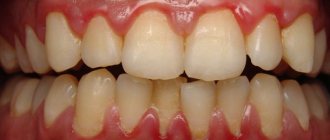
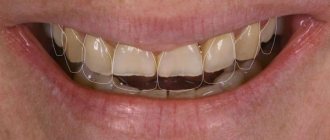
Causes of crooked teeth
In the 1980s, the term crowding of teeth syndrome (CTS) was coined to refer to an abnormality that defines crowding of the anterior teeth that interferes with satisfactory oral hygiene.
STIs affect 70% of the world's adult population. The anomaly occupies a prominent place in the structure of all dental pathologies. The syndrome can occur both during the development of baby teeth and during the eruption of permanent teeth. In the first case, the prevalence is 34%, and in the second - 68%.
As a person grows, the degree of crowding of teeth may increase, as changes occur in the periodontal tissues: the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth becomes less stable. According to research, the older the age group of patients, the higher the percentage of people requiring orthodontic medical interventions. Thus, we can talk about the pattern of distribution of the anomaly by age and the absence of a pattern of distribution by gender.
The main reasons for the development of crooked teeth include:
- Quick replacement of temporary teeth with molars (up to 6-7 years). The jaw bones do not have time to develop, so there is not enough space for teeth. However, there is no data on why some children change their teeth earlier. This is an individual feature caused by abnormalities in the growth and formation of teeth.
- Bad childhood habits such as thumb sucking or pacifier use. As a result, the risk of malocclusion and abnormal tooth growth increases.
- Congenital malocclusion. Changing the size of the jaw (less often the shape) negatively affects the position of the molars, premolars, canines and incisors.
- Location and name of teeth
- Incomplete development of the alveolar process and the basal part of the upper jaw.
- Macrodentia, which means an excessive increase in the size of one or all teeth.
- Narrowing of dental arches due to soft tissue dysfunction. Dysfunction can be caused by hormonal imbalances, injuries, metabolic disorders, heredity and predisposition, and malocclusion.
- Appearance of third molars - “wisdom teeth”. This reason is typical for people of mature age, when the teeth are already formed and there is no room for the “eight”.
- Extra teeth - having extra teeth.
Congenital factors of diseases include: dysfunction of lip closure, anomaly of the frenulum of the tongue, infant swallowing, mouth breathing. Prolonged mouth breathing in childhood leads to deformation of the facial skeleton:
- the lateral parts of the upper jaw come closer together, as a result of which the upper jaw develops incorrectly;
- the hard palate becomes higher and narrower.
As a result, the upper row of teeth becomes much narrower. Subsequently, similar changes occur in the lower jaw. All this leads to torsion.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult your doctor. Do not self-medicate - it is dangerous to your health!
Stages of dental development
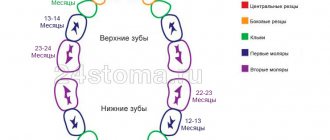
There are four conventional stages of dental development in humans . The division into such periods is fair if we are talking about both milk and permanent teeth. MORE· The first stage is the laying of the beginnings of teeth. The formation of the dental rudiments of primary teeth occurs in the embryo in the sixth to eighth weeks of intrauterine development. First, an epithelial plate is formed, then enamel caps. The formation of the beginnings of permanent teeth occurs in the fifth month of intrauterine development of the fetus. The first to be laid are the incisors, then the small molars and canines. The last to be laid are the rudiments of the large molars (in the sixth month of the child’s life) and wisdom teeth – “eights” (only in the fourth or fifth year of the child’s life). · The second stage is differentiation. Differentiation of dental buds usually occurs at the twelfth (maximum fourteenth) week of fetal development inside the womb. During this period, cells are formed - builders of the surface tissue of the tooth (enamel) and cells - builders of dentin (the layer of the tooth located under the enamel). In medical science, such building cells are called adamantine blasts and odontoblasts, respectively. · The third stage is histogenesis. The next stage of dental development is histogenesis. This is the formation of hard dental tissues. The process of histogenesis begins in the fourth month of the baby’s intrauterine development. First, dentin is formed, and then the outer and most durable tissue of the tooth and the entire human body - enamel. · The fourth stage is the development of tooth roots . The development of the roots of both baby and permanent teeth begins after the baby is born. Typically, tooth root development begins shortly before tooth eruption begins. The development of tooth roots ends with the formation of the root apex - this occurs two years after the start of eruption.
Stages and symptoms of the disease
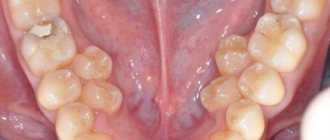
A predisposition to the development of anomalies can be identified already in early childhood by consulting an orthodontist. During the examination, the specialist will find that there is no space between the baby’s teeth. This sign indicates that, with a high degree of probability, there will be no room left in the permanent dentition for tooth eruption. As they appear, the problem will only get worse. Timely identification of negative factors in children will help normalize the situation even at the stage of taking a bite of milk. However, very often specialists are faced with the fact that even with congenital prerequisites, patients turn to a specialist only during the period when the permanent dentition is fully formed and there are clinical signs.
The anomaly is characterized by varying degrees of severity, which causes clinical symptoms and possible complications. The degree of development of pathological signs also affects treatment tactics, as well as prognosis. Depending on the symptoms of dental crowding, there are 3 degrees of damage.
- A mild degree of anomaly is characterized by minimal changes in the position of 1-2 teeth in the dentition. In order for them to take the correct position, only 2-3 mm is missing. The problem does not extend to the remaining teeth; they occupy a clearly defined place;
- With a moderate degree of anomaly, the problem affects only individual teeth. They rotate around their axis, are offset relative to the teeth and can tilt. Their displacement corresponds to 5-6 mm;
- In the case of severe anomalies, its manifestations are clearly visible to others. The aesthetics of a smile is disrupted due to deformation of the dentition; some teeth are pushed out of the dentition. The arch shape has been changed.
The main disadvantage of the anomaly is that crowding of teeth leads to deterioration in the aesthetics of the dentition. This is especially noticeable with severe injuries. However, this is not the only problem.
With this position of the teeth, the chances of quality cleaning are significantly reduced. The prerequisites will be created for the formation of dental plaque, which will affect the change in the shade of the enamel, manifest as tartar deposits, and the presence of bad breath. Lack of proper hygiene will lead to the development of other dental diseases and the appearance of additional symptoms. Also, incorrect position of the teeth can lead to injuries to the mucous membrane. Symptoms will be supplemented by manifestations such as bleeding, inflammatory or erosive process.
What is the danger of a wedge-shaped defect?
The wedge-shaped defect is interesting because today most dentists (at least in our country) have no idea about the cause of this disease.
Out of the goodness of their hearts, they, of course, try to alleviate the physical and moral suffering of patients by hiding wedge-shaped defects behind fillings, veneers or crowns. But problems with these structures arise much faster than with exactly the same ones, but installed for some other reason. So, if on the same day, by the same doctor, two separate fillings were built on the same tooth from the same material (and the best one at that): one covered a wedge-shaped defect, and the second covered a carious cavity of approximately the same size. size, then the second has a much better chance of celebrating its tenth anniversary. This causes justifiable bewilderment of the patient and no less justified anger of the dentist. The search for those to blame begins...
And for a long time, erosion and abrasion were considered the culprits of this disgrace. Abrasion is the mechanical abrasion of a tooth by solid foreign bodies, and erosion by liquid or gaseous ones. Therefore, a hard toothbrush in the first case and acidic foods (citrus fruits, carbonated water, juices) in the second were declared the main enemies.
Both theories are interesting, not without arguments and have numerous supporters. We also agree that both processes contribute to the progression of the wedge-shaped defect, that is, they are aggravating factors. But they cannot be the root cause. If only because wedge-shaped defects are found not only in people, but also in animals. You can’t suspect horses of using too hard brushes or cats of abusing Coca-Cola. Any solid body, no matter how strong it may seem, is subject to abrasion under the influence of regular mechanical loads. Tooth enamel is no exception. Although this is the hardest tissue of the human body, it can nevertheless be completely worn out as a result of daily use. In some advanced cases, only the roots may remain from the teeth.
In addition to direct abrasion of the rubbing surfaces of the teeth themselves, mechanical stress leads to damage to the enamel at the neck of the tooth (in the vast majority of cases, on the outside). That is, to the formation of a wedge-shaped defect. The fact is that a tooth is not an absolutely rigid structure. It tries to absorb the rather significant load that falls on it when chewing and swallowing food (up to 100 kilogram-force or 1000 newtons), partly due to micro-bending relative to its vertical axis. Simply put, the tooth bends, and the maximum stress, according to computer modeling data, occurs precisely at the neck of the tooth. The enamel in this place has a minimum thickness. In addition, the tooth in this part experiences tension, while in other places it experiences compression. And the tensile strength of enamel is 40 times less than the compressive strength.
As a result, cracking and subsequent peeling of the enamel occurs with the formation of a V-shaped defect. Just like how the paint flies off a metal rod or the chocolate icing on a frosted cheesecake cracks when you try to bend them. This is the mechanism of development of the disease. But this is not yet the reason, since all people’s teeth are subject to abrasion, and not everyone has a wedge-shaped defect. The primary source of this misfortune is initially the inharmonious closure of the dentition - a violation of occlusion or, in Russian speaking, a malocclusion.
In fact, a correct bite is an extreme rarity, and the majority of the world's population lives their lives happily without realizing that they have such a problem. An insignificant proportion of 99.9% of people with non-ideal occlusion consult an orthodontist. And even then, the first and almost always the only goal of those who dare to undergo orthodontic treatment is aesthetics. Only a few remember that teeth should not only “stand straight,” but also function correctly.
This is how the picture of the disease forms into a single whole: the patient has minor deviations in bite (or significant ones, but left without treatment) => the load when chewing food is distributed inharmoniously (some teeth work less, others overwork for them) => hard-working teeth wear out faster fellow quitters => as a result, flat areas of rubbing are formed on them => during chewing, instead of cutting the food bolus, it is crushed => in order to crush the food, the jaws have to develop greater force => the enamel cannot withstand the load, cracks and flies out => a wedge-shaped defect.
Why is it important to fix the problem in time?
Any orthodontic irregularities are potential dental problems in the future.
Improper closure leads to abrasion of the enamel on the cutting edge of the teeth (all or only on one side if the bite is asymmetrical).
When teeth are crowded, it is more difficult to remove plaque - this causes caries, and with insufficient care - gum disease.
If prosthetics are required in the future, placing an implant may not be possible or there may even be restrictions on placing a bridge. So first you will need to correct the position of the remaining teeth.
With severe crowding of teeth and a noticeable narrowing of the jaw, aesthetic problems are added: teeth look unsightly, asymmetry of the lower part of the face may occur.
Treatment by an orthodontist is not an aesthetic procedure. A beautiful smile is what you get as a bonus; the main acquisition is a correct bite and maintaining dental health in the future.
Causes of hyperesthesia
A generally accepted classification of pathology has been developed, based on which the dentist makes a conclusion about the causes of increased tooth sensitivity. The classification systematizes predisposing factors. By comparing them with a specific case and making instrumental diagnostics, the doctor makes a conclusion about the origin of the pathology and classifies it as one of the varieties.
By localization:
- limited
- it affects one or more teeth. Usually these are ground teeth, teeth with a wedge-shaped defect; - generalized
- affects most of the dentition, sometimes the entire row. Progressive erosion of the enamel, exposure of the neck of the tooth during periodontitis, and increased tooth abrasion lead to generalized erosion.
By origin:
- caused by loss of hard dental tissues
. Its appearance is provoked by carious cavities, enamel erosion, increased abrasion, orthopedic preparation (grinding) for prosthetics; - not associated with the loss of hard dental tissues
. It occurs if the neck or root of the tooth is exposed, which can be caused by periodontal diseases, general diseases - endocrine pathologies, neuroses, gastrointestinal pathologies and others. Visually, in such cases, the enamel appears intact.
Medical errors can also be the cause. Hypersensitivity occurs if, during the finishing treatment of the filling, healthy tissue was sanded, the filling technique was violated, the enamel was over-etched, or ultrasonic teeth cleaning or whitening was performed incorrectly.
A lot of calls to clinics occur precisely because of incorrect bleaching. Hyperesthesia can occur after the procedure when it is performed without taking into account contraindications and the characteristics of the patient’s teeth.
The high incidence in women is due to hormonal and metabolic disorders, especially a decrease in estradiol. They show decreased levels of magnesium and calcium, and bone tissue shows lower density. Therefore, women undergoing dental treatment should undergo additional studies as prescribed by a dentist-therapist.
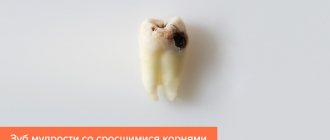
Wisdom teeth and crooked teeth
Wisdom teeth are one of the causes of crowding. Previously, wisdom teeth were needed: at the age of 20-30, other molars were worn down due to rough food, and the growing eight teeth were used for chewing food. In modern people, the chewing load is less, and the jaw is also lower, and the figure eight has not yet atrophied, so there is often no room for them.
The 8's are still trying to cut, but due to lack of space, they either grow at an angle or squeeze and move the other teeth, causing crowding as a result.
You can examine the rudiments of teeth on x-rays as early as 12 years of age. This way you can see if they are growing correctly or at an angle. If the jaw is small, wisdom teeth can be removed before the rash appears so that they do not cause any problems. But it is not at all necessary to simply remove them, since when they break out, they will make chewing easier and can serve as a support for dentures.
Diagnosis of torsion
Diagnosis of pathology consists of a clinical examination and additional research methods. At the first stage, a physical examination is carried out: the specialist determines the position of the teeth, the degree of displacement, the current inclination and / or inversion.
The second stage is radiological research methods: radiographs are prescribed to identify the causes of crowding and identify possible rudiments of extra teeth. The method is also effective for determining the current location of wisdom tooth buds and the extent of their presence.
To obtain the most accurate results, the results of computed tomography, teleroentgenogram and orthopantomogram are examined.
Teleradiogram is a panoramic radiography of the skull in frontal or lateral projection. The study allows you to study the profile, jaw and craniometric dimensions (parameters of the profile, joints and ratio of the skull bones), which are necessary for choosing therapy.
Orthopantomography (a circular panoramic image of the teeth) allows you to get an idea of the location and number of germs in the teeth, estimate the free space for teeth that have not yet erupted, and study the number of crowns, their angles, shape and size.
The curve or sagittal compensation curve must be measured. This is a line drawn along the cutting edges of the front teeth and the buccal cusps (cracks) of the chewing teeth. With crowded teeth syndrome, the severity of the curve of Spee increases and exceeds 2 mm.
In addition, biometric methods are used to assess dental shrinkage:
- The Pont method evaluates the degree of compression of molars and premolars. This method allows you to identify the cause of crowded teeth, as well as choose the optimal treatment method, taking into account the individual characteristics of a particular patient. The Pon method consists of comparing the transverse dimensions of the molar crowns of a particular patient with the average size.
- The Corkhouse method establishes the relationship between the length of the anterior region and the width of the incisors. The method consists of determining the length of the anterior part of the maxillary arch, which is then compared with the calculated individual norm. As a result, we can conclude that the dentition is lengthening or shortening. The length is measured along the middle jaw from the point between the central incisors to the intersection of the jaw with a line passing through the Pont measurement points.
- The Snagin method allows you to identify the causes of the syndrome and choose the optimal treatment method. It is based on measuring the width of the dental crowns, the arch along the premolar line and the parameters of the apical base (a conventional line running along the apex of the roots of the upper and lower jaw). If the lack of free space for teeth is associated with underdevelopment of the maxillary bones, a discrepancy occurs between the width of the apical base and the size of the mesiodistal teeth.
Treatment methods for crooked teeth
Modern orthodontic designs can successfully treat crowding. Based on the characteristics of the clinical picture of the pathology, one or another correction procedure may be indicated.
Braces
Most often, such treatment is justified if the pathology is not too serious. The course of correcting the defect will take several months; if you follow all the specialist’s recommendations, the effect of treatment is noticeable and lasting. For each patient, the time for using the systems is selected individually - it depends on the age group, the quality of the periodontal tissues and the presence of concomitant diagnoses. Various models of such structures allow you to align the jaw row due to the formation of an oval of the correct shape formed by an arch. Thus, abnormally overgrown organs end up in the right place.
Removal of a tooth
If there is insufficient free space in the row of the lower jaw, especially in the stage of a developed type of crowding, the patient has no choice but to resort to the removal of part of the organs. First, the outermost lateral teeth, also called wisdom teeth, are amputated. If the clinical situation is too advanced, sometimes even such a radical measure is not enough and the premolars must be removed. This mainly affects the lower jaw, since it is much more susceptible to deformation and mechanical stress than the upper jaw. Due to this, its natural size becomes a little smaller over time, and with such a diagnosis this is quite an aggravating factor. Depending on the severity of the disease, the course of treatment can range from 2-3 weeks to 1.5-2 months. After removal of all necessary organs, the installation of orthodontic structures is indicated. The cost of the removal procedure is standard and depends on the region, clinic and the cost of pain medication.
Extension
Such treatment will be effective only if the pathology is not very pronounced. It is carried out by lightly smoothing the enamel surface (mechanical separation principle) or installing spacers (physiological separation option). The first case is the opportunity to free up to 0.5 cm of the interdental space. It should be noted that many experts consider separation to be a fairly worthy alternative to amputation of jaw fragments. The procedure is carried out quickly, sometimes 2-3 visits to the dentist are enough.
Leveling devices are used for initial and moderate severity of anomalies.
- Aligners.
With the help of aligners, treatment proceeds much slower (within 1 year), but this procedure is much more comfortable for the person. The cost of structures is several times more expensive than braces, but the effectiveness of such treatment is much higher.
The principle of crowding relief is to apply light but constant pressure to the row of jaws. With the help of the habituation reflex, organ fragments are transferred to the correct position. There is a psychological “memorization” of the teeth in the desired position, which develops during the treatment process and is gradually corrected with each subsequent removable aligner. They are transparent and thin in appearance and are not difficult to wear. The course of treatment is about a year. Their cost is determined by the complexity of the correction and the number of aligners performed.
- Expansion of the dentition using plates.
Such manipulations are allowed only after a thorough study of the qualitative condition of periodontal tissues. The doctor records the presence of the amount of hard bone required for the procedure. The manipulation itself is carried out in several ways, but plates are often used. The effect is achieved due to the systematic pressure of the expansion plate on a number of jaws and gradually giving its fragments the correct position. Products are made individually. The best results in this case are observed in children and adolescents, whose bones are not yet fully formed and are more susceptible to changes in position than adults. Standard design: metal plate, mounting screws and spring. The devices are secured with clips. The course of treatment depends on the situation. Typically this is a period of 6 to 12 months.
Treatment of wedge-shaped defect
Let's first consider traditional methods of treatment.
Applications of various preparations: varnishes, ointments, remineralizing solutions, etc.
The main advantage of this method is compliance with the most important Hippocratic principle: “Do no harm.” Indeed, this method of treatment will not harm the teeth. And it can bring benefits in the form of getting rid of hypersensitivity. True, after 10-15 visits, a single application is only enough for a few hours/minutes. It is impossible to eliminate the resulting defect by application, but you can get rid of the pain for some time.
Using toothpastes that reduce sensitivity (desensitivity)
This method includes all the advantages of the previous one, plus it has one more advantage - low cost. One tube of paste costs much less than 10-15 visits to the dentist, but the effect is approximately the same. Just as in the first case, it will not be possible to eliminate the defect itself and its further development. The maximum that can be achieved is the disappearance of pain in the necks of the teeth.
Filling with various materials
Glass ionomer, compomer, flowable or universal composites.
The most common treatment option for wedge-shaped defects. There are even more advantages: the pain disappears immediately after the first visit, and most importantly, the defect itself is eliminated and a fairly good aesthetic result is achieved. The trouble is that the cause of the disease cannot be eliminated by the most modern, best, most durable, most expensive filling.
This means that the mechanical load on the neck of the tooth will continue its negative impact. As a result, the fillings either fall out entirely, or (most often) remain in place, but at the same time they tear off one of their surfaces from the tooth, forming a gap into which food debris and bacteria become clogged. The photo clearly shows a dark strip between one surface of the filling and the tooth, the so-called “mourning border”.
It is undesirable to leave everything as it is - in addition to the progression of the wedge-shaped defect, you can now also get caries in this place. The old filling is removed, a new one is placed, and everything begins for the second round.
Installation of veneers
A veneer here means a ceramic veneer that covers the entire anterior and chewing (cutting edge of the front teeth) surfaces of the tooth.
This method is even better than the previous ones. In addition to superior aesthetics, it is sometimes possible to eliminate the cause (and therefore prevent recurrence of the disease for some teeth). But this will call into question the strength of the veneer itself. The maximum load will fall on it, and this structure is fragile to a certain extent. It may not be able to withstand the efforts from which the tooth’s own enamel has even been lost.
Therefore, veneers for wedge-shaped defects are most suitable for wealthy housewives and other citizens who have enough time and finances to regularly replace those that fail with new ones.
Manufacturing of artificial crowns (metal-ceramic or all-ceramic)
A radical, but very effective solution to the problem. Provided that the edge of the crown covers the wedge-shaped defect with a margin. But often this very reserve is not there - the defect is already located at the level of the gum, and grinding a tooth below the level of attachment of the gingival margin for a crown is strictly contraindicated. In addition, while protecting some teeth, crowns can put others at risk.
It turns out that even such generally reliable structures as crowns do not always solve the issue completely. A wedge-shaped defect can continue its destructive development on a tooth covered with an artificial crown and on neighboring teeth.
All of the above treatment options have one common drawback - they do not normalize the bite or eliminate the cause of the disease. Therefore, even if some of you, dear ladies and gentlemen, were helped by just toothpaste or a banal filling that has served faithfully for several decades, then consider yourself lucky. “Lucky” is such a capacious term in medicine, meaning that, despite inadequate treatment, a change in the living conditions of the body led to spontaneous self-healing.
In this case, destruction, mobility, installation of a large composite restoration or removal of the antagonist tooth will lead to the elimination of the etiological factor of the wedge-shaped defect. But a patient, much less a doctor, should hardly count on such dubious “luck.”
One of the most important tenets of medicine is: “Treatment must be predictable.” That is, to give a positive result in the maximum possible number of patients. In our opinion, it is not possible for a doctor who considers a wedge-shaped defect to be a “disease of unknown etiology” or who knows the cause, but for some reason ignores it, to achieve such a result.
Recommendations for using braces
Although braces can correct even severe crowding, it will take time and repeated visits to a specialist. In addition, the patient needs to change eating habits and pay more attention to oral hygiene.
- Brush your teeth under the orthodontic product. Orthodontists have developed a number of recommendations, compliance with which will make using the device more comfortable:
- Brushing your teeth after every meal is mandatory. The optimal solution would be to purchase a professional toothbrush, in addition to using dental floss and an interdental brush.
- Avoiding seeds and nuts while wearing braces. Particulate matter can damage the structure, resulting in the need for replacement. Care should be taken when handling any solid food: raw vegetables, fruits, meat fibers. It is not recommended to chew them - it is better to cut them into small pieces and chew them thoroughly.
- Excluding viscous products from the menu (caramel, nougat, chewing gum). They clog the grooves in the shoulder straps and are almost impossible to clean.
- Reasonable consumption of hot and cold drinks. A sharp change in temperature leads to thermal expansion of the metal elements, as a result of which the braces can peel off from the enamel.
- Regular visits to a specialist and immediate contact with him in the event of damage to the structure.
Additionally, caution should be exercised when consuming coloring foods and beverages while treating crowding. Coffee, strong tea, and soda can stain the transparent elements of the braces system and make it more noticeable.
After fixing the device, the patient may experience discomfort and pain in the jaw area during the first two weeks. Such manifestations are natural and should not cause concern. Over time, the discomfort disappears, and the bandage becomes familiar.
Modern designs are made from the most delicate materials, but soft tissue injuries may occur during installation. In order not to damage the gums, it is necessary to use plastic wax, provided in time by a specialist. If the mucous membrane is still red and swollen, it is recommended to use anti-inflammatory drugs until the wound is completely healed.
Forecast. Prevention
When treating crowded teeth syndrome, the prognosis is favorable in most cases. Thanks to the use of modern therapeutic methods, it is possible to restore the aesthetic appearance and functionality of the maxillofacial apparatus. The prognosis for restoration of the gums and maxillofacial area directly depends on the degree of development of crowding and the timeliness of contacting a specialist.
Depending on the degree of development of the patient’s pathology, the duration of full treatment ranges from 1.5 to 3 years.
If left untreated, plaque and tartar appear, and gingivitis, caries, and various periodontal diseases may develop. This leads to premature tooth loss.
The best method of prevention is a systematic visit to the dentist. The doctor at the appointment will help to timely identify negative factors, predisposition to anomalies and take measures to reduce negative consequences.