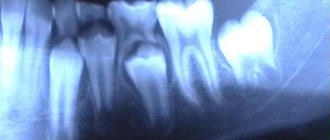
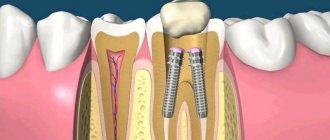
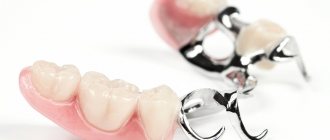
One of the signs of moderate and severe periodontitis is tooth mobility caused by atrophy of part of the bone tissue of the tooth root. In order to prevent further loosening and loss of teeth, restore their appearance and chewing function, the CELT Dentistry Department uses fiberglass teeth splinting.
This technology is rightfully considered effective and gentle and is a worthy alternative to solid and ligature tires. And numerous positive reviews from patients who have undergone the procedure of splinting teeth with fiberglass in our clinic speak for themselves.
Splinting mobile teeth with fiberglass
allows you to fix the teeth in the optimal position and achieve an even distribution of the load between them. The procedure allows you to reduce the occlusal load, eliminating the risk of damage to the retaining bone and periodontal ligament. Thanks to it, you can avoid even greater loosening and displacement of mobile teeth.
Splinting of 1 tooth using Glass Span threads without composite - RUB 2,000.
Splinting of 1 tooth with light-curing composites—RUB 3,000.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a consultation with a dentist-therapist is 1,000
Make an appointment
Indications
- Periodontal disease;
- Pathological conditions of the gums, in which they become inflamed and bleed;
- Oral injuries;
- Severe displacement of the dentition;
- Severely exposed tooth roots.
Contraindications
- Allergic reaction to materials or anesthesia;
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Neoplasms of a malignant nature;
- Pathologies of bone tissue;
- Inflammation of the oral cavity;
- Poor quality of oral hygiene procedures.
Fiberglass splinting technique
Fiberglass threads have been used in dentistry relatively recently. The prices for splinting teeth with fiberglass are affordable, and the effect of the procedure has earned high marks from both doctors and their patients.
The procedure is carried out in several stages by an experienced specialist and includes the following:
- In order to prepare teeth for installation of a splint, they are cleaned of deposits, abrasive surface treatment is carried out, during which a horizontal recess is created for laying fiberglass tape, and the surface of the teeth is etched;
- Laying the tape into the recess is carried out gradually, inserting it into the spaces between the teeth;
- A light composite is applied and polymerized;
- The surface is sanded.
Fiberglass dental prosthetics: when and why
Restoring a tooth using a pin
Fiberglass for splinting teeth
Adhesive bridge prosthetics
Many people associate the word “fiberglass” with construction work, but not with dental treatment. At the same time, fiberglass is one of the modern materials actively used in dentistry. With its help you can solve several problems at once. For example, using a fiberglass pin, doctors restore a tooth affected by pulpitis.
Features of splinting the anterior teeth of the lower jaw
The procedure requires creating horizontal indentations on the inner surface of the teeth. It is desirable that its height and depth be about 2 mm. A tape is placed in it and a light-curing composite material is applied. The number of teeth involved may vary and is determined depending on the condition of the front teeth. In addition to the most mobile ones, fixed teeth are necessarily involved: most often these are fangs. This approach allows you to remove the load from the movable incisors by transferring some of it to the canines.
Clasp prosthesis
This method refers to removable splinting. The clasp prosthesis is represented by a structure that is made in the form of a metal arch with claw-shaped processes and multi-link clasps that fix each tooth individually. The prosthesis also has crowns under which the supporting teeth are installed, this helps protect patients from stress. The specified splinting design is selected for each person individually, based on the condition of the dentition, bite and other related factors.
Among the main advantages are:
- reliable fixation;
- proper load distribution;
- there is no need to grind crowns;
- comfort and convenience compared to many designs;
- durability.
There are also minor drawbacks. Some people feel discomfort in the mouth for the first time after installing dentures; when there is a need to install clasps on the front row, metal crowns do not look very aesthetically pleasing. This type of splinting is also not suitable for those who are extremely missing teeth.
Important! The duration of wearing the clasp construction exceeds 7 years, but experts advise using it as temporary, since there is a risk of bone tissue atrophy. In this case, if it is not possible to restore a loose tooth, it is best to remove it and replace it with a high-quality implant.
How is the effect achieved?
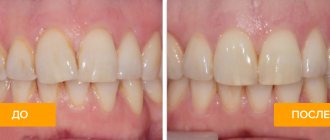
Looking at the photo of splinting teeth with fiberglass, you can see that the group involved in the splint is one whole and absolutely motionless... and this effect is not deceptive. The fact is that when illuminated, the fiberglass tape becomes very hard, and its fixation on the teeth makes it possible to redistribute the chewing load between the teeth. Even if the patient bites on one tooth, the load will be distributed over all teeth that are involved in the splint. This approach eliminates the loss of contact between teeth, which is observed with periodontitis. With it, each tooth receives maximum load, which leads to even faster progression of the disease. Thanks to the use of fiberglass tape, the process of bone atrophy slows down and often stops completely.
The main causes of loose teeth
Loose teeth in any case is a serious symptom that indicates the development of a pathological process in the body. Experts have identified several main reasons affecting tooth loosening:
- periodontitis;
- periodontal disease;
- gingivitis;
- congenital gum pathologies;
- jaw injuries;
- unbalanced diet;
- tumor formations in the jaw and gums.
The most common cause of this condition is periodontitis, which is inflammation of the periodontal tissue. In this case, the root is exposed and the teeth begin to loosen. Periodontal disease can also often cause loosening; its result is a lack of strength between the tooth and the surrounding tissues. In any case, when one of these diseases is diagnosed, careful and long-term treatment is necessary to help fix the teeth.
On a note! Sometimes a similar condition can be caused by the absence of neighboring teeth when dental implantation and prosthetics were not carried out in time. In this situation, doctors also prescribe splinting and restoration of the lost unit.
Advantages of fiberglass splinting
In addition to the fact that fiberglass is a biologically compatible material that will not cause allergic reactions and inflammation, the splinting procedure with fiberglass thread has other advantages. She:
- is able to provide long-term reliable stabilization of the dentition;
- eliminates the need for depulpation and grinding of large amounts of dental tissue;
- does not spoil the smile, since the splint is installed on the inner surface of the teeth and is not visible;
- It is carried out quite quickly (usually one visit to the dentist is enough);
- allows you to reduce or eliminate gaps between teeth.
Moreover, the splint itself is compact, so it will not cause discomfort when eating and will not affect diction. It can be used as a support for an artificial tooth. If the need arises to remove the fiberglass tire, it will be easy to do, and the defect left behind can be easily sealed.
The CELT clinic performs effective, absolutely painless and prompt splinting of teeth with fiberglass thread. When carrying out restoration, simultaneously with installing a splint, our specialists can also perform dental prosthetics.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Why do you need splinting for periodontitis and periodontal disease?
In the vast majority of cases, treatment with splinting is carried out for severe periodontal diseases, which entail mechanical deformation of bone tissue and gums. In this case, the necks are exposed, giving the tooth increased mobility. Fastening such teeth to each other (or, even better, with elements tightly seated in the thickness of the gums) helps prevent their premature loss.
In addition, permanent or temporary splinting should solve the following problems:
- Prevent pathological loosening of teeth and fix them in the socket.
- Evenly distribute the chewing load across all elements of the dentition.
- Stop tooth movement and bite changes.
- Stabilize the situation while a permanent splint is being manufactured, if necessary.
- To consolidate the result of orthodontic treatment after wearing braces, aligners or vestibular plates.
In case of severe periodontal pathologies, the installation of permanent fixation structures is proposed. If we are talking about orthodontic treatment, then during therapy the teeth “get used” to being in the “correct” place, and after removing the splinting they no longer move.
If in the case of anterior teeth the procedure can be carried out only for aesthetic reasons, then splinting the chewing teeth is always aimed at restoring the natural function of the teeth - chewing food.
Indications for splinting
Most often in dentistry, temporary splinting of the lower and upper jaws is performed. This procedure is performed for the following indications:
- Pathological placement of individual teeth, both congenital and resulting from trauma and other deformations.
- Displacement of an entire row of teeth.
- Significant deposition of stone below the gum level.
- Exposure of the neck and even the root.
- Formation of deep periodontal pockets.
Orthopedic method
This method of treatment is used in the absence of one or more units. To fix moving elements, fixed orthopedic crowns and removable clasp dentures are used. The structures are made from an impression of the patient’s jaw, which makes them comfortable to wear. Crowns and prostheses reliably hold moving elements and also replace missing ones, restoring the full functionality of the row.
It is possible to restore one lost tooth, without crowns and without grinding down adjacent teeth.
In order to restore a missing tooth, the dentist may suggest making a bridge (adjacent teeth are ground down and covered with crowns) or installing an implant.
Fiberglass threads offer another option for closing the defect of a missing tooth. To do this, a small piece of fiberglass is “glued” to the adjacent teeth. If the missing tooth is large enough, a cross or a more complex frame is modeled on this segment. The missing tooth is modeled using light-curing composite material on this segment/framework.
This restoration has high aesthetic properties, and most importantly, does not damage neighboring teeth. However, the adhesive prosthesis cannot tolerate heavy chewing load. Therefore, there are a number of restrictions on its use. Most often it is used for the anterior and lateral groups of teeth, excluding chewing teeth (large molars).
Splinting with fiberglass tape
Splinting with tape gives a temporary effect - even if the procedure is carried out in compliance with the standards, and the patient adheres to the doctor’s recommendations, the service life of such structures does not exceed three years. If there are splints on the front teeth, but there are no molars, then there is a high probability of the splint breaking after a short time due to excessive overload. Therefore, it is advisable to restore the missing row so that the pressure becomes uniform.
Crowns last longer, but if periodontitis is in the initial phase, it is better to abandon this method, since it involves grinding down healthy teeth under the structure.
Clasp dentures have many advantages, especially if it is necessary to restore a large number of teeth and eliminate their mobility.
Materials
Today, dentistry uses different materials as splints, and not only their strength is important, but also aesthetics. The most common:
- Fiberglass;
- silk;
- armid thread;
- ceramics;
- composite;
- polyethylene.
Flexible materials create a durable splinting frame, fixed on the inside of the row. All materials are of increased strength, do not deform, do not shrink, are safe for gums and enamel, and are resistant to moisture and high temperatures. The cost of dental splinting in Moscow depends on the intervention technique, the complexity of the clinical case, and the material.
System properties and advantages
The ceramic material is very thin and fully compatible with other biological tissues. Due to the hydrophobicity of the system, the destruction of restoration areas by moisture is prevented.
The strength of the glass does not allow small dangerous fragments to fall off. Glas Span is completely safe and environmentally friendly. Does not wear out and is not subject to temperature influences. Does not unravel when cutting and does not unravel when modeling (unless necessary).
GlassSpan splinting tape has a number of advantages over other similar systems:
- does not require specialized equipment for operation;
- does not lengthen or shrink;
- maintains durability and constant physical properties even at high temperatures;
- absorption of a small amount of moisture, due to which it does not enter the prosthesis;
- the material is colorless and invisible in the mouth;
- durability, resistance and elasticity;
- high micromechanical retention;
- ensuring aesthetics;
- the work does not require special scissors, gloves or other tools;
- retains ductility, lasts a long time and wears out slowly.
Release form
Packaging: glass capsule.
The set includes:
- ceramic tape (GlasSpan Tape) - length 27cm (3 by 9cm), width 2.00mm;
- small cord (Rope Small) - length 27cm (3 by 9cm), width 1.00mm;
- medium cord (Rope Medium) - length 27cm (3 by 9cm), width 1.50mm;
- large cord (Rope Large) - length 27cm (3 by 9cm), width 2.00mm.
One set contains 4 glass capsules.
How should you care for your teeth after splinting?
In order for the procedure to give the maximum effect, and the frequency of visits to the dentist to repeat it is minimized, it is necessary to follow the recommendations for oral care. The main points include:
- Mandatory cleaning after every meal.
- Additional use of an irrigator in combination with dental floss.
- Eating non-solid and pre-chopped foods.
- Avoiding excessively cold or hot foods.
- When using the jaw-closing technique, food intake must be done using a tube or catheter.
By following these points, you can ensure the necessary comfort and avoid complications. It is also necessary to periodically visit the dentist for a preventive examination.
Indications
- Pathologies of the gums and periodontium, accompanied by mobility and displacement of teeth;
- loosening of units due to jaw injury;
- exposure of roots, pronounced gum pockets;
- consolidation of the result after orthodontic treatment with braces.
Teeth are placed on splints for a short (up to 1 month) or long (up to 1 year or more) period. Maintenance therapy for periodontal disease
provides for permanent splinting. The decision on the duration of treatment and the method of fixation is selected separately in each clinical case.
Interlig - instructions for use
A. PERIODONTAL RETAINER
- Preoperative;
- Isolate the working area with a rubber gasket and place wedges in the interdental spaces to prevent resin from leaking in these areas;
- Mark the location where the groove will be created;
Creation of a groove is an optional procedure and depends on the clinical situation
- Create a groove 0.8 mm deep and 2 mm wide;
- Treat with phosphoric acid 37% for 30 seconds; rinse and dry (the area with exposed dentin should not be dehydrated);
- Apply the adhesive according to the instructions for direct composite restorations,
- Light-cure each retainer segment for 20 seconds;
- Apply a layer of composite to the restorations (hybrids, microhybrids or nanoparticles), filling half the groove;
Resins containing microparticles should not be applied to retainers.
- Cut the fiber with scissors or a scalpel to a length shorter than the length of the groove. Excessive length of the Interlig will make it difficult to place. Place the Interlig in the groove and press it over the composite;
- Press and light-cure each fiber segment for 40 seconds;
Cover the remaining segments of the retainer with a strip of foil to prevent polymerization of the unpressed parts
- Apply a second layer of composite to completely cover the groove;
The composite should protrude slightly beyond the groove
- Photopolymerize the composite covering the fiber;
- Remove excess composite, perform occlusal adjustment, final finishing and polishing;
- Apply a final coat of adhesive to fill in any uneven areas; photopolymerize each segment for 20 seconds,
- Final result.
B. PRODUCTION OF DIRECT FIXED PROSTHESIS
- Preoperative;
- Mark the location where the tooth will be separated after extraction;
- Place after extraction;
- Due to gum retraction, after tooth extraction, the tooth should be trimmed 1-2 mm below the designated space; after cutting, the tooth should be convex and have a smooth surface;
- Open the canal through the root, remove all pulp tissue and fill the cavity with a composite (phosphoric acid and adhesive must be used);
- Isolate the area and make a groove 0.8 mm deep and 2 mm wide on the abutment teeth and on the extracted tooth;
- Place the extracted tooth with a small amount of composite in the vestibular part; Do not etch with nitric acid at this point as this composite will be removed. Photopolymerize the composite;
- Apply phosphoric acid 37% for 30 seconds, rinse and dry without dehydrating the dentin;
- Apply the adhesive according to the instructions for direct composite restorations. Light cure each retainer segment for 20 seconds.
- Apply a layer of restorative composite (hybrids, microhybrids or nanoparticles), filling half the slot;
- Using scissors or a scalpel, cut the Interlig fiber slightly smaller than the groove to facilitate insertion;
- Place the Interlig in the groove and press it over the composite: press and light-cure each fiber segment for 40 seconds.
- Cover the remaining segments of the retainer with a strip of foil to prevent polymerization of the unpressed parts.
- Apply a second layer of composite to completely cover the groove. The resin should extend slightly beyond the groove. Photopolymerize the composite;
- Remove excess composite, make occlusal adjustments, final finishing and polishing; Apply a final layer of adhesive to fill in uneven areas,
- Final result.
C. INDIRECT FIXED DENTURE (WORKING MODEL)
- In the oral cavity, create a groove on the supporting teeth (0.8 mm deep and 2 mm wide and give the required shape;
- Apply plaster sealant to the groove and surrounding areas;
- Choose an artificial tooth from a reserve or one made in a laboratory,
- Apply adhesive and photopolymerize each segment for 20 seconds;
- Fill half of the groove with composite. Do not light cure.
- Using scissors or a scalpel, cut the Interlig fiber to a size slightly smaller than the groove. Place the Interlig into the groove;
- Press and light cure each segment for 40 seconds,
- Cover the remaining segments of the retainer with a strip of foil to prevent polymerization of the unpressed parts.
- Apply a second layer of composite to completely cover the Interlig fiber and groove. Light-cure each segment for 40 seconds;
- To remove the part, remove the plaster using a drill or disk; Do not press it while removing it from the model as the connections may break. Perform occlusal adjustments, final finishing and polishing;
- The prosthesis is ready. Cement it in preparation (groove) according to adhesive cementation techniques.
D. STRENGTHENING TEMPORARY FIXED PROSTHESES
- In the prosthesis, create a groove 0.8 mm deep and 2 mm wide;
- Apply adhesive to the groove and light cure each segment for 20 seconds;
- Using scissors or a scalpel, cut the Interlig fiber to a size slightly smaller than the groove;
- Fill half of the groove with composite; do not photopolymerize;
- Place the Interlig fiber into the groove;
- Press and light cure for 40 seconds;
- Cover the remaining segments of the retainer with a strip of foil to prevent polymerization of the unpressed parts.
- Apply a second layer of composite to completely cover the grain and groove. Light cure each segment for 40 seconds;
- Perform final finishing and polishing;
- Final result.
Consequences
With periodontitis, the destruction of jaw tissue often occurs rapidly. If the moving units are not strengthened in a timely manner, they will simply fall out. And only implantation will help restore the dentition. The need for the procedure is determined by the doctor, based on the results of the examination and x-ray studies. Reviews confirm the good effectiveness of the intervention; patients quickly adapt and get used to the splint.
Alekperov Roman Borisovich Dentist-orthopedist, doctor of the highest category
What does “constant wearing” mean?
The patient does not have the ability to remove the splint until it needs to be replaced
Alekperov Roman Borisovich Dentist-orthopedist, doctor of the highest category
At what degree of periodontitis is it possible to splint teeth?
At the initial stage
Alekperov Roman Borisovich Dentist-orthopedist, doctor of the highest category
If I am afraid of surgery, is it possible to have anesthesia in advance?
No, only premedication is possible (providing psychological control to the patient by pre-administering medications)
Alekperov Roman Borisovich Dentist-orthopedist, doctor of the highest category
Can there be any complications during the operation?
No complications are possible during splinting
Technical qualities
Dentists who use GlassSpan in their practice claim that this system is easier to work with than other analog ones, since the product does not become contaminated.
Many of these materials require pre-treatment or impregnation with special resins and compounds before starting work; they cannot be touched by gloves without introducing dirt. This circumstance complicates the process of restoring the tooth and attempting to fix the splint in the mouth.
The splinting tape of the system is thin and quite flexible , while other reinforcing materials are much thicker. It can be cut with any scissors, which cannot be done with material from other manufacturers. They can only be cut with special scissors.
The tape contains ceramic fibers, but not plastic . Ceramics are more stable in parameters, do not absorb moisture, and do not require additional processing than plastic. The transparency of ceramic fibers is more aesthetically pleasing and does not wear out.
If, when polishing or adjusting a restoration, plastic fibers are accidentally exposed to temperature, the process of fusion will begin. The material will quickly become contaminated and the doctor will have to redo the work.
This does not happen with the material of the GlassSpan system - you can easily polish it, because... there is no reaction to temperature changes.
The cord is also different. This is the only type of fiber that has a round braided shape - twisted into a hollow rope. It is more practical and convenient for performing splinting, artificial extension of columns and strengthening of prostheses. Typically, ropes are inflated with a flowable composite or layer-by-layer material.
The GlassSpan system also stands out for its patented surface treatment method - it has ceramic etched fiber, which guarantees complete final adhesion to the composite.
Some other types of fibers must first be coated with resin without undergoing a proprietary treatment, which reduces bond strength.
Areas of application
In practice, GlassSpan is used if necessary:
- perform periodontal strengthening (splinting) of loose lateral and frontal dental elements;
- provide rapid palliative treatment;
- bring diseased and reimplanted units back to normal;
- temporarily strengthen bridge-type prostheses;
- post-orthodontic preservation;
- form a long-term or temporary connecting bridge structure;
- quickly replace a removed or fallen out tooth element;
- perform adhesive splinting against the background of pathologies of periodontal tissues;
- carry out microprosthetics;
- restore the tooth using an intracanal pin.