September 9, 2022 Which remedy should I choose for a sore throat or diseases of the oral mucosa? Almost all diseases of the oral cavity are accompanied by inflammation. Inflammation is a pathological process that develops in response to a damaging factor.
There are three stages of inflammation:
- 1. Damage to cells and tissues. At this stage, symptoms of the disease appear, including pain.
- 2. Increased vascular permeability , release of inflammatory mediators. Swelling appears and symptoms persist.
- 3. Restoration of damaged tissues. At this stage, recovery occurs.
Therefore, a remedy for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity must eliminate pain, inflammation and pathogens.
Various drugs are used to treat inflammatory diseases, including antiseptics and NSAIDs.
Content:
- The importance of choosing the right medicine
- Conditions that must be met by high-quality compositions 2.1. Iodine preparations 2.2. Chlorine 2.3. Preparations based on hexethidine
- For what purpose is it used?
- Indications for use
- How to rinse your mouth correctly
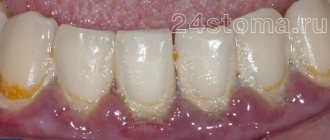
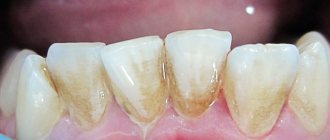
For various dental diseases, doctors often prescribe oral antiseptics.
They reduce the severity of painful symptoms, wash away pathogens from mucous membranes, and improve local blood circulation. With their help, it is possible to slow down the spread of microbial flora and speed up regeneration reactions. of mouth antiseptics on the market , but this does not mean that all of them are safe and effective. During treatment, it is necessary to use exactly the product prescribed by the dentist. Self-selection of medications often makes therapy ineffective or creates conditions for relapse of infection.
Types of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NSAIDs come in non-selective (classical) and selective (selective) actions:
| TYPE | ACTION | ||
| type: | Classic NSAIDs | action: | They block the production of an important enzyme, cyclooxygenase-1, which is responsible for protecting the gastric mucosa |
| type: | Selective NSAIDs | action: | They block only cyclooxygenase-2, which is responsible for inflammation. That is, they have a targeted effect on inflammation.2 |
The importance of choosing the right medicine
It is impossible to completely destroy microorganisms living in the human mouth. But when treating some diseases and conditions, it is necessary to temporarily reduce their number for a short time. Modern antiseptics help a lot with this.
It should be understood that those solutions that are used to treat the skin should not be taken by mouth. Firstly, it is fraught with poisoning. All sanitizers for external use are not intended for oral use.
Secondly, such therapy is always pointless. This is explained by the fact that the human mouth is inhabited by bacteria. Unsuitable products are inactivated by salivary proteins. This means that they do not work on the mucous membranes of the tongue and gums.
Side effects and contraindications
Despite the fact that the antibiotic has proven itself well for toothache and inflammation, its use is contraindicated in case of kidney and liver pathologies, diabetes mellitus, and taking certain medications. Prescribed with caution to children, elderly patients, and pregnant women.
Possible side effects:
- dermatitis, urticaria, skin rashes and other allergic reactions;
- diarrhea, nausea;
- kidney and liver damage;
- headache;
- anemia;
- candidiasis of the mucous membranes.
Dental antibiotics are an irreplaceable thing. The drugs prevent a serious complication, but subject to the right choice and strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations.
Author: Zhukov M.A.
Conditions that quality compounds must satisfy
Good developments used by dentists for aseptic purposes must meet a number of requirements:
- exhibit high activity against fungi, viruses, bacteria;
- provide a reliable clinical effect when used in low concentrations;
- in the case of systemic absorption, do not have a pronounced negative effect on the body or internal organs;
- be characterized by a minimal risk of synthesization;
- do not cause poisoning if used in the dosages established by the manufacturer;
- have a neutral smell and taste.
Among the most popular medications that meet these requirements:
- made from iodine;
- including chlorine;
- containing hexetidine.
Let's look at each type of mouth antiseptic in more detail.
Iodine preparations
Iodine is a substance that exhibits pronounced antiseptic properties. It destroys many fungi and microbes and acts as an effective antiprotozoal. Relieves pain, deodorizes, helps to quickly stop bleeding. They are allowed to cauterize wounds.
When treating mucous membranes, undiluted iodine is not used - it must be diluted in the required proportion. Otherwise, you can get a burn to the delicate membranes, which will take a long time to heal.
Iodine must not be combined with alkali, mercury, enzymes, or oxidizing agents. It is also pharmacologically incompatible with ammonia and ethers.
Chlorine
The most prominent representative of the chlorine-containing group is chlorhexidine, a biguanide derivative. It oxidizes and chlorinates proteins, causing their denaturation. As a result, a pronounced deodorizing and antiseptic effect is ensured, pathogenic tissues are destroyed.
Chlorhexidine is found in many oral antiseptics. It is even included in preventive toothpastes. It destroys gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, fungi, anaerobes, herpes, facultative aerobes. With regular use, the content of pathogenic microorganisms in saliva is reduced by approximately 80-90%. As a result, the rate of plaque deposition is reduced and stone prevention is ensured.
The therapeutic effect of chlorhexidine is explained by the interaction of its positively charged molecules with negative groups of molecules in the bacterial cell wall. The component quickly penetrates the inflammatory focus, reaches the cytoplasmic layers of the microorganism and kills it.
Interestingly, the product is selectively absorbed onto enamel hydroxyapatite . This means that it does not allow bacteria to multiply on the surface of the dental crown. Since it binds tightly to proteins, the therapeutic effect is prolonged - the release of antiseptic substances occurs gradually.
In addition to antibacterial activity, chlorhexidine also exhibits a weak analgesic effect. It is important to remember that its use on an ongoing basis leads to dysbacteriosis. Therefore, there is no need to use chlorhexidine-containing drugs on an ongoing basis.
Do not combine the additive with soap, alkalis, or anionic detergents. It should be taken into account that it increases the sensitivity of the human body to chloramphenicol, cephalosporins, and aminoglycosides.
Preparations based on hexethidine
Hexethidine is a cell membrane destroyer. It accelerates the death of pathogenic organisms and disrupts the synthesis processes necessary for the spread of pathogenic flora. The antifungal activity of the drug is associated with its ability to interfere with the formation of compounds necessary for the formation of the fungal membrane.
It has been established that hexetidine is effective in pathologies caused by:
- mushrooms of the genus Candida;
- Proteus;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Medicines containing the component relieve pain, stop the spread of inflammation, deodorize and envelop wounds. They help with candidiasis, stomatitis, glossitis, periodontal disease, aphthae, and increased bleeding of the gums. Hexethidine is allowed to treat microtraumas and purulent-inflammatory areas. It is also used in the antiseptic treatment of root canals in the treatment of periodontitis and pulpitis.
Dental antibiotics for periodontal disease and periodontitis
Antibacterial drugs are often used in treatment regimens for periodontal disease. Moreover, each clinical case requires a special approach. Therapy is aimed at restoring normal microbial flora. Antibiotics are prescribed in the form of tablets, injections, ointments, and gels. The medicine is selected by a periodontist taking into account the severity of damage to periodontal tissues and the results of a diagnostic examination.
It is necessary to distinguish between periodontal disease and periodontitis, despite the similarity of symptoms:
- unpleasant odor;
- soreness;
- swelling, bleeding gums;
- feeling of unpleasant taste;
- pathological mobility of teeth.
Periodontitis is a consequence of exposure to pathogenic bacteria. Whereas periodontal disease often develops against the background of a metabolic-dystrophic disorder. Other provoking factors of pathology:
- genetic predisposition;
- pathological bite;
- gum injuries due to incorrectly selected dentures and crowns;
- deposits in subgingival pockets;
- hormonal imbalance;
- gastrointestinal exacerbations;
- infectious respiratory diseases;
- abnormal attachments of the frenulum;
- diabetes.
Although there are some differences, both diseases can lead to complete tooth loss. Severe forms require long-term treatment, including antibiotic therapy. Antibiotics used in dentistry for periodontitis and for the prevention of periodontal disease are prescribed in a course (up to 10 days), in the form of tablets, injections and topically.
Proper oral hygiene and nutrition are of great importance. If there is a deficiency of macro- and microelements in the body, an effective drug is selected. Professional teeth cleaning, at least 2 times a year, and regular removal of microbial plaque with high-quality pastes will prevent the development of periodontal disease.
For what purpose is it used?
Antiseptic solutions, gels and ointments are used for dental pathologies that require an integrated approach. They allow you to quickly stop the inflammatory process, efficiently cleanse the mucous membranes of infectious agents, and reduce pain in the teeth and gums. Their use is relevant during the recovery period after dental surgery (including the removal of a diseased tooth), to relieve swelling, and eliminate foul odor.
It should be remembered that drugs of this group can cause negative side reactions. So, sometimes instead of the long-awaited recovery, patients receive:
- tissue irritation;
- itching;
- peeling;
- increased sensitivity of the gums.
If such negative symptoms appear, you should stop treatment and get a second dental consultation . It is possible that the disorder was caused by other drugs that the patient applied to the tissue in parallel with the disinfectant medication. Therefore, it is advisable to immediately clarify the situation.
Medicines for inflammation of gums and teeth
Antibacterial drugs are effective against inflammatory processes of tooth roots and gumboils. These are purulent diseases in the subnaosteal or subgingival part. They appear in the form of purulent sacs on the gums. Incorrect and untimely treatment leads to surgical intervention.
The main reasons for the appearance:
- jaw injury;
- complication after improper treatment of pulpitis and tooth extraction;
- consequences of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza;
- mechanical damage to gingival tissue;
- advanced forms of caries;
- inflammation of gum pockets;
- hypothermia.
Fluxes come in different types: ossifying, ordinary, serous-albumic, purulent, fibrous. They are manifested by symptoms such as general weakness, fever, severe toothache radiating to the temple, swelling, pathological mobility of teeth, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, redness in the localized area.
An antibiotic for toothache that has developed as a result of gumboil helps at the initial stage of the disease. Medicines relieve symptoms. Additionally, vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
The operation is prescribed in advanced cases. The abscess is opened under local anesthesia, cleansing is carried out, and drainage is installed to release residual purulent masses. After surgery, the patient will have to take antibacterial drugs prescribed by the dentist.
Therapeutic treatment with antibiotics has a cumulative effect, so it is important to follow the dosage and not stop taking it prematurely. The choice of means depends on the cause of inflammation, the age of the patient, the characteristics of the disease and the degree of its neglect.
You can use drugs such as Amoxiclav, Lincomycin, Azithromycin, Citrolet, Clindamycin, Trichopolum, Biseptol.
The drugs are prescribed taking into account contraindications and individual tolerance. To avoid microbial resistance of the body, use for more than 10 days is contraindicated.
In childhood, flux is rare, but leads to serious consequences due to the accelerated spread of infection in the body. At the slightest sign of suppuration, you should immediately contact a specialist. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the source of the inflammatory process and generally strengthening the body and immune system.
Indications for use
Each medicine has its own indications for use. Among the common diseases that are successfully treated with the described dental medications are:
- stomatitis;
- tonsillitis;
- angina;
- periodontal disease;
- periodontitis;
- gingivitis;
- ulcers;
- period of gum recovery after tooth extraction.
Medicines reduce the risk of infection and speed up healing if bacteria have entered the wound. But in order to get positive dynamics with their help, you must strictly follow all medical prescriptions and rinse regularly.
Osteotropic antibiotics: what they are and what they are used for
Osteotropic antibiotics are often used in dental practice. An antibacterial drug (ABP) is prescribed:
- to eliminate the inflammatory-purulent process (chronic and acute) with peristitis, abscess, odontogenic sepsis, pericoronitis;
- as a prophylaxis against infectious complications after implantation and surgery;
- patients at risk (patients with diabetes, cardiovascular problems).
Antibacterial therapy is contraindicated for surgical interventions on bone tissue, bleeding, and large-area wounds in the oral cavity.
How to rinse your mouth correctly
In many ways, the results of the procedure are determined by the correctness of its implementation. These are the basic rules that dentists are asked to adhere to:
- Regularity. There is no point in rinsing your teeth and gums only when the urge arises. If the dentist says to use the solution every few hours, that’s what you should do. Otherwise, it will not be possible to achieve positive dynamics.
- Under no circumstances should the prepared medicine The optimal temperature is 36-40 degrees Celsius. If a hotter liquid is used, the affected area will heat up, and high temperatures are known to create suitable conditions for the further spread of pathogenic organisms.
- Do not swallow antiseptic. Most of the drugs in the group presented on the pharmaceutical market are not intended for internal use. They negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- You don’t just need to take the solution into your mouth and immediately spit it out, but hold it in the area of the affected tissue for about a minute. Such mouth baths are considered the most effective.
Using antiseptics wisely and giving preference to proven means, you can significantly bring recovery closer even with advanced dental diseases.
What to prepare for rinsing gums at home?
Chamomile
A powerful natural antiseptic used to eliminate inflammation. Among herbs for rinsing gums, chamomile occupies a leading place.
How to use:
Pour 1 tablespoon into a glass of boiling water, let it brew for 40 minutes and rinse 3 times a day after meals.
Oak bark
Oak bark is an indispensable rinse for gums. Has an astringent and hemostatic effect.
How to use:
Pour 3 tablespoons of bark into a glass of boiling water, keep in a water bath for half an hour, strain, bring the volume to 200 milliliters with boiled water and rinse 5 times a day after meals.
Sage
Rinsing with sage has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
How to use:
Pour 200 milliliters of boiling water over 1 tablespoon of leaves, leave for 40 minutes, rinse 3 times a day after meals.
Baking soda
A baking soda rinse for gums reduces pain and promotes healing.
How to use:
1 teaspoon per glass of boiled water. If your gums are inflamed, rinsing with soda should be done after eating, after brushing your teeth. Use immediately, do not store!
Salt
Rinsing gums with salt has a disinfecting effect.
How to use:
1 teaspoon of salt per 1 glass of boiled water. To enhance the medicinal effect, it is best to rinse with salt and soda at the same time!
5% iodine solution
Has an antimicrobial effect.
How to use:
To rinse your gums with iodine, one drop per glass of boiled water is enough. It is better if it is lightly salted, for example, sea salt.
Propolis
The waste product of bees relieves pain well and heals wounds.
How to use:
Propolis for rinsing gums is used in the form of an alcohol tincture: 30 drops per 1 glass of boiled water, rinse 3 times a day after meals.
If you don’t have time to brew herbs, you can just as easily use pharmaceutical alcohol tinctures made from them to rinse your gums.