Teething is one of the most important periods in a child’s life. This happens at about six months of age, but it is difficult to name the exact timing, since this process occurs individually for each baby. What do parents need to know about the names of their child’s teeth and the pattern of their appearance?
Name of a child's teeth
What are baby teeth?
Milk teeth are the teeth that are the first to erupt in humans. Their rudiments are formed in the womb, at approximately 5-7 weeks of pregnancy, and by the age of three the child already has 20 teeth. Milk teeth differ from permanent teeth in structure (they are smaller and have a different shape), and the bite does not contain small molars, or premolars.
X-ray of baby teeth
Scheme of baby teeth eruption
Normally, baby teeth begin to appear after the child reaches 5-6 months, but this period depends on a number of factors, including the quality and characteristics of the child’s diet, the region of residence and even the weather. Some children are born with one or more teeth; most often they must be removed because they interfere with normal sucking.
On a note! Milk teeth erupt symmetrically according to the so-called antagonizing principle, that is, teeth of the same name appear approximately simultaneously, and the process begins from the lower jaw. The exception is the lateral incisors, which begin to erupt from above.
Numbering of baby teeth
First, the two lower central incisors are shown, then the two upper ones, which are located directly above them. This order of teething ensures contact between the teeth and gives the baby the opportunity to begin to practice chewing solid foods. By the age of one year, a child, as a rule, has eight teeth. Next, two fangs grow - first on the lower jaw, then on the upper, after which the teeth of the chewing group (molars) erupt. At three years old, children can already fully bite and chew solid food.
Approximate order and pattern of appearance of baby teeth
| Name | Age, months |
| Central incisors on the lower jaw | 6-7 |
| Central incisors on the upper jaw | 8-9 |
| Lateral incisors, upper jaw | 9-11 |
| Lateral incisors, lower jaw | 11-13 |
| Upper molars (first) | 12-15 |
| Lower molars (first) | 12-15 |
| Fangs | 18-20 |
| Second molars | 20-30 |
Internal anatomy of the tooth
What structure do teeth have in an adult, what parts do they consist of, and what can cause so much pain? If you look at the crown from the outside and mentally “climb” inside, the tooth consists of several layers.
- Enamel. This is the outer layer of the tooth and the hardest part in the human body, consisting of mineral prisms. Its thickness is minimal in the neck area and becomes as strong as possible on the “working” surface of the tooth.
On the outside, the enamel is covered with pellicle - a special organic film, without which acids have a negative effect on the teeth, dissolving enamel minerals.
- Dentine. This is the structural basis of the tooth, a hard, durable tissue that consists of a collagenous base substance that forms the tubules. Odontoblast processes are located inside the dentinal tubules.
Dentin is the primary tissue of the tooth.
In lower vertebrates (fish, amphibians), teeth consist only of dentin. In higher vertebrates, starting with reptiles, enamel and cement appear in the teeth “Anatomy of human teeth” Dr. med. Gaivoronsky I. V.
- Pulp. It consists of loose connective tissue in which nerves and blood vessels pass.
- Root. The part of the tooth, normally not visible to the eye, is located in the alveolar socket of the jaw. On the outside, the root is covered with a protective layer - cement, which is a complex of lime salts, collagen fibers and special cells called cementocytes. The structure of cement is similar to bone tissue, but it does not contain blood vessels or living cells, so it does not grow or renew itself.
- There are many connective tissue fibers around the root of the tooth. They are called periodontium or periodontal ligament. These are the “ropes” that hold the tooth root in the bony alveolus.
How does the process work?
When the time comes for teething, the baby usually becomes restless, begins to put toys and other things in his mouth, bites his chest with his gums, and begins to salivate profusely. Parents may notice a small bump on the gum filled with fluid; the mucous membrane in this place becomes red and swollen. After some time, white spots clearly appear through the soft tissues - this means that the tooth is ready to be born.
Milk and permanent teeth
Important! If the lump becomes too large and causes serious discomfort to your baby, you can ask the doctor to cut it to “help” the tooth get out.
The body's reaction to teething depends on its individual characteristics. In some children this process is asymptomatic, in others the temperature rises, a runny nose, redness of the throat, diarrhea, sleep and appetite worsen.
Attention! If teething is difficult, accompanied by fever and other symptoms, it is better for parents to consult a doctor. Typically, in such cases, antipyretic and analgesic drugs are prescribed, as well as ointments and gels that reduce discomfort in the gums.
Types of teeth
You can relieve discomfort from teething by massaging your gums (performed with a clean finger) or by purchasing a special stimulator ring at the pharmacy.
- When do children's fangs change to permanent ones?
What to do if baby teeth are delayed?
The absence of signs of teething in a child at a time when other children already have several teeth is not a cause for concern. The exact timing depends on several factors, including:
- genetic characteristics;
- climate and living conditions;
- feeding habits (in children who are breastfed, teeth usually appear later than in “artificial” children);
- quality of child care;
- nutrition and living conditions of the mother during pregnancy;
- the presence of chronic diseases and pathologies.
Numbering of teeth in dentistry for children
A situation where teeth are completely missing in a one-year-old child should be a cause for concern - sometimes this is a variant of the norm, and sometimes it indicates disorders in the body.
Important! The most common pathologies that can affect the timing of teething are dysfunction of the endocrine system and rickets.
Less common is a disease called edentia, or the absence of tooth buds, which can be diagnosed using x-rays.
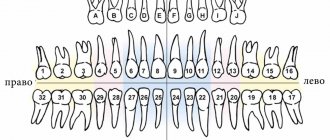
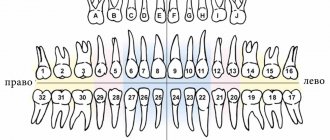
International Viola system: a convenient diagram of the arrangement of a person’s teeth by numbers
The described method is very convenient and most common in dentistry. It has received international recognition and has been generally accepted among dentists since 1971, called the two-digit Viola system. The convenience of such a system lies primarily in the fact that there is no need to create a special map of a person’s teeth, the numbering is easily calculated in the mind and information about the condition of certain dental units of the patient can be easily conveyed in an oral conversation, by telephone or by e-mail.
However, many people, having read this far, may say: but our teeth were counted completely differently, and the map contains completely different designations! That’s right, because in addition to the Viola system, there are several other systems that can be used by dentists.
Caring for baby teeth
Children should be taught oral care procedures from early childhood. After the first teeth appear, it is recommended to gently wipe them once a day with a clean piece of gauze soaked in boiled water. As your baby gets older, you can purchase your own soft-bristled brush and brush your teeth with water. After the baby reaches one year of age, it is recommended to purchase a special paste and teach him how to care for the oral cavity on his own.
Teeth of the upper and lower jaw
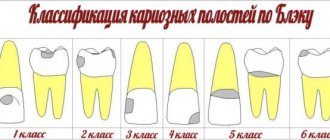
Milk teeth, like permanent teeth, are susceptible to decay and caries, which can appear even in children under two years of age.
On a note! The main feature of childhood caries is multiplicity, that is, it often affects not one, but several teeth, penetrating into the deep layers of tissue.
At the spot stage, the disease is treated with fluoridation; in case of an extensive pathological process, cleaning of carious cavities and removal of infected tissues is necessary.
Formula for recording baby teeth using the Haderup system
Dental formula
Dental patients look with curiosity at the notes on the examination card, on which numbers, corners, and sometimes letters are written. We are talking about a system of numbering teeth without naming them: that is, a diagram written on paper, where each place corresponds to a tooth.
Thus, one of the popular formulas for adults in Russia consists of four blocks [1]
| 87654321 | 12345678 |
| 87654321 | 12345678 |
The teeth are numbered from front to back as they are seen by the dentist examining the oral cavity. Using this diagram of teeth, he describes their general condition using symbols:
- dash—tooth missing;
- the number is circled - treatment is required;
- the figure remains unchanged - a healthy tooth.
Roman numerals are used to designate baby teeth.
| V IV III II I | I II III IV V |
| V IV III II I | I II III IV V |
There are other recording methods, but their general essence is the same - to clearly show the condition of the dentition, so that all specialists involved in the treatment of the patient can immediately see problem teeth and build the correct tactics of help.
When do permanent teeth appear?
The replacement of baby teeth with permanent teeth occurs once in a lifetime, in early preschool age. Permanent teeth are divided into two groups: replacement teeth, that is, those that have “twins” in the primary dentition, and additional teeth (premolars and molars). The timing of the eruption of permanent teeth is also individual and depends on genetic factors, region and living conditions, and quality of nutrition.
Structure of a baby tooth
| Name | Age, years |
| Molars (sixths) upper and lower | 6-7 |
| Central incisors on the lower jaw | 6-7 |
| Central incisors on the upper jaw | 7-8 |
| Incisors on the side of the lower jaw | 7-8 |
| Incisors on the side of the upper jaw | 8-9 |
| Fangs on the lower jaw | 9-10 |
| Fangs on the upper jaw | 11-12 |
| Premolars (4s) | 10-12 |
| Second premolars (5ths) | 11-12 |
| Second molars (7s) | 11-13 |
| Third molars (wisdom teeth) | 17-25 |
Dental formula
For reference! The eruption of permanent teeth usually does not cause children any discomfort - after the roots are reabsorbed, the baby teeth fall out on their own, and permanent teeth appear in their place.
During this period, parents need to monitor the child’s proper oral hygiene, as well as ensure that the permanent teeth grow evenly, without gaps or distortions. If the bite has defects, it is necessary to consult an orthodontist as soon as possible to correct it. Find out about the alveoli in the mouth from the article.
- Molars in children: order of eruption
Video - Baby's first teeth
What does the diagram of a child’s teeth look like with the numbers of each unit?
The pattern of baby teeth in children differs from the pattern with numbers in adults. Doctors specially designate milk teeth with different numbers so as not to confuse themselves and their patients: after all, a child who was treated for a milk bite in childhood will soon grow up and begin to go to the dentist for treatment of already permanent dental units. And if the same numbering is used in both cases, then there will be incredible confusion in the treatment history - but such a history in the dental record is often extremely important for the further competent and effective elimination of problems of the dental system.
Therefore, the numbering order for baby teeth in children is as follows: the serial number remains the same as in adults (1st, 2nd – incisors, 3rd – canine, etc.), but the segments of the jaws are designated by numbers 50 and 60 for the upper right and left segments and numbers 70 and 80 for the lower left and right, respectively. And when the dentist informs parents that their child has caries on the 82nd tooth, you don’t need to immediately imagine a baby shark with several rows of sharp baby teeth, we are only talking about the second lower right incisor. According to the counting scheme, permanent teeth in children are no different from the scheme of adult molars.