The treatment tactics for caries depend on the cause of the pathological process and its neglect. This is the most common dental disease, characterized by gradual tooth decay. The pathology goes through several successive stages; at first, the patient may not feel anything; in complex cases, complete loss of dental units is possible.
It is not difficult to detect the disease, because most of the symptoms are quite obvious. However, it is better to prevent the occurrence of carious lesions by following preventive recommendations, and then a snow-white smile will delight you for many years.
What types of caries are there?
There are several stages of the disease. They have a certain appearance and symptoms.
How to determine the stage of caries:
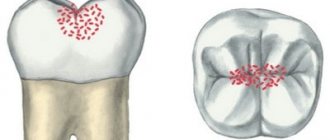
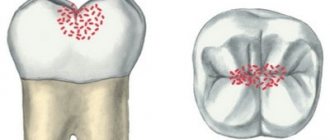
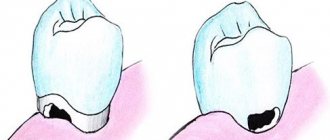
- In the spot stage: a white spot is observed on the surface of the enamel (focus of demineralization). The spot gradually turns brown. Enamel is the densest tissue in the human body, but due to various cariogenic factors it is gradually destroyed. Detecting the white spot is quite difficult.
- Medium caries: characterized by damage to the enamel-dentin junction in the form of a cavity, short-term sensitivity.
- Deep: extensive lesion affecting the deep layers of dentin. Pain appears from different types of irritants: mechanical, temperature, chemical.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using a visual examination and an x-ray. The image will show violations of the integrity of the enamel and dentin with uneven contours.
General recommendations for treatment
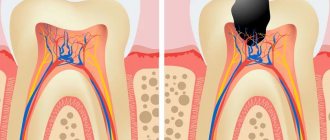
Traditional preparation of the defect is carried out using a drill. If the carious cavity is located within the dentin and does not affect the pulp, then after thorough cleaning, a filling is applied. However, sometimes with a small cavity, applying a multi-layer filling (insulating pad + filling material) is impossible. This feature is taken into account when treating caries on the contact surface of premolars and molars.
Another way to treat shallow caries in dentistry is to use a composite material with adhesive properties. In this case, extensive preparation and creation of a wide cavity is not required. Another method involves polishing a carious defect with remineralization of the enamel with medicinal applications, electrophoresis with a 1% sodium fluoride solution and other approved medications.
Medium caries is treated only by deep preparation and filling. In this case, the cavity is cleaned until the affected tissue is completely removed. High-quality sanitation ensures reliable fixation of the filling and increases its service life.
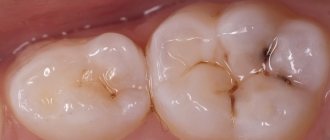
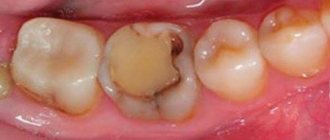
What does caries look like on teeth?
Not all patients know how to identify dental caries. To do this, you need to come to the dentist for an examination.
Black cavities of varying sizes are found on the chewing units. The pathological process develops in the natural depressions of the enamel: fissures, pits.
This disease leads to the destruction of hard tissues and cosmetic defects. There are black cavities on the front teeth, noticeable when talking or smiling:
The danger of decompensated form
Acute caries is dangerous for many reasons. The advanced form of the disease often leads to the following problems:
- development of pulpitis and periodontitis;
- development of periodontitis;
- tooth splitting;
- tooth loss.
In addition, the decompensated form is a signal of a disruption in the functioning of the entire organism. Untreated caries is often a consequence of decreased saliva production and a decrease in its bactericidal properties, which affects the general condition of the oral cavity as a whole. In pregnant women, this can affect the general physical condition of the expectant mother and the health of the fetus.
How does caries form?
The causes of caries are poor hygiene and the presence of bacteria in the oral cavity.
There are many bacteria in the human oral cavity. These bacteria feed on food debris that remains on the surface of the enamel after eating. Bacteria “love” foods high in carbohydrates: sweets, flour. During their life, bacteria produce acid, which destroys teeth.
Caries occurs in both adults and children. This disease spreads in each person at a different rate.
Factors contributing to the rapid development of caries:
- insufficient or lack of oral hygiene;
- excess carbohydrate foods: flour products, sweets, carbonated drinks;
- low buffering capacity of saliva, when acids and alkalis are not sufficiently neutralized in the oral cavity;
- insufficient fluorine and calcium content in enamel;
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- severe somatic pathologies suffered in childhood (tuberculosis, rickets);
- reduced immunity.
Answering a frequent question from patients: “Why do caries form on teeth?”, we note that the most important factor is insufficient hygiene. All dentists strongly recommend brushing your teeth regularly and using floss to clean the gaps. Without careful hygiene, bacteria will destroy teeth one by one, leading to serious complications.
Causes
Caries is the result of the activity of pathogenic microflora in accumulated plaque or tartar. A person’s immune status plays a major role in the development of carious defects. At particular risk are persons with autoimmune pathologies, AIDS, HIV, metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, and those taking immunosuppressive therapy for organ or tissue transplantation for a long time. The following factors can contribute to the development of caries:
- smoking, alcoholism;
- inadequate oral hygiene;
- natural aging (decrease in the body’s defenses, changes in the biochemical properties of saliva);
- metabolic disorders;
- endocrine pathologies;
- lack of food discipline (including prolonged fasting, poor nutrition, anorexia, bulimia);
- gum recession of various nature;
- excessive consumption of sugar and carbonated drinks;
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- bite pathologies;
- violation of hygiene rules when wearing braces and other orthodontic structures for the treatment of pathological occlusion.
Despite the variety of causes, eating disorders, bad habits and organ pathologies are the main etiological triad leading to the development of caries. Caries is not an independent disease. The pathogenetic link in the demineralization of enamel and destruction of the tooth body is a violation of the body's defenses.
What happens if caries is not treated?
- For a long time, the disease may not bother the patient in any way. When the destruction of hard tissue has reached a significant extent, sensitivity appears during eating.
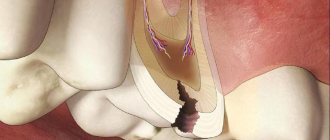
- If you do not consult a doctor at the first stage, the carious process will go further and reach the pulp (nerve). Spontaneous severe pain appears. Treatment of pulpitis will be required.
- If the patient does not seek help at this stage, the infection spreads beyond the root. Periodontitis occurs. The prognosis here is unfavorable, since such a tooth often needs to be removed to eliminate the infection.
Therefore, timely visit to the dental clinic will help to avoid acute pain and complications.
Granuloma
Granuloma is advanced periodontitis. Symptoms of the process:
- A purulent sac in the periapical area, which is visible on x-ray.
- The process does not give a clearly defined clinical picture for a long time.
- If the process worsens, then unbearable pain is observed.
Treatment consists of delayed filling of the root canal with a temporary calcium-based filling material. This material in the canal used for filling is periodically renewed, usually after six months the granuloma resolves. If not, then a resection of the apex of the tooth root is performed, along with the granuloma.
What to do if caries appears on teeth
First of all, you need to immediately contact your dentist. When a tooth is destroyed due to caries, treatment cannot be delayed. Otherwise, the complications described above arise. It is worth noting that no available means at home will relieve the patient of this problem. Only a dentist can cure this disease.
You should also pay attention to your oral hygiene:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day.
- Use floss and mouth rinses.
- Visit your dentist for a checkup every six months.
- Come for professional hygiene every 6 months.
Dentists will help you select individual hygiene products (brushes, pastes, threads, rinses) at your appointment. The doctor will also determine why dental caries appears in your particular case and give the necessary recommendations.
How is caries treated?
The treatment is carried out in professional dentistry by a general practitioner and is absolutely painless. This treatment is carried out in one visit, and several teeth can be treated in one visit.
Sequence of treatment stages:
- Examination of the oral cavity. Carrying out diagnostics: a targeted diagnostic image of one tooth or computed tomography of the jaws (if multiple caries is detected during the examination). This is done in order to make an accurate diagnosis and see the volume of destroyed tissue.
- Local anesthesia: selected individually according to health conditions. Only after the desired area of the oral cavity has become numb does the doctor proceed to the next manipulations.
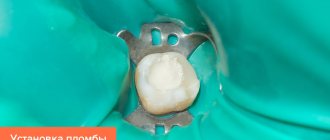
- Placement of isolation: the doctor places a rubber dam on the desired area - this is a latex plate that isolates the tooth from the rest of the oral cavity. The rubber dam creates comfortable conditions for the doctor, the patient, and also allows you to create dry, sterile conditions for placing a filling. This is necessary for the filling to serve for a long time and with high quality.
- Preparation of enamel, dentin: necrectomy. The doctor uses a drill to drill out the destroyed tissue.
- Treating the cavity with antiseptic solutions, applying an adhesive - a special solution that, like glue, reliably bonds hard tissue to the filling.
- Filling with light-curing materials. The anatomical shape of the tooth is restored, and the color is carefully selected.
- Polishing and grinding so that the filling does not feel different from your own teeth. Also, using special guidelines, the doctor checks whether the filling is too high or does not interfere with the normal closure of the jaws. Excess is removed, sharp edges are sanded.
- The doctor gives recommendations after treatment. If a tooth has been severely damaged by caries, then in addition to a filling, an orthopedic onlay or crown may be required. This is due to the fact that the filling is not as strong as enamel. Over time, cracks and chips are possible. Orthopedic structures will help protect the treated tooth from these complications.
After these stages, the tooth is completely free of caries. Next, you will need to maintain regular hygiene, come for preventive examinations and professional cleaning.
Historical reference
It is believed that the “history” of caries begins with a change in the human diet, that is, from the time when coarse, unprocessed food began to be replaced by food subject to heat, steam and other processing, as well as from the moment when “sweets” appeared. Judging by archaeological finds, for example, by the teeth of a man who lived 13-14 thousand years ago found near the city of Lucca (Italy, Tuscany region), we can conclude that already then caries was encountered and attempts were made to treat it. In the teeth found near Lucca, cavities were found that reached the pulp, and on the walls of the teeth there were traces of drilling with some stone tools. Moreover, the teeth had fillings made of plant resin with plant fragments. This means that ancient healers tried to protect carious cavities from the penetration of food, and the plants added to the resin composition apparently served as an anesthetic.
The healers of the Mayan civilization, judging by other archaeological finds, made fillings from complex plant compositions with the addition of various minerals. In ancient Rus', caries in the initial stages was treated with honey, and in advanced stages - with propolis, which was applied to the tooth cavity, previously cleaned of decay products and affected tissues; to relieve pain, they applied a cloth soaked in a mixture of vodka and table salt. In ancient Rus', caries in the initial stages was treated with honey, and in advanced stages - with propolis, which was applied to the tooth cavity, previously cleaned of decay products and affected tissues; to relieve pain, they applied a cloth soaked in a mixture of vodka and table salt. In medieval Europe, where the development of medicine was hampered by the dogmas of the church, it was believed that caries developed due to the activity of “tooth worms”, and it was treated with poisons and hot metals introduced without anesthesia into the dental cavity affected by the disease. Moreover, these manipulations were carried out not by doctors, but by barbers. The poor people, having no means for “treatment”, received very strange, unscientific recommendations from the “doctors”: sit under the moonlight with your mouth open, tie a frog to your jaw, apply a mixture of oil and bird droppings, “rub” the affected area with the tooth of a deceased person , etc.
In the 15th century, healers began using metals, including gold, to fill teeth. In 1790, John Greenwood, the personal dentist of the first US President George Washington, came up with a primitive device for drilling teeth, where a foot drive from a spinning wheel was used to rotate the drill. More than 80 years later, in 1871, the American doctor James Morrison patented a dental drill he invented, which gave impetus to the development of therapeutic dentistry. Throughout the 20th century, therapeutic dentistry developed rapidly, adding more and more new techniques, materials and tools for the treatment of dental diseases, including caries. Today, caries treatment is the most common dental service, with high treatment effectiveness at any stage.