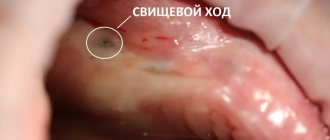
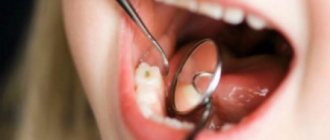
Periostitis is a purulent inflammation of the periosteum, the tissue covering the bone of the upper or lower jaw. Over time, the inflammation spreads to other tissues of the oral cavity , and a painful and unpleasant abscess can grow on the gum.
Periostitis is of two types: acute and chronic . the acute one , it goes on very quickly. Inflammation is manifested by asymmetric swelling of the cheek on the side of the diseased tooth and enlargement of the lymph nodes, and an increase in temperature is observed. Chronic periostitis can pass without obvious symptoms, while negatively affecting the condition of the child’s teeth, destroying them from the inside. The chronic form often occurs due to untreated acute periodontitis, pulpitis or due to injury.
Why is periostitis dangerous?
It is impossible to delay the treatment of periostitis , as this can lead to very dangerous consequences:
• acute purulent periostitis – it is manifested by swelling and hardening of the gums, tooth mobility, and increased body temperature. The child's appetite and sleep deteriorate. In this situation, the baby urgently needs medical attention and hospitalization;
• and dentia - the inflammatory process can quickly spread into the bone tissue, damage the rudiments of permanent teeth and destroy them. In the future, because of this, a tooth will not be able to grow .
• f legmon – inflammation of the tissues located under the skin, accompanied by severe swelling, thickening and suppuration. If not treated in time, it can cause blood poisoning.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an allergist-immunologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) - maintenance course (excluding the cost of the drug) | 8100 rub. |
Signs of periostitis in a child:
• aching or nagging pain in a tooth or gum. Moreover, painful sensations intensify with any touch (including during meals);
• redness and swelling of the gums;
• when a lump appears above or below a tooth;
• o tech cheeks;
• enlargement of the lymph nodes (usually on the side where the source of inflammation is located);
• bad breath ;
• elevated temperature . It may not be present, but even if the temperature is normal and other symptoms are present, the child must be taken to the doctor;
• capriciousness and lethargy of the child.
First aid
call an ambulance immediately . Doctors may decide on emergency hospitalization if the patient has difficulty breathing, a swollen tongue, or symptoms indicating intestinal damage.
What to do before the doctors arrive?
First aid, which should be provided at the first symptoms of angioedema in children, involves clearing the airways, checking breathing intensity, heart rate, and blood pressure. Sometimes it is necessary to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation, so after the first case, parents are recommended to take first aid courses. At the final stage, medications should be administered to the child.
First aid equipment includes:
- glucocorticosteroids (“Prednisolone”, “Dexamethasone”);
- antihistamines;
- adrenalin.
Sequence of administration: adrenaline, then glucocorticosteroid, then antihistamine. If the reaction is moderate, then adrenaline is excluded.
| Adrenalin | It is injected intramuscularly into the thigh (middle third outside) at the rate of 0.01 mg for each kg of the child’s weight. If there is no effect, then the injections are repeated every 15 minutes. |
| Glucocorticosteroids | Injected intramuscularly into the buttock or intravenously. You can pour the medicine from the ampoule under the tongue - this way the effect will come faster. The dosage of Prednisolone is from 60 to 150 mg, Dexamethasone is from 8 to 32 mg. |
| Antihistamine | Intramuscular injection is preferable. It is possible to take a pill, but the effect will come later. The dosage depends on the medicine. For example, “Loratadine” – 10 mg, “Cetrizine” – 20 mg. |
Important! In case of swelling of the larynx, a tracheostomy is performed urgently.
Causes of periostitis:
• of thorough oral care Small children do not yet know how to properly take care of their teeth, so plaque and food debris accumulate in the gum pockets, which can cause inflammation;
• injury to the gums . Children, especially toddlers, love to put almost everything in their mouths. Foreign objects can not only injure the gums, but also introduce harmful microbes into the wounds;
• to caries and its complications . Baby teeth are more vulnerable, so any defect can cause infection;
• angina , tonsillitis . _
How to prevent cheek swelling: preventive measures
To prevent the manifestation of an unwanted symptom, you must follow certain recommendations:
- Maintain good oral hygiene. It is especially necessary to monitor the child’s performance of all procedures. It is important to brush your teeth twice a day, use dental floss and mouthwash.
- Visit the dentist periodically - at least twice a year. If unpleasant symptoms occur, a visit to the doctor should be made immediately.
- Strengthen the gums and roots of the teeth by rinsing with herbal infusions and eating solid plant foods.
- Eat rationally and balanced. The body must receive the entire complex of vitamins and minerals around the clock.
No one is immune from problems, but preventative measures will help reduce the likelihood of their occurrence.
Treatment of periostitis
The main thing to remember is that you cannot try to treat periostitis on your own . There are several actions that absolutely cannot be performed while waiting for a doctor’s appointment, so as not to aggravate the disease:
• apply hot compresses , rinse with soda or drink hot drinks and decoctions. Heat will only increase swelling;
• give painkillers , and even more so antibiotics;
• try to cut the abscess yourself .
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have a swelling of the cheek, you should first consult a dentist.
If the cause of the swelling is not dental, your doctor will refer you to other specialists:
- see a therapist for bacterial and viral infections;
- see a neurologist for neurological diseases;
- to an ENT specialist for inflammation of the ear and salivary gland;
- see a nephrologist for kidney pathologies;
- see a traumatologist or maxillofacial surgeon for trauma to the lower jaw.
Read also: What herbs increase and decrease blood pressure?
HOW TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT at the PsorMak Institute for Healthy Skin
1. Click the button you see below -
Make an appointment
2. Fill in the fields in the form that appears. Be sure to check the correct phone number so that our specialist can reach you. After filling out, click on the “Submit” button.
3. Wait for our specialist to call. He will answer any of your questions and agree on the date and time of your visit to PsorMak.
The initial appointment includes:
- Visual examination , which will allow the specialist to get a general understanding of the condition of your skin and the pathology itself.
- Collecting anamnesis - finding out information about the development of the disease, living conditions, previous diseases, operations, injuries, chronic pathologies, allergic reactions, heredity, etc. Together with a general examination, this allows you to make a fairly accurate diagnosis and choose a method of treatment and/or prevention.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis is made by a doctor based on the results of studying the medical history and life of the child in combination with a dental examination. The patient’s complaints, the presence of somatic diseases, and whether he is taking medications that may cause the development of gingivitis are clarified.
Then the doctor conducts an external examination, paying attention to maxillofacial anomalies, the condition of the teeth and gums, and makes a diagnosis. The dentist does not require the help of other specialists, since the disease clearly manifests itself externally and does not require instrumental examination.
How to relieve your baby's condition with medications
If your baby is bothered by sore gums and begins to behave restlessly, you can give him a mild pain reliever that is appropriate for his age.
For the youngest, it is better to use candles, and older children can be given a special suspension. These drugs, in addition to a sedative effect, have mild antipyretic properties. In addition, pharmacies sell a special anesthetic gel, a small amount of which should be applied to the surface of the inflamed gum. However, you should not get carried away with such gels, since most of them promote increased salivation and also cause numbness, which makes the baby feel uncomfortable.
Important:
Before purchasing one or another medication to alleviate a child’s teething condition, you should definitely consult a pediatrician to rule out side effects.
Complications of flux
Complications with these localizations of phlegmon can be much more severe than with superficially located purulent foci with clear local manifestations. It is especially important to emphasize the danger of developing phlegmon of the floor of the mouth, taking into account the probable anaerobic component of the microflora.
Therefore, if there are complaints about difficulty swallowing, an increase in the volume of the tongue, its pushing towards the hard palate, a forced position of the head, you should urgently seek help from a dentist in order to avoid the development of the most common complication with this localization of phlegmon - anterior mediastinitis.
What to do after removing a baby tooth: general recommendations
In dental clinics, milk teeth are removed under anesthesia. An exception is made only for moving, strongly swinging units. Anesthesia is selected differently:
- local - a small injection with preliminary anesthesia of the gums;
- nitrous oxide sedation - delivering laughing gas through a mask to reduce anxiety;
- under anesthesia - with multiple removals or individual indications for treatment during sleep.
When local anesthesia is used, the lip and cheek in the area of the tooth being removed lose sensitivity. Sensations are restored within 1.5-3 hours, and during this period of time parents should keep an eye on the baby and distract him.
Strange sensations of numb tissues lead to the fact that children begin to bite them with their teeth. And since there is no sensitivity, the bite can severely injure the lip or cheek from the inside. To prevent this from happening, you should keep your child busy with something interesting - watch cartoons or play your favorite games.
Nutrition after baby tooth extraction: how much you can’t eat, choice of foods
The second point that adults need to consider is nutrition. And this is not only the traditional question of how much you can’t eat after a baby tooth is removed. Dietary restrictions apply to:
- fasting interval time - 2 hours after removal;
- choice of products - for several days you need to remove solid foods from the menu, offer the child purees, jellies, omelettes, instant baby cereals.
The drinking regime also has its own peculiarities:
- Avoid drinking through a straw and carbonated drinks;
- give up fermented milk products - kefir, fermented baked milk, drinking yogurt;
- remove excessively cold or hot drinks;
- drink a lot during the first 24 hours.
Rodikova Tatyana
Children often ask what a baby tooth looks like after removal. I show. Many guys ask to take the tooth with them. Children place their extracted teeth under their pillow at night and receive gifts from the “tooth fairy.” A pleasant fairy-tale tradition that turns removal into a small adventure.
Do's and Don'ts after tooth extraction in a child
The child leaves the doctor's office with a sterile swab in place of the extracted tooth.
The cotton wool is removed after 20 minutes. The first three days after the surgical procedure you cannot:
- actively engage in sports - experience significant physical activity;
- warm up the area of the extracted tooth - apply compresses, visit a bathhouse, sauna;
- pick the hole with sharp objects (toothpicks, matches), touch with your tongue or hands;
Correct behavior after tooth extraction;
- chew food on the side opposite the removal site;
- Gently rinse your mouth after meals (take some water, hold it and spit it out);
- brush your teeth with a soft brush, avoiding the socket.
- take medications prescribed by the doctor in a dosage appropriate to your age;
- Apply ice to the cheek in the area of the extracted tooth to reduce pain.
Adults are advised to distract the child from thoughts about the removed tooth. It is best to keep your baby busy with calm board games, watching a favorite fairy tale, or reading books.
This approach will reduce stress and relieve the child from worrying about the dental procedure. It will also help to avoid unnecessary investigative curiosity and studying the wound in the gum.
How to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction in a child
Rinsing in the first days after removal is strictly prohibited. Aggressive active movements can cause a clot to fall out of the socket and cause bleeding.
Instead of rinsing, the pediatric dentist-surgeon will definitely recommend oral baths. They are easy to make. The child puts an antiseptic solution into his mouth, holds it at the removal site for several minutes and gently allows the liquid to flow out by simply opening his mouth slightly.
The composition for the baths can be almost any. A weakly concentrated saline solution or soda solution is recommended for children. For older children, you can offer Miramistin, Chlorgesidine solution - sold in any pharmacies.
Soldatenkova Alina
Most recommendations after tooth extraction are aimed at preserving the blood clot in the socket. It is very important that it does not fall out. The clot serves as a natural protection for the wound from bacteria and accelerates healing. It is especially important to monitor the socket when removing the 4th milk tooth in children (chewing). Healing of wounds after extraction of incisors or fangs occurs faster and usually without consequences.
Literature
- Khomenko L. A. Therapeutic dentistry of children. Textbook for university / ed. 2007 – pp. 643-722.
- Ismailova G. T. Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis // Bulletin of surgery of Kazakhstan. - 2011. - No. 4. — P. 124-125.
- Drobotko L.N., Strakhova S.Yu. Acute stomatitis in children // Issues of modern pediatrics. - 2010. - T. 9. - No. 2. - P. 146-149.
- Suerkulov E. S., Yuldashev I. M., Mamyraliev A. B., Toktosunova S. A., Tsepeleva A. S., Sooronbaev A. A. Prevalence and structure of the incidence of stomatitis in children // Bulletin of Science and Practice. 2022. T. 4. No. 11. — P. 91-96.
- Suerkulov E. S., Yuldashev I. M., Mamyraliev A. B., Zhumashova N. K., Yuldasheva G. I. Complex therapy of inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa in children // Bulletin of Science and Practice. 2022. T. 5. No. 5. — P. 96-104.
- Pankrusheva T.A., Maravina I.N., Chekmareva M.S. Research on the development of the composition and technology of tablets for the treatment of stomatitis // Scientific result. Medicine and pharmacy. – T.4, No. 1, 2022. – P. 78-87.
- Instructions for medical use of the drug HEXORAL® aerosol: , .
- Instructions for medical use of the drug HEXORAL® solution: , .
- Instructions for medical use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS: , .
- Instructions for medical use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC: , .
- Instructions for medical use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA: , .
Up to contents