Complications of bruxism
How the disease can be complicated if symptoms are ignored and intervention is delayed:
- hypertrophic changes in facial muscles;
- difficulties in mobility of the lower jaw;
- gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis;
- fibrosis of soft tissues;
- lichen planus on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- malocclusion;
- carious lesions;
- grinding down teeth to the base;
- joint dysfunction;
- tooth loss;
- violation of facial aesthetics;
- depression, sleep problems.
Causes of Bruxism
There are several theories about the appearance of bruxism in adults. Psychological theory attaches great importance to the emotional state of a person in the development of the disease. Thus, factors favoring the development of bruxism may be the following:
- stress;
- high psycho-emotional stress;
- social and everyday disorder, troubles;
- frequent affective states.
The disease is called the disease of businessmen. People who undergo high psycho-emotional stress and take on great responsibility experience tension, which leads to involuntary muscle spasms during sleep. But it is important to understand that positive-minded patients can also suffer from this disease.
According to the neurogenic theory, the causes of bruxism in adults lie in disruption of the central and peripheral nervous system. This leads to neurological and movement disorders, muscle spasms. The validity of this theory is confirmed by the fact that, along with bruxism, sleep disorders (apnea, snoring, somnambulism) are often observed; tremor, epilepsy, enuresis - bedwetting. Tonic muscle tension can also be associated with damage to the trigeminal nerve.
Dental theory is based on the assumption that bruxism develops as a result of disturbances in the structure and function of the dental system. These include the following:
- bite defects;
- incorrect position of teeth;
- supernumerary teeth;
- crowded teeth;
- violation of the integrity of the dentition (partial adentia);
- incorrectly selected dentures and orthodontic structures;
- overestimation of fillings according to the bite;
- diseases of the temporomandibular joint.
Dental diseases lead to uneven distribution of the chewing load, and therefore the chewing muscles do not work properly. Her overexertion leads to nighttime cramps.
According to osteopathic theory, muscle contraction is an attempt by the neuromuscular system to eliminate blockage of the cranial sutures and restore craniosacral rhythm. This may be the result of birth trauma, malocclusion and posture, diseases of the cervical spine, etc.
Other theories about the origin of bruxism are not widely accepted, but some researchers link the problem to impaired nasal breathing, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), parasitosis, frequent chewing of plates or pads, and other factors.
In any case, the causes of bruxism in an adult can be different, so it is difficult to do without a comprehensive diagnosis and the involvement of several specialized specialists.
Ask a Question
What to do if your child grinds his teeth in his sleep
In addition to the above, the following measures can be taken:
- Review your daily routine. If you suspect that your child is overtired, reduce the load. For example, pause clubs and sections, discuss attitudes towards school performance, and in general, do not overload the child’s nervous system.
- If a child grinds his teeth in his sleep after moving, changing schools or other significant events, give him time to get used to it. Be sure to ask about possible problems and discuss how best to proceed.
- If the child is very impressionable, consider the option of mild sedatives, and establish a sleep and rest routine.
- Check the level of calcium and magnesium, and if necessary, add foods or medications rich in these microelements to your child’s diet.
- Make sure your child sleeps comfortably and soundly. A good mattress, comfortable pajamas, and fresh air do not completely eliminate bruxism in children, but they help reduce nighttime tension.
What not to do:
- Diagnose your child yourself, especially serious ones. Remember: if a child grinds his teeth at night, this is not an illness.
- Run to the pharmacy for pills against internal parasites. We repeat: no connection has been identified between worms and night teeth grinding. Parasites can aggravate the condition, as they also cause discomfort at night, but they are definitely not the cause of bruxism.
- Wake up the child and prohibit him from grinding his teeth. He simply will not understand what you are talking about, since he does not realize and does not remember what he did.
- Look for how to remove teeth grinding in your sleep at one time. There are no such recipes.
Bruxism is a problem that lies at the intersection of dentistry, neurology, and gastroenterology. In serious cases, it may be necessary to visit several specialists and change several treatment regimens. At the same time, this is a fairly typical problem. Start with a visit to Mira dentistry. Together we will try to figure out why the child grinds his teeth and how we can help him.
Signs of Bruxism
An episode of nighttime teeth grinding lasts about 10 seconds. The number of episodes may vary and they may occur every night or occasionally. A characteristic symptom is grinding or clicking of teeth, but the patient himself rarely notices this feature, because sleep is not interrupted. Usually the patient learns about the problem from the lips of relatives and people living with him.
Associated symptoms of bruxism are the following:
- pain in the jaw, teeth;
- headache;
- pain in the facial muscles;
- dizziness;
- drowsiness.
Causes of involuntary teeth grinding
The most common and direct cause of the disease is considered to be excessive stress. People who cannot cope with it suppress stress during the day, and at night it makes itself felt through teeth grinding. From a psychological point of view, the cause of the disease may be agoraphobia, or fear of open spaces. Somatic causes include poor-quality dental fillings, malocclusion, diseases of the nervous system and hereditary predisposition.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of bruxism involves studying the patient’s complaints, as well as assessing indirect signs based on the results of a routine visual examination. The leading method of objective diagnosis is the use of Brux Checkers - special mouthguards that are made on the basis of a plaster cast of the patient’s jaw. These aligners allow the detection of occlusal obstructions. The doctor issues brux checkers to wear overnight, after which the patient submits them to the clinic for analysis. Using diagnostic aligners, a specialist determines which teeth bear the greatest load.
Electromyography and polysomnography methods make it possible to register the pathological activity of the masticatory muscles and confirm the diagnosis of bruxism.
But, as a rule, it is possible to understand the reasons only with the help of comprehensive diagnostics. So, in the case of bruxism in adults, psychosomatics may occur, so consultation with a psychologist or psychotherapist will be required.
Diagnosis of the disease in adults
Treatment cannot be started if the exact causes of the disease have not been established. In order to get a complete picture of the disease, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination. When the first signs appear, consultations with specialized specialists will be needed:
- dentist;
- therapist;
- neurologist (neuropathologist) - for disorders of the nervous system;
- psychologist (psychotherapist) - if there are changes of a psychological nature;
- maxillofacial surgeon;
- otolaryngologist;
- somnologist, etc.
If teeth grind due to malocclusion, treatment of bruxism and rehabilitation should be carried out in dentistry. The same applies to persons with pathological abrasion of enamel, constant loss, cracks, chips and other defects. However, if a person has worn down the hard surfaces of their crowns, this does not mean that the jaw grinding habit is progressing at the moment. Perhaps these are just the consequences of interpersonal and individual problems left in the past.
Sometimes a polysomnographic study is indicated. During the procedure, contractions of the masticatory muscles are recorded while the patient is asleep. In this way, doctors can exclude epilepsy as one of the factors in the development of the disease.
An informative method is to use brooks checkers. These are special mouthguards for wearing at night, with the help of which it is possible to determine where the greatest tension is localized and how much the pathological process is related to the bite and the location of the dentition.
Using electromyography, the performance of muscle fibers is assessed at rest and during physical activity.
Complications of bruxism
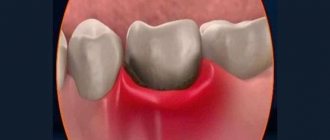
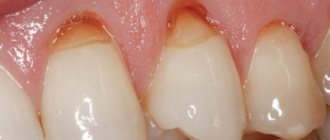
If the disease is observed for a long time, pathological abrasion of the tooth enamel, increased sensitivity of the enamel, and the appearance of a wedge-shaped defect, cracks and chips may develop. Constant trauma to the periodontal tissues can lead to periodontitis, loosening and loss of teeth. The service life of fillings and orthopedic structures (prostheses) in patients with bruxism is shorter due to high mechanical load.
The consequence of the disease can be dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, accompanied by pain in the jaw and neck, hypertrophy of the masticatory muscles.
Frequent injuries to the soft tissues of the oral cavity can lead to inflammatory diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis.
Pathological closing of the jaws during sleep complicates orthopedic and orthodontic treatment. Many dental restoration methods may not be available to patients, so it is important to pay attention to the disease in order to be able to receive comprehensive care in case of dental diseases or tooth loss.
Special exercises and massage
Exercises and self-massage will help in the treatment of bruxism:
- Squeezing your jaw with your palms below on both sides, you need to press lightly with your fingers, massaging it in a circular motion. It is advisable to repeat such manipulations, which help relieve tension from the problem area, every day for at least 2-3 minutes.
- Chin muscle training. With your mouth slightly open, you need to push your jaw back with your fingers. The procedure is repeated several times during the day, at least 10 times in 1 approach.
- Chewing gum exercise. You need to roll the chewing gum balls from one corner of your mouth to the other. It is better to do this before going to bed, until you feel tired in your muscles, then the likelihood that your jaw will be clenched tightly in your sleep will sharply decrease.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Why does a child breathe rapidly during sleep: the baby breathes quickly, reasons
Treatment methods for bruxism
Comprehensive treatment of bruxism may include medication, psychotherapy, physical therapy, and dental methods. This approach demonstrates the greatest efficiency.
The doctor will develop a treatment plan based on the severity of the disorder. It is very important to identify the causes in order to select adequate therapy.
In the case of exposure to psychogenic factors, the basis of treatment is cognitive behavioral therapy: the patient’s mastery of relaxation and self-control methods, psychotherapeutic trainings, art therapy, etc.
Drug therapy is aimed at reducing convulsive muscle activity. The main groups of funds include:
- magnesium, calcium preparations;
- B vitamins;
- mild sedatives;
- sleeping pills, etc.
Treatment of bruxism with botulinum toxin is also classified as a medicinal method. Botulinum toxin injections block nerve impulses entering the muscles, which relieves the muscles from involuntary spasms. The effect of botulinum toxin preparations is not permanent - after several months the injections are repeated. It is important to understand that this is rather a way to combat the symptom. Injections do not help eliminate the causes of the disease.
In some cases, osteopathic treatment may be recommended: manual therapy, massage, warming up the muscles with compresses.
The dental approach involves the participation of different specialists: periodontist, dental therapist, orthopedist, orthodontist. In the absence of pathologies in the dental system, protective rubber or plastic mouth guards are made, which helps prevent the consequences of bruxism in adults. According to indications, the following activities can be carried out:
- selective grinding of teeth;
- correction of bite by wearing mouthguards, braces;
- restoration of the integrity of the dentition: prosthetics and implantation.
Correction of bite defects is possible only after the patient’s condition improves. The installation of fillings and veneers, and splinting of teeth may be postponed due to the high risk of damage to structures.
Who will save you from bruxism – a dentist or a psychologist?
Yes, bruxism is a problem, both psychological and dental. In the first case, the doctor may advise you to take a sedative, rest more, get enough sleep and avoid overexertion.
Dentists give more practical recommendations. If you have missing teeth, you need to fill the gap. Fortunately, dental implantation offers different ways to restore teeth in terms of time and money.
Fluoridation of teeth and the use of strengthening toothpastes to maintain enamel will help compensate for the aggressive consequences of bruxism.
Prevention of bruxism
Bruxism can be prevented by paying attention to oral health: it is important to see a dentist in a timely manner, treat diseases of the teeth and gums, and restore the integrity of the dentition if teeth are lost. If you have bite defects or crowded teeth, you should consult an orthodontist.
Prevention involves normalizing the psycho-emotional state, giving up bad habits, coffee and energy drinks; maintaining a daily routine and proper nutrition.
Specialists from STOMA clinics will help adult patients get rid of bruxism: with us you can get help from all specialized doctors - from dental therapists to periodontists and orthodontists.
Symptoms and consequences of bruxism
- chips and cracks appear on the tooth enamel;
- the chewing surfaces of the lateral teeth are erased and smoothed;
- in the area of the masticatory muscles there is tension and soreness in the morning;
- after sleep there is pain in the neck and head.
Due to thinning and abrasion of the enamel, teeth become sensitive and react painfully to hot and cold, sour and sweet foods.
Violation of the natural anatomy of the teeth impairs the quality of chewing. It becomes more difficult for a person to bite and chew food.
With prolonged bruxism, teeth become so thin that they begin to break, become loose and shift. As a result, the bite is disrupted, a crunch appears, and persistent pain in the jaw joints begins.