We understand what causes unpleasant sensations in a “dead tooth” and determine how to solve the problem. Most of us go to the dentist to restore the beauty of our smile or get rid of painful sensations. One of the most common dental operations is removal of the dental nerve. Of course, at the end of therapy, the patient expects that pain will no longer bother him.
However, quite often a treated tooth without a nerve with a filling or under a crown begins to hurt. To understand why a tooth without a nerve hurts, you need to find out how the pulp removal procedure occurs and figure out what exactly causes the pain.
Causes of pain
There are many reasons why a dead tooth may begin to cause pain. Most of them are associated either with the lack of adequate treatment and care, or with the development of the inflammatory process. The most common reasons are:
- Incomplete nerve removal. If the nerves were not completely removed, the tooth will hurt in case of the slightest inflammation.
- Poorly cleaned channel. After the nerve is removed, the dead tooth is filled, but if the canal was poorly or incompletely cleaned, microscopic particles remain under the filling material. Over time, they cause inflammation and, as a result, pain.
- Poor quality filling. When filling, the material must be inserted into the canal completely, to the very end. If part of the canal is not sealed, pathogenic microflora begins to develop there. A variant of this reason can be considered the use of low-quality filling materials. They quickly collapse, causing the channel to open.
- Inflammatory processes in the gums or periosteum. Inflammation that develops next to a dead tooth begins to spread to nearby tissues, causing pain.
Whatever the reason, if a dead tooth starts to hurt, you need to contact a dentist. Delay can lead not only to the destruction of the crown, but also to the rapid spread of inflammation.
In what cases is the nerve removed from a tooth?
First, let's look at why pulp removal (dental nerve) or depulpation is performed. The need for depulpation arises for several reasons. Practicing dentists identify the following indications for this operation:
- the occurrence of pulpitis: damage to the neurovascular bundle due to the spread of caries,
- extensive deep carious cavity: if the defect is more than 50% of the total volume of the crown, then a filling cannot be placed (it will not hold well and will quickly fall out), and other restoration options - pins, inlays, crowns - involve depulpation,
- the presence of several carious cavities: grinding down the enamel and removing infected dentin can significantly increase the size of the defect, i.e. again, the crown will have to be restored in such a way that pulp removal will have to be carried out,
- mechanical trauma: when a horizontal root crack is detected, for example, periodontitis: inflammation of the tissues of the ligamentous apparatus-1 surrounding the roots.
Symptoms
Most often, painful sensations occur during chewing or eating hot or cold food. Some patients complain of almost constant, aching or throbbing pain.
The inflammatory process can develop rapidly. In this case, the pain is usually sharp and severe. May be accompanied by swelling of the gums and swelling of the face. Sometimes the inflammation lasts for years, and since the patient does not experience severe pain, he delays the visit to the dentist, aggravating the situation.
Questions and answers on: tooth hurts under a filling
The most common questions patients ask after tooth filling concern pain.
- Question : “A month ago, I had a tooth healed using paste to kill the nerve and installing a temporary filling, but it hurts when pressed. Also, the gums on the cheek side were swollen. After the temporary filling fell out, I did not install a new one. What to do? Is it related to the root or the nerves?” Answer : “Most likely, the periosteum became inflamed because the canals were not treated in time. It was necessary to treat them and put a permanent filling. In your case, the tooth needs to be removed, but if you consult a doctor urgently, there is a small chance of saving it.”
- Question : “Can a tooth hurt after filling? It’s been 2 hours since the filling was placed, but I feel a little pain.” Answer : “Mild pain in a filled tooth is a natural physiological reaction to surgical intervention in the dental cavity. Periodic painful sensations may be felt for 2 months until complete healing. They will pass unless the pain becomes more severe and increasing.”
- Question : “Yesterday we got a filling, but the tooth still hurts. A small rash and itching appeared near him. I can’t stand it any longer, what should I do?” Answer : “You need to see a doctor to replace the filling. You have developed an allergic reaction to it. This is quite a rare occurrence."
- Question : “A week ago I was treated for caries and a filling was placed at the 6th unit below. But the tooth did not stop hurting. It especially bothers me at night; I can’t sleep due to the throbbing pain. Should a tooth hurt after filling?” Answer : “Most likely, the dentist treated you for deep caries due to periodontitis or chronic pulpitis and made a mistake, guided only by a visual examination of the oral cavity. In any case, it was necessary to take an x-ray of the tooth affected by caries. We urgently need to remove the filling and treat the canals.”
- Question : “2 weeks ago a permanent filling was placed without removing the nerve, but it still hurts me to chew. In addition, the tooth reacts to cold and hot food and at times there is aching pain.” Answer : “Such symptoms may indicate the development of chronic pulpitis or the development of an abscess inside the tooth.”
If various pains appear in the tooth after the filling procedure, then the only recommendation is to contact a qualified specialist. After all, the reasons can be completely different.
What to do if a dead tooth hurts
At the first appearance of pain, you should contact your dentist. Since in most cases pain is a consequence of the inflammatory process, the doctor must carry out a diagnosis.
It is imperative to assess the condition of the gums, diagnose (or exclude) diseases such as periodontal disease, periodontitis, etc. Gum disease is difficult to treat, and timely diagnosis will help to prescribe the right treatment in time.
After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment aimed at eliminating the causes of pain:
- If inflammation is detected, anti-inflammatory drugs or antibiotics may be prescribed.
- The old filling is removed, the canals are cleaned, and the filling is performed again.
- The darkened crown of the dead tooth is additionally whitened to restore the aesthetics of the smile.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
A specific treatment plan is prescribed individually, based on the results of the examination and the general condition of the patient’s teeth and gums. Sometimes pain in a dead tooth is a consequence of a whole range of dental problems.
Features of nerve removal
Experienced doctors perform depulpation only as a last resort. But sometimes it is impossible to do without it. What is the procedure? First, an x-ray is taken, from which the dentist draws conclusions about the condition of the pulp (nerve tissue), areas around the root and gets an idea of how deep the inflammation has spread. The specialist assesses the length of the nerve and the features of its location, then gets to work and acts in several stages:
- anesthesia: local anesthesia to relieve the patient of inevitable discomfort. Modern drugs make it possible to carry out all manipulations absolutely painlessly,
- caries removal: the dentist drills out the affected areas of enamel and dentin using a drill,
- nerve removal: using a special tool called a pulp extractor, which is screwed into the canal, the dentist removes the neurovascular bundle in several stages,
- expansion and cleaning of the canals: carried out so that the doctor can efficiently clean the canals from remnants of nervous tissue and prepare them for filling. The channels are expanded with thin burs, which help to level and smooth the inner surface of the walls,
- filling: a material specially designed for filling (for example, gutta-percha) is injected to the entire depth of the root. The consistency of this substance allows you to fill the cavity entirely so that there are no empty areas left there. The upper part is covered with composite material. In some cases, a large inlay is placed or a crown is installed over the filling.
A tooth left without a nerve is called “dead.” It becomes insensitive to irritants, and enamel mineralization stops. It loses its whiteness and acquires a dark shade. To restore an aesthetic appearance, the dentist may suggest performing intra-canal whitening, installing a veneer or an aesthetic ceramic (or metal-ceramic) crown.
Prevention
If you have dead teeth, care must be taken to preserve them. A crown that does not receive nutrients is fragile. Over time, it can deteriorate and tooth mobility appears. Prevention of diseases in such diseases is very important.
It is imperative to ensure proper daily oral hygiene. Teeth should be brushed with a suitable toothpaste; the brush should not have very hard bristles. After eating, you need to rinse your mouth with special compounds. This will help get rid of food debris and minimize the risk of developing plaque, tartar, and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
It is important to undergo regular examinations by the dentist, and at the first appearance of pain or signs of disease, immediately go to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Can a filled tooth hurt and react to heat without nerves?
With proper depulpation, the organ should lose any sensitivity, including to temperature changes. Therefore, the occurrence of a reaction to thermal effects probably indicates the incompetence of the doctor, who made a mistake and did not remove all the nerve endings. But sometimes carelessness has nothing to do with it; the cause may be a hidden channel that is not even visible on an x-ray. And another option in which a reaction to hot manifests itself is proximity to a sick neighbor in the dentition.
Pain under the crown when pressing
If after dentures there is pain under the crown of a dead tooth when biting, there may be several reasons. The tooth begins to hurt due to mechanical stress in the near future after prosthetics in the following situations:
- poor-quality filling, which was already mentioned earlier;
- due to incorrectly chosen shape or size of the crown, poor fit to the tooth;
- The fixation of the prosthesis is impaired due to an insufficient amount of cement: this allows food to get under the crown and the development of infection.
If pain does not occur immediately, but some time after installation of the prosthesis, this may be due to the following factors:
- violation of the tightness of the filling, crown;
- improper care of dentures and poor oral hygiene, which contributes to tissue infection and inflammation;
- the expiration date of the prosthesis (usually about 5 years).
Another reason for rapid tooth destruction under the crown, resulting in pain, is treatment with potent drugs for severe diseases, chemotherapy, and radiation exposure.
Attention! Unpleasant sensations without acute pain immediately after prosthetics are accompanied by the process of getting used to the crown. This goes away within two to three days after completion of the procedure. If the pain does not go away within the specified time, but rather intensifies, you need to urgently go to the doctor.
We correct other people's mistakes. Dental retreatment with a 10% discount
Moscow
Pulp - structure, functions, features
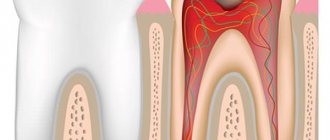
The pulp is also called the dental nerve. This is a soft connective tissue that contains a collection of nerve fibers, lymphatic and blood vessels. It is located in the tooth cavity (pulp chamber of the crown part of the tooth and in the root canals). Along the edge of the pulp there are cells, the processes of which are immersed in the dentin of the tooth. Thus, the pulp is closely connected with the hard tissues of the tooth. Through these connections, the trophic function is carried out; the pulp “nourishes” the walls of the tooth. Pain and mechanical sensitivity are also provided by the processes of pulp cells.
The blood supply to each tooth is provided by the common arteries and veins of the maxillofacial area. Small capillaries extend from them and enter the pulp, feeding the tooth. This structure protects the tooth from inflammation, proliferation of pathogens and other pathological processes.
The rich blood supply to the tooth also causes pain during inflammation. When the pulp becomes infected, a massive rush of blood occurs to its capillaries to provide a protective reaction, and swelling occurs inside the tooth. Enlarged vessels and soft tissues compress the nerve endings of the pulp, causing pain.
Is it possible to cure a tooth on your own?
Remember: it is impossible to cure a tooth on your own, without the help of a specialist!
All means - medications, folk recipes - have only a temporary, disinfecting and alleviating effect. To get rid of pain, you need to make a correct diagnosis and eliminate the cause, and this can only be done by a dentist in a specialized medical institution using modern diagnostic and treatment technologies. Recommendations for self-treatment of a tooth under a filling can lead to the development of complications even faster.
Preventive actions
Dead teeth can be considered problematic (prone to any dental disease except pulpitis), so they require more careful care. To preserve them and prevent pain, it is necessary to carry out prevention:
- Balanced diet
. Daily meals should contain sufficient amounts of essential minerals and vitamins. - Correct and thorough oral hygiene
. Use a toothpaste recommended by your dentist at least twice a day, and use dental floss and mouthwash after each meal. - Regular visits to the dentist
. By visiting the clinic once every three months, you are guaranteed to be able to identify emerging problems with dead teeth. Once or several times a year, it is worth doing cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), which is the best diagnostic technique today. The finished 3D image shows what is impossible to see in targeted and panoramic images. CBCT results allow you to study the condition of the jaws from all sides, turning images on the monitor at any angle. This technique best identifies problems with pulpless teeth even in the initial stages.
At the same time, the best prevention in this case is to avoid the need to remove the roots. Lead a healthy lifestyle, adhere to the recommended diet, regularly take care of your oral cavity, and then you won’t have to look for the answer to the question: why does a dead tooth hurt and what to do about it.