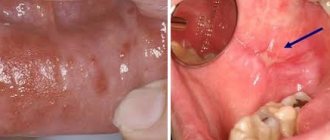
A tongue burn is an injury that damages the mucous membrane, and in some cases even muscle tissue. This problem brings a lot of discomfort - from pain and the inability to eat or drink liquids to death. It is very important to urgently contact a specialist who, after studying the cause of the burn, will prescribe treatment. If you neglect the help of a qualified dentist, serious complications can occur, including necrotic decomposition of soft tissues and infection of the entire body.
Types of tongue burns
Depending on the cause of origin, the following types of injury are distinguished:
- Chemical burn of the tongue or oral cavity - when tissues are damaged as a result of exposure to aggressive chemical compounds;
- Thermal - when the surface was exposed to a high temperature object.
- Electrical - occurs as a result of tissue contact with electricity. For example, when performing dental procedures. Electric current affects not only the tissues of the tongue, but the entire body as a whole.
Diagnostics
An in-person examination by a dentist is enough to detect the problem. Sometimes a doctor can immediately diagnose and prescribe treatment. But if the disease is not of a dental nature, additional examination will be required.
For diagnostic purposes the following is carried out:
- general blood test to identify an infectious process;
- FGDS for detection of peptic ulcer;
- biochemical blood test for glucose content and determination of hormone levels if endocrine disorders are suspected;
- examination by a neurologist and conducting tests to diagnose damage to the nervous system;
- blood test for HIV and hepatitis B, C to find the cause of immunodeficiency;
- examination by an otolaryngologist to detect acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis).
Carrying out all types of diagnostic procedures is not necessary; often the cause is determined at the initial stage. Based on the results of the examination, a treatment regimen is selected.
Symptoms of a tongue burn
Symptoms depend on the extent of soft tissue damage:
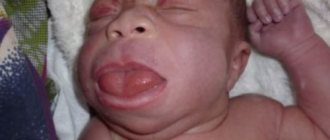
First degree - a burn occurs due to short-term exposure to high temperature tissue. The patient experiences slight redness and swelling of the mucous membrane. Often, a burn condition is provoked by consuming too hot food or liquid.
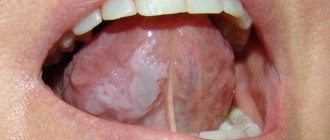
Second degree – swelling of the mucous membrane, redness, and multiple blisters on the surface are observed.
Third degree - accompanied by tissue death, large blisters, redness of the surface, the organ itself seems to “change its consistency.” As a rule, it occurs due to exposure to gases, liquids at elevated temperatures, or chemical compounds.
The fourth degree is a severe lesion when the tissues are charred. This burn condition is rarely compatible with life.
Treatment Options
Treatment is closely related to the cause of the condition. Possible treatment regimens:
- antibiotics + antisecretory drugs + histamine receptor blockers + proton pump inhibitors for peptic ulcer disease;
- antifungal agents in the form of capsules, tablets or drops for candidiasis;
- opening the salivary ducts and removing blockages;
- correction of hormonal disorders with hormone replacement drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs and local antimicrobial agents for glossitis;
- infusion therapy and oral rehydration solutions for dehydration;
- antibiotic therapy for acute tonsillitis;
- antiretroviral therapy for immunodeficiency due to HIV.
The positive effect of treatment occurs immediately or after 3–5 days. If there is no improvement, a change in therapy or re-examination may be necessary.
There is no need to live with pain in the tongue and endure it, hoping for self-healing. It is better to consult a doctor in a timely manner, discover the cause and remove it, than to wait for serious complications.
Read also: Why does the tongue have a white coating?
Dear patients! Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33
Be healthy and happy!
How to properly treat a tongue burn?
Treatment methods depend on the type of thermal injury.
What to do in case of a thermal burn of the tongue?
- rinse your mouth with cool water;
- apply ice or a cold object to the damaged area;
- treat the burn site with a disinfectant solution;
- rinse with a disinfectant to prevent bacteria from entering the oral cavity;
- use local anesthetic compounds;
- while the tongue is recovering, eat liquids, fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins C and B. Avoid spicy, pickled foods, foods that can have a mechanical effect on tissue (nuts, crackers, seeds, etc.).
- rinse the mouth thoroughly;
- neutralize aggressive chemicals. Depending on the source of the burn, a specific neutralizer is used;
- After neutralization, the burning sensation should go away. For pain relief, it is worth using anesthetics and antihistamines;
- if the mucous membrane is severely burned, with damage to the structure of the tongue and muscle tissue, it is necessary to urgently go for an examination to a doctor.
If there are bubbles on the surface of the tongue, you should urgently seek help from a dentist! Under no circumstances should you open blisters yourself! You may need hospital treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
How to treat a chemical burn of the tongue?
Note! If the oral cavity is burned with an alkaline solution, it cannot be rinsed with water, since moisture promotes more active penetration into the soft tissues of the tongue.
Glossodynia - what is it?
Burning mouth syndrome, or glossodynia, is discomfort and even pain in the mouth, tongue, gums, and mucous membranes, which is accompanied by a feeling that the mouth has been scalded with boiling water or medicine. This condition may be accompanied by dry mouth (xerostomia) and loss of taste or smell. Sometimes people with a burning sensation in the mouth and tongue complain that they cannot feel anything - not even the temperature of the food [1].
This condition develops suddenly, but may begin with a slight tingling sensation in a limited area of the mouth, and then spread further or intensify only in that same area. Symptoms of this condition are described by subjective complaints; they can be combined or single:
- feeling of burned mucous membranes, burning pain. Most often, a burning sensation in the oral cavity is felt on the tongue, especially along its front edge and sides, as well as on the lips, on the inside of the cheeks, in the throat or throughout the mouth;
- a feeling of tightness, burning and dryness of the mucous membrane in the mouth, from severe to occasional;
- change in taste, up to the complete loss of this sensation;
- the appearance of an unusual taste in food and drinks, such as bitterness or metallic;
- decreased or loss of sense of smell;
- a feeling that sensitivity in the mouth has disappeared, the mouth seems to be frozen [2].
Symptoms of burning the oral mucosa can manifest themselves in different ways throughout the day over several days and even months. Sometimes they begin at a certain time of the day, for example after waking up, and by the end of the day they decrease or, conversely, intensify in order to disappear imperceptibly and return again in the morning. The subjective characteristics of pain associated with burning mouth syndrome can vary significantly. Among people with similar diseases and other life factors and conditions, the symptoms of this condition, their intensity, duration and prevalence can vary greatly [2].
Separately, it should be noted the great social and personal significance of glossopyrosis. The fact is that sensations in this state can affect the quality of life in all its aspects: nutrition, sleep, rest and restoration of physical strength, communication, reactions to some irritants. Those suffering from constant pain cannot get enough sleep or rest peacefully; they have difficulty eating and communicating. In an attempt to find the source of the problem and somehow eliminate it, they begin to pay a lot of attention to this condition. Thus, many note that with the appearance of glossopyrosis, spots have formed in their mouth, the papillae have enlarged, or the tongue has begun to look unusual. As practical observations have shown, in 50% or more cases such changes are actually normal, are in no way related to burning mouth syndrome, and the person had them before, he just didn’t notice them [2].
This is very important for diagnosis, because the appearance of some real clinical signs, obvious manifestations of trouble may indicate that burning mouth syndrome did not arise on its own, it is not idiopathic, but there are some problems, prerequisites for its occurrence [3].
How exactly to neutralize a chemical burn in the mouth?
Carbolic acid is well neutralized by glycerol.
Baking soda and water neutralize acidic compounds.
If alkali gets into your mouth, rinse the cavity with citric acid diluted in water.
If exposed to aggressive household chemicals, the mouth should be rinsed with cool running water.
It is important! Tongue burns take a long time to heal. Unfortunately, these tissues cannot be made motionless for a certain time; the tongue is constantly in motion. On average, it can take several weeks for the tongue to recover from injury.
Treatment of a burn to the oral cavity in a child
According to statistics, a large percentage of patients who turn to a doctor for help as a result of a burn to the mouth or tongue are children. Young patients up to a year and older can unknowingly “taste” household chemicals or alcoholic drinks accidentally left on the table by their parents. Also common causes of burns are eating too hot food.
The mucous membrane of a child’s tongue is more delicate and thin, and therefore requires more delicate handling in case of a burn. For treatment, you must urgently contact a pediatric dentist.
Causes of Burning Mouth Syndrome
This condition may be associated with any general somatic or dental disease, or it may occur on its own. As a rule, burning mouth syndrome is a condition in which its source is unknown. It occurs spontaneously, and the patient cannot indicate the cause or trigger for the complaint.
There are several theories about the development of this pathology, but none of them have yet been proven. Researchers of this problem have made several assumptions as a theory of the origin of the syndrome. One of the most common is the theory of sex hormone deficiency, since complaints of chronic burning of the tongue are often made by pre- or postmenopausal women. True, when checking studies in this area, reliable statistical significance was not established, but, nevertheless, as a theory, this reason is supported by many practitioners [3].
“Among patients with burning mouth syndrome, women were more common. According to some studies, there were 10.3 times more women with complaints typical of this condition than men.”
Saperkin N.V., Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Department of Epidemiology, Microbiology and Evidence-Based Medicine PIMU [1]
There is an assumption that certain autoimmune processes, especially those that occur in old age, may also be background for the occurrence of burning mouth syndrome [2].
It is possible that this disease occurs in people with neurological or mental disorders, depression. But this is also not the leading theory, since there are studies indicating that it was not depression that led to the onset of the syndrome, but on the contrary, burning mouth syndrome became one of the reasons for the development of a depressive episode. The same spectrum of causes of burning in the mouth includes cancerophobia, especially in people who have quit smoking and are afraid of developing cancer of the lip or tongue, as well as in people with a fear of household transmission of STDs [2].
Injuries can lead to the syndrome, including those not noticed by a person, associated with his habits, congenital or due to pathologies with malocclusion, dental anomalies. Some researchers note that individual changes in the sensitivity and density of the oral mucosa can lead to the development of glossopyrosis. A correlation has been noted between mental lability and increased sensitivity of taste buds: in such people, the incidence of burning mouth syndrome was higher. In general, the approximate list of conditions and diseases in which the syndrome may appear is quite wide [3].
- In women, there is a deficiency of estrogen or progesterone.
- Autoimmune pathology.
- Neurological disorders, PTSD.
- Psychiatric disorders.
- Chronic irritation of the mouth, such as from improper dentures.
- Sensory defects.
Diseases that may cause a burning sensation in the mouth:
- Anemia.
- Parkinson's disease.
- Deficiency of B vitamins, zinc.
- Neuropathy.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Taking medications.
- Diabetes mellitus type 2.
- Sjögren's syndrome with xerostomia.
- Candidiasis of the oral mucosa, esophagus.
- Herpes.
- Cracked tongue.
- Allergies, including contact ones.
- Hiatal hernia.
- HIV.
- Myeloma.
- Oncological diseases [3].