30.05.2019
Progress does not stand still! It is with this obvious truth that I would like to begin today’s article. This applies to all areas of our lives, and by a happy coincidence, dentistry included! Every year, more and more new materials enter the dental market: safer, more aesthetic, and more practical to use. A constantly developing dentist now has in his arsenal high-tech devices and modern materials that allow him to provide high-quality, comfortable, and most importantly, safe dental care.
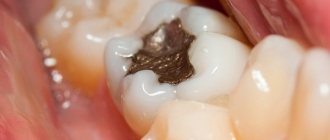
However, this was not always the case. Just some 10-15 years ago, treatment methods were still actively used that were not only unaesthetic, but also far from safe. The most striking example of this is amalgam fillings.
In historical essays, fillings similar in composition began to be used more than 100 years ago. Amalgam was an alloy of various metals, such as mercury, silver, tin, zinc, copper, etc.
The creation of such a material was made possible thanks to the ability of mercury to dissolve other metals in itself.
Example of an amalgam filling (work taken from the Internet)
Its main advantages were considered to be: strength, lack of visible abrasion and chipping, antiseptic properties of silver, and the ability to inhibit the progression of caries. The last point is very controversial, because under amalgam fillings, in the vast majority of cases, we find a recurrence of caries.
Obvious disadvantages include:
- Low aesthetic characteristics (metallic colored filling);
- Inability to restore the anatomical shape of the tooth (cusps and fissures);
- High thermal conductivity (increased sensitivity when eating cold and hot food);
- Technical difficulties at work.
And last but not least -
- Constantly released mercury vapor into the oral cavity.
The last point is now being studied especially carefully. After all, scientists have proven that mercury is a heavy metal that cannot be eliminated from the body on its own. Moreover, it has a destructive effect on human nerve cells. And if the patient has amalgam fillings in the oral cavity, on the side teeth, the structural elements of these fillings permanently enter the human body. Thus, chronic toxic effects of heavy metals occur.
Doctors all over the world have recognized the harm of amalgam and not only refused to place such materials, but also urgently recommend getting rid of such fillings.
Relatively recently, in the United States, the dental association created standards for the safe removal of amalgam fillings. This is called the SMART protocol. The essence of this protocol is that it is necessary to minimize the contact of the removed filling with the body of the patient, as well as the doctor and assistant.
Types of amalgam
Doctors use different amalgams to fill teeth. They differ in the concentration and ratio of metals in the composition. Some types contain a lot of silver and very little copper (less than 6%) - this is called silver amalgam in dentistry. In others, on the contrary, copper predominates - it can account for up to 30-37% - this variety is called high-copper and is considered the most advanced of the existing ones. There are options with and without zinc, as well as with the inclusion of expensive and rare metals (palladium, platinum).
Photo: mercury amalgam fillings
Read the article on the topic: types of dental fillings. Find out which ones are considered the best today.
To do this, the following requirements must be met:
- The skin, hair, and clothing of the patient and medical staff must be carefully covered.
- The seal is drilled with a special bur that does not create dust, with the supply of a large amount of water.
- The procedure for removing amalgam fillings is performed in a rubber dam using a hood or vacuum cleaner.
- It is necessary to ventilate the office after this manipulation.
The process of removing an amalgam filling (example provided from the Internet)
All these conditions must be observed, because during the removal of the filling, toxicity increases tenfold.
Important information! Patients during pregnancy and lactation should avoid removing amalgam fillings to avoid negative effects on the child’s body.
At the Atribeaute Clinique aesthetic dentistry department, strict monitoring of compliance with the SMART protocol is carried out. After excision of amalgam fillings, we carry out restoration with a composite material that can completely restore the aesthetic and functional characteristics of the tooth, while remaining 100% safe and hypoallergenic for the entire period the restoration is in the oral cavity.
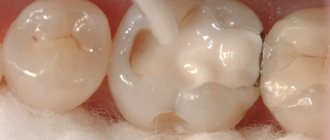
Tooth restoration with Enamel composite material (the work of dental therapist Tamara Valerievna Kudzieva)
Is it worth changing an amalgam filling?
Some experts believe that amalgam fillings should be completely replaced with modern composite materials. However, any repeated tooth irritation may do more harm than good. Therefore, fillings are changed only in some cases.
Indications for replacing amalgam fillings
- Caries developing around a filling.
- Large fillings (amalgam fillings are not suitable for reconstruction of large cavities).
- Weakened teeth. If only thin walls of the tooth remain, amalgam can cause them to crack.
- Replacement of an amalgam filling for aesthetic reasons, as its color differs from the natural color of the tooth.
There are several situations when it is advisable not to replace amalgam fillings with composite ones. These are usually small fillings that are placed correctly. Any intervention can lead to later complications, so only a doctor can say for sure whether the filling is worth changing.
How filling is carried out - description of the process in stages
The installation of an amalgam filling can be divided into several independent stages. Let's take a closer look at this sequence:
- preparatory measures: this includes cleaning the teeth from plaque and stone, administering anesthesia and fixing the rubber dam. Next, the doctor prepares the carious cavity, removes all affected tissue and carries out disinfection treatment. In this case, the thickness of the tooth walls should be slightly greater than required when filling with modern composites. A small cut should be left at the junction of enamel and dentin to improve retention. The tooth is washed and dried,
- application of a gasket: required to reduce tooth sensitivity, which can develop due to the increased thermal conductivity of the material. Its optimal thickness is 1-1.5 mm,
- amalgam mixing: carried out mechanically using a special electric mixer,
- installation of a filling - amalgam is applied in small layers using a special gun, waiting until it completely condenses before the next application. It is important to prevent the material from becoming porous and to remove all excess mercury. The cavity is filled, after which the edges are carefully removed, immediately forming a preliminary crown shape.
The amalgam is applied in small layers.
The final modeling of the restored area involves the application of tubercles and fissures. After this, occlusion control is required, for which special articulation paper is used. The filling itself is ground and polished only after a day. In this process, it is important to prevent overheating and evaporation of mercury, so water cooling is usually used.
Glass ionomer cement
A glass ionomer filling is considered temporary, but it is very durable and adheres tightly to the tooth. It replaced the classic types of dental cements. The material does not allow achieving the required level of aesthetics, therefore it is used as a spacer under the polymer.
The main advantage of glass ionomer cement is the presence of fluoride in its composition. Thanks to this, tooth tissues are strengthened, acquiring increased protection against caries. The material can be self-hardening and light-curing.
Additional Information. The use of glass ionomer cement is widespread in pediatric dentistry. This gentle material is used to install a permanent filling for a child.
When is it better to choose a different composite?
Dental amalgam has a number of contraindications. Thus, its use is not allowed if the patient has an individual intolerance to the components included in its composition. The material is also not used if the patient has dentures or crowns with metal fragments in his mouth.
The remaining contraindications will be similar to all restrictions that are relevant for filling with any other materials. It should be noted that many refuse this option due to an exaggerated fear of mercury poisoning. The material is only suitable for restoring chewing teeth; for restoring a smile, you should choose a more aesthetic option.
Therapy - prices for dental treatment
| NAME OF SERVICE | COST, RUB. |
| Application anesthesia | RUB 100.00 |
| Infiltration anesthesia | RUB 600.00 |
| Conduction anesthesia | RUB 600.00 |
| Rg | RUB 300.00 |
| Trephination of the tooth crown | RUB 300.00 |
| Applying an insulating pad | RUB 500.00 |
| Applying a therapeutic pad | RUB 300.00 |
| Light filling 1st surface | RUR 2,200.00 |
| Light seal 2nd surface | RUR 2,900.00 |
| Partial pinless tooth restoration with light-curing material | RUR 3,700.00 |
| Chemical filling 1st surface | RUB 1,500.00 |
| Chemical seal 2nd surface | RUR 2,200.00 |
| Partial pinless tooth restoration with chemically cured material | RUB 3,000.00 |
| Polishing the filling | RUB 100.00 |
| Polishing a filling placed in another clinic | RUB 500.00 |
| Restoration of a tooth stump for a crown using a chemically cured material | RUB 3,800.00 |
| Restoration of a tooth stump for a crown using light-curing material | RUR 4,800.00 |
| Using an anchor or parapulp pin | RUB 1,000.00 |
| Using fiberglass pin | RUB 1,500.00 |
| Veneer made of light material | RUR 5,000.00 |
| Splinting in the area of the 1st tooth | RUB 1,700.00 |
| Opening of the tooth cavity and medicinal treatment | RUB 500.00 |
| Mechanical and medicinal treatment of the 1st channel | RUB 1,000.00 |
| Repeated medical treatment of the 1st canal for complicated periodontitis | RUB 400.00 |
| Mechanical and medicinal treatment of the 1st difficult canal | RUB 1,700.00 |
| Application of arsenic paste | RUB 300.00 |
| Filling the 1st channel with paste | RUB 1,000.00 |
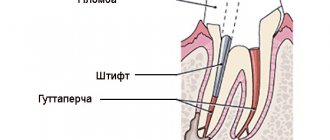
| Filling the 1st canal with gutta-percha | RUB 1,000.00 |
| Temporary filling of the 1st channel | RUB 500.00 |
| Removing a foreign body from the canal | RUB 2,000.00 |
| Unsealing, mechanical and medicinal treatment of the 1st channel | RUB 1,700.00 |
| Unsealing, mechanical and medicinal treatment of the 1st difficult canal | RUR 2,300.00 |
| Unsealing, mechanical and medicinal treatment of the temporarily sealed 1st channel | RUB 300.00 |
| Removing the anchor pin | 1000.00 rub. |
| Temporary filling | RUB 300.00 |
See the price list for all dental prices
If, when treating caries, the doctor made a mistake or carried out incorrect treatment of the pulp, then caries will definitely begin to grow and progress. This can lead to periodontitis, in which it is necessary to thoroughly and thoroughly clean and seal the dental canals. If this is not done, the infection will go deeper and periodontitis will transform into periostitis. Dentists call “periostitis” inflammation of the periosteum, or the so-called “flux”. If it is not treated in a timely manner, the inflammatory process will affect the entire body and the person may lose a tooth. To reduce the risk of medical errors during treatment and filling of dental canals, it is advisable to carry out such endodontic procedures under a microscope.
When fighting caries, great attention should be paid to preventive measures. This means that the patient must carry out high-quality oral hygiene procedures and undergo regular medical examinations.
It is necessary to destroy caries in the first stages of its manifestation. To do this, it is necessary to use differentiated diagnostic technology. Then the doctor will not have to use a drill. He can do just fine with minimally invasive treatments.
Use of ceramics
Ceramics are quite hard and do not change color or size over time. This explains its popularity in dentistry. Filling carious holes with ceramics does not occur immediately in the patient’s mouth. First, impressions are taken of both jaws, then individual inlays are made, which are securely attached to the recesses.
Restoring crowns with ceramic inlays takes longer than any other, but the results are worth it. The inserts stay in place perfectly, and the tooth under such a filling experiences a uniform load. Ceramic materials can have different compositions.
Important!
Composition of modern amalgams:
- silver (66–73%), provides strength and resistance to corrosion, causes expansion when hardening;
- tin (25–29%), increases the plasticity of amalgam;
- copper (2–6%), gives strength and ensures that the filling adheres to the edges of the cavity, also has antibacterial and anti-corrosion properties;
- zinc (up to 2%), reduces the oxidation of other alloy metals;
- mercury (up to 3%), the main reagent, solvent, causing the formation of amalgam.