01.12.2019
Penetration of bones and tooth roots into the maxillary sinus indicates perforation of the latter. A similar complication may be accompanied by treatment at the dentist. Perforation of the maxillary sinus occurs quite often. From this article you will learn the causes of this pathology, signs of perforation, methods of diagnosis and treatment, as well as prevention. Photos of tooth roots in the maxillary sinus can also be seen in the sections of the article.
Reasons for the breakup
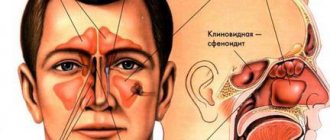
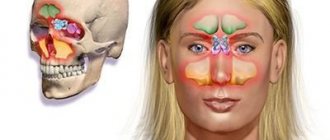
The sinus, called the sinus or maxillary sinus, is not characterized by tightness. It interacts with the nasal cavity through a small gap. As a rule, a sinus rupture occurs in the area of its lower part.
This happens due to the characteristic structural features and against the background of certain diseases, namely:
- The roots of molars and premolars are located very close to the sinus. In some cases, the bone layer is quite thick and reaches 1 cm. However, sometimes the barrier can be less than 1 mm in thickness.
- The first and second molars in the root part can be located directly in the sinus cavity and are separated only by the mucous membrane.
- Rapid thinning of the bone layer due to inflammatory diseases in acute or chronic form, including cysts, periodontitis and periodontitis.
- Thin trabeculae of bone in the maxillary tissues.
All these factors can cause a sinus rupture during dental treatment. In this case, there may be no violation of the technology of performing dental procedures. This may be a result of each patient's individual anatomy. Let's figure out why the tooth root penetrates the maxillary sinus.
Sinuses hurt – how to treat?
The primary and most important recommendation is to visit a doctor.
You should not self-medicate, especially with chronic pain. In this situation, you simply cannot do without advanced diagnostics. The most comprehensive examination of the sinuses and paranasal area is carried out using nasal endoscopy and computed tomography. Therapeutic treatment , for example for sinusitis, consists of prescribing vasoconstrictor, mucolytic and antimicrobial drugs. The main goal is to suppress the inflammatory process and normalize the outflow of contents from the sinuses. Additionally, outside the stages of exacerbation, physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, UHF sinuses, can be prescribed. Salt rinses and inhalations also have a fairly good effect. For temporary pain relief, the use of painkillers, for example, NSAIDs (Nise, etc.) is allowed.
Of course, surgical treatment , especially for anatomical changes and chronic inflammatory conditions. Which depends on the root cause of sinus pain:
- For chronic sinusitis, various sinusotomies: maxillary sinusotomy, polysinusotomy, etc.
- For a deviated nasal septum – septoplasty.
- For adenoid hypertrophy - adenotomy.
Your counterpart specializes in endoscopic paranasal surgery. This is a more gentle effect, which allows you to minimize the time of both cure and recovery period. Discharge from the hospital usually occurs within 24 hours after surgery.
More detailed information about the surgical treatment of ENT organs is located on the corresponding page: Treatment of ENT diseases
Frequent cases
Perforations of the maxillary sinus occur, as a rule, as a result of the dentist’s work during dental treatment. Tissue ruptures are typical for the following situations:
- Tooth extraction.
- Dental implantation.
- Endodontic therapy.
- Tooth root resection.
If perforation occurred during a tooth extraction operation, this may be a consequence of unskilled and excessively rough work of the dentist, as well as the individual characteristics of the structure of the maxillary sinus of the patient himself. If the dental roots are located directly in the sinus cavity, perforations during the removal of molars are almost inevitable.
One of the complications during endodontic therapy can also be perforation of the tooth root, which in most cases is associated with perforation of the sinus floor. This situation can occur as a result of excessive expansion of the root canals, as well as when using brute force when installing pins and compacting cement for fillings. In this case, most often not only the root of the tooth may be in the maxillary sinus, but also its fragments and particles of filling material. And this is dangerous for the patient.
When a rupture occurs during installation of an implant or during filling a root canal, as well as as a result of inserting pins into the root of a tooth, this in the vast majority of cases is a therapeutic error by a specialist. Sometimes you can find the roots of a wisdom tooth in the maxillary sinus.
What can be included in therapy during treatment?
Don’t know how to treat maxillary sinusitis besides pills? You need herbal preparations. They are good both in the treatment of existing inflammatory processes and as a preventive measure. Their effectiveness is explained by the special composition of active components. As a rule, these are herbal extracts.
Each capsule of this product contains a whole set, including up to 10 or more medicinal plants. It is this composition that helps to quickly eliminate the causes of the disease - any viruses and bacteria in the body, and also helps to cure sinusitis or sinusitis at an early stage.
Just one capsule a day - and your sinuses breathe freely, and your health remains normal even during seasonal colds!
Tooth root cyst in the maxillary sinus
Removal of the tooth root is considered the most effective method of treating cysts localized in the apex area. When the patient has not been carefully examined, and the dentist does not have information about the thickness of the bone tissue that separates the cystic wall from the sinus floor, and also in the case when it is necessary to remove a large amount of jaw bone, rupture of the sinus tissue quite often occurs.
Chronic rhinosinusitis
characterized by parietal thickenings caused by hyperplasia of the mucosa and partial fibrous changes in it. The thickness of the mucous membrane ranges from 4-5 mm.
Sinonasal polyposis, hypertrophic sinonasal rhinosinusitis. Non-tumor inflammatory swelling of the mucous membrane.
Recently, there has been an increase in the number of fungal sinusitis. Chronic forms occur under the guise of polypous recurrent sinusitis, the MRI picture is nonspecific, and laboratory diagnosis is difficult. There may be a change in the bony walls of the sinuses due to hyperostosis or destruction of the sinus wall as a result of prolonged pressure from the fungal body.
Symptoms
When perforation and entry of the tooth root into the maxillary sinus occurs during dental resection procedures, characteristic signs of rupture appear, including:
- Bleeding from the tooth socket with small air bubbles, the number of which increases when you try to exhale sharply through your nose.
- Bloody nasal discharge from the side of the ruptured sinus.
- A sharp change in the timbre of the injured patient’s voice, characterized by nasal sound.
If there is a tooth root in the maxillary sinus, the symptoms cannot go unnoticed. Sometimes, after resection, the patient begins to complain about difficult passage of air through the resulting hole, as well as pressure and heaviness in the projection of the maxillary sinus.
When perforation occurs during implantation or endodontic therapy, signs of such a complication include:
- Specific failure of the instrument or material for implantation after some effort to move it into the jaw.
- Changing the position of the instrument used in the resulting wound.
- The appearance of small air bubbles and blood discharge from the hole.
Perforation may not be detected and repaired immediately after a sinus rupture, which leads to infection of the sinus cavity and is accompanied by signs of acute sinusitis or sinusitis.
The following symptoms are typical for such pathologies:
- Acute intense pain in the sinus area of the upper jaw.
- Swelling of the nasal mucosa on the side of the injury, accompanied by difficulty in nasal breathing.
- Discharge of purulent secretion from the nose.
Systemic complications and symptoms of intoxication appear, which are characterized by chills, headaches, weakness and increased body temperature. But how to detect the root of a tooth in the maxillary sinus?
Old sinus perforation
If the defect is not detected and eliminated in a timely manner, acute inflammation will subside. Within a month, the patient develops a fistula. It connects the gum surface and the sinus cavity. Signs of a chronic inflammatory process appear. This will be a serious complication.
The patient has complaints:
- The presence of dull pain in the upper part of the cheek, of a constant nature. They radiate to the eye area and temporal region.
- Feeling of nasal congestion on one side.
- Separation of pus from the nose and from the fistula on the upper jaw.
- Swelling of the middle third of the face on the affected side.
- Air movement through the defect.
- Difficulty speaking.
- Getting fluid from the mouth into the nose.
Therapy of old processes is associated with significant difficulties. Patients are indicated for surgical treatment in a hospital.
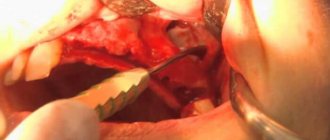
Operation stages:
- Opening of the main sinus of the upper jaw.
- Removing foreign bodies.
- Excision of necrotic areas and granulations.
- Excision of tissues forming the fistula.
- Closing the defect.
After the operation, drug therapy with the use of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and decongestant drugs is mandatory for a course of two weeks.
Diagnostics
For an experienced dentist, specific testing may not be necessary to confirm a maxillary sinus perforation.
If we are talking about tooth resection, then such a complication as soft tissue rupture is accompanied by a typical clinical picture. If the dentist is in doubt when perforation occurs during endodontic treatment, the following additional examinations may be required:
- Probing the hole formed after tooth extraction, as well as the root canal. For this purpose, a thin probe is used. In this way, it is possible to establish the absence of a bone bottom in the wound. During the study, the instrument passes through soft tissues without hindrance.
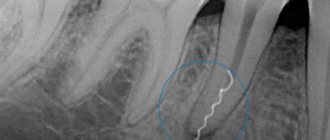
- Carrying out an X-ray examination of the sinuses. The resulting images will show darkening in the sinus cavity, indicating the accumulation of blood in this area, as well as filling material and fragments of teeth and implant. In some cases, contrast radiography may be required with the introduction of a special substance into the perforation cavity.
- CT scan. This diagnostic method makes it possible to detect ruptures and the presence of foreign bodies. In this case, the image is as accurate and informative as possible.
- If the perforation is old, it is recommended to donate blood for a general examination, based on the results of which it will be possible to draw a conclusion about the presence or absence of an infectious focus in the body.
After carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures and confirming the fact of a rupture of the maxillary sinus, the dentist will prescribe appropriate treatment. So, a person has a tooth root in the maxillary sinus - what to do?
Prevention is the best remedy for sinus inflammation
Of course, no one can be 100% insured against sinusitis and more severe inflammatory processes. Prevention will help strengthen the immune system and build a protective barrier against viruses, bacteria and infections. To prevent sinusitis without symptoms in an adult or child, you should follow simple rules:
- Avoid hypothermia. Yes, low temperature in itself does not provoke colds and runny nose. But it causes a narrowing of blood vessels and makes the mucous membranes more vulnerable to viruses and infections. In cold, rainy and windy weather, it is important to properly insulate - and you will not face chronic inflammation of the sinuses.
- Rinse your nose more often. This should be done in the fall during epidemics of colds and flu, as well as in the spring during the flowering of trees and shrubs. For rinsing, ordinary saline solutions are suitable, which effectively remove bacteria and allergens.
- Eat properly. The immune system weakens due to lack of nutrients. Include more natural products in your diet - fresh meat and fish, grains and slow carbohydrates, vegetables and fruits. It’s better to avoid processed foods and fast food, or at least reduce their consumption to a minimum.
- Drink vitamins. Nowadays there are many special vitamin complexes and supplements with herbal active ingredients. They work gently but effectively: the result is noticeable within 1-2 weeks. And most importantly, they are completely safe, non-addictive and have no side effects.
Treatment
The choice of treatment for maxillary sinus perforation depends on the changes that occur as a result of the rupture. Non-surgical treatment seems possible in case of violation of the integrity of the tissues during tooth extraction, when the pathology was detected immediately, and according to the results of the radiographic examination it is clear that there is no infection of the sinus cavity and there are no foreign bodies in it. With such a clinical picture, the doctor, as a rule, tries to preserve the blood clot formed in the hole as much as possible. In addition, preventative measures are taken to prevent wound infection.
For this purpose, a small gauze swab soaked in an iodine solution is inserted into the hole. As a rule, the tampon is self-fixed in the wound cavity. However, sometimes it may be necessary to place a stitch in the gum. Treatment with an iodide solution should be carried out for 6-7 days until the defect disappears and full-fledged granulations are formed. It is not recommended to remove the tampon from the socket during treatment, as this can damage the clot and lead to infection of the wound.
When a tooth root is found in the maxillary sinus, everyone should know what to do. In some cases, the doctor decides to close the defect with a special plastic plate, which is secured to adjacent teeth with clasps. Thus, it is possible to achieve separation of the sinus and oral cavity.
Structural features
The maxillary (maxillary, main) sinus is located inside the bone of the upper jaw. It is delimited from the oral cavity by the alveolar process. It forms the bottom of the cavity. The volume of the cavity of the upper jaw can be up to ten cubic centimeters. She has a communication with the nasal cavity. The inside of the cavity is lined with mucous tissue.
The structure has features that make it easy to damage:
- Sometimes the thickness of the bone plate between the bottom of the cavity and the roots of the teeth does not exceed one millimeter.
- There is a variant of the location of the roots of the second and first molars, when they penetrate into the cavity and are delimited from it only by the mucous membrane that lines the sinuses.
- The bone plate quickly thins out during inflammatory processes.
- Small thickness of trabeculae of the upper jaw bone.
Such structural features cause slight damage to its wall, even when the doctor did not violate any rules and did not apply significant force.
Preventing inflammation
In addition to preserving the wound, preventive therapy is carried out aimed at preventing the development of the inflammatory process. Most often, antibacterial drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. In addition, drops are prescribed for instillation into the nasal passages, which have a vasoconstrictor effect. Treatment can be carried out both on an outpatient basis and while staying at home.
If the examination reveals the presence of a foreign body in the maxillary sinus, then treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting. Therapy consists of surgical intervention to open the cavity and remove the tooth root from the maxillary sinus.
How to cure sinusitis, sinusitis and other inflammations?
What you definitely shouldn’t do is diagnose yourself and buy medications without a prescription or doctor’s recommendations. If sinusitis is mild, then the body will quickly cope with the source of the problem and defeat the infection or virus. But if sinusitis has become chronic, special therapy is needed:
- medicines that clear the air passages;
- antibacterial drugs to eliminate infection;
- rinsing the sinuses with antibiotics;
- surgical intervention in selected cases;
- regular preventive measures.
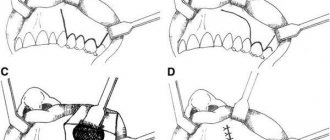
Of course, it is better to prevent sinusitis from becoming severe. Indeed, in this case, surgical intervention cannot be avoided. Why is this scary?? Just look at the image below, the hand-drawn picture of surgical techniques will give you a chill between your shoulder blades!
Complications
Rupture of the maxillary sinus is a serious consequence of dental procedures, the treatment of which most often occurs in an inpatient setting. What is the risk if the tooth root has grown into the maxillary sinus?
Self-treatment of the problem using traditional medicine methods can lead to even more serious complications, including:
- Severe inflammatory process in the sinus cavity with further infection of adjacent tissues. Then osteomyelitis develops in the upper jaw.
- Transition of the inflammatory process to other cranial sinuses, including the sphenoid, frontal and ethmoid.
- Loss of healthy teeth located in the perforation area.
- Formation of foci of pus, phlegmon and abscesses.
Due to the immediate proximity of the brain, and the fact that the tooth root has gone into the maxillary sinus and the latter has ruptured, the occurrence of an infectious lesion of the meninges cannot be ruled out. The next stage of serious complications may be meningitis or meningoencephalitis, which are life-threatening for the patient.
If your sinuses hurt without a runny nose?
This in most cases indicates a chronic pathology, the most common of which is chronic sinusitis or sinusitis of the maxillary sinus. This condition is characterized by periodic pain in the maxillary sinuses. During the period of exacerbation, pain is accompanied by catarrhal symptoms: serous-purulent discharge, rhinorrhea, postnasal drip, etc.
Other ENT causes of pain without manifestations of rhinorrhea (runny nose) are the conditions described in the previous section: deviated nasal septum, neoplasms, adenoids, dental pathologies, etc.
It should be remembered that pain in the sinuses may not be of otolaryngological etiology, for example, in neurological conditions: neuritis of the cranial nerves, migraine, fibromyalgia, etc. Therefore, it is important to promptly assess the condition and exclude more serious pathologies. In this regard, diagnosis should be carried out in sufficient depth, especially in chronic pain.
Sign up for a consultation
Prevention
As for preventive measures regarding perforation of the maxillary sinus, they consist of following the following rules:
- A thorough and comprehensive examination of the patient before undergoing serious dental procedures, including tooth resection or implantation.
- Correct assessment of the anatomical features of the jaw structure of each patient.
- Strict compliance with all technological requirements for complex dental procedures.
General information about sinus lift surgery
A sinus lift is a surgical procedure that uses the human maxillary sinuses (maxillary sinuses) to fill the bone deficiency in the area of the anterior chewing teeth. The essence of the operation is to separate the mucous membrane from the jaw bone and fill the resulting space with osteoplastic material.
Surgery requires preliminary anesthesia, which can be either local (with or without sedation) or general. Access to the maxillary sinus depends on the type of sinus lift:
- Open method. An incision is made on the front surface of the upper jaw. The technique is performed in cases of severe bone volume deficiency and is considered quite traumatic. The graft healing process lasts on average 3-6 months, after which dental implantation can be performed.
- Closed method. This sinus lift is often performed together with implantation, since the incision is made at the site of the future installation of the artificial root. This operation involves less trauma, but is used only for small deficits, up to 4-6 mm.
The duration of the operation depends on its type, but on average it lasts 1-2 hours. During the rehabilitation period, the patient must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations in order to prevent serious complications from occurring. These include, first of all, proper oral hygiene, as well as taking the necessary medications.
Accelerated rehabilitation
After the operation, you will receive free medications and instructions with rules of behavior during the rehabilitation period. We have collected the necessary set of drugs to improve your well-being at home. Please take them as prescribed by your doctor and follow the recommendations to avoid unpleasant consequences.
For quick recovery after surgery, our Center offers its own method of rehabilitation in 1-2 days. The procedures allow us to minimize the formation of possible hematomas, swelling, and eliminate pain. The program uses:
Microcurrent therapy
A weak pulse current normalizes metabolic processes, activates ATP production, and improves tissue nutrition. Regeneration starts, healing accelerates, swelling decreases. Muscle spasm goes away.
PRP plasma therapy
Injections of purified and platelet-enriched plasma from one’s own blood trigger cellular regeneration processes using the body’s internal reserves. The manifestation of edema and hematomas is reduced.
Biostimulation of the face
Lymphatic drainage drugs D-NUCLEO and MesoSculpt C71 help reduce swelling. Active anti-inflammatory components improve blood flow, increase tissue nutrition, and improve healing.
No hospitalization required
Operations in our Center are performed by operating teams of experienced maxillofacial surgeons with ENT training in a sterile operating room. The treatment is as gentle and minimally traumatic as possible; a 24-hour hospital stay is not required; you will go home the same day .
The intervention lasts about an hour, under sedation. After completion, the patient quickly returns to clear consciousness without unpleasant consequences or risk of complications. After 30-40 minutes you can safely go home. For patients with concomitant cardiovascular diseases, a day hospital is provided . You can lie down for the time necessary for recovery under the supervision of our anesthesiologist-resuscitator.
Carrying out a sinus lift after a maxillary sinusotomy
Sinus lifting for sinusitis is not performed under any circumstances, so the patient is first treated for the inflammatory process. Surgical intervention to replenish bone tissue deficiency after a manipulation such as maxillary sinusotomy is considered possible. The doctor must take into account that the patient has a history of a similar procedure and act much more carefully.
Sinus lifting after perforation of the maxillary sinus is dangerous because the risk of infection in the sinus increases. This occurs due to perforation of its wall, especially with an open operating technique. To avoid such complications, the doctor carefully plans each step of the future surgical intervention, focusing on the data of instrumental studies, in particular computed tomography.
What are the dangers of sinus injury?
Since the complication does not always manifest itself immediately, symptoms of sinusitis that arise after a few years force the patient to consult a regular ENT doctor. Treatment, as a rule, does not bring results - in most cases the cause is not found. You start going from one doctor to another, and precious time is lost. The longer a foreign body is in the sinus, the higher the risk of tumor formation. If sinus perforation is left unattended, it can lead to:
- chronic sinusitis and sinusitis
- inflammation of the roots of adjacent teeth
- osteomyelitis of the jaw
- encephalitis and meningitis
Why you should entrust your treatment to the ENT Department of Dentistry
ENT dentistry is a comprehensive approach to the treatment of complications in the maxillary sinuses after dental treatment
The symbiosis of two areas - dentistry and otolaryngology - makes it possible to identify the cause, assess the situation, and select competent treatment tactics.
The ENT department of the Doctor Levin Center has been providing assistance for many years when problems arise after treatment and removal of teeth located on the border with the maxillary sinus. Surgical treatment is carried out by candidates of medical sciences, maxillofacial surgeons with otolaryngological training .
Patients come to the Center after a painful search for a solution to the problem. Repeated treatment by an ENT doctor in the hospital does not bring results. But a thinking patient should understand that if there is concern on the side of the sinuses where endodontic treatment once took place, you need to contact an oral and maxillofacial surgeon with ENT training. Only in this case can a comprehensive assessment of the situation be made and an adequate treatment plan drawn up.
Alternative to sinus lift for sinusitis
Modern dentistry offers several alternative methods that allow you to install implants without sinus lifting. Such surgical interventions have appeared quite recently and cannot yet be characterized by high demand and ideal results. But if a sinus lift is strictly contraindicated for a patient, then these methods can be used.
Ultra-short implants
Specific structures about 5 mm long are used, which are installed in the existing volume of bone tissue. The main disadvantage of such implants is the unnatural distribution of the chewing load, which leads to problems with their functioning. To install such a structure, a sufficient volume of the alveolar ridge is required, as well as certain characteristics of the bone tissue (it should not be too porous) for tight fixation.
Zygomatic implants
They are used only for massive restoration of the dentition. Implants are structures of about 40 mm, which are fixed at an angle into the zygomatic bone. To carry out the manipulation, general anesthesia is required in almost all cases. The operation is considered one of the most traumatic in implantology.
Basal implants
The essence of the surgical intervention is the use of a non-standard shape of implants to bypass the maxillary sinuses. Such a surgical intervention is very traumatic and dangerous with a number of complications, but it allows you to avoid an additional sinus lift procedure. Indications for the installation of basal implants are very limited.