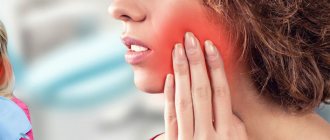
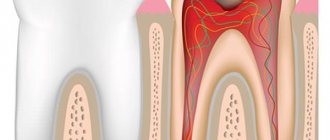
Many people are familiar with the phenomenon of gumboil - when the cheek next to a sore tooth swells literally before our eyes and painkillers do not relieve acute pain. This is the periosteum of the tooth becoming inflamed, or, as doctors say, odontogenic periostitis of the jaws has developed. This disease in itself is a complication of dental problems (periodontitis, periodontitis), but in the absence of proper treatment, such inflammation can also cause the development of even more serious complications.
Why can the periosteum of a tooth become inflamed?
The most common is odontogenic periostitis of the jaws, that is, an inflammatory process provoked by diseases of the teeth or periodontal tissues. Deep caries, pulpitis, periodontitis (inflammatory process at the apex of the tooth root), periodontitis - all these diseases, if not treated in time, lead to the appearance of gumboil. Also, one of the reasons for the development of the inflammatory process may be alveolitis - inflammation of the tooth socket, which in some cases occurs after tooth extraction. Inflammation of the periosteum after tooth extraction usually develops in those patients who do not rush to see a dentist when the first signs of complications appear in the postoperative period.
Much less common is toxic periostitis, caused by infection through the blood or lymph (usually due to some general infectious disease). The disease can also be caused by injuries to the jaw bone or surrounding soft tissue.
Let's sum it up
A timely visit to a qualified dentist will help eliminate purulent inflammation of the gums and restore good health.
People who pay little attention to daily hygiene are susceptible to the development of pathology. Bacteria and microbes easily penetrate through damage to the surface of the tooth, causing an outbreak in the pulp. Since there are nerve endings in this area, the inflammatory process is painful and painful. The disease has a rapid course and develops within a day. In the absence of proper treatment, an abscess threatens to damage the jaw bone, tooth loss and generalization of infection in the body.
Most often, flux is detected in adults. Due to bad habits and poor hygiene. People overloaded with work and everyday problems put off visiting the hospital until later. They are interested in what to do if the gums are inflamed, painful, swollen and pus comes out at home. Without professional treatment, advanced diseases provoke inflammation of the root dental tissues.
In young children, the disease manifests itself with mild symptoms. This is due to reduced immune activity in children who are not able to adequately resist infection. The child needs treatment for the initial manifestations of flux, otherwise the weakened body will have to face dangerous complications.
The Dentika clinic has modern equipment and high-class dentists with a rich medical practice. Specialists will quickly determine where the pockets of pus are located in the gums and how to remove them.
Inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth: symptoms
Depending on the form and localization of the process, symptoms may be as follows:
- General symptoms: severe pain in the area of inflammation, swelling, noticeable swelling, discoloration of the gums, mobility of the dental unit, which served as a source of spread of the pathological process. Depending on the location of the source of infection, facial swelling will look different: when inflammation develops near the front teeth, the upper lip or middle third of the face swells; when inflammation occurs near the chewing teeth, the cheek, sometimes the lower eyelid, and parotid area swell. You can evaluate what different types of edema look like during inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth using a photo.
- Acute serous periostitis of the lower or upper jaw is accompanied by severe redness of the mucous membranes, rapid development of edema, and increased body temperature. The general symptoms of this form of inflammation are especially pronounced.
- In the acute purulent form of the disease, severe sharp pain is characteristic, and the pain subsides under the influence of cold and becomes stronger when exposed to heat. Sleep and appetite are disturbed, the temperature rises noticeably, and the patient’s general condition worsens. Pain in most cases radiates along the branches of the corresponding nerves. For example, acute purulent periostitis of the lower jaw can make itself felt by pain in the neck, chin, ear and temporomandibular joint. Purulent periostitis of the upper jaw most often provokes pain in the orbital area, temporal bone, and ear.
- The chronic form of the disease is quite rare, and chronic periostitis of the lower jaw usually develops. The symptoms are mild, the swelling is almost unnoticeable and can gradually develop over a very long time. Pain and discomfort appear from time to time (periods of exacerbation).
At the initial stage of the inflammatory process, it usually has a serous form, later, without treatment, it becomes purulent. With a large accumulation of pus, the formed abscess can burst with the flow of purulent contents into the oral cavity. At the same time, the swelling decreases and the pain subsides. In this case, some patients calm down, believing that the problem has been solved, and are in no hurry to see a dentist. In fact, this is only temporary relief, since the pathological process can resume at any minute.
Rinse for painful sensations
Rinses are also widely used - both homemade and pharmacy. For example:
- 100 ml of water, a teaspoon of soda, a teaspoon of soda, iodine - 5 drops. Used to relieve swelling and remove purulent contents
- 1 spoon of sage per glass of boiling water (decoction), anise - 10 drops. Provides pain relief and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- 1 glass of warm water, 1 tablet of furacillin. Powerful antibacterial effect, reducing swelling.
The drug chlorhexidine has a good aseptic effect; so-called dental elixirs can be used to relieve pain.
It is important to understand that all the methods listed above are only first aid for toothache; if you stop there, you will soon inevitably need tooth extraction!
To eliminate pain, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of the problem. This can only be done in a dental clinic, where modern equipment ensures comfortable and painless treatment.
Periostitis in children
In children, the inflammatory process usually develops as a result of untreated caries of baby teeth, infectious diseases or injuries. Due to the peculiarities of the physiology and anatomy of the child’s body, as well as due to the immaturity of the child’s immune system, the pathology develops quickly and rapidly, and the infection quickly spreads through the bloodstream and lymph flow, so multiple lesions can form.
Periostitis of the upper jaw in a child requires special attention, which, when localized in the palate, may not change facial features - swelling forms inside the oral cavity and can only be noticed by the characteristic convex swelling on the palate. The abscess gradually grows, capturing the mucous areas of the pharynx and tongue, which causes pain when swallowing and chewing. If a child develops symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, or painful swallowing, it is imperative to check whether such a condition is caused by developing gumboil.
Types of dental abscess
Pyogenic bacteria enter healthy gum tissue through the bloodstream or due to mechanical damage. An abscess appears in the area of the affected element. When the abscess matures, the mucous membrane acquires a bluish tint, and a whitish spot or characteristic bubble appears. With its rupture, a fistula is formed in the periodontium, through which the contents flow out. This phenomenon does not lead to the disappearance of the problem, the inflammation remains. The pathology is indicated by the flow of pus from the gums when pressing on the affected area. There are several types of abscess:
- Desnevoy. The lesion is on the surface of the soft membrane and interdental papillae. The cause of infiltration is associated with the ingress of food debris and mechanical injuries. If detected early, it responds well to treatment.
- Periapical. A common type of pathology that develops as a result of untreated carious lesions or periodontitis. Infection of the dental root system leads to the accumulation of exudate in the upper part of the root. When immunity decreases, the periosteum of the unit and the mucous membrane are affected, a fistula is formed, purulent sacs appear above the gum, and pus is released.
- Periodontal. The infiltrate develops inside the gum tissue. Infected contents accumulate in the mucous membrane, forming a protrusion in the periodontal pocket. Due to the lack of a channel for fluid to flow out, damage occurs to the bone and soft tissue surrounding the diseased element. There is a high probability of developing periodontitis.
- Pericoronal. The pathological process is characteristic of erupting units. Bacteria and food debris fall under the “hood” of the mucous membrane. As a result, pus accumulates above the tooth, the gums swell and cause pain. The disease is dangerous due to complications: swelling of the neck, angina pectoris.
- Periodontal-endodontic. Infectious damage to the pulp and periodontal tissues occurs. There is a risk of periodontitis.
Flux is characterized by several stages of development, which have characteristic manifestations:
- Serous. Lightning current. The inside of the cheek and mucous membranes swell within a couple of days.
- Purulent. Continuous, debilitating, throbbing pain in the unit. Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane. Hyperthermia.
- Diffuse. Swelling and soreness of the entire surface of the oral cavity, affecting the nose, lips, and outer cheeks.
- Chronic. Gradual progression over months or years. Long-term remissions are followed by relapses. As the swelling decreases, the inflamed areas remain firm.
Possible complications and diagnosis
If the disease is not treated properly, very serious complications soon develop: osteomyelitis (purulent inflammation of bone tissue, provoking its necrosis), phlegmon (a diffuse purulent process that affects nearby tissues and requires immediate surgical intervention), sepsis (a general infection of the body, often ending in the death of the patient ). Each of these conditions requires emergency medical care and long, painstaking treatment. Therefore, it is better not to let the situation lead to complications and contact a dentist at the first signs of an inflammatory process.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will need to conduct a differential diagnosis using instrumental diagnostic methods (radiography, CT). This disease is similar in symptoms to acute periodontitis, acute inflammation of the salivary glands, lymphadenitis, and osteomyelitis. Therefore, in order to prescribe adequate treatment, it will be necessary to exclude these conditions and accurately determine the cause of the patient’s poor health.
Pulpitis
Inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth is one of the most common diagnoses with which patients come to the dentist. Most often, pulpitis occurs due to untreated caries, which destroys the hard tissues of the tooth and reaches its core. As already mentioned, pulpal pain when pressed is very sharp, they are characterized as a “lumbago”. Nerve endings give the most severe symptoms, so it is very difficult to tolerate this phenomenon. You should not rely only on painkillers. It is better to consult a dentist to get timely help for your tooth.
Inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth: treatment
Periostitis of the lower and upper jaw requires almost the same treatment, despite some differences in symptoms and localization of lesions. Moreover, complex therapy will be required, which will quickly eliminate the infectious-inflammatory focus and prevent relapses:
- Surgery. Opening the purulent sac with removal of the contents and thorough cleaning of residual pus is a mandatory procedure in this case. The intervention is performed under local anesthesia. At the initial stage of the disease (with its serous form), it is possible to do without surgical intervention. In this case, the doctor carries out endodontic treatment (depulpation, cleaning and treatment of root canals, antibacterial therapy).
- Drug therapy. Prescribing antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate inflammatory phenomena (swelling, hyperemia, fever, pain) and infection.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. Iontophoresis, ultrasound or laser therapy, electrophoresis, paraffin therapy - all these procedures are usually aimed at resolving compactions formed as a result of the pathological process. As a rule, physiotherapy is used for chronic forms of the disease, but in some cases it can be used in the complex treatment of acute purulent forms.
Antibiotics for inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth are prescribed during the treatment process; they are necessary to eliminate the bacterial infection, which is one of the causes of the development of the purulent-inflammatory process. The doctor selects medications based on the severity of the disease, the general condition of the patient’s body and the possible presence of concomitant diseases. Along with antibiotics for periostitis of the jaw, antihistamines (antiallergic) are also prescribed as treatment, which can reduce the drug load on the immune system, as well as calcium supplements.
The success of treatment largely depends on the patient’s timely visit to the doctor and the effectiveness of the therapy itself. And if in the first case everything depends on the patient - his conscious attitude towards his own health, then in the second the success of treatment is completely determined by the qualifications and experience of the dentist to whom the patient turned. A competent specialist with extensive clinical experience will quickly and successfully cope with even such a complex disease, while an amateur can further aggravate the problem. Therefore, choosing a good specialist is important here - these are the specialists who work at the 32 Dent clinic. Our doctors have extensive experience in successfully treating any purulent-inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, including periostitis.
Prevention
- A healthy lifestyle and daily oral care using personal hygiene products will help prevent the development of gumboil. For cleaning, use a medium-hard brush.
- After each meal, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with a special mouthwash or use dental floss. Instead of a pharmaceutical composition, it is allowed to use an aqueous solution of food salt, sea salt or an alcoholic tincture of propolis.
- Do not use non-sterile objects as toothpicks. Such actions lead to mechanical injuries and infection.
- Periodic professional dental cleaning helps remove stone, which provokes the development of inflammation of the gums with pus.
- The daily diet must be supplemented with fresh vegetables and fruits. Apples, carrots and other solid plant foods cleanse plaque from enamel and strengthen teeth.
It is also important to treat dental defects immediately and undergo regular clinical examinations at least twice a year. It is much easier to prevent dental disease than to treat its negative consequences. You should be attentive to your health and not ignore the warning signals that your body gives.
How to treat inflammation of the periosteum of a tooth before visiting a doctor?
Self-medication for any purulent processes is very dangerous, so it is recommended to consult a dentist at the first symptoms of the disease. However, before visiting a doctor, the patient can alleviate his condition somewhat by applying cold to the cheek on the affected side and rinsing his mouth with an antiseptic solution at room temperature (chlorhexidine soda-saline solution, chamomile or sage decoctions). Here's what you absolutely can't do:
- Apply warm compresses and drink hot drinks.
- Apply any bandages yourself or use medications without a doctor’s prescription.
- It is better not to take analgesics before visiting the dentist.
- If you are undergoing surgery (opening an abscess), you should not take aspirin, since it changes the rheological properties of the blood and can cause bleeding.
How to cope with pain?
Toothache is always a good reason to see a doctor; it’s worth taking the time to avoid complications!
If professional dental care is not possible, first aid is to relieve pain and minimize inflammation.
Analgesics of various effects used in dentistry - tempalgin, ketorol, nurofen; standard dosage regimen - 1-2 tablets every 4 hours; The effect of the drugs begins within the first 15 minutes and lasts up to 6 hours.