Normally, a person grows 52 teeth over a lifetime: 20 milk teeth and 32 permanent teeth. Supernumerary teeth are “extra” dental units that appear in addition to some incisors, canines, premolars or molars. In various medical sources, the phenomenon is called hyperdontia, supradontia or polyodontia. A superset can include 1–2 teeth or reach several hundred dystopic structures, be true or false.
Supernumerary teeth - what are they?
Supernumerary teeth (hyperdontia) are “extra” teeth. This anomaly occurs quite often: 5% of people have more than 32 teeth. Moreover, in 70% of cases one supernumerary tooth grows, in 25% of hyperdontia - 2 teeth, and only 5% of people - 3 or more. In women and men, this anomaly occurs with the same frequency.
Hyperdontia is not an individual human norm. This is a disease that has its own coding according to ICD 10. It corresponds to the alphanumeric code K00.1.
Causes of dental diseases in humans
The main cause of dental diseases is the activity of bacteria, which results in caries. But there are other factors that affect oral health:
- heredity and genetic pathologies;
- quality of drinking water;
- ecology of the urban environment;
- nutritional features;
- professional activity.
In most cases, it is impossible to change anything from this list. Therefore, it is important to at least be able to promptly recognize the symptoms of dental disease and consult a doctor as soon as possible to avoid complications.
Kinds
Supernumerary teeth can be located:
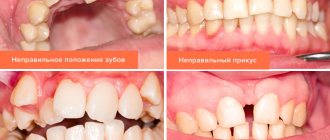
- in the dentition with a change in the correct position of normal dental elements;
- in atypical places (dystopic teeth), for example, on the palate or on the front surface of the gums;
- in the bone tissue of the jaw and do not erupt into the oral cavity (impacted).
Depending on the shape of the crown, supernumerary teeth can be of several types:
- lumpy;
- spiny;
- chisel-shaped;
- pineal;
- split;
- fused.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of polyodontia is carried out exclusively by a specialized doctor - an orthodontist, who conducts a preliminary examination of the oral cavity and dentition, refers the patient to x-rays (orthopantomography) and analysis of anthropometric casts of teeth made of plaster. Such models are made for a more detailed study of a specific anomalous phenomenon, on the basis of which a diagnosis is then made and treatment is prescribed.
Table of normal human teeth. Deviation from the norm - polyodontia
When examining plaster models made on the basis of dental casts, the doctor measures the size of the teeth, and then analyzes the data obtained based on a special table by Wetzel and Ustimenko. The length of each row of teeth must be measured. This indicator may fluctuate depending on such characteristic individual characteristics of a person as crowding of teeth or the presence of large gaps between them. In the first case, the length will be less than normal, and in the second, a little longer. To diagnose asymmetry, the distance from the midline of the palate (or hyoid frenulum) to the far point of the dentition in one direction or the other is determined.
Reasons for appearance
Medicine does not give an exact answer why the program fails in the human body and supernumerary teeth appear.
Hypotheses explaining the etiology of the phenomenon:
- Atavism hypothesis . Supernumerary teeth are a return to the original number of dental elements, which was normal for human ancestors (it is believed that they had 6 incisors on the upper and lower jaws).
- Theory of splitting of the tooth germ . Hyperdontia is a consequence of impaired activity of the dental plate during embryonic development, as a result of which a significantly larger number of dental buds are formed from it. The hypothesis is supported by the increase in recent decades in the number of cases of the appearance of extra teeth as a result of the influence of unfavorable environmental conditions, thyroid diseases and other negative factors.
Where do excess teeth come from?
This dental anomaly in adults and children occurs in 7% of cases when visiting a dentist. Statistics say that 70% of patients with polyodontia may have only one extra tooth, 25% of people with pathology may have a pair of teeth, and 5% of patients with pathology may have three or more abnormally growing teeth. The reasons for this not entirely normal dental growth are not fully known, but there are several hypotheses:
- Atavism - our ancestors were programmed at the genetic level with six full-fledged incisors on each jaw, so they are trying to remind of themselves with such an anomaly in the development of teeth in modern humans.
- Intrauterine failure at the level of embryonic development of the fetus, when the tooth germ is split. The cause of the failure may be illness or bad habits during pregnancy, taking medications, poor environment, etc.
Since these are only assumptions, it is therefore difficult to say whether it is possible to prevent this anomaly or reduce the risk of its occurrence. Of course, we cannot influence genetics and nature, but maintaining a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy for the sake of the health of the unborn child is in any case necessary.
Symptoms
The main symptom characteristic of hyperdontia is the presence of extra teeth in the oral cavity, which often interfere with talking, eating, and also spoil a person’s appearance. However, in children and adults, supernumerary teeth can also have slightly different clinical manifestations, which will be discussed below.
Symptoms in children
Supernumerary baby teeth appear in a child before birth or in the first months of life. In this case, the main symptoms are associated with difficulties in breastfeeding: it becomes more difficult for the baby to latch onto the nipple and suck milk. He begins to be capricious and refuse to breastfeed. The skin on the mother's chest is injured with the formation of deep and inflamed cracks.
Symptoms of hyperdontia of primary teeth in older children are similar to symptoms of the eruption of normal dental elements, which may be accompanied by:
- moderate increase in temperature;
- soreness of the mucous membrane and swelling in the area of the growing tooth;
- excessive salivation;
- swelling of the nasal mucosa with difficulty in nasal breathing;
- loosening of the stool.
Symptoms are especially severe when teeth erupt in the area of the upper palate.
At 2 years of age, hyperdontia negatively affects the development of speech in a child. It becomes difficult for children to pronounce individual sounds and this cannot be corrected by speech therapy techniques. In addition, injury to the tongue or mucous membranes often occurs, which leads to chronic inflammatory diseases in the oral cavity.
In school-age children, an increase in the number of teeth often becomes the cause of ridicule from peers, the development of complexes and disruption of social adaptation.
Symptoms in adults
Hyperdontia in permanent teeth is more common than in primary teeth.
Dystopic supernumerary teeth
Dystopic supernumerary teeth are additional teeth outside the normal dental arch. They erupt in the palate and on the lingual surface of the gums.
The clinic is caused by the presence of excess dental elements in the oral cavity:
- sound pronunciation disorders;
- changes in the normal position of teeth up to their dystopia: rotation around their axis, curvature of the growth angle;
- severe malocclusion;
- injury to the mucous membranes with the development of inflammatory diseases in the oral cavity;
- Often the presence of hyperdontia leads to disturbances in chewing function and chronic digestive problems.
Dystopic supernumerary teeth can cause psychological problems: poor smile aesthetics makes a person withdrawn and uncommunicative. Psychological problems provoke symptoms of chronic diseases of the nervous, digestive, endocrine and other systems - in medicine the phenomenon is called psychosomatics.
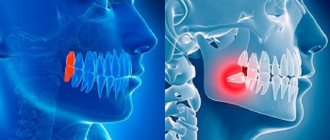
Impacted supernumerary teeth
Impacted supernumerary teeth do not erupt into the oral cavity and remain in the bone tissue of the jaw. Often they do not manifest themselves until complications develop, and in most cases they are discovered accidentally during examination.
Symptoms:
- pathological loosening of normal teeth;
- bulging of the bone (when the impacted tooth is close to the edge of the jaw);
- periodically occurring aching pain over the area of occurrence.
With the development of complications (formation of cysts, osteomyelitis of the jaw), the symptoms will be characteristic of the resulting pathological condition.
One of the most difficult situations in dentistry is the combination of supernumerary teeth and impacted third molars (“wisdom teeth”). At the same time, excess dental elements can take up free space in the dentition, but unerupted “eights” have a negative impact on the root system of the remaining teeth and can cause serious complications
Features of polyodontia in adults and adolescents
In adults, after complete replacement of complete teeth, the presence of additional units can lead to additional pathologies:
- chronic rhinitis, sinusitis when the wall of the maxillary sinuses is perforated by the roots of supernumerary impacted structures;
- interdental caries - due to teeth fitting too closely to each other.
Retention and dystopia
Adults are characterized by 2 main types of supernumerary teeth:
- Dystopic teeth are the name given to teeth with deviations in the direction of growth. The peculiarities of the formation of supernumerary units very often lead to dystopia. This is due to the fact that the space on the dental arch line is limited, and the roots of normal teeth simply push the “intruder” towards the cheek or palate.
- Impacted teeth – impaction occurs when a tooth loses its growth impulse and remains embedded in the jawbone. Impacted teeth can cause the adjacent normal teeth to become loose and cause them to shift and change the bite. Often cause pain.
On a note! According to statistics, hyperdontia accounts for up to 2% of cases of dental problems. Of these, 70% are associated with the appearance of single supernumerary teeth, 25% with a couple of such formations, and only in 5% complex multiple complexes of 3–4 or more teeth can be found.
Diagnostics
Identifying erupted supernumerary teeth is not difficult. Often, patients themselves, already at the initial examination, complain that they have a tooth that should not be there.
The situation is more complicated with hyperdontia with impaired eruption . In such cases, the main diagnostic method is x-ray (panoramic radiography). It allows you to clearly visualize all dental elements, both normal and supernumerary, as well as their location. The disadvantage of the technique is that the X-ray image is flat and cannot be used to characterize the exact relative position of all teeth and their root systems. Therefore, patients often undergo additional computed tomography .
How is removal carried out?
If the abnormal tooth is single and it is not difficult to get to it using surgical instruments, then there will be no problems, and the tooth will be removed using a standard method. If there are several teeth, they are located in hard-to-reach places, have several roots, or have not fully erupted - in this case, removal is carried out as follows:
- The doctor administers an anesthetic so that the patient does not experience pain during the procedure.
- A small incision is made on the mucous membrane.
- If the roots of the tooth are deep, the doctor may make a small hole using a special bur to provide access to the root system of the tooth.
- The tooth and root are removed using forceps.
- Next, the area is disinfected using antiseptic agents.
- Stitches are applied.
- To avoid complications, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc. may be prescribed.
Please note that before surgery, an X-ray diagnosis is required. In this way, the doctor assesses the condition of the root system and other features. Only after the diagnosis is carried out is the issue of tooth extraction decided.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures for hyperdontia:
- relieving symptoms of eruption of supernumerary teeth, which are especially relevant for children;
- removal of supernumerary teeth;
- orthodontic treatment
Relief of teething symptoms
Relevant for young children, since in adults this period proceeds almost unnoticed.
Since supernumerary teeth give symptoms similar to the signs of the eruption of normal milk teeth, their therapy will be the same:
- When the temperature rises, it is recommended to take Ibuprofen or Paracetamol in the form of rectal suppositories or oral suspension. Such medications can both relieve pain and fever, and eliminate signs of inflammation of the soft tissues of the gums or palate.
- Local agents with an anesthetic effect in the form of a gel or ointment (Dentinox, Kalgel, Solokoseryl). They have a rapid analgesic effect and a slight anti-inflammatory effect.
- For children over two years of age, treatment with folk remedies is possible: decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula, lemon balm), bee products (honey and propolis). Rinsing your mouth with solutions prepared according to traditional recipes helps relieve pain and prevent the occurrence of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
Sometimes supernumerary baby teeth only partially erupt. In this case, part of the crown remains in the jaw tissues. In such cases, a special massage, electrical or vibration stimulation is prescribed to stimulate eruption.
Removal of supernumerary teeth
The fate of the supernumerary tooth depends on many factors:
- In primary occlusion, all unnecessary elements are removed , as they negatively affect the growth and development of the maxillofacial system.
- All dystopic teeth (especially if they are loose), as well as impacted ones (even if at the time of their identification they do not cause any complications) are subject to mandatory removal
Typically, extraction surgery for well-formed supernumerary teeth is not particularly difficult.
A supernumerary tooth can be saved in the following cases:
- if it is located in the dental arch and does not cause malocclusion;
- has the shape of a regular tooth and does not cause a cosmetic defect;
- the root and crown are healthy and correctly formed, and the adjacent complete tooth is destroyed due to caries or injury.
Removal in a simple case
- Before any removal, an x-ray is required to determine the number of roots, their size and relationship with other teeth.
- After this, the doctor performs anesthesia and removes the dental element.
- If necessary, after surgery, sutures are placed on the soft tissues.
Removal of impacted supernumerary teeth
In order to carry out the operation accurately and without complications, the doctor needs to carefully examine the patient and plan the sequence of his actions.
- At the first stage, a survey radiography and computed tomography are performed to determine the exact topography of impacted dental elements.
- The tooth extraction operation is performed under local anesthesia, but in difficult cases the patient may be offered general anesthesia.
- Whenever possible, the supernumerary tooth is approached from the lingual side.
- After peeling off the mucous membrane, the bone tissue is opened and the crown and root parts of the tooth are extracted.
- If necessary, large bone defects are closed with osteoplastic materials, and the mucous membrane is sutured.
After the operation, the patient continues treatment at home, which includes taking antibiotics and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions.
During the rehabilitation period, it is recommended to avoid eating too hard, hot or spicy foods, and to carefully brush your teeth on the operated side.
Sometimes, when a supernumerary tooth is located in the dental arch, has a developed crown of regular shape and a root with a normal structure, and the adjacent complete tooth is destroyed due to injury or caries, the defective dental element must be removed, followed by its replacement with a supernumerary one using orthodontic means.
Orthodontic treatment
After the removal of primary supernumerary teeth, the doctor decides what to do next. In the best case scenario, the baby does not need orthodontic treatment and simply visits the dentist for routine preventive examinations. In severe cases, the child will require the help of an orthodontist, including temporary prosthetics. This is necessary in order to:
- the child's jaw could grow and develop;
- after the age of six there were no problems with the eruption of permanent teeth;
- fully correct existing problems with the dentition.
After removal of excess permanent teeth, patients undergo bite correction. Modern orthodontics has at its disposal numerous options for braces or aligners, which allow you to quickly straighten your teeth and restore the beauty of your smile.
Prevention of dental diseases
Some people are not even aware of what dental diseases with inflammatory processes and pathologies are provoked in other vital organs. For those who are not in the know, we inform you: these are gastritis, ulcers, tonsillitis, thrombosis, heart attack and stroke! And the pathogenic bacteria are to blame for everything, which, multiplying in the oral cavity, enter the throat, stomach, blood vessels and even the heart.
To prevent dental diseases, follow simple rules that will help significantly improve your oral health and overall well-being.
- Stop smoking.
A bad habit provokes vasoconstriction and deterioration of blood supply to the mucous membrane, which results in a lack of nutrients necessary for teeth and gums. - Eat a balanced diet.
The abundance of flour and sweet foods in the diet contributes to an excessive increase in microorganisms and inevitably leads to caries and its complications. Take care of strengthening your enamel by taking vitamin complexes. Then the disease when “teeth crumble”, which occurs due to a lack of calcium in the body, will not be scary for you. - Brush your teeth 2 times a day.
Regular hygiene is one of the most effective ways to keep your teeth safe and sound. In addition to the traditional use of brushes and pastes, you should not neglect dental floss. Flosses effectively remove food debris between the teeth, preventing the development of many diseases. - Get preventive examinations once every six months.
It is easier to cure any disease if it is detected at the beginning of its development. Some dental diseases in dentistry have symptoms that cannot be identified on their own. For example, caries at the junction of teeth is visible only on an x-ray.
A person is not able to influence factors that cause various types of dental diseases, such as poor ecology, heredity, and stress. However, with a responsible attitude towards hygiene and prevention, the risk of dental diseases can be significantly reduced or, at least, their treatment can be facilitated.
Consequences
Untimely or improper treatment of hyperdontia can cause serious consequences, the correction of which may take a long time:
- severe malocclusion;
- speech defects that cannot be corrected;
- constant injury to soft tissues leads to chronic inflammation with a high risk of developing benign and malignant neoplasms in the oral cavity;
- Impacted teeth are a common cause of chronic osteomyelitis of the jaw.
The lack of correction of hyperdontia in children is especially dangerous, since it often causes disturbances in the correct formation of jaw tissues. Supernumerary teeth can cause the death of the rudiments of permanent teeth or their improper eruption.
Therefore, if there are any signs indicating the appearance of excess dental elements, or if impacted teeth are detected, you must urgently seek advice from a dentist!
Features of polyodontia in children
Possible symptoms of hyperdontia in childhood:
- intrauterine formation of teeth (a child is born with several teeth);
- the appearance of teeth in the first months, weeks and even days of life;
- delayed eruption of baby teeth.
This has unpleasant consequences:
- problems with feeding the baby - he does not latch onto the nipple well and sucks weakly;
- swelling of the mucous tissues can spread to the nasal area and cause breathing problems;
- poor closure of the dental arches causes severe salivation;
- a prolonged increase in temperature to 38C is possible.
Hyperdontia is especially harmful during the period of speech formation. Teeth located outside the general row prevent the tongue from taking the correct position when pronouncing most consonant sounds. Without eliminating the pathology, any speech therapist will be powerless.
In addition to true hyperdontia, children (less often adults) can develop the so-called false form of the disease. It is characteristic of the period of tooth change and develops during the eruption of molars next to the milk teeth that have not yet fallen out. This is a fairly common phenomenon that usually goes away on its own as the dentition finally forms. In some cases, orthodontic treatment may be required.
How much does treatment cost?
The cost of treating hyperdontia is determined by the complexity of the case. The price for a simple removal of an additional tooth is, on average, 1,500 rubles . In cases with impacted or dystopic teeth, it will be slightly higher - for its removal you need to pay from 4,000 to 15,000 rubles .
Depending on the clinic, the cost of treatment may include preoperative examination, the operation itself and postoperative management. You can accurately calculate the final price only in the dentist's chair, since it is impossible to know in advance how the operation will go, whether complications will arise, or how the recovery period will go.
Diet after removal of supernumerary teeth during polyodontia
Postoperative diet
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 21 days
- Terms: 1-6 months
- Cost of products: 1300-1500 rubles. in Week
After surgical interventions in the oral cavity, patients are recommended to adhere to a special diet, but they should not:
- too hot, hard, hot or spicy food;
- sugar and confectionery;
- coffee, cocktails and sweet drinks.
Considerable attention should be paid to rinsing and hygiene procedures, as well as enriching the menu with such products as:
- dairy products;
- cheeses;
- seafood;
- stewed dietary meat;
- fresh and boiled fruits and vegetables;
- porridge.