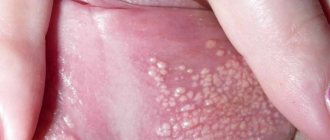
Lumps, nodules, tubercles and other lumps on a woman’s outer labia are almost always a pathological phenomenon that requires emergency medical attention. Even if the neoplasms seem benign to you, without causing acute discomfort and pain.
Most common reasons
- Such phenomena can be detected in childhood and be congenital. In this case, it is advisable for parents to check their blood for syphilis, since most often changes in the genital organs in infants indicate its presence.
- In addition, the tubercles may be a sign of abnormal development of the labia, congenital defects of the urethra and other features that do not have an infectious or viral etiology. However, this is more of a special case than a healthy phenomenon.
- We should not forget that neoplasms in the genital area can become a sign of tumor processes in the body.
- In addition, nodular fragments may indicate the development of HPV (human papillomavirus). This disease in a certain percentage of cases leads to cervical cancer.
Our doctors will help you accurately determine the etiology of your genital tubercles.
Such deviations are not a reason to be embarrassed and ignore medical help.
Leave your phone number. The clinic administrator will call you back.
Make an appointment
The doctor's consultation
1290 rub.
If the tubercles appear suddenly and can be easily felt under the skin or mucous membrane, immediately contact a specialist for advice and all necessary tests. Perhaps it is the early intervention of a specialist that will help you avoid terrible irreversible consequences.
Definition of disease. Causes of the disease
A Bartholin gland cyst is a benign round cavity (a saccular formation with thin walls and the presence of secretions of varying consistency inside) formation in the lower third of the vestibule of the vagina as a result of a violation of the outflow of secretions from the cavity and its accumulation in it.
The cyst cavity stretched by secretions can have different sizes, reaching 7-9 cm in diameter. Bartholin gland cysts are observed mainly before the age of 30 years (hormonally active reproductive age) and account for 2% of all diseases of the female genital organs with actively functioning and hormonally dependent Bartholin glands.
Before we move on to the mechanism of development of this pathology, we will consider the normal anatomy and physiology of the Bartholin glands.
Bartholin's glands or large vestibular glands are located on both sides of the vestibule of the vagina, in its lower third in the thickness of the labia majora. They are a paired organ. They got their name in honor of the Danish anatomist Caspar Bartolin Jr. who discovered them. Their size is about 1.5-2 cm, the excretory duct of the Bartholin gland, 1.5-2.5 cm long, opens on the inner surface of the labia minora at the border of its middle and posterior third. In some cases, their atypical location occurs, for example, in the thickness of the labia minora [13]
The function of the Bartholin glands is to moisturize the mucous membrane of the vulva during arousal during sexual intercourse, which prevents it from becoming dry and painful during sexual intercourse. Due to the presence of mucin in the secretion, it has a bactericidal effect.
The main causes of this disease are frequent inflammatory processes in the genital area caused by specific and nonspecific microflora, such as staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, and pathogens of sexually transmitted infections - gonococci, chlamydia, etc. Microorganisms that cause diseases are increasingly being isolated upper respiratory tract - streptococcus pneumoniae and influenza bacilli [2]
Ruptures of the soft tissues of the perineum during childbirth and trauma, surgical manipulations on the external genitalia (episiotomy - incision of the soft tissues of the genital slit during childbirth to prevent their rupture in an unfavorable place, followed by the application of raffia sutures, surgical perineoplasty - surgical plastic surgery of the soft tissues of the perineum, surgical labiaplasty - surgical plastic surgery of the labia in the form of reducing their size).
More often, in cultures of Bartholin gland cyst secretions, no growth of diagnostically significant flora is detected. The causative agents for inflammation of the Bartholin gland cyst and transition to an abscess (above we discussed the microflora leading to the causes of inflammation leading to the appearance of a cyst) can also be representatives of the normal microflora of the female genital organs, such as staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, and pathogens sexually transmitted diseases - gonococci, chlamydia, etc. Microorganisms that cause diseases of the upper respiratory tract - streptococci pneumonia and influenza bacilli - are increasingly being isolated [2]
Often cysts can be preceded by acute bartholinitis - an inflammatory process of the Bartholin gland without blockage of the duct (cysts in this case develop both after treatment after some time, and in the absence of it.
Let's sum it up
There can be many reasons for the occurrence of increased oiliness in the dermis, but the solutions to all problems are basically the same. Therefore, it is very important to figure out how to reduce or remove, get rid of excess oily skin on the face, what to do when the chosen gentle products no longer help, and what you can count on. Modern cosmetology offers many different options for influencing the dermis, but not all of them are equally safe and effective, and many problems can be completely solved with high-quality home care.
Symptoms
Bartholin gland cysts are common problems in women of reproductive age. Most often, women complain about aesthetic issues - asymmetry of the labia, swelling on one side of the labia majora. Cysts are usually asymptomatic and can be detected by a gynecologist during a routine examination. But in some cases (hypothermia, acute or subacute inflammatory process of the respiratory tract, acute or subacute inflammatory diseases of the genital tract, pelvic organs), they can increase and cause significant pain. Women with larger cysts may complain of discomfort when walking, sitting, and during sexual intercourse. If the Bartholin gland is functioning on the other side, the hydration of the vagina does not change during sexual intercourse. Due to blockage and the presence of a cyst, the Bartholin gland cannot fully function.[2] .[1]
Inflammation of the labia in women, video
Gynecologist Irina Vladimirovna Garyaeva about vulvitis in women.
Source - KVD - dermatovenerological dispensary Sources:
- ROLE OF INFECTIONS IN THE GENESIS OF VULVA DISEASES. Reutskaya M.A., Kulinich S.I. // Siberian Medical Journal (Irkutsk). – 2010. – No. 6. – pp. 239-242.
- CLINICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT OF CHRONIC VULVITIS. Kulinich S.I., Reutskaya M.A., Pokinchereda T.V., Ezhova I.V. // Acta Biomedica Scientifica. – 2013. – No. 5 (93). – P.42-48.
- Diseases of the cervix, vagina and vulva: Clinical lectures. Ed. V.N. Prilepskaya. // M.: MEDpress. - 1999. - P. 432.
- Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: etiology, pathogenesis, treatment. Levonchuk E.A. // Med. news. - 2001. - No. 4. — P. 40-43.
- Dystrophic diseases of the vulva. Diseases of the cervix, vagina and vulva. Ed. V.N. Prilepskaya. // M.: MEDpress. - 1999. - pp. 326-336.
- https://simptom-lechenie.ru/en/vulvit-u-zhenshhin-i-devochek-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
- https://www.thenakedscientists.com/science-articles
- https://woman-centre.com/vlagalische-i-vulva/vulvit/vulvit-u-zhenshhin.html
- https://simptomer.ru/bolezni/zhenskie-zabolevaniya/864-vulvit-simptomy
Pathogenesis
The resulting inflammation of surrounding tissues occurs in 3 stages:
Stage 1 - Alteration the release of fluid during Stage 2 - Exudation and blood cells from the vessels into the tissue, edema occurs.
Stage 3 - Proliferation (or productive stage) does not occur, since damaging factors continue to operate and therefore the resulting swelling, thickening of the walls, narrowing of the lumen of the canal, thickening of the secretion, resulting in blockage of the duct), the secretion of the Bartholin gland being produced, accumulating, thickening, leads to the formation of a cystic cavity formation, gradually increasing in size. Local defenses fail due to concomitant diseases, decreased general immunity and the aggressiveness of the flora that causes inflammation. Reaching a size of 4 or more centimeters, squeezing the surrounding tissues, causes pain in a woman and can, turning into an inflammatory process, cause an abscess of the Bartholin gland [2] [3] [4]
The causes and mechanism of development of Bartholin’s gland abscess are described below in the “Complication” section.
Bartholinitis and pregnancy
Infections that a woman is infected with and that cause bartholinitis can negatively affect the course of pregnancy and the development of the child. Infected mother's blood, entering the child's body through the placenta, can lead to disturbances in the formation of the baby's organs. In the early stages of pregnancy, infection can cause fetal death.
Do not delay visiting your doctor if you have symptoms of inflammation of the Bartholin gland. You can diagnose bartholinitis in our clinic, and also receive qualified help, advice and recommendations by making an appointment with a gynecologist by phone. or the feedback form at the bottom of the page.
Watch yourself, appreciate yourself and be healthy!
Complications
1) Chronic bartholinitis - chronic inflammation of the vestibular gland for more than 3 months.
In this case, a formation in the area of the labia majora, accompanied by pain on palpation of the affected gland, redness, swelling of the tissues, can be both a complication and the primary cause of a Bartholin gland cyst. Treatment is aimed at destroying the causative agent of the disease and relieving symptoms of intoxication.
2) Bartholin gland abscess [1]
Under unfavorable conditions (secondary infection (migration of bacteria from nearby areas (genital tract, cervical canal, uterine cavity, urinary system or separate foci - oropharynx, respiratory tract), weakened immunity) the cyst suppurates with the development of a Bartholin gland abscess.
Body temperature, intoxication, and a sharp deterioration in health appear. Locally, there is an increase in the size of the formation from 10 to 12 cm, a feeling of fullness and sharp throbbing pain in the perineum. Any movement can increase the pain.
On palpation - fluctuation, increased skin temperature.
An abscess of the Bartholin gland can open spontaneously, releasing pus. Since abscess formation of a Bartholin gland cyst is often associated with sexually transmitted infections, there may be clinical symptoms of colpitis, urethritis, endocervicitis, the main symptoms of which are swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane, itching, leucorrhoea
The method of treatment is planned or emergency hospitalization, during which an autopsy is performed followed by drainage of the abscess, anti-inflammatory (broad-spectrum antibiotics), detoxification therapy.
3) Cyst recurrence occurs quite often in situations such as self-opening, surgical opening or puncture of the cyst.
1. Rectovaginal fistula as a complication of excision of the Bartholin gland. This is a pathological channel between the rectum and vagina as a result of ongoing inflammation and melting of surrounding tissues.
A rectovaginal fistula may occur after removal of the Bartholin gland. Case [12] illustrates a rare and serious complication of a commonly performed gynecological procedure
Patients may complain of pain in the perineal area, pain during sexual intercourse, or bowel movements. To establish and confirm the diagnosis, after collecting an anamnesis, conducting a gynecological and rectovaginal examination, additional examinations, and consulting a proctologist. The tissue defect is eliminated using an autograft, a biological collagen plug, or a titanium clip. If a fistula is detected during pregnancy, natural childbirth is prohibited. With adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
2. Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory reaction in response to a local inflammatory process in the area of the Bartholin gland cyst. The response to the release of toxins formed during the destruction of harmful microorganisms in the absence of appropriate therapy is accompanied by a failure syndrome in many organs and systems, which can lead to death.
How to fight
What to do when your facial skin quickly becomes oily? Modern cosmetology offers a huge number of different solutions, effective to one degree or another. However, they are not at all a panacea for any problems in the body. Therefore, it is advisable to first visit a doctor who will help to accurately determine the cause of such phenomena. Only after all health issues have been resolved can you turn to the remedies described below.
Injection cosmetology
It involves influencing the skin with injections. At the same time, various drugs are injected into the middle or uppermost layers using microneedles, which in our case combat the increased secretion of sebum.
Ozone therapy
The main effect of this procedure is based on improving the delivery of ozone molecules into cells, which actively stimulates the antioxidant system. In the gas injection zone, the metabolic rate increases significantly, therefore, the elimination of toxins and other “garbage” is accelerated. At the same time, immunity and turgor increase, acne and blackheads go away, and color improves.
Mesotherapy
During this procedure, special “cocktails” made up of caffeine, hyaluronic acid, various plant extracts and essential vitamins are introduced into the middle layer of the skin. It can solve several main problems:
- slows down aging;
- removes lipid deposits;
- eliminates excessive fat.
Post-acne and pimples can also be removed after the course, or at least their visibility can be significantly minimized.
Hardware procedures
Oily facial skin type necessarily requires active care, especially the most problematic areas - forehead, nose, chin and cheeks. Properly selected options are well suited for these purposes, where special devices and equipment are indispensable:
- ultrasound phonophoresis;
- biostimulation using laser;
- darsonvalization;
- grinding with aluminum oxide or diamond chips;
- iontophoresis;
- ultrasonic peeling.
All of the above is performed exclusively in specialized offices, in which specialists must have the appropriate documents.
Microcurrent therapy
This is the name of the method of influencing the surface of the skin with fairly weak electrical impulses, fluctuating in the range of 40-1000 microamps. The procedure has a minimal list of contraindications and is also quite effective. Efficiency is achieved through a simultaneous effect on lymphatic and blood vessels, muscles and dermis. The procedure makes it possible to put even a fairly severely affected surface in order, with virtually no negative sensations.
Photorejuvenation
The essence of the technique is the correct exposure of the surface to light rays of a certain frequency. It is completely safe for health, has virtually no contraindications, and does not imply any invasion of the epidermis at all. The results of the procedure are usually visible from the first session, and the final effect occurs after 3-5 repetitions.
Aesthetic cosmetology
To quickly and without consequences eliminate excess fat, homemade formulations are sometimes not enough. Then it's time to contact a specialist. An experienced professional must first refer the patient for a medical examination to find out the causes and contraindications, and only after that makes prescriptions.
Drugs
Bb Laboratories – Two-phase serum concentrate
Curacen – for injection
Curacen Essence (20 fl x 2 ml)
Nanoneedles with ultra-thin walls 34G
Cares
For high-quality results, professional products are used that directly affect the regulation of gland secretion. They usually have a high concentration of active components, which distinguishes them from the usual analogues used in everyday life. In your care, you can use the Cream Clay Mask, which effectively restores the skin's purity and healthy appearance, or the delicate Clear Oil Cleansing oil for deep cleansing. It removes makeup, deep skin impurities, dead cells of the stratum corneum and excess sebaceous glands.
Purges
As a rule, the dermis with increased sebum secretion is quite dense, so it “clogs” much faster than any other. Without thorough cleaning and constant care, it will become very shiny. There are several types of high-quality professional cleansing:
- manual;
- combined;
- ultrasonic;
- chemical.
All options are aimed at freeing clogged pores from their contents and thereby reducing the main indicators of pollution. Similar procedures are recommended not only for increased sebum secretion, but also for acne, milia, blackheads and other defects.
Cosmeceuticals as help in a difficult struggle
It includes cosmetology and medicine, which allows it not only to fight visible imperfections, but also to eliminate the cause from the inside. This is one of the most effective and modern treatment methods. For example, the drug GHC Placental Cosmetic is able to transform the dermis at the cellular level, eliminating excess oil. In addition, it stimulates the production of natural elastin and collagen, reduces the number of existing wrinkles, normalizes the water-lipid balance, and eliminates the prerequisites for the development of hyperpigmentation. You can also use Placenta Extract, which effectively restores cell structure and normalizes their functions, and also increases skin elasticity and helps eliminate irritation and inflammatory reactions.
Solving problems with a doctor
Many people have a question about what to do and what treatment for very oily facial skin can be effective and safe. By contacting a doctor, you can find out why certain processes occur, without which it is unlikely that you will be able to choose the right therapy. Alternatively, you may also need to consult an endocrinologist who deals with hormonal imbalances, which also often cause excessive sebum production.
Usually, if you have a genetic predisposition, doctors recommend monitoring your lifestyle and diet, and regularly caring for your skin using special formulations. However, through increased secretion of the sebaceous glands, the body can signal the development of any diseases. Such manifestations cannot be ignored, especially if they arise suddenly.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of a Bartholin gland cyst (including asymptomatic cases) is often made on the basis of an objective examination: asymmetry of the genital fissure, an increase in the volume of one or, less often, two labia majora. If the Bartholin gland cyst is not inflamed, the skin over it retains its normal color. Upon palpation, the gynecologist detects a slightly painful cystic formation of elastic consistency in the thickness of the labia majora.
Laboratory tests: not specific [3] (in blood and urine tests, if the cyst is uncomplicated by inflammation, there will be no changes
Instrumental studies: ultrasound of the external genital area reveals an anechoic or hypoechoic avascular (not reflecting or poorly reflecting ultrasound, on the screen we see a round formation with thin - light walls and completely dark or light suspended contents) formation with thin walls
List of main diagnostic measures at the outpatient stage:
1. General blood test;
2. General urine analysis;
These blood and urine tests are taken as part of the standard, to prepare for surgical treatment and to exclude concomitant pathologies from other organs with their subsequent correction)
3. Smear for microflora and degree of purity.
This is an examination method in which the test material is taken from the surface of the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervical canal and urethra. The purpose of the analysis is to assess the composition of the microflora and identify inflammatory diseases. The assessment of the standing of the natural flora has in its classification four degrees of vaginal cleanliness:
1st degree – epithelial cells and a normal number of lactobacilli in the smear, pH – acidic;
Grade 2 – a small number of leukocytes, fewer lactobacilli, gram-positive diplococci are present. pH – remains acidic;
3rd degree - increased number of epithelial cells and leukocytes, decreased lactobacilli, many coccal bacteria, pH - slightly acidic or alkaline;
4th degree – a large number of epithelium and leukocytes, pyogenic microorganisms, absence of lactobacilli, pH – alkaline.
4. Bacterioscopic examination of vaginal discharge and cyst contents - allows us to identify microbial agents that caused the Bartholin gland cyst: identification of the pathogen, sensitivity to antibiotics.
5. Testing for infections (ELISA, PCR) gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia. [3]
The required scope of examinations before hospitalization:
1. Blood for antibodies to Treponema pallidum (this is the detection of total antibodies to the causative agent of syphilis) - a necessary test before hospitalization and surgery!!
2. Blood type and Rh factor.
3. General blood test.
4. General urine analysis.
5. Smear to determine the degree of purity.
6. Culture from the cervical canal.
7. HbsAg - surface antigen of the hepatitis B virus - to detect hepatitis B by its presence and determine its concentration, a necessary analysis before hospitalization and surgery!!
8. Anti HCV.
In women during menopause or perimenopause, an excisional biopsy is indicated to exclude adenocarcinoma, since at this age the risk of developing malignant tumors is greatest
VASCULAR FORMATIONS
Angiokeratoma
Angiokeratoma of Fordyce manifests as multiple, well-defined, bluish-black papules on the skin of the scrotum [Figure 7a]. They are often clinically mistaken for genital nevus, blue nevus and melanoma. Various sources indicate that 20% of angiokeratomas were misdiagnosed as melanoma [32]. Dermoscopy clearly shows pronounced reddish-dark blue lacunae with a blue-white veil [Figure 7B] [33].
Lymphangiectasia of the vulva
Acquired lymphedema and lymphangiectasia of the vulva usually occur due to damage to the lymph nodes that occur after trauma, infection, malignancy, surgery, radiation, etc. Clinically, they present as flesh-colored papules or transparent vesicles with a diffuse erythematous background. Piercing the lesion may release clear fluid. Dermoscopy reveals clearly defined, round-oval reddish lacunae with whitish septa and numerous small pinpoint lacunae. This is similar to the manifestations of lymphangioma. Dermatoscopy is relevant when lesions are sometimes confused with warts or molluscum contagiosum [34].
Differential diagnosis
Includes cystic and solid lesions of the vulva, such as epidermal inclusion cyst, hidradenoma papilliferum and lipoma [3], vulvar neoplasms; - abscess of the Bartholin gland; - bartholinitis; vulvar abscess.
— Hematoma in the vulva area – there may also be complaints about a formation in the vulva area, discomfort during sexual intercourse, and pain. But when collecting anamnesis; and gynecological examination - the woman associates its appearance with mechanical trauma, childbirth; And the location is not in the area of projection of the large vestibular gland. [1]
— Paraurethral cysts – similar complaints. On examination - swelling in the paraurethral region (the area near the urethra) [1]
- Furunculosis of the labia majora. Complaints include formations in the perineal area, general malaise, hyperemia, edema, hyperthermia. Upon examination, the formation is localized in the area of the hair follicle and sebaceous gland. [1]
BENIGN LOCATIONS
Seborrheic keratosis
Pigmented seborrheic keratosis, like its cutaneous counterpart, shows features such as polypoid structures, marrow-like structures, and finger-like structures on dermoscopy. Comedo-like structures, which are keratin-filled invaginations, are not observed in genital seborrheic keratosis due to constant friction. Milium-like cysts are usually visible because they are located intraepidermally [11,19].
Verruciform xanthoma
These are rare tumors composed of lipid macrophages that present clinically as yellowish plaques and nodules with a papillomatous surface in the anogenital areas. Dermoscopy reveals numerous yellowish papules with centrally located spiny vessels [20,21].
Treatment
Small, asymptomatic cysts may not be treated except for cosmetic purposes.
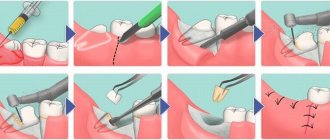
Often the clinician is tempted to simply incise the cyst or abscess because this technique may be effective for other common abscesses. However, simply puncturing a cyst or abscess of the Bartholin gland can lead to a relapse, since the edges of the tissues, when punctured or cut, very quickly close again due to the rapid healing or regeneration process [6]
Only large cysts, usually 3 or more centimeters, which interfere with daily activity and sexual life, and disrupt the aesthetic appearance of a woman’s external genitalia, are subject to surgical treatment.
The main goal of surgical treatment is organ-preserving - the formation of a canal and restoration of the function of the Bartholin gland,
Therapy in our clinic
If you notice lumps on your genitals, we recommend that you do not hesitate to contact our qualified specialists. You will be examined by our gynecologists, after which, if necessary, they will be referred to a surgeon. We will carry out the appropriate treatment, choosing the best option for you. We always strive to choose gentle techniques, but if this is not possible, our surgeon will eliminate your tumor quickly, painlessly, with a guarantee of no complications.
Many years of practice and extensive experience of our specialists allow us to vouch for the health of each patient. We recommend that you consult a doctor in a timely manner to avoid serious complications and relapses of the disease.
Catheter placement – Word
This is a modern method of surgical treatment for Bartholin’s gland cyst, especially in case of its recurrence.
Under local anesthesia, the cystic area is opened with a small incision of about 5 mm, the contents are removed and sent for bacteriological examination, the cyst cavity is washed and a Word catheter is installed in it (this is a silicone tube 55 mm long, 5 mm in diameter with a channel inside, blindly ending, with thinner walls at the end, due to which the tip can inflate into a ball, which has no analogues), inflating its rubber tip to 3 ml with a physiological solution of 0.9% sodium chloride, thereby fixing it in the cavity of the cyst. For better fixation and prevention of loss during the woman’s movements, it is recommended to apply 2-3 absorbable interrupted sutures along the contour of the catheter emerging from the cavity of the cyst. The second end of the catheter is inserted into the vagina. The catheter remains in the cyst cavity for 6 weeks. This is aimed at forming a channel for the passage of secretions, the walls of which do not grow together. The study shows that the Word catheter is an easy-to-use, low-cost outpatient procedure with acceptable short-term recurrences. Treatment costs are seven times lower than with marsupialization [7]. While the catheter is in the cyst cavity, the patient is advised to have sexual rest to avoid its loss. In a number of countries there is no such restriction, since studies have shown that the pain symptom caused by both the cyst itself and the procedure performed with the catheter in the cavity completely disappears over time (by day 6) [8]
As an alternative, a Voroda or a Jacobi ring (the catheter does not have a channel, it is harder, shaped like a ring) which is installed through 2 punctures in the mucous membrane and capsule of the cyst and the 2 ends are fastened to each other.
PRE-CANCEROR FORMATIONS
Extramammary Paget's disease
Extramammary Paget's disease is clinically characterized by erythematous plaques with oozing, ulcerated, and scaly nodules and focal hyperpigmentation. Areas of hypopigmentation can also be seen (Fig. 6a). Dermoscopy of extramammary Paget's disease reveals milky red areas, vascular structures, superficial scales, ulcers, pigment network, shiny white lines and white structureless areas [Fig. 6b]. Common vascular structures are stippled vessels and glomerular vessels [22]. Paget's disease is often mistaken for melanoma due to features such as irregular pigmented globules, white negative pigment network, and structureless blue-gray areas [23].
Erythroplasia Keira
It is the genital counterpart of Bowen's disease and has similar dermoscopic features. Glomeruloid vessels are characteristic, located in clusters or diffusely, which can be used to differentiate Queyre's erythroplasia from other causes of chronic balanitis. In addition, linear vessels and brown dots can be seen [24]. Dermoscopic features in pigmented Bowen's disease include pigmented streaks combined with other features such as comedo-like structures [25].
Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
This is a common cause of genital itching. About 15% of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasias are pigmented. Typical findings are milky white or pink areas associated with punctate or glomerular vessels and papillomatous structures. In the pigmented version, brownish dots with clearly defined boundaries and brain-like structures are visible [26].
CONCLUSIONS
Dermatoscopy has become important in the diagnosis of non-pigmented dermatoses and for differentiating benign lesions from equivocal and malignant lesions [1, 28]. Many dermatologists in modern practice have included dermatoscopy in their routine work. Although this does not eliminate the need for biopsy, the technique avoids unnecessary biopsies of benign lesions. It also helps us carefully select the biopsy site for suspicious or atypical pigmented lesions.