to the doctor, make an appointment when the first symptoms of periostitis appear. This will significantly shorten the treatment time and save costs. Our specialists will provide effective medical care regardless of the severity of the disease. We will take care of your health!
Signs of dental flux
Adults experience the disease much more often than children. Periostitis never goes unnoticed. It causes severe discomfort, worsens the quality of life, and forces you to take painkillers.
In most cases, patients complain of:
- unpleasant pulsation in the gums;
- pain;
- tissue swelling;
- inflammation of the gums;
- swelling of the cheek;
- an increase in the size of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- increased painful symptoms when talking, eating solid food;
- numbness of the lip/chin.
Gels and ointments
Ointments are used for topical application. In particular, this is Vishnevsky’s ointment, which stops the development of the purulent process. The birch tar included in its composition increases blood circulation in tissues and accelerates their natural regeneration.
Among modern gels, it is recommended to use the drug Metrogyl Denta, which contains antibacterial components in the form of Chlorhexidine and Metronidazole.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details! Ask your doctor about contraindications and side effects.
Compresses and lotions for periostitis
Compresses and lotions have a local anti-inflammatory and disinfecting effect, they destroy pathogenic microbes and will help get rid of swelling on the mucous membrane. You can use the drug Dimexide, which is diluted with water until a concentration of 20-30% is reached. The compress is applied to the area of inflammation and left for about an hour.
Soda lotions also help a lot. Baking soda is diluted in a volume of two teaspoons in 200 ml of water. You can moisten a cotton pad or several layers of gauze with the solution and then apply the lotion to the affected area of the gum.
Good therapeutic effectiveness is also observed when using salt compresses. It is enough to dissolve a couple of teaspoons in 100 ml of warm water. A gauze swab soaked in the solution should be applied to the inflamed area and held between the gum and cheek for at least half an hour.
What causes periostitis?
To understand why the tissues of the periosteum become inflamed, you need to understand how carious tooth damage develops in general if it is not treated and is not prevented in any way.
First, a section of enamel and dentin are destroyed. Then the infection descends lower - into the root canals of the tooth. At this stage, a person usually experiences toothache - since a living nerve is affected, which, under the influence of infection, becomes inflamed and begins to gradually “die”, that is, actually rot. If the patient does not go to the doctor even then, but decides to give himself a test of masculinity and endures the pain (or “seizes” it with handfuls of painkillers and muffles it with rinses), then the nerve will rot and the pain will recede. However, this, of course, does not mean a cure. Because further along the open root canals, food debris can get into the tooth cavity or into the gum pocket - and suppuration will begin there. There is not always a way out for this pus, but a way out is needed - and it is found: the pus passes into the soft tissue of the periosteum. That is, a bag filled with pus forms in the periosteum. In this case, as a rule, the patient feels pain, which can radiate to the ear, neck or even eyelid (if periostitis is on the upper jaw). And on the gum of the tooth that caused the inflammation, a seal can form and then pain can be felt not only when biting on the diseased tooth, but also on neighboring teeth.
However, caries is a common, but not the only reason for the appearance of gumboil. Sometimes suppuration occurs due to improper tooth extraction - and such patients come to VivaDent to treat the consequences of unsuccessful surgical interventions in other clinics.
Although it also happens that even mechanical trauma to the gums and jaw tissue can cause gumboil - for example, in athletes who have received a blow to the jaw.
Also among the diseases that can cause the appearance of gumboil are pulpitis, periodontitis and periodontitis.
And sometimes swelling of the cheek is caused by improper eruption of “eights” - that is, wisdom teeth.
How to approach gumboil treatment in 2022
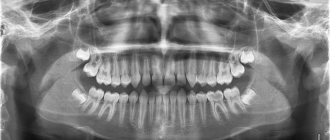
This is a common disease, so many people know what flux is and how to deal with it. But it should be clearly understood that eliminating only the symptoms of the disease does not eliminate its cause. An immediate visit to the dentist will significantly reduce the likelihood of complications! The method of treatment depends on the location and form of inflammation. First, the dentist will examine a panoramic photograph of the teeth to assess the condition of the pulp and roots. At an early stage, you can limit yourself to taking antibiotics and painkillers. The advanced purulent form is treated with surgery under local anesthesia. An incision is made next to the diseased tooth, through which all the pus is drained. Then antiseptic treatment is carried out. In some cases, drainage may be left in the incision for better drainage of infected fluid. This manipulation allows you to quickly relieve swelling and eliminate the possibility of blood poisoning. In particularly advanced cases, the tooth may be removed.
Stages of drug treatment
- Relieving swelling with antibiotics and antibacterial drugs. They must be selected by a doctor individually, taking into account the nature of the disease and the patient’s health status.
- Eliminating the cause of the abscess.
If periodic exacerbations are observed, then periostitis becomes a chronic disease, the doctor prescribes strengthening drugs: calcium glucanate and immunomodulators, vitamin complexes.