What it is?
The narrowing of a row of teeth is a decrease in the jaw arch in transverse size. This pathology is characterized by a decrease in the width of the palate and its deepening .
The narrowing can affect either one or two jaws . The entire jaw does not always undergo abnormal development. In some situations, only partial deformation is noted, only on one side of the dentition.
Most often, narrowing is diagnosed in the upper jaw. The susceptibility of this pathology to the upper jaw is explained by its spongy structure, which creates a looser structure.
The anomaly mainly affects the lateral sections in the premolar area. In this case, deformation of the dentition is formed along its entire length, or only in the anterior section.
The pathology is characterized by deepening of the palate and lack of proper closure of the antagonist teeth.
The anomaly may differ in the severity of the abnormalities and the clinical form of manifestation . With pronounced deviations and lack of treatment, the pathology can lead to narrowing of the lumens of the nose, causing dysfunction of nasal breathing.
There is also a violation of diction and the process of chewing food, due to the non-closing of the antagonists’ teeth.
How to express the shortening of the dentition, read in the next publication.
In this article we will talk about methods of treating open bite in adults.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/ryadov/udlinenie.html we consider the problems associated with lengthening the dentition.
Bilateral and unilateral narrowing
Reducing the width and increasing the depth of the palate, closure disorders are a complication. According to statistics, the upper jaw is more susceptible to pathology. This flaw leads to complications in organs related to teeth:
- The cause of deterioration in breathing occurs due to a decrease in the volume of the nasal cavity.
- Due to the small space, diction deteriorates, as the tongue becomes inactive.
- Food begins to be chewed worse - loose teeth cause problems with digestion.
Classification
According to the clinical manifestations of narrowing of the jaw arch, the anomaly is divided into several forms, each of which has its own characteristics :
- Narrowing of the jaw along its entire length . It is characterized by an elongated anterior section towards the frontal region. In this case, the teeth have a fan-shaped position. The lateral incisors fit tightly to the central ones.
- Tight jaw. The main sign of the anomaly is a saddle-shaped shape and compression of the dentition in the area of premolars and molars.
The compression in this case is uneven and does not extend to other parts of the jaw.In addition to narrowing, the pathology of this form is manifested by a violation of the direction of growth of the lateral teeth, which begin to protrude towards the cheeks or tongue.
- Narrowing of the anterior section . With this anomaly, the dentition of the frontal area has a V-shape. The incisors protruding forward form an acute angle and are tightly arranged.
- Trapezoidal shape . The jaw arch has four corners and its appearance resembles a trapezoid. The incisors are very crowded, but do not protrude forward. Their rotation around their axis is often noted.
- Uneven development . It is characterized by a narrowing of the jaw arch in certain areas. It differs from other pathologies by the manifestation of crowding only in certain segments.
Regardless of the form of the anomaly, their clinical picture may worsen over time, leading to even greater deviation of the teeth and narrowing of the jaw arches.
General overview
By narrowing we mean a condition of the dentition characterized by an altered anatomical shape. With natural development, the upper section has an ellipsoidal structure, and the lower section has a parabolic structure. Any deviation from the norm is considered an anomaly requiring orthodontic correction.
Geometric specificity causes reduced transverse dimensions with narrowing, expressed in one- or two-sided form. The consequence of the development of the anomaly is an increase in the palatal depth, leading to a violation of occlusion. As a rule, pathology is detected on the maxillary arch, which is caused by the peculiarity of the bone structure, which has less density.
The negative consequences that arise during the long course of the pathology include not only violations of the functionality and aesthetics of the jaw, but also such factors as:
- Difficulties in the respiratory process associated with contraction of the nasal cavity;
- Disorders of diction and articulation caused by limited space for the tongue;
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract caused by poor quality food processing.
The choice of treatment method depends on the indications of the clinical picture, allowing one to determine the type of anomaly.
Why does it happen?
Numerous clinical observations have made it possible to identify the causes of jaw narrowing .
The main ones include:
- Late transition of the child to solid food. Chewing hard foods promotes the development of jaw bones, which is important during the period of active growth of a child.
- Premature removal or loss of baby teeth. In this case, the absence of chewing activity and the release of dysfunctional space play a role.
- Disruption of metabolic processes leading to changes in the structure of bone tissue.
- General pathologies that provoke the appearance of constant nasal breathing or impair the functions of speech and swallowing.
- Having bad habits. For example, constant sucking of a pacifier or fingers. This group of reasons also includes a child falling asleep with a bottle in his mouth or being later weaned from it.
- Anomalies in the development of the muscular apparatus of the jaw and tongue.
- Genetic predisposition.
Diagnostics
The wide variety of forms of the anomaly often complicates the diagnostic process. In order not to make a mistake in making a diagnosis, in addition to visual examination, several research methods are used.
These include:
- Pon's method . Allows you to determine the relationship between the width of the mesiodistal fragment, which includes 12 teeth, and the width of the jaw arch;
- Howley-Herbst diagram . Helps to identify the degree of narrowing;
- anthropometric analysis . It is made using models made of plaster to identify abnormal areas and the degree of occlusion;
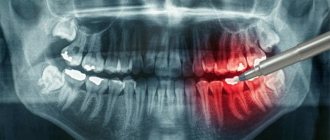
- teleradiography . Designed to determine the nature and type of narrowing;
- radiography . Aimed at studying the area of the palatal suture: determining its structure and width;
- orthopantomography . Used to obtain a general picture of the condition of the jaw and study the structure of its tissues.
In addition, external and functional characteristics are taken into account.
Treatment
Treatment of narrowing of the dentition is carried out only for certain indications and using special devices.
Before correction, the doctor prepares the dentition, which includes removing or treating bad teeth, replacing old low-quality fillings with new ones, and professional oral hygiene.
Once the cause of the pathology is identified, work is carried out to eliminate it.
Indications for expansion
Dilation is prescribed if observed:
- violation of the closure of teeth of the same name in opposite rows;
- abnormal position of single specimens or groups: extension, reversal;
- pronounced violation of facial aesthetics;
- excessive deepening of the palatal arch, leading to dysfunction of nasal breathing;
- regular injury to the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- frequent inflammation of periodontal tissues resulting from incorrect position of teeth.
We will tell you in a separate review whether myogymnastics is effective for distal occlusion.
In the next article we will talk about the consequences of expanding the dentition in adults.
Follow the link https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/okklyuzii/mezialnyiy-prikus.html, read about ways to correct mesial bite.
Expansion devices
Treatment methods are prescribed depending on the shape and location of the anomaly.
Most often, during therapeutic treatment I use the following devices :
- Derichsweiler apparatus. Refers to non-removable screw structures. Designed for correction of the upper jaw, which is narrowed along its entire length, in particularly difficult cases.
This design is used mainly in children in the late period of a mixed dentition or with a permanent one formed. The device has a strong effect on bone tissue.The device is a metal two-part base of a beam type, which is fixed on the supporting teeth. The base is connected using a special spacer screw, which moves the two parts of the base apart during adjustment.
Restoration of the normal size of the jaw is achieved by gradually breaking the palatal suture. Thanks to this, with the help of a screw device, the apical base is expanded in the sagittal and transverse directions, covering the area of the nasal septum.
The use of this design, in some cases, allows one to avoid surgical intervention. But since the device is a rather aggressive technique, it is used quite rarely.
- Expansion plates equipped with springs and expansion mechanism. They are a more gentle option and are used to correct the jaw during the period of milk or early replacement teeth.
This device consists of a base that exactly follows the arc of the sky. The device has a built-in small mechanism that allows for minor correction of the jaw shape.The plate is attached to the supporting teeth using metal clasps, which allows it to be removed at any time.
Wearing this device allows you to correct the shape of the jaw arch by expanding the palatal suture and directly transforming the bone tissue in the area of the alveolar bone, due to the tight fit of the base of the plate.
These devices are capable of restoring the normal shape of the jaw arch only in childhood. Surgical methods are most often used to treat adults.
Surgical methods
Surgical correction of the arch can act not only as an independent method . It is often used in conjunction with hardware treatment.
The following methods are used for surgical treatment :
- Tooth extraction .
This method allows you to obtain free space, due to which expansion will be possible. Typically, premolars are suitable for extraction. To obtain a positive treatment result, it may be necessary to remove 2 teeth to ensure uniform jaw growth on both sides. - Perforation of the jaw bone .
To do this, the mucous membrane is peeled off, after which, using a dental bur, through holes are made in the bone at an equal distance from each other. The holes are connected with a small groove. Then an expansion mechanism is installed, due to which the jaw expands, and the perforated area is filled with new bone tissue.
Reasons for formation
The development of the jaw in children occurs under the influence of the tongue, its chewing and facial muscles. When some pathology appears in the activity of these muscles, a modification of all parameters of the arches occurs.
Prerequisites for jaw reduction:
- If baby teeth have fallen out or been removed.
- The chewing load decreases and free space appears in the rows, which causes deterioration in the functioning of the jaw.
- Parents started feeding their child solid food late.
- Jaw growth occurs due to a decrease in chewing severity.
- Metabolic imbalance affecting osteogenesis.
- When children acquire the habit of sucking their cheeks, tongue, etc., this causes an imbalance in muscle activity.
- Mouth breathing.
- An extremely serious aspect that leads to countless failures.
- Pathologies leading to transformation of the dentofacial apparatus, resulting in problems with speech, swallowing, and breathing.
- Genes.
Diagnostic methods
The disorder is characterized by symptoms that make diagnosis difficult, but an experienced specialist often, after one medical examination, decisively declares problems and makes a diagnosis. But additional research may be required.
- Radiography. An x-ray of the palate, which determines the condition of the palatal suture, is extremely significant.
- In addition, teleradiography and orthopantomography are often performed.
2.1. X-ray is a frontal photograph of the jaws and face, which allows you to examine the interaction of a number of teeth in the desired direction.
2.2. An orthopantomograph shows the entire area, using a camera that moves around the circumference of the head.
- Anthropometry of the dentofacial apparatus. A cast of the jaw, constructed from a special plaster, is studied in 3 mutually perpendicular projections.
- Pon's method. The essence of the method is that the total width of the teeth in the mesiodistal direction is measured, and the usual row width in the area of the initial incisors is taken from the tables. By comparing the actual value with the reference value, the jaw contraction is calculated.
- Howley-Herbst diagram Howley-Herbst method. Consists in building the jaw arch. Applying this criterion, a curved line (ellipse or parabola) is constructed, the shape of which is specific, having the shape of an exemplary arc for a particular client
Indications for expansion
This procedure applies in the following situations:
- When the upper row of the jaw narrows.
- The aesthetic attractiveness of the face is impaired.
- Incorrect condition of specific teeth.
- Pathology of occlusion.
- Pathology of nasal breathing.
- If soft tissues are damaged.
- If the periodontium becomes inflamed.
- The functionality of chewing and swallowing is impaired due to jaw contraction.
- Hereditary defects.
- Lack of space in a row.
Devices
Their effects are mechanical. Slow displacement allows you to increase the arc due to the alveolar deflection of the incisors, without breaking the palatal suture.
If a larger increase is required, in this case it is performed by opening the palatal suture.
The expansion technology is carried out using a Derichsweiler apparatus with a Hyrex screw.
- Derichsweiler apparatus
It is compact - a non-removable configuration, consisting of a metal frame with a screw, and bushings fixed on the chewing elements. It is used to expand the HF along the entire length. When the screw is turned, the frame increases. Its action is based on the rupture of the palatal suture. Thus, the size of the nasopharynx increases and breathing is stabilized. The device is used when conventional methods no longer help, and there is a question about the operational impact. Often it gives the opportunity to cancel the operation
- Expansion plates
Design-expanding mechanisms: screw, spring three-wire arc. They are considered a gentle type, correcting an anomaly in a rapid or premature hybrid occlusion. The expanding plate fits closely to the palate, repeating its configuration. It is combined with the main components with clasps, which can be removed at any time. Plates are used for minor deviations.
- Surgical intervention
The procedure is used in the most difficult cases, if completely orthodontic and myofunctional therapy is ineffective.
Used in an ensemble with orthodontic correction.
Orthodontic surgical therapy is a three-stage procedure.
First is carried out:
- preoperative preparation for surgery;
- surgical intervention;
- orthodontic correction is completed.
The most important operations:
- Elimination of the tooth for unobstructed access during surgery.
- Perforation of the jaw bone.
It is carried out with the detachment of part of the mucous membrane. Holes are made in the jaw and connected by grooves. The wounds are then sutured and an expansion device is installed.
Result
| Click to sign up for a FREE consultation |
In small children, the expansion of the jaws in most cases proceeds rapidly (sometimes after a few months it also comes to an end). And it still ends well. The outcome of treatment with orthodontic appliances for older people is by no means so predictable (it can last for years).
A long period of treatment for narrowing of teeth can be avoided by taking preventive measures:
- The main thing is the current treatment of enterobacterial and viral infections of the nasopharynx, in order to normalize breathing.
- It is also necessary to wean children from those habits that can disrupt the formation of jaw bones. For example, finger sucking, which is quite common in children.
- The position of the baby during sleep sometimes also affects the formation of the jaws (when his head rests on his chest).
- Children's nutrition simply must be in accordance with their age. Being late in switching to solid food can disrupt the formation of the jaws due to underdeveloped muscle functionality. Also, in the baby’s food, parents should include all the elements necessary for the formation of the body.
Note! Regular preventative visits to the dentist will help identify narrowing of the jaw as soon as possible. And also, together, the father and mother are obliged to carefully monitor the formation of the dentofacial apparatus of their children. As a result of identifying deviations, it is necessary to immediately take the child to the dentist.