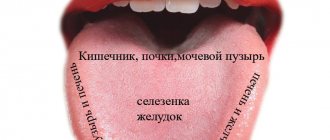
Burning sensation in the mouth and tongue - causes
Local factors:
- Decreased saliva secretion. The mucous membrane becomes dry, lips and tongue crack. Food and liquid irritate the damaged areas, and they sting quite severely.
- Fungal candidiasis. Popularly known as thrush. Fungi, during their rapid proliferation (which happens when the immune system is weakened), provoke a burning sensation in the oral mucosa and painful sensations.
- Hard dental deposits. The formation of tartar is accompanied by the simultaneous delamination of old layers. The separated particles affect the mucous membrane, causing an unpleasant reaction.
- Allergy. A burning sensation in the mouth is nothing new for those with intolerance to certain foods, medications, and even denture materials.
- Leukoplakia. Excessive keratinization on any part of the epithelium usually does not provoke tingling sensations, but this disease cannot be excluded from the list of possible persons involved.
- Diseases of the tongue. Desquamative glossitis, or “hairy” tongue, is a common cause of persistent burning sensation in the mouth. The papillae become very sensitive.
- Herpetic infection. The blisters, which quickly transform into erosions, cause severe itching and unbearable burning both in the normal state and when eating.
- Grinding of teeth. Unconscious movements of the teeth during sleep, called bruxism, automatically affects the tongue with the appearance of microtraumas on it, and, accordingly, a burning sensation.
- Lichen planus. Erosive damage to the mucous membrane, white ulcers haunt the patient during an exacerbation, causing severe discomfort.
General factors:
- Unbalanced diet
- Blood diseases
- Hormonal disbalance
- Stomach pathologies
- Nervous disorders
- Avitaminosis
- Insulin-dependent diabetes
- Bulimia
In these conditions, a burning taste in the mouth may appear and disappear, as it is a concomitant symptom.
Causes other than dental
A burning tongue can be caused by factors unrelated to dentistry:
- Glossitis and stomatitis are quite often diagnosed in patients with HIV infection
psychological disorders;
- heartburn;
- drug therapy;
- hormonal imbalance;
- endocrine diseases;
- avitaminosis;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- blood diseases;
- previous radiation and chemotherapy;
- unbalanced diet.
Glossitis and stomatitis are quite often diagnosed in patients with HIV infection, diabetes mellitus, and hyperthyroidism of the thyroid gland.
Disruption of the normal microflora of the oral cavity occurs in chronic diseases of the digestive tract.
How does burning in the mouth and tongue manifest?
The symptom is clearly noticeable, may occur sporadically and disappear on its own. This happens when taking bitter medicines or eating spicy foods (“fire” in the mouth). A slight irritation of the mucous membrane may bother you after dental procedures; this is quite normal.
True diseases can be assumed if:
- Dryness and burning in the mouth often appear in certain areas of the oral cavity
- Unpleasant sensations intensify and are accompanied by numbness
- The tingling becomes constant
In most patients, the burning sensation manifests itself in the morning, intensifies during the daytime and subsides towards night.
Associated symptoms
Many pathologies, in addition to burning and redness of the tip of the tongue, are accompanied by numbness and swelling. In some cases, cracks appear on the surface of the mucosa, which can subsequently bleed. Scarlet spots due to candidiasis are hidden by a cheesy coating. Sometimes tingling of the organ is accompanied by the appearance of white bubbles throughout the oral cavity.
Diagnostics
How to find out what exactly caused the burning sensation in the mouth and tongue? Only a specialist can determine the reasons. First you need to visit the dentist. If there are no visible local causes that could cause this problem, you need to go to a therapist. The patient will be prescribed tests (urine, blood - general analysis and sugar, biochemical studies). It is necessary to exclude sexually transmitted diseases and AIDS. It would be useful to consult an endocrinologist - perhaps it is due to hormonal fluctuations. Based on complete information, a preliminary diagnosis can already be made. Get ready for the fact that at the same time you will have to visit a gynecologist, nutritionist, infectious disease specialist, oncologist and doctors of other specialties.
Drug treatment
At the initial stage of the disease, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis. The oral cavity is treated with antiseptics: hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, furatsilin, Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt, Rotokan.
For severe itching, Lidocaine, Novocaine or analgesics are used as pain relievers.
Inflammatory processes will be relieved by steroid drugs - hydrocortisone ointment, Prednisolone.
The following will help in the fight against viruses: Acyclovir, oxolinic or florinal ointments.
Solcoseryl will ensure the fastest regeneration of oral tissues.
Metrogyl Denta and Cholisal have complex properties: analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial.
If the cause of tongue tingling is iron deficiency in the body, initial therapy consists of prescribing folic acid, cyanocobalamin - vitamin B12.
Allergy treatment occurs in two directions. The first is to eliminate contact with the irritating object. The second is treating the affected areas with Hydrocortisone and taking antihistamines: Loratadine, Mebhydrolina, Clemastine, Chloropyramine.
Itching of the tongue due to xerostomia (dry mouth) is eliminated by treating the inflamed area with sea buckthorn oil. Eating acidic foods normalizes salivation.
Clemastine
Treatment for bruxism depends on its factors. If the cause of the disease is dental, the defect is eliminated by making protective mouthguards and installing removable structures. Subsequently, cosmetic restoration of the teeth is possible. If the pathology is of a psychoneurological nature, mild sedatives and sleeping pills, as well as drugs containing Ca and Mg, are indicated.
For candidiasis, the affected organ is treated with ointments: Clotrimazole, Amphotericin, Decamine, as well as a solution of hexetidine or Lugol in glycerin. For the treatment of children, the listed drugs are supplemented with rinsing with potassium permanganate powder diluted in water or lubricating the inflamed area with brilliant green. Antifungal drugs are prescribed internally: Pimafucin, Flucostat.
An obligatory part of treatment is taking vitamins B, C, and retinol.
Burning mouth - treatment
The main goal is to eliminate the root cause found at the diagnostic stage. If it is not associated with dental pathology, the oral cavity is sanitized, worn fillings are removed and new fillings are placed, and dentures are corrected. Stomatitis and glossitis often require antibiotics. Candidiasis is treated with antifungal drugs.
General diseases are treated by a doctor of appropriate specialization, prescribing complex treatment depending on the type of pathology. Measures are being taken to improve immunity, normalize stomach function, stabilize blood glucose levels, and treat neuroses.
At home, you can alleviate the condition by rinsing your mouth with warm infusions of oak bark, sage, and chamomile. 1 tbsp is enough. per standard glass of water. Brew like tea, let cool and rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day. To prevent a burning sensation in the mouth, avoid or at least minimize spicy foods and caustic ingredients in your diet; it is better to avoid alcohol altogether.
Preventive measures
Preventive measures against a “burning” tongue include the following:
- Proper dental and oral hygiene.
- Clean your tongue daily with a special cleaner (but not with a brush!).
- Compliance with drinking regime.
- Avoiding allergens, in particular food ones.
- Controlling blood sugar levels.
- Timely treatment of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Compliance with the principles of balanced nutrition.
- Regular preventive examinations with a dentist (at least 2 times a year).
Diagnostic measures
The only correct decision regarding the appearance of the symptoms described above is to contact a knowledgeable specialist. Only a doctor can conduct a competent examination and identify the true cause of the discomfort. Thus, the main diagnostic procedures include:
- general blood analysis,
- taking a swab from the throat.
Tests can determine the true cause of the problem.
Having the test results in hand, the doctor can significantly narrow the range of suspected diseases and even immediately make an accurate diagnosis. It is likely that at the stage of identifying the source of the problem, consultation with highly specialized specialists - a dentist, neurologist, gastroenterologist - may be required. Without knowing the exact doctor’s conclusion, you should not make any attempts to solve the problem yourself, otherwise you can only worsen the situation.
Vitamin deficiency and allergies
Such conditions also cause pain in the tongue. Vitamin deficiency most often occurs in the spring, when the child’s body is especially weakened. The cause of its manifestation is considered to be a severe lack of vitamins of one group or another. If a child has pain in the tip of the tongue or other parts of it, and red and white pimples appear on them, then this may well be a manifestation of vitamin deficiency. In addition to inflammation of the organ of speech, this pathology manifests itself in the formation of small cracks on the lips, peeling of the skin in the corners of the mouth, conjunctivitis, and the appearance of dandruff. If there is a lack of vitamin P in the body, in addition to blisters and pimples on the tongue, the child is bothered by loose stools. A lack of ascorbic acid is reflected in the appearance of white formations, bleeding gums, swelling, and the presence of hemorrhages on the skin.
If for this reason the child’s tongue tip hurts, what should parents do? Getting rid of a child from this condition is carried out by replenishing the lack of vitamins. This will eliminate the symptoms of the emerging pathology.
Often a child’s tongue hurts due to allergic stomatitis. It can be caused by citrus and red vegetables (carrots, beets and tomatoes), cocoa, chocolate, exotic fruits (papaya, passion fruit, mango), as well as strawberries and raspberries. When a food allergy occurs, red blisters and spots appear on the tongue, as well as on the oral mucosa. White pimples are observed at the tip of the speech organ. To eliminate discomfort and pain, you will need to remove allergenic foods from the child’s diet.
Diagnosis of pinching the tip of the tongue
To find out the cause of tongue tingling, a thorough examination of the oral cavity is necessary. If there are rashes on the organ of taste or gums, it is necessary to take a smear for genital infections. If the patient has dentures, an allergy test should be performed. If oral diseases are excluded, the patient should be referred to a general practitioner for further examination.
Herpetic infection
If a child’s tongue hurts, the causes of this condition may lie in the occurrence of painful ulcers. They entail uncomfortable sensations. The main cause of the disease is the herpes virus, which begins to multiply when the immune system reacts to foreign organisms.
The pathology manifests itself sharply. The child's tongue begins to hurt and the temperature rises. The baby becomes excessively sleepy, and when examining the oral mucosa, multiple blisters and ulcers are noticeable. Most often, the tip of the child’s tongue hurts. The baby's saliva becomes more viscous.
In addition to the tongue, rashes affect the surface of the cheeks, lips, and sometimes also appear at the entrance to the pharynx. These bubbles are watery and very small. They are grouped on the reddened mucosa. Over a short period of time, the bubbles open. The affected areas are covered with a yellowish-gray film. After it peels off, painful ulcers appear.
What can cause an itchy tongue?
A phenomenon such as itching of the tongue and lips can be caused by one of many different factors. Here are the most common causes of this unpleasant symptom:
- mechanical injury: the tongue of both a child and an adult may begin to itch due to banal biting or damage of another nature, for example, as a result of a burn. Very often, the culprit is rubbing the mucous membrane with the sharp edges of a crown, an incorrectly fitted prosthesis or an incorrectly adjusted brace system. Also, this symptom may well be a consequence of the use of low-quality cosmetics or oral hygiene products,
Tongue injury can cause itching
“Somehow this happened to me too. Right in the middle of the day, for no apparent reason, my tongue itched. And let me tell you, this is not a pleasant feeling! And your hands just reach out to scratch at least a little! In general, I immediately decided that it was because of the spicy food, at home I thoroughly cleaned my tongue with a brush, and in the morning the itching appeared again, and most importantly, only on one side. At lunchtime I ran to the dentist, and he immediately said that it was all about the sharp crown. It apparently became so uncomfortably worn over time, and as a result, it scratched the tongue. This is where it started to itch...”
LudaKam, 31 years old, Saratov, from correspondence on a thematic forum
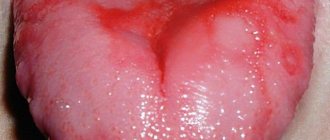
- Oral diseases: one of the most common causes of itching is a disease such as glossalgia. In this case, it is usually the tip of the organ that begins to itch, but in some cases patients experience severe itching on the sides. Associated symptoms include burning, pain, tingling in the tongue, as well as dryness of the oral mucosa. Quite often, the disease develops against the background of strong emotional experiences and stressful situations, but the disease can also be triggered by injury to an organ, taking certain medications, or malfunctions in the internal systems of the body,
The photo shows glossitis of the tongue - Gastrointestinal pathologies: problems in the gastrointestinal tract in most cases are reflected specifically in the condition of the tongue. For example, pathologies such as gastritis, ulcers or pancreatitis can provoke itching and burning in an organ,
- stress and depression: against the background of severe nervous exhaustion, some changes occur in the composition of saliva and the volume of its secretion,
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements: sometimes due to a lack of B vitamins, iron and folic acid, the tongue begins to itch very much,
- allergy: such a manifestation may well be an allergic reaction of the body to some irritant, for example, to hygiene products, the presence of an allergen in the oral cavity in the form of metal parts of braces or a prosthetic device,
- candidiasis: the development of a fungal infection often becomes the body’s response to a sharp weakening of the immune defense. In this case, along with itching, burning and tingling occurs, and a dense cheesy coating appears. Quite often, the cause of this problem is long-term use of antibiotics. By the way, in children the disease in question develops almost twice as often as in adults.
This is what a fungal infection on the tongue looks like
Other possible provoking factors include the constant irritating effect of tobacco smoke, abuse of too spicy, salty or acidic foods - in such cases, it often begins to tingle and itch directly under the tongue. Excessive consumption of low-quality alcoholic beverages can also lead to the development of this symptom.
Appearance in children
Children often face this problem. The appearance of similar symptoms in a child almost always indicates the development of candidiasis. Here it is necessary to conduct a careful visual examination of the oral mucosa for the presence of a dense white coating with a cheesy consistency - this is the very first sign of the pathology in question. If your baby is still very young and cannot tell you about the symptoms that are troubling him, pay attention to whether he is constantly sticking out his tongue. This is how little children usually make it clear that they feel discomfort in the organ.
Stomatitis is common in infants
A common accompanying symptom is burning, and this is a good reason for parents to worry. Here you need to monitor the child’s psycho-emotional state, make sure that he does not experience any serious worries or stress. If you suspect that the cause of the itching lies precisely in the psychological state of the baby, it makes sense to show him to a neurologist. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe a course of sedatives. A childhood disease such as scarlet fever can also provoke itching in the tongue and even in the throat. In any case, if suspicious signs of pathology appear, the child should be shown to a doctor as soon as possible.
Therapy with folk remedies
Regardless of whether a person is being treated with medication or not, he can use “grandmother’s recipes.” Home techniques will reduce burning and inflammation in the oral cavity.
One common way to relieve itching on the tip of your tongue is to suck on an ice cube. But this will only relieve irritation for a short time, so it is recommended to use more effective means:
- Dilute a teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of warm water. Rinse several times a day for 30 seconds after meals.
- Grind chamomile and sage; the latter can be replaced with St. John's wort. Take one tablespoon of plants, add hot water and leave for forty minutes. Rinse 5-6 times a day.
- Rinse your mouth with honey diluted with boiled water, while swallowing the liquid.
- Cosmetic oils of sea buckthorn, rose hips, and sage will soften the inflamed area. They lubricate the affected area.
Redness and burning of the tip of the tongue occurs for various reasons, and they are not always harmless.
Therefore, in order to prevent the development of the disease and avoid complications, it is recommended to consult a doctor to receive qualified assistance.
The tip of the tongue stings: treatment
People often go to the dentist with the complaint that the tip of the tongue is red and stings. Treatment for these symptoms cannot be started immediately, as the doctor must first find out the cause of their occurrence. Infectious lesions of the oral cavity require antibacterial or antifungal therapy. For this purpose, Amoxicillin and Nystatin tablets are used. For herpes, the drug Zovirax or the drug Acyclovir is prescribed. If the cause of the disease is incorrectly selected prostheses, they must be replaced. For stomatitis, the oral cavity is treated with a solution of baking soda.