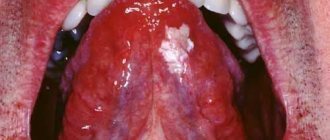
Tongue cancer is a fairly common pathology in the structure of malignant neoplasms of the head and neck organs (about 55% of cases), and in the general structure of malignant neoplasms it accounts for 0.45%. The average age of those affected is 60 years, men suffer from it 3 times more often than women. But the tumor can also occur in young people and even children.
- Causes of tongue cancer
- Symptoms of tongue cancer
- Methods for diagnosing tongue cancer
- Treatment of tongue cancer
- Prevention
Most often, cancer is localized on the lateral surface, a little less often on the root of the tongue, and very rarely in the area of its back and tip. [1,2]
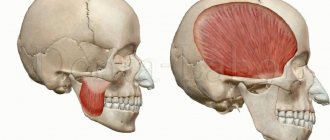
Anatomical structure of the tongue
Causes of tongue cancer
The following risk factors have been described that significantly increase the likelihood of developing tongue cancer:
- Use of tobacco products in various forms (smoking, chewing, sucking).
- Alcohol abuse.
- Infection with human papillomavirus.
- Chemical and thermal damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue, including conditions after burns.
- Chronic trauma to the tongue, for example, biting it, rubbing it with dentures, etc.
- Hereditary predisposition.
Also of great importance are precancerous diseases, which with varying degrees of probability lead to the development of tongue cancer:
- Leukoplakia.
- Bowen's disease.
- Post-radiation stomatitis.
- Chronic ulcers and fissures.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Ulcers or changes in the mucous membrane that have existed for more than 2 weeks should be grounds for contacting a doctor. The initial examination is traditionally carried out by a dentist, who, if necessary, will refer the patient to an oncologist. But if you contact an oncologist yourself first, this will in no case be a mistake. [1.8]
Discomfort and pain in the frenulum area
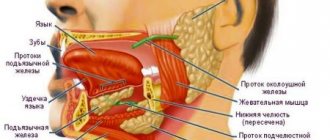
The frenulum serves as a connector between the tongue and the oral mucosa. A large number of nerve endings are concentrated at the site of these connections.
The occurrence of painful sensations may be associated with physical damage to this place and with inflammatory processes. The thing is that the tongue is a special organ in the human body, and because of the nerve clot under the tongue, it is difficult to determine the exact location of the pain.
After all, besides it, in the oral cavity, in the area of the tongue, there are:
- salivary gland;
- muscles;
- nerves;
- vessels;
- bone.
Every part of the oral cavity can be a source of pain. And it’s difficult to identify this on your own. Problems with the frenulum are most often associated with injury. Because of her stretching, we feel pain. You can get it when talking or eating heavy and dry food. In addition to the physical problem, the cause of pain is stomatitis. The disease is associated with inflammatory processes not only of the tongue, but also of other elements of the oral cavity. It is provoked by an allergic reaction and erosions resulting from physical impact and other diseases. This problem is often encountered by visitors to dental clinics.
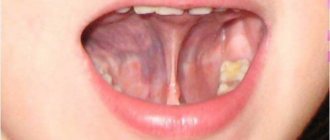
A short frenulum brings discomfort and pain
Each person's body is unique. This also applies to the bridle. Of course, its structure is the same for everyone, but its length is not. When the bridle is too small, then the risk of damage increases. Usually this problem is solved at a fairly young age. It is surgically trimmed and no longer bothers its owner.
But what to do if painful sensations bother a person only from a certain side? If you have such symptoms, consult a doctor immediately.
If you have pain under the tongue on the left or right, then there is a risk of purulent inflammation of the lower jaw. The results of a trip to the dentist can confirm this. But sometimes pain is associated with other diseases. Painful sensations on one side of the tongue are associated with an inflamed salivary gland and disorders of the lymph nodes. Self-treatment of such diseases is dangerous to health. Incorrectly selected medications can worsen the patient’s condition and lead to diseases such as pancreatitis, meningitis, encephalitis, myocarditis, etc. Therefore, the use of special medications is allowed only after visiting a therapist and undergoing tests.
Pain on one side is a sign of a serious problem. Traumatic tongue cancer
Symptoms of tongue cancer
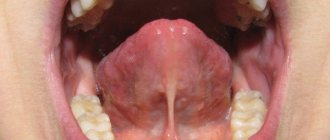
In many cases, tongue cancer is discovered by patients themselves, who complain of non-healing ulcers, nodules or papillomas. These tumors gradually increase in size and begin to interfere with the patient's chewing and swallowing. Speech may also be impaired. [4]
Malignant tumor of the tongue
Depending on the clinical picture, three forms of tongue cancer are distinguished:
- Ulcerative. It appears as a non-healing ulcer that grows in size, may bleed, and eventually begins to emit a foul odor.
- Knotty. Cancer looks like a dense nodule with clear edges. There may be white spots on its surface.
- The papillary form has the appearance of a dense plaque that rises above the surface of the tongue.
According to the nature of growth, there is an exophytic form of cancer, which grows in the oral cavity, and an endophytic form, spreading into the thickness of the tongue, as well as a mixed one. The exophytic form often looks like cauliflower growths that can ulcerate and bleed. The endophytic form is more characterized by compaction of the tongue tissue, which upon palpation looks like a dense infiltrate without clear boundaries. [1]
In later stages, the following symptoms may occur:
- Pain of varying degrees of intensity, which can radiate to the ear, temple, and back of the head. Some patients mistake it for a sore throat or pharyngitis.
- Increased salivation - hypersalivation. Occurs due to irritation of the mucous membrane by cancer breakdown products.
- Bad breath. It is the result of infection of the tumor or its disintegration. [5]
Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is a viral disease that is accompanied by a sore throat, discomfort at the base of the tongue and fever. First, the temperature rises and the throat begins to hurt, and after a while the root of the tongue and its side become covered with red spots, and its body becomes pale pink. Symptoms manifest themselves through vomiting, dizziness, and a rash all over the body, starting from the groin.
Treatment involves a gentle diet, bed rest, taking medications, strengthening the immune system, and physical therapy. With scarlet fever, the patient should be protected from communication with other people, as the virus can infect others.
Methods for diagnosing tongue cancer
Examination of the tongue and oral cavity
Diagnosis of tongue cancer involves a comprehensive examination, which includes the following manipulations:
- Examination of the oral cavity.
- Palpation of the tumor and areas of regional lymph nodes.
- Verification of diagnosis using cytological examination. To do this, a puncture biopsy and/or impression smears from the tumor are taken.
- MRI - evaluates the soft tissues of the head and neck, as well as the degree of tumor invasion in them.
- CT with contrast - helps to evaluate the presence of cancer growth in the bones, in particular in the lower jaw.
- Ultrasound examination of the area of regional metastasis can identify metastases.
According to indications, endoscopic examination of the pharynx, chest x-ray and other diagnostic methods can be performed, which are aimed at clarifying the extent of the malignant process and detecting distant metastases. [3.6]
Treatment of tongue cancer
The following methods are used to treat tongue cancer:
- Surgical intervention.
- Radiation therapy.
- Chemoradiation therapy.
Surgery is the main radical treatment method. In this case, preference is given to organ-preserving operations so that a person can talk, chew food and swallow it. The extent of the operation will depend on the size of the tumor and the involvement of surrounding tissues in the process. In some cases, it may be necessary to remove tissue from the floor of the mouth, resection of the jaw, and even complete removal of the tongue. If metastases are present, the lymph nodes in the neck are removed at the same time. To cover the resulting defects, skin flaps are used; for jaw plastic surgery, fragments of ribs, fibula, or artificial implants are used.
Surgery for tongue cancer
For large tumors or in the presence of unfavorable histological factors, combined interventions are performed. In such cases, radiation therapy is performed after surgery. In some situations, it is possible to carry out radiation therapy as an independent treatment method. In this case, the irradiation zone includes the tumor itself and the area of regional metastasis.
In the presence of distant metastases, positive resection margins, perineural invasion and other unfavorable factors, chemoradiotherapy is performed after surgery. [8]
When carrying out systemic therapy followed by chemoradiotherapy, the following chemotherapy drugs are used:
- Cisplatin (preferably) as monotherapy.
- Cetuximab as monotherapy.
- Carboplatin + fluorouracil.
- Fluorouracil + hydroxyurea.
- Cisplatin + paclitaxel.
- Cisplatin + fluorouracil.
- Carboplatin + paclitaxel.
If simultaneous chemoradiotherapy is indicated, cisplatin + radiation therapy to the primary lesion of at least 70 Gy is used.
For anti-relapse chemotherapy, the following combinations of drugs can be used:
- Docetaxel + cetuximab. In the absence of progression, therapy with cetuximab is continued.
- Paclitaxel + carboplatin + cetuximab. In the absence of disease progression, treatment is also continued with cetuximab.
2nd line chemotherapy may include one of the regimens listed above, and it is also possible to add nivolumab, pembrolizumab, afatinib. [1]
Causes of pain
The tongue is an organ involved in making sounds and pushing food and drink down the throat. When problems arise, it becomes difficult or impossible to perform natural functions. Therefore, it is important to know what causes pain at the root of the tongue.
Pain at the root of the tongue can provoke glossitis, tonsillitis, inflammation, injury and nerve damage, and the formation of tumors.
The correct diagnosis can be made after an examination, including anamnesis, examination, and blood tests.
The causes of the painful condition include:
- Inflammatory processes occurring in the palatine and lingual tonsils.
- Inflammation of the tissues of the tongue, pharynx and larynx.
- Mechanical or chemical injury to an organ.
- Progression of tumor formations.
- Diseases of the sublingual salivary gland.
- Inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes.
Pain in the tongue can be either a symptom or an independent disease.
Prevention
Prevention of tongue cancer involves reducing exposure to risk factors and regular dental checkups. In order to minimize the likelihood of developing this disease, it is necessary to give up smoking and alcohol abuse, as well as the use of chewing mixtures. Monitor your oral health carefully. Chronic injury to the tongue should not be allowed; teeth must be treated and dentures adjusted in a timely manner. If long-term (more than 2 weeks) formations are detected, you definitely need to consult a doctor as soon as possible. [1.7]
| More information about treatment at Euroonco: | |
| ENT oncologists | from 5100 rub. |
| Chemotherapy appointment | 6900 rub. |
| Emergency oncology care | from 12100 rub. |
| Palliative care in Moscow | from 44,300 rubles per day |
| Radiologist consultation | 11500 rub. |
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Bibliography:
- Clinical recommendations. — Malignant neoplasms of the oral cavity. Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. — 2022.
- MM. Soloviev. — Practical Oncology • T. 4, No. 1 – 2003, Cancer of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue (reserves for improving treatment results), 2003
- A.L. Yudin. — Cancer of the tongue and floor of the mouth: modern aspects of diagnosis — Bulletin of Radiology and Radiology No. 5, 2015.
- Clinical protocol for diagnosis and treatment. — Malignant neoplasms of the oral cavity. The Republic of Kazakhstan. — 2015.
- Malignant tumors of the organs of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue. Educational method. manual./O.P. Chudakov, L.E. Moiseichik, T.B. Lyudchik, L.G. Bykadorova. - Mn.: BSMU, 2007. - 39 p.
- V.A. Soloviev. — Possibilities of ultrasound diagnosis of tumors of the tongue and floor of the mouth. — Oncology. Journal named after P.A. Herzen, 4, 2015. doi: 10.17116/onkolog20154418-21.
- A.R. Gevorkov. – Independent conservative and combined treatment of tongue cancer. – Oncology. Journal named after P.A. Herzen, 4, 2014.
- Rodrigo Arrangoiz. — Oral Tongue Cancer: Literature Review and Current Management. - Сancer Rep Rev, 2022. - Volume 2(3): 1-9. - doi: 10.15761/CRR.1000153.