In children from the age of 5, temporary milk teeth begin to fall out and are gradually replaced by permanent ones, which will serve for the rest of their lives. Many parents are interested in the question: how many teeth change in childhood? All baby teeth fall in, and permanent teeth grow in their place. They change in the same order as during teething. But parents should know that at the age of 6-7, the baby begins to grow his first permanent molars (sixth teeth) - they are the ones that remain for life. Children's fifth molars are the last to fall out and are replaced with permanent molars. Teeth are completely replaced by about 12-14 years, but it all depends on the individual characteristics of the body and various other factors.
Often, during tooth replacement, some non-standard situations and features can be observed, because of which parents begin to worry. Let's take a brief look at the most common questions:
What reactions of a child’s body are possible during the period of loss of baby teeth and growth of permanent teeth?
Replacing teeth is almost painless. The loss of baby teeth occurs on their own after their root is completely absorbed or removed at home, and if the permanent tooth is already growing, but the permanent one has not yet fallen out, the help of a pediatric dentist is required. When permanent teeth erupt, pain usually does not occur. Very rarely, there may be a slight increase in body temperature, itching of the gums or discomfort in the abdomen. In this case, the child does not need treatment, but it is recommended to visit a dentist.
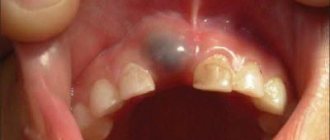
The main symptoms of the pathology
Retention in dentistry is quite common, and there are some signs by which this pathology can be detected:
- pain in the gums, radiating to the ear and temporal part;
- regular injury to the same place in the oral mucosa;
- numbness and swelling;
- painful sensations when opening the mouth and while chewing food;
- mobility or displacement of teeth;
- deterioration of general health due to the inflammatory process (fever, weakness, chills, etc.);
- the appearance of a cyst or abscess.
Why can a lot of time pass between the loss of baby teeth and the eruption of permanent teeth?
Most often, the front teeth grow quickly. And canines and baby molars (premolars) can be delayed. After a temporary tooth falls out, it may even take 4-6 months until a permanent tooth erupts in that place. Just expect it and take good oral care. But if this period begins to exceed six months, so as not to worry, it is better to visit a doctor. After examining the child, he will be able to decide whether the permanent tooth needs to be stimulated to grow.
Content:
- Why is it necessary to replace baby teeth with permanent ones?
- When do the first baby teeth fall out?
- Which baby teeth fall out first?
- Drop order
- At what age do radical units appear?
- Possible abnormalities in the child
- Why do empty spaces remain unoccupied for a long time?
As the child grows, the baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones. This is a natural process, without which the full functioning of the dentofacial apparatus is impossible. But parents should treat it with the utmost responsibility, since very often violations in the sequence of loss of temporary units cause serious malocclusions that have to be treated in the future.
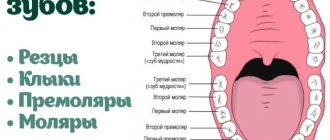
Which teeth should an eight-year-old child have?
Every child who has reached the age of eight should normally have the following permanent teeth - 4 lower and 4 upper incisors, sixth molars. Sometimes there may be individual deviations in teething within plus or minus six months.
Why is it necessary to treat caries in childhood if you then have to remove baby teeth with filled roots?
If an empty space forms in the dentition, this contributes to the fact that the remaining milk teeth shift, and along with them, the rudiments of permanent teeth also shift and they begin to grow incorrectly under them - in one place the formation of cracks begins, and in another - the teeth fit alone another. A filled, treated baby tooth will save space for a permanent tooth. Untreated teeth infect the rudiments of permanent teeth with infection, which causes their deformation and even complete absence.
Physiological causes of pathology
The primary dentition is not immediately replaced by primary teeth. After a baby tooth falls out, a certain period of time must pass. Only after this does the molar appear. Subsequently, he completely takes the place of his predecessor. But some children, even 3 weeks after the loss, do not even have a hint of teething. Parents are starting to worry. However, this does not always indicate the presence of the disease. There are cases when the dental body began to erupt only after 1 or 2 months. There could be many reasons for this. In addition, there are cases that even adults retain their baby teeth. Only a specialist can determine this.
One of the reasons why a baby tooth falls out and a new one does not grow is the absence of its rudiments. Pathology can be diagnosed using an x-ray. In this case, the patient is given dental plates, and upon reaching adulthood, a new dental body is implanted. There is no other way to solve the problem.
But there are teeth, the formation of which occurs quite late. These are eights. Their rudiments are formed only in adolescence - at 13 or 14 years old.
Parents should remember that they should go to the hospital in a timely manner in all cases if any pathology is noticed in the child’s oral cavity. If more than three months have passed since the tooth loss, and there is also redness and swelling of the gums, then you cannot do without the help of a doctor. Such symptoms indicate that the dental body cannot erupt. In this case, the edge of the gums may acquire a blackish tint. In this case, the specialist must open the gum so that the new tooth can emerge.
When considering the question of why the baby fang fell out and the molar (or other teeth) does not grow, it is necessary to establish the causes of the pathology. They are as follows:
- Infections that affected the formation of dentition rudiments.
- Serious mechanical injuries.
- Incorrect dental treatment.
- Lack of calcium in the body.
- Unbalanced child's diet.
- The presence of caries, which slows down the development of the permanent tooth.
Why can a 7-14 year old child sometimes experience pain when all his teeth are intact?
Yes, this can happen, but in this case the pain occurs not in the tooth itself, but in the jaw, which is growing rapidly at this age. Since permanent teeth are almost twice as large as baby teeth, they need much more space. Therefore, large new teeth can sometimes overlap each other or grow at an angle, getting out of the dentition. As the jaw grows, they align and settle into place. But a qualified specialist can competently assess this situation, as well as the risk of anomalies and developmental defects. That is why in this case you will need to consult an orthodontist.
Problems when changing bites
Sometimes a situation arises that a child “grows a tooth under a tooth” - the permanent one has already appeared above the gum, and the temporary one is firmly held in its place. This happens when the resorption process of one or more milky roots is disrupted. This is also a reason to contact pediatric dentistry - after all, no one can say in how many days a loose baby tooth will fall out, and its “stubbornness” leads to the dystopia of a permanent one.
Dental doctors remove even such semi-loose teeth with anesthesia, so as not to cause discomfort to children. Only a specialist can decide what to do when changing the bite. Regular monitoring by the dentist during such an important period will help to avoid the formation of an abnormal relationship of the dentition, which will require further treatment by an orthodontist.
If a child’s baby tooth is loose, then you shouldn’t guess how long it will take for it to fall out; it’s better to consult a doctor without delay for qualified advice.
At the Shifa clinic, children are treated with modern equipment using the latest materials. The center has all the conditions for an accurate diagnosis of the condition of primary and permanent dentition, and this is the key to correct medical tactics. The dentists of the Shifa clinic find an approach to every child and master the most advanced methods of assistance, constantly improving their professionalism in Russia and abroad. Contact the best doctors who will help solve any dental problem!
At what age should a bite be corrected?
You can start correcting your bite at 4-5 years of age. In this case, the growth of permanent teeth will be even, in the place intended by nature. Therefore, there is no need to carry out subsequent long-term bite correction. In any case, if there is a malocclusion, the problem can be eliminated efficiently and as quickly as possible by contacting a qualified orthodontist as early as possible.
| Teeth | Dairy (temporary) | Permanent | ||
| Jaw | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper |
| Central incisors | 6-12 months | 8-12 months | 6-7 years | 6-8 years |
| Lateral incisors | 10-16 months | 9-13 months | 7-8 years | 7-8 years |
| Fangs | 17-23 months | 16-22 months | 9-10 years | 11-12 years old |
| First Premolars | — | — | 10-12 years | 10-11 years |
| Second Premolars | — | — | 11-12 years old | 10-12 years |
| First Molars | 14-18 months | 13-19 months | 6-7 years | 6-7 years |
| Second Molars | 23-33 months | 25-33 months | 11-12 years old | 11-13 years old |
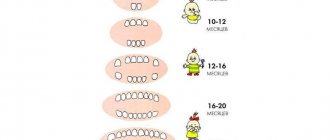
Timing of eruption of molars
The rudiments of teeth begin to form already in the eighth week of intrauterine development; these are the future milk teeth. The rudiments of molars are at 20, their localization in the child’s jaw is much deeper. It is important that not all the teeth that the baby will erupt as he grows up will later fall out; some of them will immediately become permanent.
On average, a baby's first tooth appears at six months of age, and not later than three years - the child already has a mouth full of teeth.
Let's figure out when it's time for molars to erupt:
- At approximately seven years old, the baby will have molars, sixth teeth (in the dental formula), and from the ages of eleven to thirteen – seven teeth (also molars). It should be taken into account that such teeth do not have milk analogues; they simply erupt from scratch, immediately becoming permanent.
The remaining molars will be licked to replace the milk teeth.
- Between six and eight years of age, the central incisors should appear.
- From seven to nine - the lateral incisors will erupt.
- From ten to twelve years of age, the child will develop premolars (the fourth and fifth teeth on the dental formula).
- Between the ages of nine and thirteen, the molars will erupt.
And already in adulthood, wisdom teeth may appear, although not everyone has them, and this is not a particular problem.
Remember that these are only approximate dates and you should not immediately get upset if your child deviates from these indicators. And if you are very worried, it is better to see a dentist so that he can dispel all doubts.
How to avoid problems
To avoid problems associated with delayed growth of molars,
Expectant mothers must adhere to some rules:
- Avoid bad habits, since smoking and drinking alcohol can negatively affect the development of tooth buds.
- Carefully monitor your oral hygiene and visit your dentist promptly.
- Take care of your health, do not contact sick people during pregnancy.
- Try to strengthen your immune system in every possible way.
- Avoid eating unhealthy foods.
- Do not self-medicate.
- Do not take antibacterial drugs under any circumstances without a doctor's prescription.
After the baby is born, remember these recommendations:
- Oral hygiene should be performed from the moment the first baby tooth appears.
- If caries is detected, do not forget about timely treatment. Baby teeth are highly susceptible to carious lesions.
- Protect your baby from injury.
- Remember that the child must eat properly and receive all the vitamins and minerals necessary for growth from food.
- Limit your intake of sweets.
- Make sure that sucking a pacifier or thumb does not become a bad habit. This may affect the development of the bite.
- After eating, the baby's mouth should be rinsed.
- Choose a suitable toothbrush and toothpaste for your child.
- Be sure to include solid foods in your diet, this will help ensure proper load on the jaw.
If you notice that a child’s molar does not appear for a long time, this is not a cause for concern. It would be a good idea to visit a pediatric dentist. Don't forget that all babies are individual, so the timing of the eruption of molars is different for everyone.