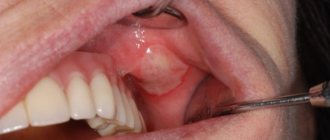
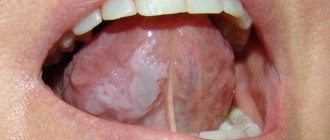
Ulcers caused by trauma
The main reason for the appearance of ulcers when the mucous membrane is injured is infection in the wound. Most often, white rashes occur due to the habit of biting nails or the tip of a pencil or pen.
Fans of seeds and hard toothbrushes may also be at risk. Many people believe that hard bristles remove plaque better. Actually this is not true. If you carefully brush your teeth with such a brush, you can damage the enamel, gums and cause inflammation.
Other causes of mucosal injury:
- uncomfortable dentures;
- braces or other orthodontic structures;
- habit of unconsciously biting your cheek or tongue;
- exposure to mucous membranes with drugs or acids.
How to treat?
It is enough to remove the irritating factor and wait 1 - 2 weeks. Usually the ulcers go away on their own. If this does not happen, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Herpetic or aphthous?
It will be somewhat more difficult to distinguish between herpetic and aphthous stomatitis. The latter got its name from the Greek term “aftha”, which means “ulcer”.
If with herpetic stomatitis there are many ulcers, but they are small, then with aphthous stomatitis there are few of them, and the size can reach 7–8 mm.
The second important distinguishing feature is the absence of swelling of the gums with aphthous stomatitis.
If you are looking for differences between herpetic and aphthous stomatitis, then the third thing you should pay attention to is the localization of the rash. Aphthous is characterized by the appearance of ulcers in the oral cavity, while herpes infection can spread to the border of the lips.
Ulcers caused by oral diseases
White sores in the mouth can appear due to diseases of the oral cavity. The most common cause is stomatitis. It comes in several types:
- aphthous;
- herpetic;
- bacterial;
- fungal.
| White ulcers in adults and children occur with aphthous and herpetic stomatitis. This disease can appear due to stress, untreated caries, lack of vitamin C, or overexertion. It is better not to self-medicate, but to immediately consult a doctor. Recommendations, in addition to medications, may include treatment of caries, a balanced diet, stress reduction, etc. |
| There are two separate forms of stomatitis - Bednar's aphthae and Setton's aphthae. The former develop only in a child due to injury to the mucous membrane or poor oral hygiene. Such rashes are also called erosions. Setton's aphthae is a more complex and painful phenomenon. It begins with the appearance of compactions, which then develop into painful ulcers. They most often form on the inside of the cheeks, in the corners of the lips and on the sides of the tongue. |
| Another cause of white sores is gingivitis. In smokers, such rashes are much more common due to the effects of nicotine on the mucous membranes. Those who have poor oral hygiene, reduced immunity and hormonal imbalances are also at risk of encountering gingivitis. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis: when the tissue that supports the tooth is affected. And this is a direct path to tooth loss. |
Types of disease
According to ICD-10, aphthous stomatitis is assigned code K.12. Within the code there are three qualifying diagnoses, including K.12.0 - “recurrent aphthae of the oral cavity,” which also includes aphthous ulcers.
According to the form of occurrence, acute and chronic aphthous stomatitis are distinguished. The first is characterized by the appearance of ulcers and severe hyperemia - swelling, redness of the mucous membranes. Severe pain occurs, especially when eating or talking. Submandibular lymph nodes may enlarge and body temperature may rise.
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis may be the result of improper or untimely treatment, as well as the inability of the immune system to cope with the disease. It is characterized by periodic exacerbations. Outside of exacerbation, symptoms may be erased or completely absent.
The disease is classified into three forms depending on the severity:
- light. From 1 to 2 afts up to 10 mm in size. Moderate pain during mechanical action, relapses occur no more than 2 times a year;
- average. Up to 5 aft, the course of treatment takes up to 3 weeks. The pain is quite pronounced, there is an enlargement of the lymph nodes, relapses up to 2 times a year;
- heavy. Multiple aphthae appear, severe pain. An increase in temperature occurs, and symptoms of general intoxication appear. Treatment takes up to a month, relapses occur up to 6 times a year.
Also, according to the form of occurrence, the following types of inflammatory diseases are distinguished:
- fibrous: blood microcirculation in the upper layer of the mucosa is disrupted, aphthae appear, covered with a fibrous film (plaque). Such ulcers heal completely within 14 days. The disease affects the mucous membrane of the lips, the lateral surfaces of the tongue, and transitional folds. This stomatitis recurs up to 3 times a year;
- necrotic. The epithelium is destroyed, the mucosal area dies. Replacement of tissues with normal epithelium takes from 14 to 30 days. This aphthous stomatitis is not accompanied by acute pain; it is usually observed in patients with severe diseases, including blood pathologies;
- grandular. Damage to the ducts of the minor salivary glands occurs. In this regard, aphthae form close to the glands, and drying of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity occurs due to a decrease in saliva production. Ulcerations are painful and heal within 1–3 weeks;
- scarring. Damage to the cavity of the salivary glands leads to the involvement of connective tissue in inflammation. Aphthae are observed both at the location of the glands and on the mucous membranes of the pharynx and palate. The disease develops into large painful ulcers (up to 1.5 cm). Healing takes up to 12 weeks; after the acute process, pronounced scars remain;
- deforming. The most severe form of the disease, which provokes changes in connective tissue. Aphthae heal extremely slowly, which is accompanied by deformation of the palate, lips, and sometimes narrowing of the oral cavity occurs (if aphthae was observed in the corners of the mouth).
Ask a Question
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
How to treat herpes stomatitis? Unfortunately, the herpes virus, once entered into a person’s blood, remains in a “dormant” state for the rest of his life. But treatment of viral stomatitis is possible provided that you do not delay visiting the dentist when the first signs of the disease are detected. During the period of therapy, in order to avoid infecting loved ones, you should eat and drink from separate containers and avoid kissing. The patient is recommended a diet that excludes spicy, smoked, sour and salty foods, which can irritate the damaged oral mucosa, and an increased drinking regimen (up to 2.5 liters per day), aimed at combating the manifestations of general intoxication of the body.
Organization of diagnostics
If a person goes to the hospital with complaints of discomfort and pain in the oral cavity, the doctor first conducts a survey to diagnose associated lesions. Then tests are prescribed:
- allergy test;
- bacterial culture from the site of inflammation to identify the type of infection - viral, fungal or bacterial.
A general blood test and blood serum test are required. If necessary, a referral for diagnostics from specialists of a different profile is issued.
Only after a full examination, identification of the etiology and type of the disease is it prescribed how to treat inflammation in the mouth. Independent actions will only aggravate the condition and provoke complications.
- Diseases of the tongue and oral cavity: photos and names of diseases of the mucous membrane in adults, methods of treatment
How to distinguish herpes sore throat from stomatitis?
Despite the fact that these medical terms have the same grammatical root, herpetic sore throat and herpetic stomatitis are two different diseases. Unlike stomatitis, herpes sore throat occurs not due to the penetration of the herpes virus, but as a result of an adenovirus infection (in particular, the Coxsackie A virus). Children are more likely to suffer from this disease than adults. The rashes are localized, for the most part, on the soft palate and tonsils. Typical symptoms of stomatitis include pain in the abdomen and abnormal bowel movements.
Attention!
The disease begins acutely, with a jump in temperature to 40 degrees, and is severe, so differential diagnosis should only be carried out by a doctor.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammation of periodontal tissues, which includes the teeth, ligaments, cementum and gums. Periodontitis as a disease is a consequence of gingivitis - a minor inflammation of the gums, the main cause of which is neglect of oral hygiene. If with gingivitis the inflammation spreads exclusively to the soft mucous membranes, then with periodontitis the ligaments that hold the teeth in the sockets are affected. This is why in 90% of cases when this disease is diagnosed, tooth mobility is observed, which eventually leads to their loss.
The most common causes of the disease are the following:
1. Improper or irregular oral care
. Dental plaque, which is present on the surface of the teeth and in the spaces between teeth, is not as safe a substance as it might seem at first glance. Soft and easily removed at the beginning, it goes through certain cycles of “development”. The result is the mineralization of plaque and its transformation into hard tartar. This process in most cases is observed in those who do not pay due attention to daily oral care or use an incorrectly selected toothbrush, toothpaste and mouthwash.
2. Poor blood supply to the gums
. Periodontitis is one of the most common problems among smokers. Substances contained in tobacco smoke lead to a narrowing of the blood vessels in the oral mucosa and their fragility, which impairs the blood supply to the gum tissue and supporting apparatus of the teeth. A slowdown in blood circulation and, as a consequence, the development of periodontitis is also facilitated by a lack of chewing load caused by eating habits (for example, the predominance of soft foods in the diet).
3. Nutrient Deficiency
. The lack of fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs, a sufficient amount of fish, meat and dairy products in the diet quickly leads to a lack of essential substances in the gum tissue. If poor nutrition is a permanent habit, then over time the metabolic processes in the gums are disrupted, which creates the ground for inflammation and periodontitis. A deficiency of vitamins A, C and group B can lead to negative consequences.
Treatment of periodontitis
Professional teeth cleaning is an integral step in the treatment of periodontitis. This procedure removes physical obstacles (plaque and tartar) that prevent the gums from returning to their previous position and tightly covering the teeth.
Drug treatment - the use of antiseptics for topical use. This need is due to the high risk of spread of inflammation and infection to other tissues.
Surgery
At an advanced stage of periodontitis, when the inflammation has spread deep into the bone tissue, surgical intervention becomes necessary. Such manipulations include partial excision of the gums (gingivectomy), washing of periodontal pockets with medicinal solutions, removal of stones, and flap operations. In some cases, surgical treatment of periodontitis involves the implantation of bone tissue substitutes or the application of collagen or artificial membranes to restore the supporting apparatus of the tooth.
Compliance with oral care rules
Without regularly removing plaque and protecting the oral cavity from bacteria, it is impossible to achieve sustainable results in the treatment of periodontitis. Hygiene procedures twice a day with properly selected products, the use of dental floss and rinses will help make recovery faster.
Prevention
To avoid relapse, it is recommended to use rinses with an antiseptic effect, observe the rules of oral hygiene, and consult a dentist in a timely manner, because simple caries can become one of the factors in the development of pathogenic processes in the mouth. It is also recommended to get rid of bad habits, minimize the consumption of foods that irritate the mucous membranes, strengthen the immune system, and carry out professional cleaning of the oral cavity.
The mechanism of formation of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
Bloody blisters in the mouth in most cases are not life-threatening. They are formed as a result of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. When microtrauma occurs, harmful microorganisms attack the damaged area.
After this, a number of responses are activated in the human body:
- The immune system is activated. Monocytes and leukocytes, as well as macrophages, instantly arrive at the damaged area, attacking the harmful pathogen and quickly destroying it.
- Immune cells die. This is a signal for other cells and substances are released in the affected area that are mediators of inflammation of the mucous membrane - serotonin, histamine and bradykinin.
- These substances cause a strong spasm of the circulatory system and the outflow of blood is hampered. After the spasm is relieved, all accumulated blood immediately flows to the site of inflammation. It moves at high speed and under pressure. A detachment of the mucous membrane occurs in the mouth, and a bloody blister appears.
Bad breath: how to get rid of it?
Halitosis or bad breath often accompanies us during oral diseases. The reasons for its appearance may be pus in the mouth, long-term use of certain medications, diseases of various body systems, and stress.
First of all, you need to understand the causes of the odor and visit a dentist, who will determine the disease and prescribe the appropriate treatment. At the same time, if nothing bothers you, then you need to pay more attention to hygiene:
- Carry out thorough brushing of your teeth 2 times a day using floss or special brushes;
- rinsing the mouth after every meal;
- use of rinses;
- professional cleaning of the oral cavity by a dentist 2 times a year.
The last point is especially important. Even if you are not bothered by your teeth or gums and there is no pain, a preventive examination by a dentist is mandatory. In many cases, it is better to prevent the development of the disease than to treat complications.