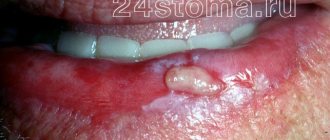
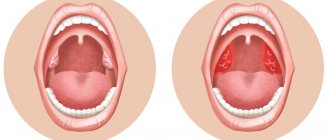
Often, the dentist prescribes antibiotics to the patient after the removal of a wisdom tooth in order to avoid unpleasant consequences or complications. The main indicators of antibiotic therapy include the development of the inflammatory process in the formed hole. More information about the choice of antibacterial drugs will be discussed in this article.
Antibiotics after wisdom tooth removal
Is it worth taking them?
Taking antibacterial drugs after removing the figure eight is necessary to relieve pain or at least to minimize it. Antibiotics are also necessary to prevent the development of the inflammatory process. Typically, antibiotics are used in the form of solutions, injections, ointments or tablets. They resort to their use only in extreme cases, when conventional drugs are unable to cope with inflammation or suppuration.
Pain after wisdom tooth removal
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed in the following cases:
- if the wall of the hole formed after tooth extraction is damaged and this can provoke an infectious inflammation that will eventually affect most of the bone;
- care of the hole after removal was insufficient. That is, ignoring antiseptic solutions for mouth rinsing can lead to the fact that small particles of food can accumulate in the hole, which is why pathogenic bacteria will multiply there;
- with a weakened immune system, the stress that occurs during tooth extraction can reduce the patient’s oral defense against infection;
- failure of the blood clot that closes the entrance to the formed hole can cause the infection to spread throughout the body.
Wisdom tooth removal is perhaps one of the most difficult dental operations, so doctors often prescribe various antibiotics to patients to relieve painful symptoms. It is worth noting that antibacterial drugs are used not only after the procedure, but also before it.
Wisdom tooth removal
The main factors why doctors prescribe antibiotics after tooth extraction:
- when there is a possibility of gumboil or pustules developing in the patient’s gums after removal surgery;
- if the integrity of the gum tissue has been compromised;
- when bleeding or other complications appear that cannot be eliminated without the use of antibacterial drugs;
- the presence of one or more chronic diseases;
- weak immunity.
If at least one of the above factors is present, the doctor resorts to the use of antibiotic drugs. But these are not all the reasons. There are other indications for the use of antibiotics. More on this below.
Antibiotics
Side effects
Long-term use of antibiotics may cause side effects
Their manifestation can be triggered by incorrect selection and prescription of the drug, as well as if the rules for its use have been violated.
The pharmacodynamics of antibiotics is based on the absorption of the active substances of the drug by the intestines, followed by its distribution throughout all tissues of the body.
The active substances of the antibiotic undergo breakdown in liver cells and, together with bile, feces and urine, are excreted from the body.
With long-term use of the drug, the following side effects may occur:
- Development of dysbacteriosis or candidiasis.
- Attacks of nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
- Allergic dermatitis on the skin of the body and face.
- Minor vascular bleeding in the oral cavity.
- Kidney and liver dysfunction.
- Weakening of the body's protective functions.
Important! If side effects occur, you should immediately stop taking the drug and replace it as prescribed by your doctor.
Indications for use
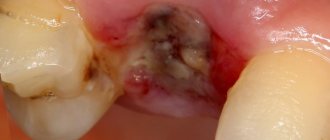
If a secondary inflammatory process develops, it is, of course, necessary to take antibiotics after wisdom tooth removal. We are talking about damage to the periosteum, trigeminal nerve, alveolar ridge of the patient's jaw and socket tissue, which can cause serious complications.
How to take antibiotics after tooth extraction
These complications primarily include:
- alveolitis The main symptom of this disease is 2-day pain in the area of the socket that appears, general weakness of the body and fever;
- periodontitis. Occurs due to an inflammatory process that affects the periodontal gum tissue;
- periostitis. A fairly serious disease that occurs as a result of inflammation of the periosteum of the jaw. Often the disease is accompanied by flux, that is, swelling of a person’s facial tissues;
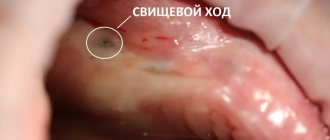
- osteomyelitis. A dangerous complication after tooth extraction, accompanied by the appearance of fistulas through which purulent mass from the patient’s gums comes out.
Flux on the gum
On a note! For patients suffering from problems with blood clotting, cancer and high blood sugar, antibiotics must be prescribed. This is due to the fact that the weakened immune system of patients is not able to fight the development of infection.
What drugs do doctors prescribe?
Many different drugs offered by modern medicine are used in dental practice as a post-operative intervention. People have most likely heard about many antibacterial drugs from advertising, but not all of them can help. Below are the drugs that doctors most often recommend using after removal of the figure eight.
- Wisdom tooth hurts
Table. Review of the most common drugs.
| Name of the drug, photo | Description |
| Flemoxin | An effective drug with a wide spectrum of action, the active substance in which is penicillin. The use of this antibiotic will relieve inflammation and reduce the patient’s body temperature. The duration of treatment and dose are determined only by the attending physician. |
| Lincomycin | Used in dentistry to treat many diseases. Often used after wisdom tooth extraction. It is not recommended to use Lincomycin in patients suffering from liver or kidney disease, or during pregnancy. |
| Sumamed | An antibacterial drug available in the form of tablets, syrup or capsules. Has anti-inflammatory and bactericidal properties. The product has some contraindications. For example, it should not be taken by patients who have individual intolerance to certain components. Side effects are extremely rare. |
| Amoxicillin | An excellent anti-inflammatory drug that prevents the development of infection in the body. It is used in medicine as a broad-spectrum agent, so it can be prescribed not only to adult patients, but also to children. |
| Amoxiclav | A combination drug that doctors prescribe to patients of all age groups. The active substance is penicillin, so before using the drug you need to check whether the patient is allergic. It is not recommended to take Amoxiclav for patients suffering from renal failure. |
| Azithromycin | An antibacterial drug used in the treatment of large areas of inflammation. If you are highly sensitive to individual components of this product, it is not recommended to use it. The same applies to patients suffering from problems with the kidneys and liver. |
All of the above drugs have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect on the body. These are potent drugs, so you should not take them on your own. Otherwise, serious complications may arise in the form of other pathologies.
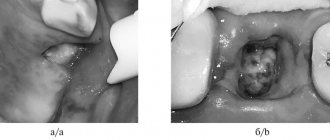
View of the socket of an extracted wisdom tooth
Video: Antibiotics after tooth extraction
Diagnosis of tooth root cyst
To make a diagnosis and carry out appropriate treatment, the dentist collects and analyzes the medical history. During the initial diagnosis, many patients report the fact of endodontic treatment performed to eliminate periodontitis or pulpitis. Some patients indicate an exacerbation of the disease after intraoral dissection.
Radiography is used as the main diagnostic method. Below is a photo and x-ray of a dental cyst.
To obtain an x-ray, several methods are used, the first method is based on contact intraoral x-ray, the advantages of this technique:
- determining the degree of destruction of the jaw bones;
- assessment of the condition of the tooth root and tooth canal;
- assessment of the quality of canal filling;
- identifying the presence of perforations and fragments of instruments and materials in the tooth canal;
- determination of the relationship between the cyst and the roots located near the teeth.
The second method of performing radiography is an orthopantogram; the procedure is a panoramic photograph of both jaws and the maxillary sinuses of the upper jaw.
Another method of the procedure is a survey X-ray in the nasomental projection; the X-ray covers the bones of the skull from the nose to the chin; using the image, the doctor assesses the condition of the maxillary sinuses and detects cysts that have grown into the nasal cavity.
In addition to radiography, to detect a tumor, the patient may be prescribed an electroodontic diagnostic procedure. This technique helps to assess the degree of such an indicator as the electrical excitability of the teeth that are located next to the cystic tooth. If the value exceeds 60 microamps, the dentist prescribes endodontic treatment to the patient.
For diagnostic purposes, histological and cytological studies are used to determine whether the neoplasm is benign or malignant.
Diagnosing a dental cyst is not difficult, but only qualified dentists can carry it out in a hospital setting; under no circumstances try to independently determine the presence of a cyst and do not take therapeutic measures; strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Brushing your teeth after wisdom tooth removal
Postoperative care is needed after wisdom tooth removal so that the recovery process goes quickly. If you ignore personal hygiene products, you can provoke the development of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity, which is called alveolar osteomyelitis. According to statistics, approximately every fifth patient develops this disease after removal of the figure eight. To prevent the development of pathology, you must follow the recommendations of doctors. At a minimum, careful oral care is required for 5-7 days from the date of surgery. Below are step-by-step instructions for brushing your teeth after wisdom tooth removal.
Step 1: Change the bandage according to your doctor's instructions. After the tooth is removed, the dentist will apply a gauze bandage or cotton swab to the resulting hole. They need to be changed every 40-50 minutes. As a rule, after a few hours the bleeding stops, but if this suddenly does not happen, you should consult a doctor. Dentists say that in the first day after tooth extraction, small drops of blood may appear along with saliva. This is quite normal unless the bleeding is heavy.
Change your tampon or bandage promptly
Step 2. It is not recommended to brush your teeth in the first 24 hours after surgery. The same applies to rinsing solution and dental floss, which it is advisable to avoid using on the first day. Otherwise, the recovery process may be delayed due to damage to the blood clot that protects the socket from infection. The fact is that when brushing with a toothbrush with hard bristles, not only can the blood clot be damaged, but also the sutures placed after tooth extraction can come apart.
Start brushing your teeth a day after extraction
Step 3. For 3-4 days after surgery, you should avoid the wound in your mouth when brushing your teeth. During this period, you need to rinse your mouth with a special solution made from warm water and a small amount of salt. This procedure will speed up the healing process of the wound, but it is not recommended to spit out the solution itself. Just tilt your head a little to let it drain on its own. Oral rinsing is done in the same way. If you rinse vigorously, a vacuum may form in your mouth, causing damage to the blood clot.
Avoid the site of tooth extraction when brushing for 3-4 days
Step 4. Starting from the third day after wisdom tooth extraction, you can use a brush to clean your teeth, but this must be done with extreme caution. For cleaning, be sure to use a product with soft bristles, and it is not recommended to spit out the paste after the procedure, as is the saline solution. During the recovery period, all actions must be careful so as not to damage the gums and wound.
- Ear hurts after wisdom tooth removal
Use a soft toothbrush
Step 5. On the 4th day after the operation, doctors allow you to brush your teeth as usual, that is, using dental floss and toothpaste, which you can already spit out. But this does not mean that you do not need to be careful with the area where the tooth was previously removed. Also, do not forget about cleaning the surface of the cheeks and tongue, because this is where most of the bacteria accumulate, which can cause the development of infection in the mouth.
Rinsing your mouth and brushing your teeth
Step 6. It is necessary to avoid the development of infection, because even if all the doctor’s instructions are followed, it may still appear. If any suspicious symptoms are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor. Such symptoms include fever, problems with swallowing food or breathing, and so on. The appearance of severe swelling or suppuration at the site of tooth extraction should also be a reason for promptly seeking help from a doctor.
Difficulty swallowing food
Video: Is it possible to brush your teeth after tooth extraction?
Symptoms
The danger of a dental cyst lies in the fact that signs of pathology appear only when the neoplasm reaches a relatively large size. In the early stages, small cysts do not manifest themselves in any way, meanwhile the infectious process covers an increasingly larger area of healthy tissue. In the initial development of pathology, cysts are discovered by chance during routine examinations or treatment of other diseases.
The duration of the formation of a dental cyst takes only 1-2 days; as it develops, the following symptoms may occur:
- unpleasant and even painful sensations in the tooth, which intensify when chewing solid food;
- protrusion of the gum of a tooth, in the area of the root of which a cyst forms, the growth of the gum becomes larger over time, redness is observed;
- the formation of a fistula in the area above the root of the tooth, the release of serous or purulent accumulations from it;
- general weakness and malaise;
- increase in body temperature.
Note! When a dental cyst occurs, the symptoms are not immediately visible; they appear in the later stages of development. The pain when a tumor appears is aching in nature, but it is less pronounced than the pain caused by caries and pulpitis.
If a clinical picture occurs and you suspect a pathological process, be sure to consult a doctor. Under no circumstances should you resort to self-treatment - the dental cyst must be removed. In addition, taking the wrong medications can worsen the patient’s overall well-being.
Sometimes there is no pain in the oral cavity; instead, the basis of the clinical picture is intense headaches. The cause of this phenomenon may be a cystic formation in the maxillary sinus.
Are there any contraindications?
When prescribing antibacterial drugs after removing the figure eight, the doctor must take into account the characteristics of the patient’s body and diseases, if any. The dentist must know about the presence of problems with the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) or other body systems, because the choice of certain medications will depend on this.
Extracted wisdom tooth
Patients suffering from gastrointestinal diseases need to take antibiotics in the form of solutions or in effervescent form. This will significantly speed up the process of absorption of the active components of the antibiotic, due to which the contact of the surrounding flora with the active substances will be as short as possible. In addition, to avoid unpleasant consequences, doctors often prescribe antibacterial drugs to their patients along with gastroprotectors (special substances that protect the mucous membrane of the human stomach).
Antibiotics after tooth extraction
In rare cases, antibiotics can be prescribed intramuscularly, but this also happens if there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract. The form of the drug, dosage and duration of the treatment course, of course, should be determined by the doctor after examination. Self-medication is highly discouraged, because the incorrect use of potent drugs will not only not help speed up the recovery process, but will also provoke other health problems.