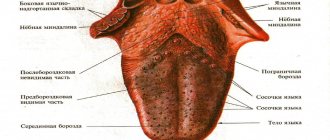
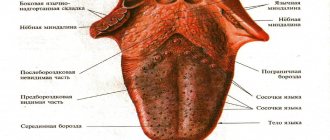
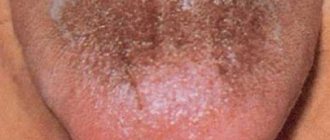
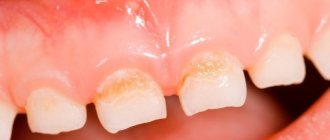
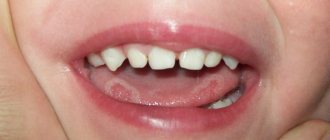
If on child's language bubbles appear, do not try to get rid of them yourself. Surely there were reasons for their occurrence, and only a specialist can accurately determine them. First, the doctor must find out what exactly triggered the formation of painful blisters on the child’s tongue. The reasons vary. Most often, white blisters appear due to a fungal infection or thrush. Also, their occurrence could be detected by severe dysbacteriosis or as an allergy. It should be noted that most allergic reactions manifest themselves in the form of urticaria, diathesis or dermatitis.
Causes of bubbles on a child’s tongue
In order to help the child as quickly as possible and prescribe appropriate treatment, it is necessary to determine the causes of the formation of bubbles on the child’s tongue. The very first reason why the mucous surface of a child’s tongue becomes covered with pimples is thrush. Often, this disease affects young children whose immunity is severely weakened. Small white bubbles form not only on the surface of the tongue, but throughout the entire oral cavity.
Treatment consists of frequent wiping of the mouth with a tetraborate solution, which contains glycerin. Sometimes doctors prescribe glycerin-based borax. All these drugs are easily available and are available even without a doctor's prescription. Therapy is carried out as follows. Take a piece of clean bandage and wrap it around your index finger, then moisten it generously in the liquid and gently wipe your tongue, and then your entire mouth. Try not to press on the tongue as this may trigger the baby's gag reflex. A similar treatment of the oral cavity should be carried out after each meal.
Causes
Milia occur in patients with a thick form of oily seborrhea, characterized by hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands and changes in the chemical composition of sebum and creating a favorable background for the development of acne.
There are closed comedones - whiteheads (milia) and open comedones - blackheads (blackheads). Thick seborrhea is also characterized by the appearance of deep cysts of the sebaceous glands - atheromas and acne vulgaris. Milia have the appearance of small rounded dense nodules of a white-yellowish hue, 0.5-3 mm in size with clear boundaries, protruding above the surface of the skin and resembling millet grains (popular name - “millet”). Milium is characterized by an uninflamed head, since the whitehead does not have a natural outlet and contact with the environment. Milia do not change in size for a long time. When microorganisms enter the milium, inflammation may develop with the formation of an abscess. Milia (milia) can often be found on the wings of the nose in recently born babies; they are considered borderline conditions in newborns and soon disappear spontaneously without any treatment.
Milia are recognized based on an examination of the skin by a dermatologist-cosmetologist based on characteristic external signs.
Another reason for the formation of pimples on a baby’s tongue is dysbacteriosis.
With dysbacteriosis, pimples cover the mucous membrane of the child’s tongue and externally resemble small ulcers. Treatment should be started immediately, since such bubbles cause severe pain.
In cases where pimples turn into ulcers, you should pay attention to the condition of the child’s intestines. After all, it is possible that exactly the same ulcers appear there as on the surface of the tongue. Therefore, if you notice even small pimples on a child’s tongue, you should undergo an examination of the whole body. This will allow us to determine the causes of this phenomenon and begin appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of molluscum contagiosum
The incubation period of the disease ranges from two weeks to several months, but most often the rash appears on the 14-15th day.
At first, single rashes appear, then there are more of them. Molluscum contagiosum can affect any area of the skin except the palms and soles. In children, exposed areas of the arms and legs, as well as the face and neck are most often affected. In adults, the genital area and the inner thighs are most often affected.
In the typical form of the disease, the rashes are located only in one anatomical area; in the generalized form, they spread throughout the body.
Rash
The elements of the rash look like protrusions (papules), firm and painless to the touch, pink or flesh-colored, with a pearlescent top. In the center of the papule there is a small depression, from which, when pressed, a white pasty mass is squeezed out. Papules have a round or oval shape, the size usually varies in the range of 2-5 mm, but sometimes the nodules merge, and then such formations can reach a diameter of 1 cm or more.
More about the symptom
Itching
In some cases, the rash is accompanied by itching, which intensifies when scratching. Under no circumstances should papules be scratched, as this can lead to a bacterial infection. The presence of a bacterial infection is indicated by redness of the skin around the papules, swelling, and suppuration.
More about the symptom
To cure blisters on a child's tongue
In order to eliminate bubbles on a child’s tongue that have formed due to dysbiosis, it is first necessary to undergo treatment aimed at restoring full intestinal functions. If this is a small child, then first you need to deal with nutrition. For example, you can add white cabbage to the cutlets, previously minced through a meat grinder. Cabbage plays the role of a “broom” and removes all harmful elements from the children’s intestines.
If we are talking about the digestion process of infants, then the mother should reconsider her diet. Treatment of blisters can be carried out only after consultation with a doctor. The specialist will select the drug that will not harm the baby.
Methods for diagnosing molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum can be confused with manifestations of other diseases, including serious ones such as syphilis or cancer. Also, the activity of the molluscum contagiosum virus increases with a decrease in immunity, so in 20% of cases molluscum contagiosum accompanies HIV infection. This means that when rashes appear that correspond to the description of molluscum contagiosum, a medical examination is required to rule out such options.
When contacting a dermatologist, the doctor will examine the patient, make a diagnosis and suggest a treatment method.
Inspection
In most cases, the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is made by a dermatologist based on the results of an examination of the patient.
PCR diagnostics
Since HIV often accompanies molluscum contagiosum, PCR diagnostics for HIV can be prescribed.
More information about the diagnostic method
Serological blood test
When molluscum contagiosum is detected in adults, a serological blood test is prescribed to identify sexually transmitted infections (hepatitis B and C, HIV, syphilis, etc.).
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Quite often, children develop pimples on their tongues caused by an allergic reaction of the body.
If there is an allergy, the child's tongue becomes covered exclusively with white blisters. This is their main feature. First, you need to exclude foods that could cause allergies from your diet. You will also temporarily have to give up scented soaps, powders and other detergents of synthetic origin. Believe me, regular baby soap or laundry soap will be much more beneficial in this case. Try to wet clean your home and remove dust more often. It is recommended to treat blisters on the tongue of infants with a regular soda solution.
Dear mothers, do not forget that only a qualified specialist can accurately determine the cause of bubbles on the child’s tongue and prescribe the necessary course of treatment.
Do not self-medicate at home, because the most valuable thing is at stake, namely the health of your baby! The main reasons for the formation of bubbles on a child’s tongue
Pediatric mammology
Hello, dear parents!
Allow me to introduce myself: Sergey Vladimirovich Kaplunov – I am a pediatric surgeon and pediatric oncologist. And today I would like to talk with the parents of my potential patients aged 0 to 18 years on such a very rare topic as pediatric and adolescent mammology. The relevance of this topic is due to the fact that parents do not know who to contact with this or that problem that has arisen in such a sensitive and intimate area, and doctors - pediatricians, gynecologists and ordinary pediatric surgeons are not fully aware of all the variants of pathology that can occur in the area of the mammary glands in children of different ages, and therefore cannot prescribe qualified treatment.
Let me look at breast problems in children according to the age at which these situations may arise.
But first, just a little bit of anatomy: both girls and boys have rudiments of glandular tissue located immediately under the nipple area - so from these tissue rudiments in adolescence, girls will develop glandular tissue of the mammary gland, and in boys these rudiments of glandular tissue will develop. the tissues will normally remain in their rudimentary form.
I. Newborn period. During this period, the so-called “sexual crisis” often occurs, one of the manifestations of which is engorgement (swelling, thickening, increase in volume) of those same rudiments of mammary gland tissue due to the passage of female sex hormones (estrogens) from the mother to the newborn child (sometimes it can even be released scanty secretion from the nipples) – usually this condition can be observed on the 3rd – 10th days of the child’s life, followed by a slow decrease in the severity of tissue engorgement in the nipple area.
But when infections penetrate through the thin and therefore easily vulnerable skin of a baby, against the background of this transient and physiological state, purulent-inflammatory diseases such as mastitis of newborns and necrotizing phlegmon of newborns (which is often localized in the area of the anterior chest wall) can occur.
Already in the neonatal period, parents may notice various developmental anomalies associated with the mammary glands in the child, such as:
atelia - absence of a nipple (absence of a nipple can be a symptom of syndromic pathology - an anomaly in the development of all tissues of the chest wall on the side of the missing nipple);
polythelia - an increase in the number of nipples: most often there is one additional nipple (on one side), which is located along the so-called “milky line” (from the armpit to the groin area), as a rule, the additional nipple is smaller in size (the nipple itself is also reduced and the surrounding areolar area of the skin) – a vestigial appearance
II. Girls in the period from 9 months to 1.5 years. During this period of life, female children sometimes experience a “second wave” of tissue engorgement in the area of the future mammary glands and, as a rule, this condition occurs precisely in those girls whose mothers continue to feed them breast milk. This condition is explained by the fact that hormonal changes occur in the mother’s body associated with the resumption of the cyclic production of sex hormones (as before pregnancy).
III. Pre-adolescence in girls. Often, mothers are concerned about the fact that the first signs of the beginning of the formation of mammary glands in girls begin at 8–9 years of age. This very often looks like a one-sided thickening (engorgement) of tissue in the retro-nipple area, measuring no more than 1 cm (“pea-sized”) on one side. On the opposite side, such engorgement is either absent or less pronounced. So this unilateral engorgement of the tissue under the nipple (girls complain of some tactile pain in this area) can be perceived by parents as a tumor (neoplasm) or as premature development of the mammary gland. However, we must remember that tumor diseases at this age in the area of the future mammary glands in girls are extremely rare, and the asymmetry of the beginning of the growth of the mammary glands in the first few months is not a sign of pathology starting from 8-9 years of age. Moreover, it has been noticed that more often it is the tissue of the future mammary gland on the left that begins to swell. The development of glandular tissue of the mammary glands often occurs not smoothly, slowly and gradually, but spasmodically. And, as a rule, a noticeable increase in mammary gland tissue begins only from 10 to 12 years of age - at this age, tissue development occurs more or less symmetrically.
But an increase in the size of the mammary glands in girls under 8 years of age - “thelarche” - requires the attention of both parents and a doctor! Thelarche can be isolated (i.e., only an increase in the size of the mammary glands without the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics) or as one of the symptoms of premature sexual development. Premature sexual development of a girl requires, first of all, the exclusion of hormone-producing tumor processes (most often in the ovaries) and a careful detailed examination by an endocrinologist! False thelarche can be mistakenly mistaken for true thelarche (proliferation of glandular tissue of the mammary gland) - this is an increase in subcutaneous tissue in the area of future mammary glands due to adipose (and not glandular) tissue. This condition usually occurs in overweight girls, and in diagnosing this condition, the key diagnostic role is assigned to an ultrasound specialist.
IV. Teenage years. This period accounts for the maximum amount of various pathologies, because during this period the greatest activation of the development of glandular tissue of the mammary glands occurs. Let's look at just a few of the problems.
The growing mammary gland requires the most gentle approach to itself in order to avoid problems with breastfeeding in the future associated with the presence of scars on the skin and inside the breast tissue, which will interfere with the formation and release of milk and the very process of feeding the baby. In such cases, there is an equally effective alternative to surgical treatment - a puncture type of treatment, which does not leave any scars behind!, is less painful, there is no need for general anesthesia and long-term painful dressings. The choice of treatment method for a purulent process in the mammary gland (surgical or puncture or even conservative) is, of course, a matter for an experienced specialist and depends on each specific clinical situation. The main rule for parents is to contact a specialist early with inflammatory changes in the mammary gland area in a teenage girl.
The most common tumor in the mammary glands in teenage girls is fibroadenoma - a benign tumor! Cancerous tumors of the mammary glands in children under 18 years of age (carcinoma, lymphoma, sarcoma) are a rare situation.
It is believed that fibroadenoma is a hormonally dependent tumor, the development of which depends on the reaction of breast tissue to the increasing concentration of estrogen in the growing female body. Often, fibroadenomas can be multiple, ranging in size from 5 mm to 5 cm (sometimes they occupy most of the breast tissue - leaf-shaped or phylloid fibroadenoma).
The only method of treating breast fibroadenoma is a surgical approach - operations in this case (especially in adolescents) should be organ-preserving and aesthetic in nature. Incisions and sutures are made using cosmetic techniques, and only the tumor is removed without involving surrounding healthy tissue.
In this informational article, I focused only on some of the most common problems that can arise in the mammary glands, mainly in girls. A separate topic is the occurrence of tissue proliferation (increase) in the area of the mammary (mammary) glands in boys - this is especially relevant (emotional, cosmetic, social aspects) in adolescence: the so-called gynecomastia. There are also a number of nuances and differences here. This topic will be discussed in the next information article.
Kaplunov S.V.
pediatric surgeon, pediatric oncologist of the highest category
Make an appointment
Make an appointment
How does physiological mastopathy differ from mastitis in newborns?
What happens to the baby's mammary glands after birth? The endocrine system is activated, so the baby’s body needs maternal hormones less and less. The pituitary gland of a small organism begins to produce estrogens, resulting in the release of prolactin: this causes engorgement of the mammary glands in the child, from which a milky fluid can be released.
Within a week after birth, the baby experiences a condition called a hormonal crisis. Nature is designed in such a way that it is the hormonal crisis that forces the body to adapt to the world: having gone through it, the child receives certain protection from problems with the immune and neurological system.
Questions
- Which doctor treats atheroma in children?
A pediatric surgeon is involved in identifying and treating atheroma in children. - Is it possible to cure atheroma without surgery?
Sometimes in the early stages of the disease the surgeon chooses a wait-and-see approach. In 20-35% of cases, atheroma can resolve on its own. However, if the capsule is formed and the tumor is large, it will not be possible to do without surgical intervention. - How dangerous is atheroma in childhood?
Atheroma is a relatively safe tumor. It does not become malignant, rarely becomes complicated and is not accompanied by the development of permanent defects. However, this does not eliminate the need to consult a pediatric surgeon. Only a doctor can establish the correct diagnosis and select treatment. In addition, atheroma can sometimes become inflamed due to the addition of bacterial flora and cause a deterioration in the child’s well-being. - Is it possible to play sports after surgery?
After surgical removal of atheroma, it is recommended to refrain from active activities for 2-3 weeks. This will allow the tissues to fully heal and recover.