international experience
In different countries, the answer to the question: “Do you always need to remove wisdom teeth?” different. In the USA, 8s are removed already in adolescence, before they lead to problems, that is, they act according to a preventive scenario. In the CIS countries, if teeth erupt correctly and do not cause problems, they are left behind. Apparently this is due to the characteristics of healthcare models.
At the same time, many scientific works on this problem among conscript soldiers in the Russian Federation attract attention, and it is no coincidence. It is at this moment that wisdom teeth begin to actively grow and reveal previously hidden problems. And treatment often requires surgery.
Where do the folds come from?
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons and orthodontists are well aware of how wrinkles are associated with missing teeth. For example:
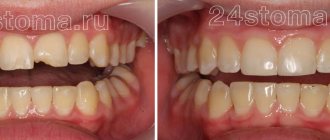
“Eights” , also known as wisdom teeth, were considered unnecessary for many years. They were never treated and offered to be removed even if they did not hurt. It turned out - and dentists recognized this - that “eights” are useful from the point of view of preserving youth. If they have grown, they act as an internal frame for the cheeks, and the removal of these teeth promises early vertical wrinkles on the cheeks and sagging of the lower part of the cheeks, the so-called jowls.
Questions and answers Why do teeth fall out?
Molars are the main support for the cheeks from the inside. If they are missing, the cheeks become sunken, and asymmetrically sunken. And depressions quickly lead to the formation of deep vertical wrinkles and strengthening of nasolabial folds. Following the loss of chewing teeth, the corners of the eyes droop, “crow’s feet” appear, and they are complemented by the same jowls and marionette lines—multiple branching folds running down from the corners of the lips, because of which the lower jaw appears to be attached to a hinge.
The canines , both upper and lower, are responsible for the curve of the lower line of the oval of the face - approximately along the edges of the lower jaw. If they are missing, the oval of the face loses its clarity, folds and sagging like a double chin form. The corners of the mouth droop, which gives the face a tired expression, and after them the nasolabial folds become stronger. The same jowls and marionette wrinkles may appear.
The absence of one or more front teeth leads to the recession of the upper or lower lip, which then transforms into wrinkles. Later, wrinkles in the area of the nasolabial triangle intensify, and sagging appears under the lower lip. The smile line goes down - now the corners of the mouth do not rise when smiling. Well, marionette wrinkles traditionally accompany the loss of a tooth, no matter where it is located.
Article on the topic
Insurance for an understudy. How to care for dentures
What is the diagnosis
Doctors often use 2 terms when describing problems with wisdom teeth.
Retention – when a tooth fails to erupt. It grew, but remained inside the jaw completely or partially. This can create a focus of inflammation, which either subsides or worsens again. But the most unpleasant consequence can be a cyst around the tooth if it has not erupted at all.
Dystopia is an abnormally positioned tooth, for example, horizontally. At first, such a tooth germ may not bother you at all. But when it starts to grow, it can lead to a lot of problems. You also need to remember that the tooth simultaneously grows in 2 directions towards the crown and towards the roots. If such a rudiment is tilted, then the tooth may appear from the side of the cheek or, conversely, grow inside the mouth and scratch the tongue.
One of the options for dystopia is a horizontal arrangement.
During the process of growth, a slightly inclined tooth in a narrow jaw can “catch” on the neighboring one, which will lead to an accident. The growing tooth will turn around and lie horizontally. Further, the growing tooth can gradually displace the remaining teeth and lead to crowding of the front teeth. This will create a new problem, not only an aesthetic one, but daily hygiene becomes more difficult and the risk of caries increases.
Often dystopia is combined with retention, which provides more reasons to remove problematic eights.
Destruction of bone structures
The supporting alveolar bone contains a spongy substance that absorbs the chewing load. If at least one tooth is missing, this load changes. Remodeling begins in the bone: its structure, shape, and volume change. In order for it to remain dense and not deform, it needs a constant load that will stimulate it. With edentia, the bone becomes less dense. The alveolar process (or the alveolar part in edentulous lower dentition) becomes narrower. The next stage of destruction is when the bone gradually loses height. Without prosthetics, it decreases by 4 mm in just a year. The width is also reduced - by 25% of the original per year. This process does not stop: if implantation is not performed, destruction will continue. Installing a bridge can only partially solve this problem. This design transmits the chewing load, which is absorbed by the surface layer of bone tissue. The deeper layers remain without constant stimulation. Because of this, blood supply deteriorates and the volume of bone tissue decreases.
When even one tooth is lost, the alveolar bone is rebuilt and resorbed. In place of the hole, a narrow ridge is formed, running along its center. The formation of this ridge complicates prosthetics. When using a removable denture, it rests on the ridge and injures the overlying gum tissue.
Another consequence of bone loss is an increased risk of injury. It especially increases for the lower jaw. With a significant decrease in the volume of bone tissue, there is a possibility of a fracture in this area, even with minor injuries.
It is not only the alveolar bone that suffers from the lack of chewing load. Over time, destruction begins to occur in the main jaw bone. This process occurs faster in the posterior parts of the lower jaw, where destruction of up to 80% of the bone tissue volume is possible in the socket area.
You have questions?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7
Bone resorption changes the characteristics of the dental system:
- oblique ridges are formed on the jaw in the sublingual area. May be accompanied by the formation of a local bedsore;
- changing the shape of the chin. In its anterior part there are two tubercles, which can protrude forward during the destruction of bone tissue;
- the muscles are attached near the top of the ridge, which can provoke pain and discomfort;
- thinning of the mucous membrane, causing discomfort even when eating or performing hygiene procedures;
- formation of functional bedsores.
Risks
There are genetic features that do not change, but there are those that depend on various factors, including age.
Facial structure
One of the easiest ways to determine whether there is a greater or lesser risk of problems with wisdom teeth is through a mirror. Let's pay attention to the face. If it is elongated from bottom to top, has narrow cheekbones, and people say a small, neat face, then there may not be enough space for wisdom teeth. But the wider the cheekbones, the wider the “bone”, the more space there is for cutting figure eights.
Also, sufficient space in the jaw reduces their crowding and creates conditions for good hygiene. And this is the best prevention of caries, not only of the seemingly unnecessary tooth that we inherited from our ancestors, but also of all other teeth.
A consultation with an orthodontist and radiation diagnostics (X-ray/MRI) will help you understand the situation.
Age dependent
Problems that can arise with wisdom teeth at different ages can vary significantly2.
In youth, the main problem is inflammatory processes during the eruption of wisdom teeth. As well as the need to remove them for orthodontic treatment.
In adulthood, those who have retained their teeth begin to experience caries. The occurrence of pulpitis and cysts usually leads to a surgeon for removal.
In old age, the main problem is periodontal disease, which usually also leads to the removal of wisdom teeth. Or it becomes a preparation stage for prosthetics.
When to panic?
How long can you go without teeth before all these unpleasant consequences appear? Here you need to figure out what happens after tooth loss.
In the jaw bone there is a so-called tooth socket. If a tooth falls out, then the number of blood vessels in the area of its former root decreases - they are no longer needed. Following this, the bone tissue around the hole begins to dissolve, and instead of the hole, a dent forms. Then the jaw drops and becomes thinner in this place.
In youth, elastic skin and rapid cell renewal allow you to live 3-5 years before tooth loss is reflected in the form of wrinkles. But after 40 years, such wrinkles appear within six months to a year after tooth loss! It is difficult to say which is more dangerous - after all, while youth allows a person to avoid prosthetics, the jawbone is destroyed. So, at any age, it is advisable to restore a lost tooth within 3 months. Otherwise, there is a risk of aging outwardly earlier than nature should!
Why is it so scary
Whether wisdom teeth need to be treated or removed immediately is not easy to decide. They are inconvenient to treat either for patients or for dentists themselves. The former “run out of steam” in the chair, trying to open their mouths wider, while the latter must show all their dexterity in order to reach the problem tooth. A dentist can even cure a difficult tooth, but the gum pockets around the gums can constantly become clogged with food, then the “carious monsters” again attack the tooth and all efforts are in vain.
If pulpitis occurs, rarely will anyone undertake root canal treatment. Roots in the amount of up to 5 pieces, adhesions, shapes in the form of hooks and squiggles, will become an impenetrable labyrinth for any speleologist dentist.
So, having suffered and spent N amount of money, many come to the logical result - “Delete!”
But removal can be just as scary as treatment. According to studies, complications occur after removal in more than 50% of cases3. They are often successfully treated, but add sick days and discomfort.
After wisdom tooth removal, there is a high probability of encountering complications.
Contraindications
It is prohibited to carry out manipulation during pregnancy, diabetes, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, or the impossibility of anesthesia due to allergies.
Laser exposure does not cause bleeding. Despite this, the use of laser techniques is not recommended for blood diseases.
Advantages
Laser therapy for extraction has a number of advantages:
- It is performed under anesthesia and is not accompanied by pain.
- Reduced likelihood of complications. Under the influence of a laser, the edges of the wound are sealed and disinfected.
- Fast execution.
- Wound sterilization.
- Short rehabilitation.
The device operates silently. There is no drilling sound or vibration.
Flaws
Like any treatment method, the laser method has disadvantages. Since the procedure is new, not all dentists are equipped with the necessary equipment. The operation must be performed by a qualified and experienced doctor. This is due to the high cost of the service.
Preparatory stage
Before the procedure, the dentist carefully examines the oral cavity. The set of preparatory measures includes:
- The location of the element to be deleted is determined.
- The patient's medical history is studied. Chronic pathologies are identified.
- X-ray diagnostics and general clinical blood tests are performed.
- The patient is prohibited from taking painkillers on the eve of the intervention.
- It is recommended to eat a large meal a couple of hours before surgery.
The dentist selects the appropriate anesthesia and sets up the laser equipment.
Carrying out the procedure
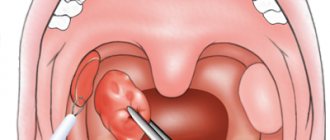
The laser extraction technique is almost identical to traditional tooth extraction. Initially, the doctor applies anesthesia. The laser beam does not cause pain when making incisions. Anesthesia helps eliminate discomfort during surgery.
Step-by-step operation:
- Dissection of the mucous membrane. Required if the tooth is hidden under soft tissue. The flaps are folded back to provide access to the unit.
- Breaking an element into pieces. A molar that has split on its own does not undergo crushing.
- Cleaning the hole from fragments. The doctor checks the socket for the absence of small bone fragments.
- Membrane installation. Prevents infection from entering the wound and the development of the inflammatory process.
- Returning the mucosal flaps to their place and applying sutures.
The technology helps minimize trauma to bone and mucous membrane tissue.
Postoperative period
During the recovery period, the patient must adhere to medical recommendations:
- Refrain from eating food for two hours after the procedure.
- Do not eat solid food.
- Avoid intensive rinsing in the first days.
- Do not heat the damaged area.
- A cold compress will help relieve swelling.
- Avoid physical activity and visiting the sauna and swimming pool.
- Perform oral hygiene daily. When brushing your teeth, do not touch the post-operative area with a brush.
The recovery period lasts up to three days. For complex procedures, dentists prescribe antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Complications
Ignoring medical recommendations and rules for sanitation of the oral cavity leads to the development of complications. Swelling and inflammation occurs in the postoperative area. If you experience any warning symptoms, pain, swelling or discomfort, you should contact your doctor.
Should I delete or not?
Yes. If diseases or complications have already arisen. Or the situation with 3 molars creates a high risk of diseases and their complications. Such cases include:
- lack of space in the dentition. Crowding – deformity – malocclusion;
- incorrect anatomical position (dystopia). The tooth grows towards the cheek, tongue, throat. May damage mucous membranes and cause ulceration;
- installation of braces to correct the bite. Freeing up space for other teeth;
- destruction of a neighboring tooth. As the tooth grows, it can damage the adjacent molar;
- problems with eruption (retention).
No. The teeth are healthy, there are no problems and no problems are expected.
Special attention. Long business trips, pregnancy, any situations that limit the possibility of providing medical care. Before these events, it is better to get advice and assess the risks, because treatment often requires surgery.
The essence of the technique
Lasers are actively used in medicine and enable doctors to perform complex surgical interventions while minimizing complications. Laser machines are used to remove tartar, plaque, and treat oral diseases.
Using a laser beam, thin incisions are made without bleeding, large-scale damage or infection of the wound. Laser exposure has an antibacterial effect.
The laser technique for removing a unit is used for severe pathologies, when the tooth is hidden under the mucous membrane and needs to be crushed into pieces.
Prevention
The right strategy, starting with teething, will help you worry less and reduce risks:
- Orthodontic consultation at a young age.
- The culture of brushing teeth using effective methods in hard-to-reach places, not only with a brush, but also:
- dental floss;
- irrigator;
- mono-beam brush.
- Preventive hygiene and examination
- Timely removal when problems are inevitable and it is better to prevent them than to treat the consequences.
The wisest decision regarding your health and wisdom teeth would be to visit a dentist in a timely manner. This will help protect you from problems and, most importantly, from consequences.
Literature:
- Iordanishvili A.K., Korovin N.V., Serikov A.A. ANATOMIC AND TOPOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE JAWS DURING ERUPTATION AND RETENTION OF WISDOM TEETH // Problems of Dentistry 2022 No. 3.
- Iordanishvili A.K., Korovin N.V. et al. AGE FEATURES OF WISDOM TEETH DISEASES//Kursk Scientific and Practical Bulletin “Man and His Health” 2015 No. 4.
- Iordanishvili A.K., Korovin N.V. et al. COMPLICATIONS AFTER REMOVAL OF WISDOM TEETH AND THEIR TREATMENT//Kursk Scientific and Practical Bulletin “Man and His Health” 2022 No. 4.
Features of wisdom teeth
Despite the anatomical structure identical to the rest of the molars, wisdom teeth have distinctive properties:
- Appearance. Although from an anatomical point of view wisdom teeth are no different from other molars, from a visual point of view they can have a rather unpredictable structure and appearance. This is especially true for the upper “eights”, because they have an unusual crown structure. The molars of the lower row have an imperceptible difference from the rest of the teeth.
- Lack of chewing function. Wisdom teeth do not take part in the process of chewing food. The loss of this function was influenced by evolution. For this reason, eights are most often susceptible to various dental diseases, because chewing food makes it possible to stimulate blood flow in the oral cavity and avoid the formation of plaque and tartar.