Pain under the tongue can serve as one of the main symptoms of a whole range of problems, from banal mechanical injuries to a number of pathologies of the oral cavity, nervous system or internal organs. Depending on the cause and location of the pain, it can have a different nature and intensity.
If you or your loved one has pain under the tongue, there is no need to panic or self-medicate - this can only lead to aggravation of the situation. Contact a dentist at a dental clinic, he will conduct a diagnosis, determine the exact cause of the discomfort and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen to effectively eliminate the pain.
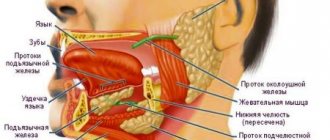
What is in the sublingual area
The tissues located on the lower jaw under the tongue are called the floor of the mouth. Due to the complexity of the structure, as well as the natural functionality of this area, a person often experiences problems accompanied by pain.
Structure of the sublingual region:
- Hyoid muscles - have an elastic structure and are responsible for the motor function of the area;
- Hyoid bone - has an anatomical shape in the form of a horseshoe, located in the muscle layer. It is the only bone in the human body that has no connections with other bones of the body;
- Nerve endings are elements of the peripheral nervous system, responsible for the sensitivity of the sublingual area to various physical, mechanical and thermal stimuli;
- Salivary glands - responsible for the production of saliva, which is involved in the process of wetting the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and the digestion process;
- Blood vessels - provide nutrition to the tissues of the sublingual area;
- Frenules are connecting folds in the sublingual area, responsible for connecting the sublingual tissues with the tongue.
Each of the above elements ensures the natural functionality of the dentofacial apparatus and participates in all physiological processes of the oral cavity.
Prevention of inflammation of the floor of the mouth
To prevent diseases of the sublingual area, dentists give recommendations on proper oral care:
- take care of your gums;
- avoid the accumulation of bacterial plaque;
- visit the dentist 2 times a year;
- prevent the occurrence of caries;
- brush your teeth 2 times a day.
But if the patient has congenital or acquired anomalies in the development of the floor of the oral cavity, such as a shortened frenulum or structural asymmetry, then you will have to be more careful to prevent injury. Some abnormalities can be treated. Come to an appointment at Family Dentistry and experienced specialists will tell you how to get rid of defects, tumors and inflammations.
Causes of pain under the tongue
Modern medicine knows dozens of different reasons that can cause unpleasant and painful sensations under the tongue in an adult, teenager and child: from a banal mechanical injury to the frenulum, leading to tissue damage, to allergic reactions causing swelling. At the same time, there is a list of the most common causes observed in most patients.
The main causes of pain under the tongue:
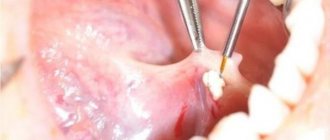
- Mechanical injuries to the frenulum and muscle tissue are the most common cause of sublingual pain. As a rule, it is observed in people with a short frenulum. It is injured due to stretching, as well as in the event of mechanical trauma to tissues, for example, during eating, hygienic brushing of teeth, etc.;
- Dental pathologies of the oral cavity – stomatitis, dental problems (caries, periodontitis, periodontitis), gumboil, etc.;
- Infectious inflammation of the oral cavity - pain often manifests itself with sore throat. During this period, it is painful for a person to eat, swallow water and saliva, stick out his tongue or simply chew;
- Cellulitis or abscess of the floor of the mouth is a significant accumulation of pus in a small area of the floor of the mouth. Causes “bursting” of internal tissues, putting pressure on peripheral nerves - this provokes pain and tactile discomfort;
- An allergic reaction can be the body’s response to various irritants. Causes swelling of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, accompanied by discomfort or pain in the sublingual area;
- Asymmetry of the hyoid bone - an anatomical disorder in the growth of the hyoid bone, can provoke excessive or nonspecific pressure on the peripheral nerves, causing pain;
- Neuralgia is a general disease of the nervous system that manifests itself in its various parts. It is often a consequence of nervous shock and is accompanied by a feeling of painful numbness in the oral cavity;
- Diseases of internal organs and body systems - some areas of the tongue may reflect (irradiate) pathologies of internal organs, which is accompanied by painful sensations in the sublingual area;
Note! Most of the above problems that provoke the development of pain in the sublingual area can be caused by bacterial infections (streptococci), fungi (candidiasis), and herpes.
Three types of inflammation of the salivary gland
Depending on the disease, there are three types of inflammation, namely catarrhal, purulent and gangrenous. First of all, a swelling forms in the area of the salivary gland, which is often accompanied by pain. The inflamed area becomes red, and the skin there is tense and shiny. The exit site of the gland duct has a limited area of edema and inflammation.
In most cases, a specific liquid is released from it, similar to saliva or pus. Body temperature rises sharply to 39 degrees. Opening your mouth becomes more and more difficult and painful. If treatment is not started on time, the disease will develop into a more severe form with serious consequences.
Symptomatic features of pain under the tongue
Pain in the sublingual area can have various symptomatic manifestations. First of all, they are accompanied by different types of pain (sharp, aching, throbbing), as well as constancy or frequency.
If you consult a doctor, it is very important to correctly characterize the pain - this will allow the specialist to narrow down the range of symptoms for differential diagnosis. For example, you may have pain in the frenulum under your tongue or pain under your tongue on the right/left.
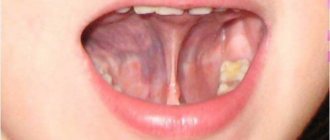
One of the characteristic manifestations of stomatitis or candidiasis is a white pimple under the tongue. Its presence may indicate the development of a fungal or bacterial process. If such a symptom is detected, treatment will include antifungal and antibacterial therapy with the prescription of antibiotics or special antiseptic rinses. The presence of pimples of a different color may indicate the presence of a wide range of problems, the identification of which requires a thorough diagnosis of the oral cavity or the entire body.
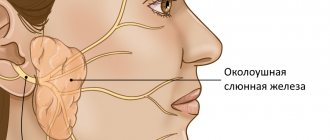
In the human body during normal development there are three pairs of salivary glands
The parotid gland is most often affected by various diseases. There are a number of diseases in which the sublingual and submandibular salivary glands become inflamed. If you do not start treatment on time or undergo inappropriate therapy, then serious complications may occur after such diseases, such as encephalitis, orchitis, meningitis, nephritis, neuritis and pancreatitis. However, do not worry, treatment often gives positive results. To avoid inflammation of the salivary glands, you just need to follow a few recommendations.
Features of diagnosis and treatment of pain under the tongue
Treatment of pain in the sublingual area should be carried out after a high-quality diagnosis to determine the root cause of the problem. Sometimes, pain in the frenulum under the tongue or in the surrounding tissues is treated by therapists or allergists, but in most cases this is done by dentists, because about 90% of all cases of treatment are associated with a dental problem.
Diagnosis of pain under the tongue is carried out in several stages:
- Initial appointment - the doctor collects anamnesis, finds out information about the nature and location of pain, and also examines the patient’s oral cavity;
- A complete diagnostic examination is carried out in the absence of characteristic symptoms of common dental diseases. It is possible to use hardware techniques (X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.);
- Differential diagnosis – a specialist differentiates the underlying pathology from similar diseases;
- Making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment - based on the data of the initial examination and diagnosis, the doctor establishes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes an adequate treatment regimen.
Note! The method of treatment and the choice of drugs to eliminate pain in the sublingual area directly depend on the root cause of the symptoms. For example, if your frenulum hurts due to a mechanical injury, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions for mouth rinsing will be prescribed, including: chlorophyllipt, hexoral, stomatophyte, alcohol tincture of calamus, stomatidine or others. If the pain is associated with the development of bacteria or fungi, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.
It is very difficult to diagnose this disease in the early stages.
In most cases, patients notice that something is wrong when the stone prevents the complete drainage of fluid. All this is accompanied by sharp pain, similar to salivary colic. At the site of inflammation, the tissues swell and become swollen. These symptoms are not constant, the pain either increases or disappears. During treatment, the stone is removed; if the situation is too advanced, sometimes the entire gland is removed.
The salivary glands under the tongue extremely rarely. But at the same time, the disease develops at a rapid pace and can have adverse consequences.
In order to maintain your health, first of all, you must adhere to the rules of hygiene and if you experience the slightest discomfort, immediately consult a doctor.
Inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue
Pain Relief Methods
Before suppressing pain localized under the tongue, it is important to establish the cause of this symptom.
If the frenulum ruptures, it is necessary to apply a disinfectant composition to the injury site and seek medical help.
Inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland is treated with the following medications:
- antiseptic;
- antibacterial;
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers.
If foci of suppuration are detected, the cavity is additionally drained.
Normalization of nutrition plays an important role in eliminating pain under the tongue. It is recommended to give preference to soft, pureed dishes at room temperature. Active saliva production speeds up the healing process. To do this, acidic foods such as sauerkraut or citrus fruits are introduced into the diet.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Pain under the tongue is a symptom, not a separate disease. It occurs when an organ is injured or against the background of various pathologies. It is possible to suppress pain only if the factor that provoked it is eliminated.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce tingling and burning, doctors recommend following a diet. All hot and spicy dishes are excluded from the menu; food should be warm, but not hot. Products are prepared by steaming, boiling or stewing so that they are soft and do not injure the surface of the tongue. It is necessary to regularly rinse your mouth with water or a weak solution of chlorhexidine: this helps get rid of tingling and also prevent inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
Conservative therapy
Treatment for a tingling tongue begins with dental care. The doctor sanitizes the oral cavity and, if necessary, changes fillings and incorrectly selected dentures. If after this the symptoms do not disappear, treatment is prescribed for the underlying disease causing glossalgia. Therapeutic regimens are selected by a specialized specialist: neurologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist.
Pathogenetic treatment includes medications that affect the nervous system, which help reduce painful paresthesias. Herbal sedatives, bromine preparations, and “daytime” tranquilizers are effective. For refractory symptoms, injections of B vitamins and trimecaine blockades are used. Local remedies provide a quick effect: lubricating the tongue with anesthesin, pyromecaine, oil solutions (vitamin A, rose hips).
Those suffering from desquamative glossitis are often prescribed physiotherapy, which includes medicinal electrophoresis, ultrasound therapy, and SMT therapy. For prolonged glossalgia, reflexology and ozone therapy help relieve tingling. To reduce the intensity of symptoms, laser therapy is used, which has an additional anti-inflammatory effect. Paresthesia of a neurogenic nature requires psychotherapy sessions.