The most common dental diseases that a child can develop are caries and pulpitis. However, there are more serious pathologies, and parents need to be aware of them.
One of these diseases is edentia, which is characterized by the absence of teeth. This disease affects both primary and permanent teeth and can develop at any age. There are four main types of edentia:
- depending on the number of missing teeth - complete or partial. The first type is uncommon, diagnosed in only 3-5% of people;
- in accordance with the causes of the disease - primary (congenital) or secondary (arising during life).
Edentia of twos can also occur - the absence of paired front teeth located in the central part of the jaw.
Types of edentia
Missing teeth and deficient bone volume are often associated with advanced age or traumatic injury. But practice shows that there are several types of such violations.
Primary adentia
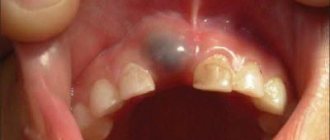
A rare pathology associated with improper development of the jaws in a baby. It is detected at the time of eruption of milk teeth or when they are replaced by permanent ones. When there are no rudiments of future teeth in the jaw, the anomaly is called true. In case of developmental delay, late appearance of units (often the crowns overlap each other, merging into a single mass) – false. According to statistics, a birth defect is the frequent absence of crowns from the second to the third chewing molar.
Secondary adentia
This type is acquired, a consequence of severe forms of periodontal tissue diseases, injuries, and somatic ailments. Indeed, a common occurrence in older people. One of the accompanying factors in the development of adentia in this category is the lack of effective and gentle methods of dental care and prosthetics in past decades. The most common types are partial edentia (several units missing) and complete edentia (no teeth at all).
What to do if there are no rudiments of permanent teeth, and baby fangs have not fallen out
In dentistry, there are rare pathologies, and there are quite common ones. One of the quite common ones is the absence of the rudiments of permanent teeth.
There are quite a lot of such patients who have lived almost to old age and accidentally learned that their fangs are actually milk teeth. Usually, the buds of permanent teeth gradually dissolve the roots of milk teeth and push them out.
And if there are no rudiments, then such a tooth can last for decades and only then begin to deteriorate. This is where it turns out that the tooth is a baby tooth, its root is defective and it is impossible to cover such a tooth with a crown. The milk tooth must be removed.
What to do in such cases? Under no circumstances should a fang be removed if it is standing straight! There are several other solutions.
- The baby tooth is removed and an implant is placed in its place. Today, this is the most competent option, which saves neighboring teeth from treatment for crowns and solves the problem once and for all.
- A much less competent option is a bridge prosthesis, when two adjacent teeth are ground down and a bridge is placed on them. This option is bad for at least two reasons. First, for a bridge you need to grind two innocent teeth, second, it is generally not recommended to include a fang in any bridge structures.
In one of these ways we solve the problem of a missing tooth. But in any case, we do not solve the aesthetic component completely in this way.
The fact is that the fang has one shape, and the incisor has a completely different shape. The canine that replaces the missing second incisor becomes a problem. For many, this is not too much of a tragedy, but some conventional girl, who has two vampire fangs sticking out instead of straight incisors, may be very worried about her appearance and look for ways to solve this problem.
In this case, the canine standing in the place of a two is converted into a two, and that’s it. You can also turn it into a deuce in several ways. It all depends on the specific situation, bite, shape of teeth, etc. and so on.
- Cosmetic restoration can be done using composite materials. It is fast, inexpensive, but not very durable and requires constant supervision by a dentist.
- You can install a veneer of the desired shape. The advantages are minimal processing of the enamel (if the shape of the fang allows it), good aesthetics, but expensive and not as reliable as a crown.
- Installation of a crown based on zirconium dioxide or metal-free (frameless). It is aesthetically pleasing, reliable, not too expensive, but sometimes requires quite strong tooth processing.
The fang itself must be much larger than the crown, plus it can erupt crookedly, bulge, stand at the wrong angle, etc. If orthodontic correction of its position is not carried out for some reason, then it will not be possible to turn it into a deuce without losses. You will have to depulp such a tooth (remove the nerve from it), sharpen it heavily, possibly correct the direction with a stump insert, and only then install a crown on it.
In general, in any case, you can find a way out of the situation. This pathology is far from the worst in dentistry, and there have long been ways to solve it competently and lastingly. You just need to find a good “your” dentist!
Reasons for the development of edentia
Primary dental edentia is a genetic disorder, the origins of which have not been fully studied. The frequency of pathology in different years is recorded in 1-2% of the population.
Complete and partial secondary adentia are diseases that dentists constantly encounter. Doctors name several reasons for the loss
dental units:
- Advanced caries, pulpitis. An indirect cause that triggers the destruction of tooth tissue. After removal of the neurovascular bundle, the tooth becomes fragile and requires careful attention. If the patient comes late, the doctor resorts to removing the unit.
- Diseases of periodontal tissues. The ligament cannot hold the tooth in the socket, and the crown begins to loosen. In the absence of proper treatment, the process spreads to the gums and destroys the structure of the jaw bone.
- Injuries. Dislocations, fractures, bruises, cracks of teeth and roots resulting from mechanical stress often lead to partial or complete loss of a row.
Less commonly, adentia becomes a consequence of previous somatic ailments - endocrine, oncological or others, accompanied by changes in tissue structure and weakening of the immune system.
Symptoms of adentia in children and adults
Diagnosis of this disease takes a long time. But there are a number of symptoms indicating its presence. It is especially important to take them into account when determining dental edentia in children. These factors include:
- reduction of jaws (both or just one);
- signs of retraction of the cheeks and lips;
- deformation of the alveolar processes;
- the appearance of wrinkles and folds approximately in the places where the twos are located;
- manifestations of muscular atrophy of the oral cavity;
- change in jaw angles.
All these symptoms can lead to the formation of a malocclusion. Malocclusions, in turn, cause certain shifts of the teeth and the formation of gaps in the jaw. In some cases, growths may form that affect the appearance and make chewing difficult.
Complete secondary adentia can be caused by caries, periodontitis, or surgical intervention. The doctor may also notice scars from injuries that led to tooth loss. Another symptom that explains the loss of masticatory organs is the presence of cancer.
It is worth noting that there is a steady downward trend in the age of edentulous dental patients. Poor ecology leads to the fact that young people are increasingly faced with this problem.
Diagnosis and detection of the disease
Edentia is a serious problem, and to solve it it is very important to promptly and accurately identify the presence of pathology and its type.
The first stage of diagnosis is to conduct a visual examination. Based on the results obtained, the doctor determines whether adentia is primary or secondary.
Then it is necessary to take an X-ray of the jaw, especially if the initial examination showed that the disease is congenital. This can only be confirmed with an x-ray, in which a specialist will check for the presence of dental follicles or identify signs of abnormal development.
When identifying the causes of adentia in children, at the initial stage of diagnosis it is necessary to find out the structure of the root system and find out how things are under the gums. Therefore, in the treatment of childhood adentia, the method of panoramic radiography is used. It allows the doctor to obtain a detailed picture, including information about the structure of the bone tissue of the alveolar processes.
Why is timely diagnosis so important?
Timely detection of adentia is of such high importance for one serious reason. The fact is that before starting any therapeutic actions, it is necessary to diagnose and eliminate all existing pathologies.
First of all, these include inflammatory infections of the oral cavity. During treatment, it is recommended to preserve the roots of the teeth as much as possible, since the absence of roots can lead to the loss of the entire masticatory organ. In addition, it is necessary to carry out complete disinfection of the oral cavity.
If the doctor suspects the development of acquired adentia, it is necessary to find out the cause of the disease as soon as possible. This is due to the fact that some pathologies can lead to complications during prosthetics. To eliminate these risks, the dentist checks for the following symptoms during the examination:
- exostoses (benign growths on bones consisting of bone or cartilage tissue);
- unremoved roots covered with mucous membrane;
- tumors and inflammatory processes;
- infections of the oral mucosa.
Types of adentia and their diagnosis
General symptoms indicating the presence of the disease were discussed above. But there are also a number of signs characteristic of different types of adentia. Their knowledge can also help to identify pathology in a timely manner.
Primary complete edentia
The rarest type of disease and at the same time the most serious. With primary complete adentia, the patient does not even have the rudiments of teeth and their roots. This pathology leads to serious consequences, namely:
- facial symmetry is disrupted;
- the correct formation of the alveolar processes of the upper and lower jaws is difficult;
- the secretion of mucus and saliva in the mouth slows down, which can cause additional inconvenience to the patient.
One of the symptoms of primary complete adentia may be paleness of the mucous membranes. The absence of baby teeth in children can also be easily determined by palpation. If such signs are present, it is necessary to urgently take appropriate measures.
Primary partial edentia
It is expressed in the congenital absence of some teeth in the patient. If partial adentia is detected in a child, the x-ray will show gaps in the root system. It should be noted that the absence of wisdom teeth is not considered edentulous.
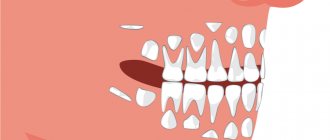
As the disease develops, diastemas and tremata are formed - spaces between the chewing organs. In simple terms, the teeth begin to “creep”: if you look at a photo of edentia in children, you will notice large gaps between the teeth.
Primary partial adentia can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. In the first case, there are no paired teeth - doubles or fangs. Asymmetrical adentia means the absence of teeth in different places of the jaw.
Secondary complete edentia
This type of disease is diagnosed when it is acquired. Its symptoms can be observed on all jaws or only on one. Both primary and permanent teeth may be missing. Secondary complete adentia is diagnosed when all the chewing organs have fallen out or needed to be removed due to another disease.
One of the main unpleasant consequences of this pathology is jaw deformation. It becomes closer to the nose, soft tissues begin to retract. Also, this type of disease is characterized by muscle atrophy, leading to disruption of the shape of the entire jaw or one or both alveolar processes.
In addition, the loss of all teeth immediately leads to everyday problems - the patient will not be able to chew independently, and will also begin to swallow some sounds.
Secondary partial edentia
This is the most common type of disease, in which several masticatory organs are missing from the dentition. The loss of canines, twos or other teeth often leads to increased sensitivity of bone tissue. This is due to the gradual wear of the side walls of adjacent teeth.
With this complication, the patient faces discomfort, due to which he gradually stops eating solid food, which is difficult to chew. Both children and adults face this problem.
Possible consequences of edentia
Tooth loss is a serious disease that can lead to various unpleasant consequences, including the development of other serious diseases. Among them are the following:
- impaired jaw development, which leads to difficulty pronouncing various sounds;
- the patient is forced to exclude solid foods from his diet, which causes problems with intestinal motility and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- development of persistent psychological discomfort. The patient’s self-assessment is distorted and depression may develop;
- in the complete absence of teeth, the jaw develops abnormally and can put pressure on any area of the head, thereby provoking the appearance of temporal tumors.
Causes of delayed teeth emergence
A lot depends on nutrition: breastfed babies depend on the quality of breast milk. Babies who grow up on artificial formulas receive slightly more vitamins and minerals, because the formulas contain a clearly calculated amount of nutrients.
- If a child does not have a single tooth at 1 year of age, this may be a consequence of some previous disease: intestinal dysfunction, impaired metabolism, as well as insufficient calcium and vitamin D.
- Teeth may be delayed due to the special course of pregnancy; perhaps the mother suffered complications during the gestation period./li>
- Eruption after 12 months may mean that the tooth is not positioned correctly in the gum, for example, it is growing horizontally.
- Congenital absence of tooth buds in a baby. These are either hereditary disorders or a congenital pathology caused by a disruption in the normal course of pregnancy. It happens very rarely.
How can parents understand that at 12 months the baby’s teeth are simply delayed and they need to be patient, and when should they sound the alarm?
Pediatric dentists allow the first teeth to be delayed for 6 months, so if after the baby’s 1st birthday not a single baby tooth has grown, you should wait a little longer. Try to find out from your relatives about the timing and characteristics of the appearance of the first milk teeth in their childhood, perhaps this is just a family trait.
But if the teeth are already delayed by more than 6 months, and the baby’s gums do not even think of swelling, then you should contact a pediatric dentist. The specialist will conduct an examination and advise what needs to be done to help teeth appear faster.
In addition to the above reasons, the appearance of teeth after 12 months may be affected by the following:
- The teeth are located very tightly in the gums.
- There are diseases of the endocrine system, for example, hypothyroidism, due to which the activity of the endocrine glands is reduced.
- The baby suffered serious systemic diseases.
In this case, the pediatric dentist will recommend a biochemical blood test; the baby will need to have the thyroid gland examined, including an ultrasound examination. After the results are obtained, the dentist will be able to prescribe the necessary course of treatment.
Make an appointment
Causes of loss of chewing teeth
In childhood, the main reason for the loss of chewing teeth is the absence or death of their rudiments. There may also be hereditary or external factors that have a direct impact on the fetus even at the stage of formation of its entire skeletal system. Parents should very carefully monitor the health of their children’s baby teeth, because if timely treatment is not carried out, the consequences can be very dire – including the premature loss of permanent ones.
In adult patients, the main cause of early tooth loss is various dental problems: pulpitis or periodontitis, as well as diseases of periodontal tissues, which begin with inflammation of the gums - periodontitis, less often - periodontal disease. In addition, these diseases can develop against the background of hormonal or age-related changes, diabetes mellitus, and metabolic disorders in the body. Loss of chewing teeth can also occur due to trauma to the jaw system or after prolonged wear, for example, of bridges.
Shift order: norm and pathology
The pathological process can be caused by various reasons. In order to deal with them, consider the normal replacement scheme. The roots of baby teeth are small. They gradually resorb (dissolve), mobility appears. The cutting order is as follows:
- Central lower incisors, first molars on both jaws.
- Central upper and lateral lower incisors.
- Upper lateral incisors.
- Lower canines.
- Premolars on both jaws.
- Upper canines.
- Second lower molars.
- Second upper molars.
- Third molars (wisdom teeth).
When the first molars erupt, no replacement occurs, as the jaw grows and the molars simply grow in place. Therefore, sometimes the patient has a question about how to distinguish a baby tooth from a molar that has already grown. “Baby teeth” are usually visually different. They have a smaller crown. If in doubt, you should consult a doctor. Only on the basis of an examination will a dentist be able to determine whether an adult’s teeth have completely changed.
Root resorption is stimulated by their contact with the crown of the growing permanent root. If there are no rudiments, resorption may occur upon contact with adjacent teeth, but sometimes this does not happen and the root is not destroyed. There is no change. As a result, an adult remains in a row of milk teeth that have not fallen out, which are called persistent.
For normal replacement, it is necessary that the rudiments of permanent teeth be formed, and they be at a depth sufficient for their crown to come into contact with the root of the milk teeth. If this does not happen, the loss is delayed or does not occur at all. Violation of the formation of primordia can occur both in the prenatal period and as a result of previous diseases or inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.