If we proceed from the generally accepted canons of the formation of the dental row in a child, then by six months, maximum by 8 months, teeth should appear. However, in reality this does not always happen. Despite reaching the age of eight months, the baby does not experience teething.
Parents should not panic in such a situation, although the question of why the child has no teeth requires an immediate answer. Sometimes such a development of events is only a slight deviation from the norm, but often indicates a serious pathology.
Causes of delayed teeth emergence
A lot depends on nutrition: breastfed babies depend on the quality of breast milk. Babies who grow up on artificial formulas receive slightly more vitamins and minerals, because the formulas contain a clearly calculated amount of nutrients.
- If a child does not have a single tooth at 1 year of age, this may be a consequence of some previous disease: intestinal dysfunction, impaired metabolism, as well as insufficient calcium and vitamin D.
- Teeth may be delayed due to the special course of pregnancy; perhaps the mother suffered complications during the gestation period./li>
- Eruption after 12 months may mean that the tooth is not positioned correctly in the gum, for example, it is growing horizontally.
- Congenital absence of tooth buds in a baby. These are either hereditary disorders or a congenital pathology caused by a disruption in the normal course of pregnancy. It happens very rarely.
How can parents understand that at 12 months the baby’s teeth are simply delayed and they need to be patient, and when should they sound the alarm?
Pediatric dentists allow the first teeth to be delayed for 6 months, so if after the baby’s 1st birthday not a single baby tooth has grown, you should wait a little longer. Try to find out from your relatives about the timing and characteristics of the appearance of the first milk teeth in their childhood, perhaps this is just a family trait.
But if the teeth are already delayed by more than 6 months, and the baby’s gums do not even think of swelling, then you should contact a pediatric dentist. The specialist will conduct an examination and advise what needs to be done to help teeth appear faster.
In addition to the above reasons, the appearance of teeth after 12 months may be affected by the following:
- The teeth are located very tightly in the gums.
- There are diseases of the endocrine system, for example, hypothyroidism, due to which the activity of the endocrine glands is reduced.
- The baby suffered serious systemic diseases.
In this case, the pediatric dentist will recommend a biochemical blood test; the baby will need to have the thyroid gland examined, including an ultrasound examination. After the results are obtained, the dentist will be able to prescribe the necessary course of treatment.
Make an appointment
How many baby teeth do children have?
Milk teeth and even some molars begin to form at the stage of intrauterine development. Of course, a child has no visible teeth at birth - they begin to erupt only after 6 months. During this six-month period, they are hidden under the gums, but slowly develop and form, beginning to move outward.
In total, a child grows 20 baby teeth:
- Central and lateral incisors – 8.
- Fangs – 4.
- First and second molars – 8.
Their main function is to form a space where molars will then grow.
How to help your baby?
Initially, the dentist will take an X-ray of the baby's jaw to make sure that the baby has the rudiments of teeth inside. If there is, then eruption will happen soon. At first, the gums will swell a little and salivation will become very abundant: these are the main symptoms of the rapid appearance of teeth. You can help them a little:
- Teether toys are an excellent device for training gums; they help relieve severe itching and reduce pain.
- Mothers should learn how to gently massage their baby’s gums. It is better to massage with a clean finger lubricated with a special gel for children's gums.
- It is important to add healthy purees and healthy foods to your baby’s diet that will help the child’s body receive the necessary microelements and vitamins.
If the baby generally develops within normal limits, eats well, sleeps, is active and cheerful, then the absence of teeth at 1 year is definitely not a reason to panic. Each child develops at his own pace. In general, boys tend to lag slightly behind girls in some physiological parameters.
From this article it follows that you should not worry unnecessarily! If in any doubt, seek advice from a pediatric dentist at our Babydent
Show more tips
How many teeth should a child have per year?
During this period, baby teeth begin to cut.
They begin to break out in the following sequence on the upper and lower jaws. On the top:
- 8-12 months. Central incisors.
- 9-13 months. Lateral incisors.
- 16-22 months. Fangs.
- 13-19 months. First molars.
- 25-33 months. Second molars.
In the lower jaw, this process is distributed in time somewhat differently:
- 6-10 months. Central incisors.
- 10-16 months. Lateral incisors.
- 17-23 months. Fangs.
- 14-18 months. First molars.
- 23-31 months. Second molars.
It is worth noting that these time limits are averaged and deviations up or down by 1-3 months are considered normal.
If you want to know how many teeth a child has per year is considered normal, you should refer to the chart described above. You get that at the age of 12 months there should be 6-8 of them.
What should you pay attention to when teething?
The above symptoms of the onset of teething are characteristic of almost all infants. However, some children have additional symptoms that need to be taken seriously:
- Temperature increase;
- Formation in the mouth of small watery blisters with cloudy or clear liquid;
- Increased redness and inflammation of the gums;
- Inflamed oral mucosa, accompanied by the formation of slight erosion.
In a healthy baby, when teething, contrary to popular belief and the advice of “experienced” relatives, the temperature does not rise. If this happens, it means that the child’s body is simultaneously exposed to some kind of inflammatory disease.
Most often, the listed signs indicate the development of a viral form of stomatitis or ARVI, which is not surprising given the child’s desire to put everything in his mouth. Therefore, you need to show the child to the doctor. If the pediatrician does not detect signs of an acute viral infection, take your baby to a dentist so that he can determine what form of stomatitis your child has caught and prescribe adequate treatment. Unfortunately, pediatricians are most often incompetent in this situation.
Changing baby teeth to molars
Around the age of 4, a child’s growth spurt begins, the jaws enlarge and the baby teeth seem to move apart, with gaps appearing between them – trema. If this does not happen and by the age of 5 the teeth are still tight, you need to show the child to the dentist, as there may not be enough space for permanent teeth.
At about 5-6 years of age, baby teeth begin to become loose and gradually fall out, which indicates that the molars are already beginning to grow underneath them. Usually this process of change lasts for 5-8 years and the final formation of the dentition occurs somewhere around 14-15 years.
This happens in the following order:
- 5-6 years – lower and upper incisors.
- 7-8 years – lower and upper lateral incisors.
- 8-10 years – upper and lower molars.
- 9-11 years – upper and lower canines.
- 11-13 years – upper and lower molars.
Milk teeth are replaced by permanent molars. Their number at the age of 14-16 years is 28. At the same time, the third molars (wisdom teeth) are already formed, but they begin to grow only after 18 years. True, not all people grow them. It all depends on individual characteristics.
Symptoms of disorders
There are special formulas that show how to correlate the age of a child with the number of chewing organs cut through him and understand whether everything is going well, but we are not going to overload the reader by immediately getting to the point.
The concept of a norm in this case is very flexible, because in different sources we will find different terms. Some pediatricians insist that the eruption of the first teeth later than the eighth month of life is a pathology, others argue that this is quite normal, but it is impossible to separate pathology from the norm without studying a specific patient.
Even if there is a delay in dental development, if the child looks healthy and no systemic pathologies are detected, then parents can calm down and wait a little until the teeth begin to cut.
If the child is sick, then this may be a problem with his teeth. Early eruption, for example, can be both an individual characteristic of the body and evidence of incorrect functioning of the endocrine glands.
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose the disease, the dentist needs a detailed examination of the patient’s oral cavity. The doctor asks the patient a number of things:
- causes and timing of tooth loss;
- information about previous diseases;
- data on dental prostheses previously used by the patient.
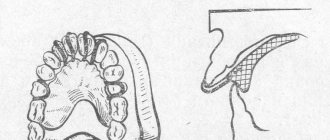
During the examination, the dentist notes the asymmetry of the face, the severity of the chin and nasolabial folds, the degree of reduction in the height of the lower part of the face, the presence of a jam, the nature of the closure of the lips, the topography of the transitional fold, the degree of mouth opening, the nature of the jaw relationship. The specialist also determines the presence of crunching in the joints, pain when moving the lower jaw and diagnoses the degree of atrophy of the alveolar processes.
The examination necessarily includes palpation of the oral cavity and radiography of the TMJ. Based on the data obtained, the doctor determines further treatment tactics (prosthetics), selects the appropriate type of prosthesis and impression material for the patient.
Possible complications
"Surprises"
The problems that nature presents when infants have their first teeth do not end with the listed troubles. Sometimes other complications are possible:
- Formation of hematomas.
A bluish-colored bubble swells on the gum. Most often it resolves over time, but sometimes if the blister is too large, surgery is required. The doctor makes a small incision on the gum to remove the bloody fluid.
- The appearance of vomiting.
This may be caused by excessive salivation. However, if vomiting is accompanied by diarrhea and fever, these may be signs of rotavirus, so it is necessary to urgently show the child to the pediatrician.
- Cough reflex.
With normal teething it does not happen. The cause of the cough may be excessive saliva secretion, which causes the baby to choke.
If a runny nose appears, take your child to the doctor
- teething probably coincided with a cold.
Important:
If your baby is experiencing fever, diarrhea and vomiting during teething, take this seriously. The cause of their appearance cannot be teething. It is urgent to call a pediatrician, since the baby’s body is at risk of intoxication due to a developing infection.
Treatment of adentia in adults
Adult patients are offered various types of removable and fixed dentures. Prosthetics on implants, installation of bridges on four implants and other prosthetic options at the patient’s choice are possible. Depending on the condition of his dental system, financial capabilities and wishes, dentists, as a rule, offer several treatment options to choose from.
When choosing a treatment method, it is important to understand the features of each design. The doctor, based on the condition of the patient’s oral cavity, offers him a choice of several prosthetic options.
Removable dentures
Partial or complete dentures should be replaced every 1.5 to 2 years. Therefore, even with complete loss of teeth, dentists offer an alternative type of prosthetics based on implants.
Clasp dentures
Dentures on a metal frame, on which an acrylic base is installed, and artificial teeth are installed on it. This solution makes it possible to significantly lighten the design of the prosthesis, making it thinner and more comfortable.
Bridges
In case of partial edentia, it is possible to install bridges. The non-removable structure is fixed on adjacent non-grindable teeth.
Implant-supported prosthetics
Implant-supported prosthetics are considered the most reliable and aesthetic way to restore dentition. The main advantages of this type of bone implantation include:
- long service life of the structure;
- aesthetic appearance;
- no need to grind adjacent teeth.
A denture installed on implants completely replaces missing teeth and performs a functional and aesthetic task.
Prevention of edentia
The best prevention is competent, timely oral care. Regular brushing of teeth and gums, preventive examinations at the dentist twice a year, giving up bad habits, switching to a balanced diet - all this will help keep your teeth healthy and strong for as long as possible.
If you or your child is experiencing this disease, do not delay visiting the dentist. Experienced therapists, orthopedists and implantologists at STOMA clinics will help solve the problem of partial or complete absence of teeth: they will select a comfortable and aesthetic prosthesis that will significantly improve the quality of life, make you more confident and beautiful.
Call and make an appointment by phone: +7 (812) 416-94-37. Our clinics are located in different areas of St. Petersburg and are open from Monday to Saturday, from 9 to 21 hours.